Deck 1: Understanding Pharmacokinetics and Drug Administration
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/90
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Understanding Pharmacokinetics and Drug Administration
1
Pharmacokinetics is:
A) The study of how drugs reach their target in the body and how the levels of a drug in the blood are affected by various factors
B) The study of how drugs can be designed using molecular modelling based on a drug's pharmacophore.
C) The study of how a drug interacts with its target binding site at the molecular level
D) The study of which functional groups are important in binding a drug to its target binding site and the identification of a pharmacophore.
A) The study of how drugs reach their target in the body and how the levels of a drug in the blood are affected by various factors
B) The study of how drugs can be designed using molecular modelling based on a drug's pharmacophore.
C) The study of how a drug interacts with its target binding site at the molecular level
D) The study of which functional groups are important in binding a drug to its target binding site and the identification of a pharmacophore.
The study of how drugs reach their target in the body and how the levels of a drug in the blood are affected by various factors
2
Which of the following is the most correct sentence concerning intravenous administration of drugs?
A) Gives predictable blood levels
B) None undergoes first pass metabolism
C) All of it undergoes first pass metabolism
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) Gives predictable blood levels
B) None undergoes first pass metabolism
C) All of it undergoes first pass metabolism
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A and B
3
Some drugs have a low oral bioavailability due to extensive metabolism in the GI tract or liver. Which dosage form can be used to best avoid this complication?
A) Controlled release tablet
B) Enteric coated tablet
C) Soft capsule
D) Sublingual
A) Controlled release tablet
B) Enteric coated tablet
C) Soft capsule
D) Sublingual
Sublingual
4
Concerning the enteral route of administration, the correct sentence is:
A) The bioavailability here is excellent as compared to parenteral route
B) Has faster onset of action as compared to parenteral route
C) Could be used by either conscious or unconscious patients
D) None of the above
A) The bioavailability here is excellent as compared to parenteral route
B) Has faster onset of action as compared to parenteral route
C) Could be used by either conscious or unconscious patients
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following preparations will give sustained drug delivery with prolonged duration of action?
A) Sugar coated tablet
B) Aqueous prepared IM injection
C) Transdermal patches
D) Sublingual tablet
A) Sugar coated tablet
B) Aqueous prepared IM injection
C) Transdermal patches
D) Sublingual tablet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For a drug with a narrow therapeutic index, the plasma concentration required for therapeutic effects is near the concentration that produces toxic effects, and such a drug require routine plasma monitoring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following statements are true about intranasal route of administration EXCEPT:
A) It is only used for administration of drugs used in respiratory conditions.
B) It has a rapid onset of action.
C) It possesses good compliance among patients
D) Few systemic side effects
A) It is only used for administration of drugs used in respiratory conditions.
B) It has a rapid onset of action.
C) It possesses good compliance among patients
D) Few systemic side effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Variation in cytochrome P450 enzyme profile between individuals can explain individual variation in drug susceptibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the plasma concentration of a drug declines with "first-order kinetics," this means that:
A) There is only one metabolizing enzyme for drug disposition
B) The half-life is the same regardless of the plasma concentration
C) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver after oral administration and has low bioavailability
D) All of them
A) There is only one metabolizing enzyme for drug disposition
B) The half-life is the same regardless of the plasma concentration
C) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver after oral administration and has low bioavailability
D) All of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In relation to the therapeutic window of a drug, which of the following sentences is true:
A) Drugs with wide therapeutic range are not potent enough compared with narrow therapeutic range.
B) A drug must exceed the maximum effective dose in order to be therapeutically active.
C) Drugs with plasma concentration below the minimum effective concentration show no therapeutic effect.
D) It is a range of concentration that determines both the safety and efficacy of drugs.
A) Drugs with wide therapeutic range are not potent enough compared with narrow therapeutic range.
B) A drug must exceed the maximum effective dose in order to be therapeutically active.
C) Drugs with plasma concentration below the minimum effective concentration show no therapeutic effect.
D) It is a range of concentration that determines both the safety and efficacy of drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is the closest description of Phase! metabolism?
