Deck 25: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
1
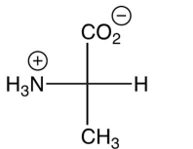
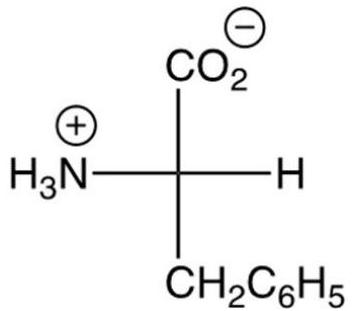
Which of the following is the zwitterion form of L-alanine?
A)
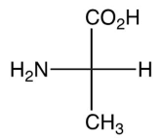
B)
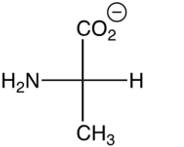
C)
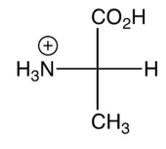
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


2
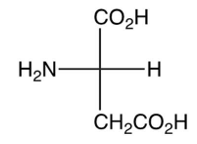
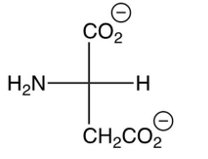
What is the pI of valine, shown below? (the 's are shown)
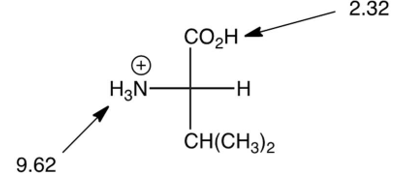
A) 2.32
B) 4.81
C) 5.97
D) 9.62

A) 2.32
B) 4.81
C) 5.97
D) 9.62
5.97
3
Which of the following is the major product of the reaction shown below? (the are shown)
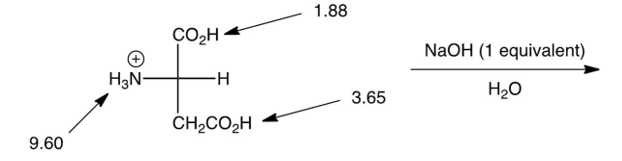
A)
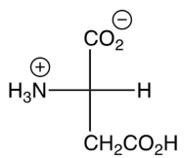
B)
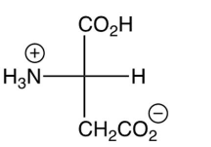
C)
D)

A)

B)

C)

D)


4
The Fischer projection shown below denotes a amino acid which has the configuration.
A) D, S
B) D, R
C) L, S
D) L, R

A) D, S
B) D, R
C) L, S
D) L, R

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the total number of different tripeptides which can result from three different L-amino acids?
A) three
B) four
C) six
D) nine
A) three
B) four
C) six
D) nine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the net charge on L-aspartic acid at a pH of 11.0 ?
A) +1
B) +2
C) -1
D) -2
A) +1
B) +2
C) -1
D) -2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In strongly acidic solution L-lysine is primarily a dication as shown below. As the is raised, which proton is lost to form the monocation?
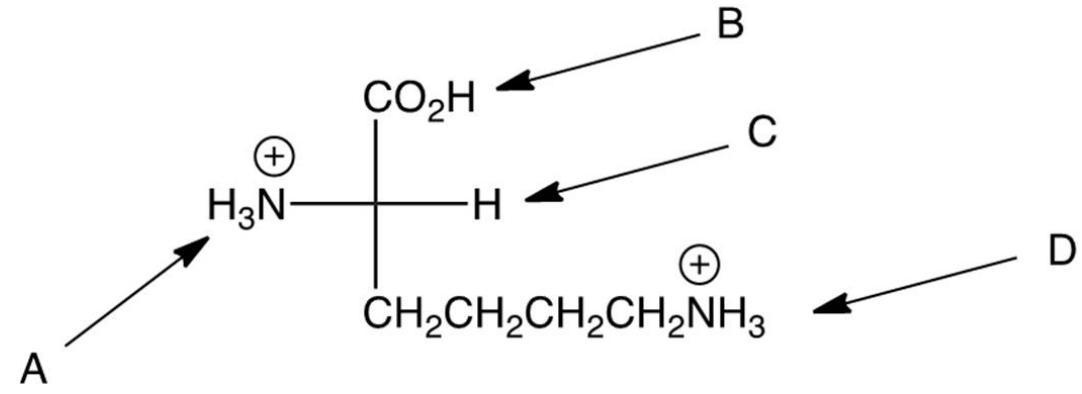
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Linus Pauling is credited with describing the -helix structure of a polypeptide. The -helix is an example of a polypeptide's
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) quaternary structure.
A) primary structure.
B) secondary structure.
C) tertiary structure.
D) quaternary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the net charge on the dipeptide lys-asp at a of 1.0 ?
Aspartic acid
Lysine (
A) +1
B) +2
C) +3
D) +4
Aspartic acid
Lysine (
A) +1
B) +2
C) +3
D) +4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A pentapeptide was found to contain the amino acids ala, gly, met, phe, and ser. Partial hydrolysis of the pentapeptide gave the dipeptides gly-ser, met-phe, ala-gly, and ser-met. What is the sequence of the pentapeptide?
A) gly-ser-met-phe-ala
B) gly-ser-met-ala-phe
C) ala-gly-ser-phe-met
D) ala-gly-ser-met-phe
A) gly-ser-met-phe-ala
B) gly-ser-met-ala-phe
C) ala-gly-ser-phe-met
D) ala-gly-ser-met-phe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the DNP derivative obtained from the reaction sequence shown below?
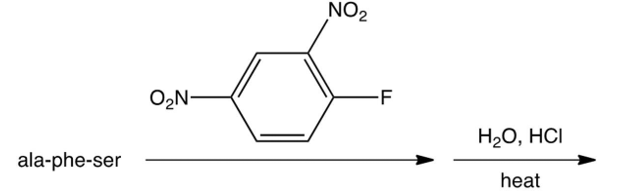
A)
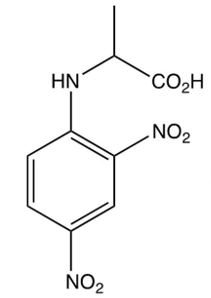
B)
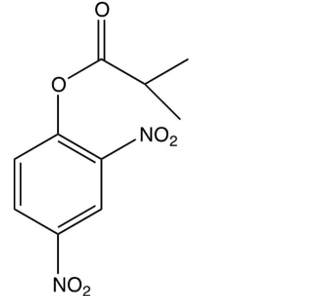
C)
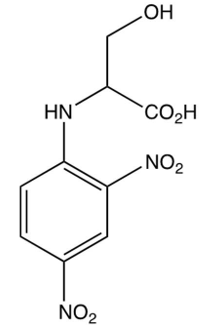
D)
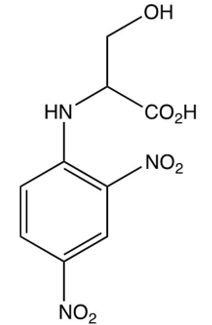

