Deck 7: Pharmacokinetics and Drug Administration: Understanding Routes and Characteristics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/68
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Pharmacokinetics and Drug Administration: Understanding Routes and Characteristics
1
Correct statements listing characteristics of a particular route of drug administration include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) Intravenous administration provides a rapid response
B) Intramuscular administration requires a sterile technique
C) Inhalation provides slow access to the general circulation
D) Subcutaneous administration may cause local irritation
A) Intravenous administration provides a rapid response
B) Intramuscular administration requires a sterile technique
C) Inhalation provides slow access to the general circulation
D) Subcutaneous administration may cause local irritation
Inhalation provides slow access to the general circulation
2
A small amount of the volume of distribution is common for lipophilic substances easy penetrating through barriers and widely distributing in plasma, interstitial and cell fluids:
False
3
If we give 2 people the same drug, all of the following will be the same except
A) mechanism of clearance
B) mechanism of metabolism
C) Half-life
A) mechanism of clearance
B) mechanism of metabolism
C) Half-life
Half-life
4
The similarity between the IV route and the rectal route is :
A) both can NOT be given to unconscious patient
B) both can be given to unconscious patient
C) both are parenteral routes
D) NON of the above
A) both can NOT be given to unconscious patient
B) both can be given to unconscious patient
C) both are parenteral routes
D) NON of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This picture represent which Route?
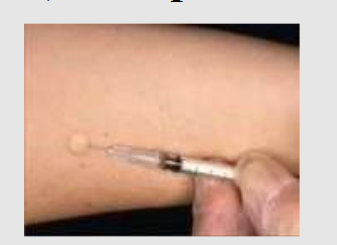
A) Intradermal to check allergy to penicillin
B) Intravenous to check allergy to penicillin
C) Intramuscular to check allergy to penicillin

A) Intradermal to check allergy to penicillin
B) Intravenous to check allergy to penicillin
C) Intramuscular to check allergy to penicillin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a patient took a drug and after 12 hours when the concentration was measured it was 800 mg so what was the initial amount of the drug ( half life = 4 hours ) ?
A) 6400
B) 3200
C) 1600
D) 800
A) 6400
B) 3200
C) 1600
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
which of those deals with pharmacokinetics :-
A) signal transduction
B) moving across biological membrane
C) NON of the above
A) signal transduction
B) moving across biological membrane
C) NON of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
if 93% of the drug eliminates in 24H what is t 1⁄2 :
A) 6 hours
B) 12 hours
C) 3 hours
D) 4 hours
A) 6 hours
B) 12 hours
C) 3 hours
D) 4 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An unconscious patient arrived to the emergency room suffers from hypoglycemia (low glucose levels in the blood), and you want to administer glucose. Other than Intravenous administration, what route of administration is BEST to be used to save his life?
A) Intramuscular.
B) Oral.
C) Inhalational.
D) intradermal.
E) Sublingual.
A) Intramuscular.
B) Oral.
C) Inhalational.
D) intradermal.
E) Sublingual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Drug X is a weak base (pKa 9.0). What percentage will be in the unionized form at an intestinal pH of 7.0?
A) 99
B) 50
C) 10
D) 90
E) 1
A) 99
B) 50
C) 10
D) 90
E) 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following condition may Increase bioavailability (after oral drug administration)?
A) A patient who also takes a drug that enhances liver enzymes
B) The administered drug is a peptide drug with 17 amino acid units.
C) A patient with a condition that increases blood flow to intestines.
D) A patient had a previous surgery to remove half of the stomach.
E) A patient with inflammatory bowel disease in small intestine
A) A patient who also takes a drug that enhances liver enzymes
B) The administered drug is a peptide drug with 17 amino acid units.
C) A patient with a condition that increases blood flow to intestines.
D) A patient had a previous surgery to remove half of the stomach.