A) Reactions which add an endogenous polar molecule to a functional group already present on a drug or one of its metabolites.
B) Reactions which occur in the blood supply.
C) Reactions which add a polar functional group to a drug
D) Reactions which occur in the gut wall.
A) Reactions which add an endogenous polar molecule to a functional group already present on a drug or one of its metabolites.
B) Reactions which occur in the blood supply.
C) Reactions which add a polar functional group to a drug
D) Reactions which occur in the gut wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The term of pharmacokinetics includes all of the following EXCEPT?
A) Clinical response to a drug ie; toxicity & efficacy
B) Drug concentration at site of action
C) Dose of drug administered
A) Clinical response to a drug ie; toxicity & efficacy
B) Drug concentration at site of action
C) Dose of drug administered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The volume of distribution (Va) for a drug highly bound to plasma protein as compared to others would be?
A) High
B) Low
C) Unchanged
D) Cannot be determined, it's an apparent parameter
A) High
B) Low
C) Unchanged
D) Cannot be determined, it's an apparent parameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Factors associated with drug absorption that can result in incomplete absorption
A) Drug metabolism by gastrointestinal flora
B) Drug instability in gastric acid
C) Presence of food in the GI tract
D) A and B
E) A B, and C
A) Drug metabolism by gastrointestinal flora
B) Drug instability in gastric acid
C) Presence of food in the GI tract
D) A and B
E) A B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Patient's age may affect a drug elimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Warfarin is metabolized by CYP450, and rifampicin is CYP450 inducer. Administration of warfarin and rifampicin together will
A) Rifampicin will decrease therapeutic effectiveness of warfarin
B) Rifampicin will increase the side effect of warfarin
C) Rifampicin of no effect on therapeutic effect of warfarin
D) Both A and B
A) Rifampicin will decrease therapeutic effectiveness of warfarin
B) Rifampicin will increase the side effect of warfarin
C) Rifampicin of no effect on therapeutic effect of warfarin
D) Both A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Dose adjustment is needed in the following situation EXCEPT
A) Elderly and newborn patients
B) Patients with renal and hepatic problems.
C) Patients with lung diseases
D) Patient with heart failure
A) Elderly and newborn patients
B) Patients with renal and hepatic problems.
C) Patients with lung diseases
D) Patient with heart failure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A type of absorption is called () Appears to depend on an oscillating carrier protein, depends on concentration gradient, no energy required. For a few drugs movement occurs faster than predicted.
A) Active transport
B) Passive transport
C) Facilitated diffusion.
D) Simple diffusion
A) Active transport
B) Passive transport
C) Facilitated diffusion.
D) Simple diffusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In case of severe renal dysfunction, the duration of action of most drugs:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Will not change
Done by: Fawzi Shihadeh, Malik Sulima
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Will not change
Done by: Fawzi Shihadeh, Malik Sulima

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The onset of effect for a drug given orally is the time for the drug to:
A) Reach the peak plasma concentration.
B) Reach the minimum effective concentration.
C) Reach the concentration of steady state.
D) Begin to be within the therapeutic concentration.
E) To be absorbed from the small intestine
A) Reach the peak plasma concentration.
B) Reach the minimum effective concentration.
C) Reach the concentration of steady state.
D) Begin to be within the therapeutic concentration.
E) To be absorbed from the small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The therapeutic range is the range of plasma drug concentrations that clearly defines optimal drug therapy and where adverse effects cannot occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements best describes first-order kinetics?

