Deck 12: Investing in Stocks and Bonds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Investing in Stocks and Bonds
1
Which is the best strategy for a beginning investor?
A) A portfolio of individual stocks
B) A portfolio of individual bonds
C) A portfolio of individual stocks and bonds
D) A portfolio of mutual funds
A) A portfolio of individual stocks
B) A portfolio of individual bonds
C) A portfolio of individual stocks and bonds
D) A portfolio of mutual funds
A portfolio of mutual funds
2
Which of the following portfolio strategies is the riskiest?
A) Investing 100 percent in a small-cap technology company
B) Investing 100 percent in a blue-chip manufacturing company
C) Investing equally in 20 stocks that are all in different industries
D) Investing 50 percent each in a small-cap technology company and a blue-chip manufacturing company
A) Investing 100 percent in a small-cap technology company
B) Investing 100 percent in a blue-chip manufacturing company
C) Investing equally in 20 stocks that are all in different industries
D) Investing 50 percent each in a small-cap technology company and a blue-chip manufacturing company
Investing 100 percent in a small-cap technology company
3
Owners of sole proprietorships generally have ____ personal liability than owners of corporations.
A) less
B) more
C) the same
D) no
A) less
B) more
C) the same
D) no
more
4
Dell is an American computer company. The founder, Michael Dell, and global technology investment firm, Silver Lake Partners, own all of the shares of Dell. It is not possible to buy shares of Dell stock on the secondary market because Dell is a
A) sole proprietorship.
B) partnership.
C) private corporation.
D) public corporation.
A) sole proprietorship.
B) partnership.
C) private corporation.
D) public corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If you buy 100 shares in a corporation that has issued 1,000 shares, your proportionate share of ownership in the company is
A) 0.01%.
B) 0.1%.
C) 1%.
D) 10%.
A) 0.01%.
B) 0.1%.
C) 1%.
D) 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A common shareholder's claim on a company's assets is residual, meaning the shareholder has a right to share in the assets and income of the corporation only after higher-priority claims from________ are satisfied.
A) bondholders
B) creditors
C) preferred shareholders
D) All of the above.
A) bondholders
B) creditors
C) preferred shareholders
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Common stockholders have
A) the right to payment of reasonable dividends.
B) the right to vote on all company decisions.
C) limited liability.
D) All of the above.
A) the right to payment of reasonable dividends.
B) the right to vote on all company decisions.
C) limited liability.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A stock dividend provides ___ benefit to a stockholder as a cash dividend.
A) as much immediate
B) not as much immediate
C) the same immediate
D) no
A) as much immediate
B) not as much immediate
C) the same immediate
D) no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A written agreement that gives your common stock voting rights to someone else is known as a
A) proxy.
B) preemptive right.
C) forfeit agreement.
D) voting assignment.
A) proxy.
B) preemptive right.
C) forfeit agreement.
D) voting assignment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Limited liability for common shareholders means the most one can lose on a share of stock is
A) the value of the share itself.
B) the prorated value of the company's debt.
C) your proportionate value of the company's debt.
D) your proportionate value of the company less its debt.
A) the value of the share itself.
B) the prorated value of the company's debt.
C) your proportionate value of the company's debt.
D) your proportionate value of the company less its debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The reason corporations give the preemptive right to stockholders is to
A) allow them to maintain their percentage interest in the firm.
B) reduce the dividend payments to the common stockholders.
C) entice them into buying more shares of stock.
D) keep control of the company within a small number of investors.
A) allow them to maintain their percentage interest in the firm.
B) reduce the dividend payments to the common stockholders.
C) entice them into buying more shares of stock.
D) keep control of the company within a small number of investors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If you own 100 shares of stock currently selling at $50 per share and the company declares a 3 for 1 split, you will have about ______ after the split.
A) 33.33 shares at $150.00
B) 50 shares at $100.00
C) 200 shares at $25.00
D) 300 shares at $16.67
A) 33.33 shares at $150.00
B) 50 shares at $100.00
C) 200 shares at $25.00
D) 300 shares at $16.67

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements concerning stock splits is true?