E) A patient with inflammatory bowel disease in small intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
administration of ammonium chloride , as a weak acid increases urinary clearance of a drug . it is reasonable to assume that this drug is :
A) strong acid
B) strong base
C) neutral compound
D) weak Base
A) strong acid
B) strong base
C) neutral compound
D) weak Base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
what is the mechanism that is responsible for absorption in the GIT :
A) active transport
B) passive diffusion
C) BOTH A+B
D) NON of the above
A) active transport
B) passive diffusion
C) BOTH A+B
D) NON of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
the oral rout of drug administration tend to be associated with all of the following except :
A) poor compliance
B) relative safety
C) rapid response
D) convenience
A) poor compliance
B) relative safety
C) rapid response
D) convenience

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the loading dose of a IV drug having a volume of distribution of 150L , if the desired plasma concentration is 15mg/L ?
A) 75mg
B) 150mg
C) 2.25 mg
D) 5 g
A) 75mg
B) 150mg
C) 2.25 mg
D) 5 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
first hepatic metabolism may occur when drug is given :
A) intramuscular
B) sublingual
C) rectal
D) subcutaneous
E) none of the above
A) intramuscular
B) sublingual
C) rectal
D) subcutaneous
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The variation in pharmacological responses to drugs among individuals can be attributed to :
A) drug - drug interaction
B) sex
C) diet
D) age
E) all of the above
A) drug - drug interaction
B) sex
C) diet
D) age
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Aspirin is a weak organic acid with pKa of 3.5 , what percentage of a given dose will be unionized at stomach pH of 2.5 :
A) 1%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 90%
E) 99%
A) 1%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 90%
E) 99%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
which of the following is related to rectal administration :
A) rectal absorption if often erratic and incomplete
B) rectal absorption if often erratic and complete
C) NON of the above
A) rectal absorption if often erratic and incomplete
B) rectal absorption if often erratic and complete
C) NON of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is true about drug absorption from GIT:
A) passive diffusion is the principle mechanism of drug absorption
B) the stomach is the major site of drug absorption
C) gastric emptying doesn't affect the rate of drug absorption
D) intestinal motility has no effect on the rate or extent of drug absorption
E) all of the above
A) passive diffusion is the principle mechanism of drug absorption
B) the stomach is the major site of drug absorption
C) gastric emptying doesn't affect the rate of drug absorption
D) intestinal motility has no effect on the rate or extent of drug absorption
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
which of the following is correct about bound protein :
A) binding is mainly done by globulins
B) the bound drug is pharmacologically ineffective
C) A + B
D) NON of the above are correct
A) binding is mainly done by globulins
B) the bound drug is pharmacologically ineffective
C) A + B
D) NON of the above are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
which of the following is true about first order kinetics :
A) most of drugs follow it
B) effected by concentration of the drug
C) ALL of the above
D) NON of the above
A) most of drugs follow it
B) effected by concentration of the drug
C) ALL of the above
D) NON of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Maintenance dose can be affected by volume of distribution. Loading dose can be affected by clearance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
1ST pass metabolism refers to
A) drug-receptor binding
B) drug-plasma protein binding
C) hepatic drug metabolism when given IV
D) hepatic drug metabolism & elimination for albumin-bound drugs
E) hepatic drug metabolism during transport from the gut to the blood
A) drug-receptor binding
B) drug-plasma protein binding
C) hepatic drug metabolism when given IV
D) hepatic drug metabolism & elimination for albumin-bound drugs
E) hepatic drug metabolism during transport from the gut to the blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Pharmacokinetics deal with
A) drug interaction with its intracellular receptor
B) dose-response quantitation
C) drug mechanism of action
D) toxicological response of drugs
E) none of the above
A) drug interaction with its intracellular receptor
B) dose-response quantitation
C) drug mechanism of action
D) toxicological response of drugs
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Drug distribution is affected by :
A) blood flow to the tissues