A) The same fraction of drug is eliminated during a given time interval
B) The same amount of drug is eliminated during a given time interval
C) The time vs. plasma drug concentration profile is as follow
D) Both A and C

A) The same fraction of drug is eliminated during a given time interval
B) The same amount of drug is eliminated during a given time interval
C) The time vs. plasma drug concentration profile is as follow
D) Both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In case of liver disorders accompanied by a decline in microsomal enzyme activity the therapeutic effect of this treatment will be:
A) Decreased
B) Increased
C) Remained unchanged
A) Decreased
B) Increased
C) Remained unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Half-life (t %) doesn't depend on:
A) Rate of metabolism
B) Concentration of a drug in plasma
C) Rate of drug elimination
D) Time of drug absorption
A) Rate of metabolism
B) Concentration of a drug in plasma
C) Rate of drug elimination
D) Time of drug absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Oral bioavailability of the drug could be affected by which of the following:
A) Gastric acidity and gastric enzymes
B) Drug formulation
C) Metabolism by liver enzymes prior to reaching the systemic circulation
D) Expression of intestinal P-glycoprotein
E) All the above
A) Gastric acidity and gastric enzymes
B) Drug formulation
C) Metabolism by liver enzymes prior to reaching the systemic circulation
D) Expression of intestinal P-glycoprotein
E) All the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Alkalinization of urine hastens (facilitates) the excretion of weakly basic drugs:
A) True
B) False
C) False, it hastens acidic drug excretion
A) True
B) False
C) False, it hastens acidic drug excretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A small Vd has an important influence on the half-life of a drug, this means that a drug with small Vd has short half-life.
A) True
B) False
C) Maybe true, but not important at all
A) True
B) False
C) Maybe true, but not important at all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Treatment of pediatric patients sometimes requires considering age- appropriate dosage forms. For example, when treating a 4 year old boy with an inner ear infection, the antibiotic dosage formulation most acceptable to them would be alan:
A) Capsule
B) Oblong large tablet
C) Oral suspension
D) Normal tablet
A) Capsule
B) Oblong large tablet
C) Oral suspension
D) Normal tablet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following phase II metabolic reactions make phase I metabolites readily excretable in urine?
A) Oxidation
B) Reduction
C) Alcohol dehydrogenation
D) Glutathione conjugation
E) None of them
A) Oxidation
B) Reduction
C) Alcohol dehydrogenation
D) Glutathione conjugation
E) None of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following drugs/or substances may inhibit the hepatic microsomal P450 responsible for the metabolism of substrate drugs
A) Grapefruit juice
B) Ethanol
C) Rifampin
D) Smoking
A) Grapefruit juice
B) Ethanol
C) Rifampin
D) Smoking

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The term bioavailability of a preparation of a drug is a measure of:
A) The relative toxicity of the preparation to laboratory animals
B) The stability of the preparation
C) The availability of the drug from natural sources
D) We simply say: BIOAVAILABLE! Means available to patients
E) None of the above
A) The relative toxicity of the preparation to laboratory animals
B) The stability of the preparation
C) The availability of the drug from natural sources
D) We simply say: BIOAVAILABLE! Means available to patients
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If 3 g of a drug are added and distributed throughout a tank and the resulting concentration is 0.15 g/L, calculate the volume of the tank.
A) 10 L
B) 20 L
C) 30 L
D) 200 L
A) 10 L
B) 20 L
C) 30 L
D) 200 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
"Ultron" is a new drug for the treatment of hiccups. When administered over a wide concentration range, three dose response relationships were defined in tested subjects. Using vomiting as an unwanted (toxic) effect, what would be the estimated therapeutic index for "Ultron"?