A) Announcement of a stock split often causes the price to rise.
B) The major reason for a stock split is to increase the shares outstanding.
C) Stock splits are like stock dividends as both increase the value of the firm.
D) After a stock split, the total value of shares increases.
A) Announcement of a stock split often causes the price to rise.
B) The major reason for a stock split is to increase the shares outstanding.
C) Stock splits are like stock dividends as both increase the value of the firm.
D) After a stock split, the total value of shares increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When a stock split occurs,
A) owners of stock end up with a lower number of shares.
B) owners of stock end up with a higher number of shares
C) the price of the share increases.
D) the price of the share decreases.
A) owners of stock end up with a lower number of shares.
B) owners of stock end up with a higher number of shares
C) the price of the share increases.
D) the price of the share decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You plan to put $1,500 in an investment account today. What will it be worth in 20 years if you invest half in corporate bonds that pay 4% per year and half in corporate stock that earns 9% per year? Assume annual reinvestment of returns and round to the nearest dollar.
A) $3,287
B) $5,285
C) $5,847
D) $8,406
A) $3,287
B) $5,285
C) $5,847
D) $8,406

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following potential investments, which is the most liquid?
A) One-year certificate of deposit
B) Checking account
C) Common stock
D) Corporate bond
A) One-year certificate of deposit
B) Checking account
C) Common stock
D) Corporate bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a disadvantage of common stock ownership?
A) Relative liquidity
B) Low interest-rate sensitivity
C) Management control
D) High potential long-term returns
A) Relative liquidity
B) Low interest-rate sensitivity
C) Management control
D) High potential long-term returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A stock that pays investors a regular dividend is a good example of a(n)
A) cyclical stock
B) income stock.
C) growth stock
D) defensive stock
A) cyclical stock
B) income stock.
C) growth stock
D) defensive stock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the last several years, Monster Beverage Corporation's stock price has increased substantially. The company has never paid its common shareholders a dividend. Monster Beverage Corporation can be classified as a(n) _______ stock.
A) income
B) growth
C) cyclical
D) blue-chip
A) income
B) growth
C) cyclical
D) blue-chip

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A stock issued by a large, stable, mature company is known as a(n)
A) blue-chip stock.
B) growth stock.
C) black chip stock.
D) income stock.
A) blue-chip stock.
B) growth stock.
C) black chip stock.
D) income stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Cyclical firms are more likely to produce
A) consumer durable goods.
B) consumer staples.
C) food and beverages.
D) health-care products.
A) consumer durable goods.
B) consumer staples.
C) food and beverages.
D) health-care products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following two stocks is least risky, assuming it is held in a diversified portfolio? Use the information below.
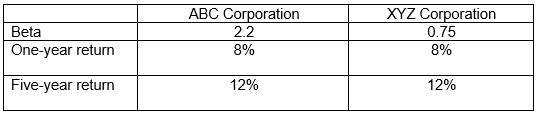
A) ABC Corporation
B) XYZ Corporation
C) They are equally risky.
D) There is insufficient information to determine risk.

A) ABC Corporation
B) XYZ Corporation
C) They are equally risky.
D) There is insufficient information to determine risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a company has 1.5 million shares outstanding at $25 per share, what is its market capitalization?
A) $1.5 million
B) $25 million
C) $37.5 million
D) $75 million
A) $1.5 million
B) $25 million
C) $37.5 million
D) $75 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A small-cap company generally has a market capitalization of less than
A) $2 billion.
B) $300 million.
C) $10 million.
D) $2 million.
A) $2 billion.
B) $300 million.
C) $10 million.
D) $2 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements is false concerning small-cap firms?
A) They often pay large cash dividends.
B) They tend to be more sensitive to market movements.
C) They are generally young, growing companies.
D) They have historically seen larger investment returns.
A) They often pay large cash dividends.
B) They tend to be more sensitive to market movements.