B) drug structure & lipid solubility
C) capillary structure & permeability
D) drug binding to plasma protein
E) all of the above
A) blood flow to the tissues
B) drug structure & lipid solubility
C) capillary structure & permeability
D) drug binding to plasma protein
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following affect drug's bioavailability except
A) 1st pass metabolism
B) drug's hydrophobicity
C) drug's chemical instability
D) drug's chemical formulation
E) time needed to reach Css ( concentration at steady state )
A) 1st pass metabolism
B) drug's hydrophobicity
C) drug's chemical instability
D) drug's chemical formulation
E) time needed to reach Css ( concentration at steady state )

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The duration of drug action correlates with all of the following except :
A) the rate of drug metabolism
B) the rate of drug excretion
C) the bioavailability of the drug
D) the administered dose of the drug
E) the molecular weight of the drug
A) the rate of drug metabolism
B) the rate of drug excretion
C) the bioavailability of the drug
D) the administered dose of the drug
E) the molecular weight of the drug

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is true regarding drug absorption from GIT
A) the ileum is the major site for drug absorption
B) passive diffusion is the primary mechanism of absorption
C) giving drug with food doesn't alter drug absorption
D) ANS has no effect on drug absorption
E) patient general health does not affect drug absorption
A) the ileum is the major site for drug absorption
B) passive diffusion is the primary mechanism of absorption
C) giving drug with food doesn't alter drug absorption
D) ANS has no effect on drug absorption
E) patient general health does not affect drug absorption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
75 mg of drug T is given orally , 15mg damaged by stomach environment , 15mg is lost during 1st pass metabolism , drug T bioavailability is
A) 40%
B) 60%
C) 75%
D) 100%
E) can't be calculated
A) 40%
B) 60%
C) 75%
D) 100%
E) can't be calculated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Drug A has a half-life of 2hours , the time needed to reach 90% of steady state concentration CSS
A) 2 hours
B) 4 hours
C) 6 hours
D) 6.6 hours
E) 8.6 hours
A) 2 hours
B) 4 hours
C) 6 hours
D) 6.6 hours
E) 8.6 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a decrease in urine pH enhance the urinary excretion of a drug , it's reasonable to assume that this drug is
A) weak acid
B) weak base
C) strong acid
D) strong base
E) neutral
A) weak acid
B) weak base
C) strong acid
D) strong base
E) neutral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The half-life of a drug is influenced by
A) volume of distribution
B) clearance
C) toxic dose
D) a & b
E) none of the above
A) volume of distribution
B) clearance
C) toxic dose
D) a & b
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
First pass hepatic effect refers to:
A) Liver metabolism of drugs delivered via the portal vein.
B) Activation of drugs by hepatic enzymes.
C) Storage of drugs in the liver.
D) Biliary excretion of drugs.
E) E-Liver metabolism of drugs delivered via the hepatic artery.
A) Liver metabolism of drugs delivered via the portal vein.
B) Activation of drugs by hepatic enzymes.
C) Storage of drugs in the liver.
D) Biliary excretion of drugs.
E) E-Liver metabolism of drugs delivered via the hepatic artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
First-order elimination process:
A) Is characterized by drug dose-dependent half-life of elimination (T1/2e).
B) Applies to a limited number of drugs in clinical practice.
C) Is not applicable to the rate of drug metabolism (biotransformation).
D) Proceeds at rates dependent on drug concentration.
E) Is characterized by all listed features.
A) Is characterized by drug dose-dependent half-life of elimination (T1/2e).
B) Applies to a limited number of drugs in clinical practice.
C) Is not applicable to the rate of drug metabolism (biotransformation).
D) Proceeds at rates dependent on drug concentration.
E) Is characterized by all listed features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Biotransformation (metabolism) of drugs usually results in products that are likely to:
A) Have wide tissue distribution.
B) Produce severe side effects.
C) Be inactive pharmacologically.
D) Interact with target receptors similar to the parent drug.
E) Be more effective than parent drug.
A) Have wide tissue distribution.
B) Produce severe side effects.
C) Be inactive pharmacologically.
D) Interact with target receptors similar to the parent drug.
E) Be more effective than parent drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When drugs are administered orally:
A) Active transport is the main mechanism of drug absorption.
B) The stomach is the major site of absorption.