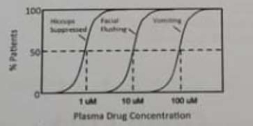
A) 0.01
B) 0.1
C) 10
D)100

A) 0.01
B) 0.1
C) 10
D)100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Metabolic transformation and conjugation usually results in an increase of a substance biological activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Generally, the rate of drug absorption is most rapid when the drug is formulated as a
A) Hard gelatin capsule
B) Solution, e.g syrup
C) Controlled.release product
D) compressed tablet
A) Hard gelatin capsule
B) Solution, e.g syrup
C) Controlled.release product
D) compressed tablet

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Ampicillin is eliminated by first-order kinetics. Which of the following statements best describes the process by which the plasma concentration of this drug declines
A) The drug is distributed to only 1 compartment outside the vascular system
B) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver after oral administration and has low bioavailability
C) The rate of elimination is proportional to the rate of administration at all times
D) The halflife is the same regardless of the plasma concentration
A) The drug is distributed to only 1 compartment outside the vascular system
B) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver after oral administration and has low bioavailability
C) The rate of elimination is proportional to the rate of administration at all times
D) The halflife is the same regardless of the plasma concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is implied by {{passive transport}}
A) Transport without energy consumption
B) Engulf of drug by a cell membrane with a new vesicle formation
C) Transport of drugs through a membtane by means of diffusion
D) Transport against conæntration gradient
A) Transport without energy consumption
B) Engulf of drug by a cell membrane with a new vesicle formation
C) Transport of drugs through a membtane by means of diffusion
D) Transport against conæntration gradient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Drug metabolism is mainly done in the kidneys and is responsible for drug elminnation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Concerning renal clearance, which of the following is correct
A) Influenced by renal disease
B) None of them
C) Both of them
D) Altered by blood flow
A) Influenced by renal disease
B) None of them
C) Both of them
D) Altered by blood flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the plasma concentration Of a drug declines with "first-order kinetics," this means that
A) The half-life is thesame regardless of the plasma concentration
B) There Is Only one metabolic for drug disposition
C) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver aftel oral administration and has low bioavailability
D) All of them
A) The half-life is thesame regardless of the plasma concentration
B) There Is Only one metabolic for drug disposition
C) The drug is largely metabolized in the liver aftel oral administration and has low bioavailability
D) All of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
you want to enhance urine elimination of a basic drug, you need to make the urine
A) More alkaline
B) More acidic
C) Urine pH of no effect
A) More alkaline
B) More acidic
C) Urine pH of no effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The oral bioavailability of most of drugs is less than 100% because
A) Both
B) Incomplete absorption
C) Neither
D) First pass effect
A) Both
B) Incomplete absorption
C) Neither
D) First pass effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which statement best describes bioavailability
A) All
B) Measurement of the rate and amount of the unchanged drug reaches the systemic circulation
C) Amount of the drug destroyed in the liver before entering systemic circulation
D) Measurement of the relative toxicity of the preparation
E) Movement of drug into body tissues over time
A) All
B) Measurement of the rate and amount of the unchanged drug reaches the systemic circulation
C) Amount of the drug destroyed in the liver before entering systemic circulation
D) Measurement of the relative toxicity of the preparation
E) Movement of drug into body tissues over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Fill the blanks-----------: In case of liver cirrhosis, half-life is---------for paracetamol and should be used in
A) Decreased, higher doses
B) Increased ,lower doses
C) Decreased, lower doses
D) Increased. higher doses
A) Decreased, higher doses
B) Increased ,lower doses
C) Decreased, lower doses
D) Increased. higher doses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The correct sentence/ s concerning prodrug is/are
A) An active drug that is transformed in the body to an inactive metabolite
B) Means inactive drug that is transformed in the body to an active metabolite
C) None of them
D) Medications that are transformed in the bods into toxic metabolites
E) Mostly, medications are prodrugs
A) An active drug that is transformed in the body to an inactive metabolite
B) Means inactive drug that is transformed in the body to an active metabolite
C) None of them
D) Medications that are transformed in the bods into toxic metabolites
E) Mostly, medications are prodrugs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Smoking is enzyme inhibitor; this can increase the half-life of theophylline in those who are smokers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not a pharmacokinetics process
A) Drug metabolites are removed in the urine
B) The drug causes dilation of coronary vessels
C) Movement of drug from the gut into circulation
D) Alteration of the drug by liver enzymes
E) The drug is readily deposited in fat tissue
A) Drug metabolites are removed in the urine
B) The drug causes dilation of coronary vessels
C) Movement of drug from the gut into circulation
D) Alteration of the drug by liver enzymes
E) The drug is readily deposited in fat tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Regarding renal excretion, the following are with importance to be considered