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which one of the following reagents is used for the visual detection of amino acids?
A) Sanger's reagent
B) dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCI)
C) ninhydrin
D) phenyl isothiocyanate
A) Sanger's reagent
B) dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCI)
C) ninhydrin
D) phenyl isothiocyanate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which one of the following is the final product of the reaction sequence shown below? 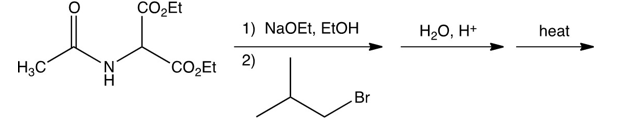
A)
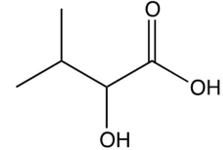
B)
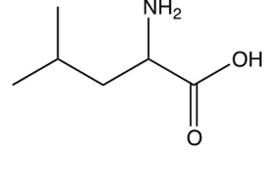
C)
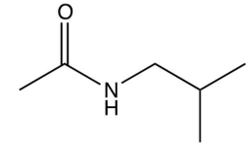
D)
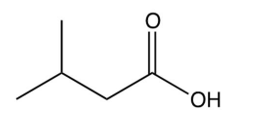

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify the missing starting reagent needed in the Strecker synthesis of isoleucine. (Assume you will get all the stereoisomers of isoleucine.)
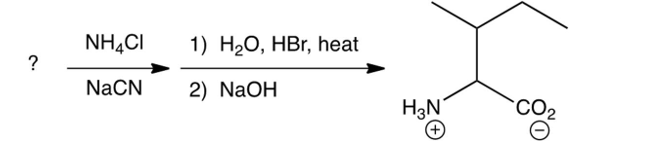
A)
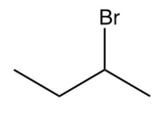
B)
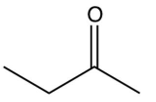
C)
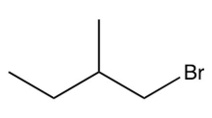
D)
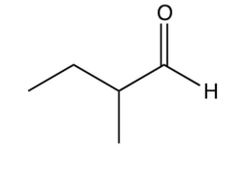

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In aqueous solution, the artificial sweetener aspartame slowly converts to the cyclic compound shown below. Which of the following best describes this reaction? 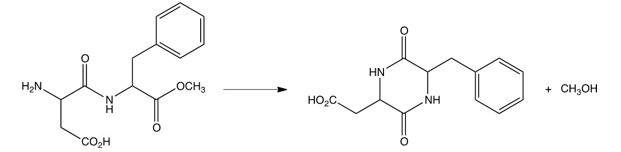
A) nucleophilic acyl substitution
B) Dieckmann condensation
C) ester hydrolysis
D) reaction

A) nucleophilic acyl substitution
B) Dieckmann condensation
C) ester hydrolysis
D) reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the abbreviated formula of the tetrapeptide shown below? (Hint: Remember to start at the -terminal end.)
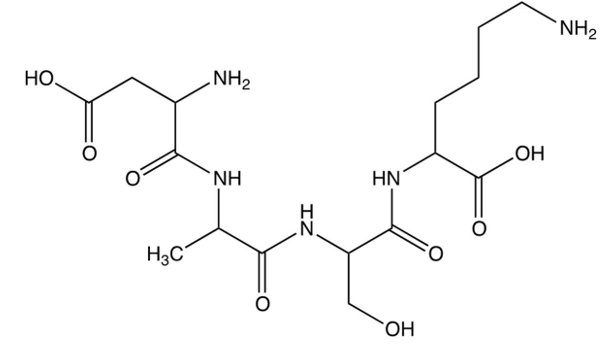
A) lys-ser-asp-ala
B) ser-lys-ala-asp
C) asp-ala-ser-lys
D) asp-ser-ala-lys

A) lys-ser-asp-ala
B) ser-lys-ala-asp
C) asp-ala-ser-lys
D) asp-ser-ala-lys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