C) Gastric emptying does not effects the rate of drug absorption.
D) The pharmacological response tend to be rapid.
E) Incomplete absorption is likely consequence.
A) Active transport is the main mechanism of drug absorption.
B) The stomach is the major site of absorption.
C) Gastric emptying does not effects the rate of drug absorption.
D) The pharmacological response tend to be rapid.
E) Incomplete absorption is likely consequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Drug administered rectally are:
A) Not subjected to first pass hepatic effect.
B) Characterized by predictable pattern of absorption.
C) In general no favored by the patients.
D) Likely to be complicated with severe vomiting.
E) Characterized by all of the listed facts.
A) Not subjected to first pass hepatic effect.
B) Characterized by predictable pattern of absorption.
C) In general no favored by the patients.
D) Likely to be complicated with severe vomiting.
E) Characterized by all of the listed facts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is true about drug binding to plasma proteins:
A) Binding is an irreversible process.
B) Bound drug is pharmacologically inactive.
C) Drug-protein complex is effectively excreted in urine.
D) Drugs are mainly bound to plasma globulin.
E) None of the listed statements.
A) Binding is an irreversible process.
B) Bound drug is pharmacologically inactive.
C) Drug-protein complex is effectively excreted in urine.
D) Drugs are mainly bound to plasma globulin.
E) None of the listed statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is the most frequent mechanism of drug transport across biological membranes?
A) Passive diffusion.
B) Active transport.
C) Filtration.
D) Carrier-mediated process.
E) All of the listed mechanism have comparable frequency.
A) Passive diffusion.
B) Active transport.
C) Filtration.
D) Carrier-mediated process.
E) All of the listed mechanism have comparable frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following process is considered a pharmacokinetic process in pharmacology?
A) Drug transport across biological membranes.
B) Drug-receptor interaction.
C) Dose-response relationships.
D) Mechanism of drug action.
E) Toxicological response of drugs.
A) Drug transport across biological membranes.
B) Drug-receptor interaction.
C) Dose-response relationships.
D) Mechanism of drug action.
E) Toxicological response of drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The elimination half-life (T1/2e) of the drug:
A) is likely to reflect the duration of drug action.
B) is correlated with the elimination rate constant (Ke) of drug.
C) is useful for the estimation of dose interval (T).
D) cannot be estimated for drugs eliminated via zero-order kinetics.
E) Is associated by all of the listed facts.
A) is likely to reflect the duration of drug action.
B) is correlated with the elimination rate constant (Ke) of drug.
C) is useful for the estimation of dose interval (T).
D) cannot be estimated for drugs eliminated via zero-order kinetics.
E) Is associated by all of the listed facts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For drug with half-life elimination (T1/2e) of 250 minutes administered by I.V. infusion the therapeutic plasma steady state concentration (Css) "95% of the theoretical value" is expected to be achieved at:
A) 67 minutes.
B) 20 hours .
C) 12 hours.
D) 2days.
E) One week.
A) 67 minutes.
B) 20 hours .
C) 12 hours.
D) 2days.
E) One week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If 88% of a drug dose is eliminated, via first-order kinetics, in 120 hours then the half-life of elimination (T1/2e) is expected to be:
A) 15 hours.
B) 40 hours.
C) 60 hours.
D) 120 hours.
E) Greater than 120 hours.
A) 15 hours.
B) 40 hours.
C) 60 hours.
D) 120 hours.
E) Greater than 120 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A pharmacological response might be delayed, reduced, or blocked by all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) Drug that goes rapid distribution.
B) a drug that does not get its site of action.
C) Abnormal target receptor.
D) Lack of absorption at site of administration.
E) The drug that is not soluble in water.
A) Drug that goes rapid distribution.
B) a drug that does not get its site of action.
C) Abnormal target receptor.
D) Lack of absorption at site of administration.
E) The drug that is not soluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Drugs that are highly bound (greater than 90%) to plasma protein are likely to:
A) Be associated with large volume of distribution (Vd).
B) Have very short half-life off elimination(T1/2e).