A) Glomerular filtration rate
B) Extent of plasma protein binding of drugs
C) Active renal tubular reabsorption
D) All of them
E) Re-absorption in distal tubules
A) Glomerular filtration rate
B) Extent of plasma protein binding of drugs
C) Active renal tubular reabsorption
D) All of them
E) Re-absorption in distal tubules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Regarding biotransformation
A) CYP2D6 accounts for the majority of P450 activity
B) Phase one reactions always precede phase two reactions
C) water conjugation is a phase one reaction
D) None of them
A) CYP2D6 accounts for the majority of P450 activity
B) Phase one reactions always precede phase two reactions
C) water conjugation is a phase one reaction
D) None of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
AII the following statements are correct concerning intravenous drug administration EXCEPT
A) It is painful and stressful for the patient
B) Drugs undergo first-pass metabolism
C) A trained staff is required
D) Risk of bacterial contamination at the site of injection
A) It is painful and stressful for the patient
B) Drugs undergo first-pass metabolism
C) A trained staff is required
D) Risk of bacterial contamination at the site of injection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A 12-month-old infant is hospitalized for nausea, vomiting, fevers. He is placed on a rectal treatment to treat the nausea and vomiting. Which of the following statements is true about this route of administration
A) Rectal irritation following administration is uncommon
B) Rectal administration ot medications is well accepted
C) Maximal biotransformation of the drug by the liver
D) Useful if patient is unconscious or vomiting
E) Allows destruction of the medication by gastric enzymes
A) Rectal irritation following administration is uncommon
B) Rectal administration ot medications is well accepted
C) Maximal biotransformation of the drug by the liver
D) Useful if patient is unconscious or vomiting
E) Allows destruction of the medication by gastric enzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The IV administration of drugs are
A) Rapidly excreted by renal
B) Undergoes the first-pass metabolism
C) Rapidly absorbed
D) bioavailable 100%
A) Rapidly excreted by renal
B) Undergoes the first-pass metabolism
C) Rapidly absorbed
D) bioavailable 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The same dose of Four different drugs was administered IV to the same lab animal on four different occasions. The following pharmacokinetic data were obtained: Drug Plasma concentration): for drug A 25 ng/mL Drug B: 12 ng/mL Drug C: 44 ng/mL Drug D:90ng/ml. which of the following drugs will have the lowest Vd the following drugs will have the lowest Vd
A) Drug C
B) Drug B
C) Drug A
D) DrugD
A) Drug C
B) Drug B
C) Drug A
D) DrugD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
33 year old female patient is brought to emergency department due to drug overdose and acute toxicity. Which routes of administration is desirable for antidote administration
A) I.V
B) S.L
C) Orally
D) S.C
A) I.V
B) S.L
C) Orally
D) S.C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
22.Clopidogrel (pro-dug) is metabolized by CYP450 is taken with rifampicin which is a CYP450 inducer. This will lead to
A) No effect on therapeutic effect of Clopidogrel
B) Increase therapeutic response of Clopidogrel
C) Decrease therapeutic response of Clopidogrel
D) Decrease the plasma concentration of Clopidogrel active metabolite
A) No effect on therapeutic effect of Clopidogrel
B) Increase therapeutic response of Clopidogrel
C) Decrease therapeutic response of Clopidogrel
D) Decrease the plasma concentration of Clopidogrel active metabolite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which statement about the distribution of drugs to specific tissues is most correct
A) Distribution to an organ is independent of blood flow
B) Distribution has no effect on the half-life ot the drug
C) Distribution depends on the unbound drug concentration gradient between blood and the tissue
D) Dist ution is independent of the solubility of the drug in that tissue
E) Distribution is increased for drugs that are strongly bound to plasma vroteins
A) Distribution to an organ is independent of blood flow
B) Distribution has no effect on the half-life ot the drug
C) Distribution depends on the unbound drug concentration gradient between blood and the tissue
D) Dist ution is independent of the solubility of the drug in that tissue
E) Distribution is increased for drugs that are strongly bound to plasma vroteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Therapeutic index (Tl) is
A) ratio used to evaluate the elimination of a drug
B) ratio used to evaluate the safely and usefulness of a drug for indication
C) ratio used to evaluate the bioavailability of a drug
D) ratio used to evaluate the effectiveness of a erug
A) ratio used to evaluate the elimination of a drug
B) ratio used to evaluate the safely and usefulness of a drug for indication
C) ratio used to evaluate the bioavailability of a drug
D) ratio used to evaluate the effectiveness of a erug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Principal organ/s for biotransformation of drugs is/are
A) Kidney
B) Kidney and liver
C) Lung
D) Liver
E) Skin
A) Kidney
B) Kidney and liver
C) Lung
D) Liver
E) Skin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Advantages of the rectal route of drug administration are
A) Suitable for children
B) A way to avoid first-pass metabolism. even partially
C) All of them
D) Suitable for unconscious patients
E) Suitable for children and unconscious patients
A) Suitable for children
B) A way to avoid first-pass metabolism. even partially
C) All of them
D) Suitable for unconscious patients
E) Suitable for children and unconscious patients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Binding of a drug to plasma proteins will tend to?
