Deck 5: Sexuality, Gender, Personality, Social Psychology and Health Psychology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/7
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Sexuality, Gender, Personality, Social Psychology and Health Psychology
1
Consider the following short run aggregate supply equation:
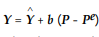 where Y is the real output
where Y is the real output 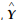 is the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
is the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
A) In the Keynesian model, b is positive because of the sticky wage assumption.
B) In the classical model, b is zero because of the price misperception assumption.
C) In the Keynesian model, b is zero because of the sticky wage assumption.
D) Both A and C are correct.
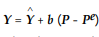 where Y is the real output
where Y is the real output 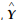 is the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
is the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?A) In the Keynesian model, b is positive because of the sticky wage assumption.
B) In the classical model, b is zero because of the price misperception assumption.
C) In the Keynesian model, b is zero because of the sticky wage assumption.
D) Both A and C are correct.
In the Keynesian model, b is positive because of the sticky wage assumption.
2
Consider the following short run aggregate supply equation:
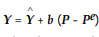 , where Y is the real output is
, where Y is the real output is 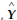 the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
A) In the Keynesian model, P is always greater than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
B) In the Keynesian model, P is always equal to Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
C) In the Keynesian model, P is always less than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
D) In the Keynesian model, P may be different than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
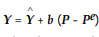 , where Y is the real output is
, where Y is the real output is 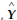 the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?A) In the Keynesian model, P is always greater than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
B) In the Keynesian model, P is always equal to Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
C) In the Keynesian model, P is always less than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
D) In the Keynesian model, P may be different than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
In the Keynesian model, P may be different than Pe because of sticky-wage assumption.
3
Consider the following short run aggregate supply equation: 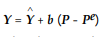 , where Y is the real output is
, where Y is the real output is 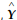 the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
A) In the classical model, P is always greater than Pe because of price misperception assumption.
B) In the classical model, P is always equal to Pe because of price misperception assumption.
C) In the classical model, P is always less than Pebecause of price misperception assumption.
D) In the classical model, P may be different than Pe because of price misperception assumption.
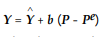 , where Y is the real output is
, where Y is the real output is 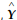 the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?
the full employment output, P and Pe are the actual and expected price levels, respectively. Which of the following is correct?A) In the classical model, P is always greater than Pe because of price misperception assumption.
B) In the classical model, P is always equal to Pe because of price misperception assumption.
C) In the classical model, P is always less than Pebecause of price misperception assumption.
D) In the classical model, P may be different than Pe because of price misperception assumption.
In the classical model, P may be different than Pe because of price misperception assumption.
4
The effort of a firm's workers depends on their real wage according to the following schedule:
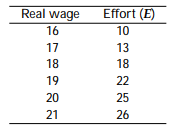
The marginal product of labour is MPN = E(400 - 4N)/30.
a. What is the efficiency wage?
b. How many workers will the firm hire?
c. Suppose an adverse productivity shock reduces the marginal product of labour to MPN = E(360 - 4N)/30. How would your answers to parts (a) and (b) change?

The marginal product of labour is MPN = E(400 - 4N)/30.
a. What is the efficiency wage?
b. How many workers will the firm hire?
c. Suppose an adverse productivity shock reduces the marginal product of labour to MPN = E(360 - 4N)/30. How would your answers to parts (a) and (b) change?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 7 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A beneficial productivity shock would ________ output, ________ the real interest rate, and________ the price level.
A) increase; decrease; decrease
B) decrease; decrease; increase
C) increase; increase; decrease
D) increase; decrease; increas
A) increase; decrease; decrease
B) decrease; decrease; increase
C) increase; increase; decrease
D) increase; decrease; increas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 7 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The exchange rate is
A) the quantity of gold that can be purchased by one unit of currency.
B) the difference in interest rates between two countries.
C) the price of one currency in terms of another.
D) the price of domestic goods relative to foreign goods.
A) the quantity of gold that can be purchased by one unit of currency.
B) the difference in interest rates between two countries.
C) the price of one currency in terms of another.
D) the price of domestic goods relative to foreign goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 7 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ball found that the disinflation in Canada had a sacrifice ratio of about
A) 0.5
B) 1.0
C) 1.5
D) 2.0
A) 0.5
B) 1.0
C) 1.5
D) 2.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 7 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