C) Be associated with wide therapeutic index (TI).
D) Have short duration of action.
E) Be characterized by low renal clearance values.
A) Be associated with large volume of distribution (Vd).
B) Have very short half-life off elimination(T1/2e).
C) Be associated with wide therapeutic index (TI).
D) Have short duration of action.
E) Be characterized by low renal clearance values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Intravenous route of drug administration is associated with:
A) Absence of an absorption process.
B) High risk of systemic toxicity.
C) Rapid response.
D) Potential risks of topical and systemic infections.
E) All of the listed features.
A) Absence of an absorption process.
B) High risk of systemic toxicity.
C) Rapid response.
D) Potential risks of topical and systemic infections.
E) All of the listed features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is the expected loading dose (Dl) of a drug having volume of distribution (Vd) value of 150 liter, if desired plasma concentration is 5 microgram/ml?
A) 225 mg
B) 450 mg
C) 750 mg
D) 1.5 mg
E) 5.0 mg
A) 225 mg
B) 450 mg
C) 750 mg
D) 1.5 mg
E) 5.0 mg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Estimation of the maintenance (Dm) of drug depends on all of the following EXCEPT:
A) The dose interval (T).
B) The desired plasma steady state concentration (Css).
C) The absorption rate constant (Ka).
D) The drug Bioavailability (F).
E) Systemic clearance (CL).
A) The dose interval (T).
B) The desired plasma steady state concentration (Css).
C) The absorption rate constant (Ka).
D) The drug Bioavailability (F).
E) Systemic clearance (CL).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
First order kinetics and zero-order kinetics are similar in:
A) Both of them are dose-dependent
B) Both of them are not susceptible to phase I and II metabolism
C) all of the listed statements are correct
D) Both of them have fixed half-lives.
E) Both of them are metabolized in the liver
A) Both of them are dose-dependent
B) Both of them are not susceptible to phase I and II metabolism
C) all of the listed statements are correct
D) Both of them have fixed half-lives.
E) Both of them are metabolized in the liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The principle organ for drug excretion is
A) intestine
B) lungs
C) kidneys
D) liver
E) CNS
A) intestine
B) lungs
C) kidneys
D) liver
E) CNS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following conditions will INCREASE the volume of distribution of medications?
A) All of the listed conditions.
B) Conditions of dehydration.
C) Hydrophilic medications,
D) lonized medications.
E) Decrease liver functions.
A) All of the listed conditions.
B) Conditions of dehydration.
C) Hydrophilic medications,
D) lonized medications.
E) Decrease liver functions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A drug was administered orally and intravenously in two different patients. The drug in both patients will be similar in:
A) Bioavailability.
B) Peak concentration.
C) Onset of action.
D) Half-life.
E) Potency
A) Bioavailability.
B) Peak concentration.
C) Onset of action.
D) Half-life.
E) Potency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A patient had given 400 mg of drug Z. After 70 hours, the amount left of the drug in the body was calculated to 12.5 mg. What is the half-life of drug Z?
A) 5.6 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 32 hours.
D) Can not be calculated
E) 12.5 hours.
A) 5.6 hours.
B) 14 hours.
C) 32 hours.
D) Can not be calculated
E) 12.5 hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the advantage of loading dose?
A) It will delay therapeutic effect of the drug.
B) It will increase the potency of the drug.
C) It will increase the half-life of the drug.
D) It will shorten the onset of action of the drug.
E) It will increase efficacy of the drug.
A) It will delay therapeutic effect of the drug.
B) It will increase the potency of the drug.
C) It will increase the half-life of the drug.
D) It will shorten the onset of action of the drug.
E) It will increase efficacy of the drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The first half-life of a first-order kinetics drug is:
A) Shorter than the second half-life for the same drug after the same dose.
B) Shorter than the second half-life for the same drug after a higher dose.
C) Similar to the second half-life. for the same drug after a higher dose.
D) Longer than the first half-life for the same drug after a higher dose.
E) Longer than the second half-life for the same drug after the same dose.