A) Decrease half-life.
B) Decrease its rate of glomerular filtration.
C) Increase its rate of biotransformation.
D) None
A) Decrease half-life.
B) Decrease its rate of glomerular filtration.
C) Increase its rate of biotransformation.
D) None

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Compared to the average adult dose, the recommended dose of a drug for elderly a patients will likely be?
A) Less than average due to increased biotransformation.
B) Less than average due to decreased renal function or excretion
C) More than average due to decreased plasma protein binding capacity.
D) More than average due to increased renal excretion.
A) Less than average due to increased biotransformation.
B) Less than average due to decreased renal function or excretion
C) More than average due to decreased plasma protein binding capacity.
D) More than average due to increased renal excretion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which one of the following statements is applicable to absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract?
A) Absorption of weak acids occurs only from the stomach and not from the small intestine.
B) Some drugs are metabolized extensively by the liver and do not reach the general circulation (first-pass effect)
C) Ingesting drugs with food always enhances drug absorption.
D) None
A) Absorption of weak acids occurs only from the stomach and not from the small intestine.
B) Some drugs are metabolized extensively by the liver and do not reach the general circulation (first-pass effect)
C) Ingesting drugs with food always enhances drug absorption.
D) None

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A patient is treated chronically with a drug (A) metabolized by CYP 3A4. Recently he administer another drug (B) which is an enzymatic inducer of the CYP2D6. Which of the following is likely to occur?
A) Longer half life of drug (A)
B) Longer half life of drug (B)
C) Enhanced pharmacological effect of drug A
D) No significant drug interaction
E) Reduced pharmacological effect of drug B
A) Longer half life of drug (A)
B) Longer half life of drug (B)
C) Enhanced pharmacological effect of drug A
D) No significant drug interaction
E) Reduced pharmacological effect of drug B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In general, biotransformation usually results in a product, which is more?
A) Likely to produce side effects.
B) Likely to distribute intracellularly.
C) Lipid soluble than the original drug.
D) Likely to be reabsorbed by kidney tubules.
E)Water soluble than the original drug
A) Likely to produce side effects.
B) Likely to distribute intracellularly.
C) Lipid soluble than the original drug.
D) Likely to be reabsorbed by kidney tubules.
E)Water soluble than the original drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Enzyme inhibitors such as Cimetidine and Erythromycin are likely to produce?
A) Increase rate of breakdown of some drugs
B) Increase free level of some drugs
C) Inhibition of certain enzymes. which break down some drugs.
D) Improvement of bioavailability of some drugs
A) Increase rate of breakdown of some drugs
B) Increase free level of some drugs
C) Inhibition of certain enzymes. which break down some drugs.
D) Improvement of bioavailability of some drugs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What does "affinity" mean?
A) A measure of how tightly a drug binds to plasma proteins
B) measure of how tightly a drug binds to a receptor
C) measure of inhibiting potency ofa drug
D) A measure of bioavailability ofa drug
A) A measure of how tightly a drug binds to plasma proteins
B) measure of how tightly a drug binds to a receptor
C) measure of inhibiting potency ofa drug
D) A measure of bioavailability ofa drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Target proteins, which a drug molecule could bind, is/are ?
A) Only receptors
B) Only ion channels
C) Only carriers
D) All
A) Only receptors
B) Only ion channels
C) Only carriers
D) All

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An agonist is a substance that ?