A) Shorter than the second half-life for the same drug after the same dose.
B) Shorter than the second half-life for the same drug after a higher dose.
C) Similar to the second half-life. for the same drug after a higher dose.
D) Longer than the first half-life for the same drug after a higher dose.
E) Longer than the second half-life for the same drug after the same dose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A drug with high clearance rate indicates:
A) It has high therapeutic index.
B) It has low efficacy.
C) It has long half-life.
D) It has high efficacy.
E) It should be administered more frequently.
A) It has high therapeutic index.
B) It has low efficacy.
C) It has long half-life.
D) It has high efficacy.
E) It should be administered more frequently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The duration of drug action depends on all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) Drug potency.
B) Drug bioavailability
C) Renal clearance of the drug.
D) Drug dose.
E) Rate of drug metabolism.
A) Drug potency.
B) Drug bioavailability
C) Renal clearance of the drug.
D) Drug dose.
E) Rate of drug metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following conditions will increase drug absorption from the intestines?
A) Increased blood flow to the intestines.
B) Decrease the dose of the administered drug.
C) Patients who already suffer from diarrhea.
D) All of the listed may increase the absorption.
E) Partial surgical removal of the small intestine.
A) Increased blood flow to the intestines.
B) Decrease the dose of the administered drug.
C) Patients who already suffer from diarrhea.
D) All of the listed may increase the absorption.
E) Partial surgical removal of the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Parenteral routes of drug administration includes
A) IM & IV only
B) IM , IV & IA only
C) SC
D) SC , IM , IV & IA
E) SC , IM & IV
A) IM & IV only
B) IM , IV & IA only
C) SC
D) SC , IM , IV & IA
E) SC , IM & IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the estimated blood concentration for ciprofloxacin if 500mg of it was given by oral route , bioavailability is 40% and volume of distribution is 20 L
A) 25mg/L
B) 10mg/L
C) 100mg/L
D) 250mg/L
E) 100g/L
A) 25mg/L
B) 10mg/L
C) 100mg/L
D) 250mg/L
E) 100g/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If 87.5% of a drug is eliminated via 1st order kinetics in 15 hours , then the t1/2 is
A) 5 hours
B) 10 hours
C) 15 hours
D) 30 hours
E) greater than 30 years
A) 5 hours
B) 10 hours
C) 15 hours
D) 30 hours
E) greater than 30 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the previous question , the expected time for Css is
A) 1 day
B) 2 day
C) 3 days
D) 5 days
E) one week
A) 1 day
B) 2 day
C) 3 days
D) 5 days
E) one week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The oral route of drug administration tend to be associated with all of the following except
A) poor compliance
B) relative safety
C) rapid response
D) convenience
A) poor compliance
B) relative safety
C) rapid response
D) convenience

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What does "pharmacokinetics" include?
A) Pharmacological effects of drugs
B) Unwanted effects of drugs
C) Chemical structure of a medicinal agent
D) Distribution of drugs in the organism
A) Pharmacological effects of drugs
B) Unwanted effects of drugs
C) Chemical structure of a medicinal agent
D) Distribution of drugs in the organism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The intensity (magnitude) and direction of drug action correlate in a predictable by way the:
A) Lipid/water partition coefficient (LWPC) of the drug.
B) Potency of the drug.
C) Molecular weight of the drug.
D) Administered dose of the drug.
E) Efficacy of the drug.
A) Lipid/water partition coefficient (LWPC) of the drug.
B) Potency of the drug.
C) Molecular weight of the drug.
D) Administered dose of the drug.
E) Efficacy of the drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Intravenous injections are more suitable for oily solutions:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is a common similarity between sublingual route of administration, and oral route of administration?
A) Speediness in response.
B) Quickness in absorption.
C) All of the listed are commonality between them.
D) Cheapness.
E) Susceptibility to first-pass effect.
A) Speediness in response.
B) Quickness in absorption.
C) All of the listed are commonality between them.
D) Cheapness.
E) Susceptibility to first-pass effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 68 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