A) Interacts with the receptor without producing any effect
B)Interacts with the receptor and initiates changes in cell function, producing various effects
C) Increases concentration of another substance to produce effect
D) Interacts with plasma proteins and doesn't produce any effect
A) Interacts with the receptor without producing any effect
B)Interacts with the receptor and initiates changes in cell function, producing various effects
C) Increases concentration of another substance to produce effect
D) Interacts with plasma proteins and doesn't produce any effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A competitive antagonist is a substance that ?
A) Interacts with receptors and produces submaximal effect
B) Binds to the same receptor site and progressively inhibits the agonist response
C) Binds to the nonspecific sites of tissue
D) None of them
A) Interacts with receptors and produces submaximal effect
B) Binds to the same receptor site and progressively inhibits the agonist response
C) Binds to the nonspecific sites of tissue
D) None of them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Tick the second messenger of G-protein-coupled (metabotropic) receptor ?
A) Adenylyl cyclase
B) Sodium ions
C) Phospholipase C
D)cAmp
A) Adenylyl cyclase
B) Sodium ions
C) Phospholipase C
D)cAmp

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the type Of drug-to-drug interaction, which is connected, with processes of
A) Pharmacodynamic interaction
B) Physical and chemical interaction
C) Pharmaceutical interaction
D)Pharmacokinetic interaction
A) Pharmacodynamic interaction
B) Physical and chemical interaction
C) Pharmaceutical interaction
D)Pharmacokinetic interaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The term "chemical antagonism" means that?
A) Two drugs combine with one another to form an inactive compound
B) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more active compound
C) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more water soluble compound
D) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more fat soluble compound
A) Two drugs combine with one another to form an inactive compound
B) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more active compound
C) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more water soluble compound
D) Two drugs combine with one another to form a more fat soluble compound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Idiosyncratic reaction of a drug is?
A) A type of hypersensitivity reaction
B) A type of drug antagonism
C) Unpredictable, inherent, qualitatively abnormal reaction to a drug
D) Quantitatively exaggerated response
A) A type of hypersensitivity reaction
B) A type of drug antagonism
C) Unpredictable, inherent, qualitatively abnormal reaction to a drug
D) Quantitatively exaggerated response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Therapeutic index (TI) is?
A) ratio used to evaluate the safety and usefulness ofa drug for indication
B) ratio used to evaluate the effectiveness of a drug
C) A ratio used to evaluate the bioavailability ofa drug
D) A ratio used to evaluate the elimination ofa drug
A) ratio used to evaluate the safety and usefulness ofa drug for indication
B) ratio used to evaluate the effectiveness of a drug
C) A ratio used to evaluate the bioavailability ofa drug
D) A ratio used to evaluate the elimination ofa drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What does the term "bioavailability" mean?
A) Plasma protein binding degree of substance
B) Permeability through the brain-blood barrier
C) Fraction of an uncharged drug reaching the systemic circulation following any route administration
D) Amount ofa substance in urine relative to the initial dose
A) Plasma protein binding degree of substance
B) Permeability through the brain-blood barrier
C) Fraction of an uncharged drug reaching the systemic circulation following any route administration
D) Amount ofa substance in urine relative to the initial dose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Drug distribution: Most of drugs are distributed homogeneously?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A characteristic of drugs eliminated by zero order kinetic processes is that the half-life is not constant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The volume of distribution of gentamicin, a highly polar watersoluble drug, is 14L
Per 70 kg. This reflects the distribution of gentamicin into?
A) Plasma
B) Plasma, and interstitial fluid (extracellular)
C) Interstitial fluid
D) Total body water
E) Adipose tissue
Per 70 kg. This reflects the distribution of gentamicin into?
A) Plasma
B) Plasma, and interstitial fluid (extracellular)
C) Interstitial fluid
D) Total body water
E) Adipose tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For continuous intravenous infusion as method of administration the time needed to achieve the concentration of steady state depends on the rate of drug administration?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For drugs that have first order kinetics, after 4 half-lives about drug will be eliminated?
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 93%
D) 100%
A) 50%
B) 75%
C) 93%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 90 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