C) They are generally young, growing companies.
D) They have historically seen larger investment returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A company with market capitalization of $2.5 billion is considered a
A) micro-cap company.
B) small-cap company.
C) mid-cap company.
D) large-cap company.
A) micro-cap company.
B) small-cap company.
C) mid-cap company.
D) large-cap company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Large-cap companies have market capitalization greater than or equal to
A) $10 billion.
B) $1 billion.
C) $100 million.
D) $10 million.
A) $10 billion.
B) $1 billion.
C) $100 million.
D) $10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A measure of market or non-diversifiable risk is the
A) beta.
B) variation.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.
A) beta.
B) variation.
C) standard deviation.
D) coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A stock paying an annual dividend of $1.10 and selling at a price of $27.50 has a dividend yield of
A) 1.0%.
B) 2.5%.
C) 4.0%.
D) 16%.
A) 1.0%.
B) 2.5%.
C) 4.0%.
D) 16%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If a stock is trading at $50 and has a quarterly dividend of $0.55, the dividend yield on the stock is
A) 1.1%.
B) 4.4%.
C) 5.0%.
D) 5.5%.
A) 1.1%.
B) 4.4%.
C) 5.0%.
D) 5.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If you buy a stock at $46 and sell it one year later for $57, your capital gains yield is
A) 19.3%.
B) 21.4%.
C) 23.9%.
D) 41.8%.
A) 19.3%.
B) 21.4%.
C) 23.9%.
D) 41.8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Aliyah purchased ABC Corporation stock for $48.90 per share. She sold the stock one-year later for $54.01 per share and collected $2.20 in dividends. What was her capital gains yield for the year?
A) 5.11%
B) 9.00%
C) 9.46%
D) 10.45%
A) 5.11%
B) 9.00%
C) 9.46%
D) 10.45%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is false regarding earnings per share (EPS)?
A) Companies with higher EPS are better investments than those with lower EPS.
B) EPS provides a rough measure of a company's profitability.
C) Investors commonly use EPS in their analysis of stock investments.
D) Better-than-expected EPS will usually cause the stock price to rise.
A) Companies with higher EPS are better investments than those with lower EPS.
B) EPS provides a rough measure of a company's profitability.
C) Investors commonly use EPS in their analysis of stock investments.
D) Better-than-expected EPS will usually cause the stock price to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The EPS ratio measures the
A) market capitalization to its market price .
B) relationship between earnings and the market.
C) investor's proportionate share of the firm's annual after-tax net income.
D) investor's proportionate share of the firm's annual dividend payout.
A) market capitalization to its market price .
B) relationship between earnings and the market.
C) investor's proportionate share of the firm's annual after-tax net income.
D) investor's proportionate share of the firm's annual dividend payout.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When comparing similar firms, a high P/E ratio is often viewed as an indication that a stock is ________ .
A) overpriced
B) underpriced
C) fairly priced
D) uncorrelated
A) overpriced
B) underpriced
C) fairly priced
D) uncorrelated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a firm has a P/E of 12 and a current price of $48, then its EPS is
A) $0.25.
B) $4.00.
C) $576.00.
D) impossible to determine.
A) $0.25.
B) $4.00.
C) $576.00.
D) impossible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
See-Saw, Inc., has a P/E ratio of 45, and SloMo Corporation's P/E ratio is 12. Based on these performance measures, which stock do you expect has the better growth prospects?
A) See-Saw Incorporated
B) SloMo Corporation
C) They have equal growth prospects.
D) This cannot be determined without knowing the past price history.
A) See-Saw Incorporated
B) SloMo Corporation
C) They have equal growth prospects.
D) This cannot be determined without knowing the past price history.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When you buy bonds issued by a company, you become a(n) _______ of the company.
A) owner
B) lender
C) partner
D) shareholder
A) owner
B) lender
C) partner
D) shareholder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A bond investor is a(n)________.
A) lender
B) creditor
C) owner
D) Both A and B are correct.
A) lender
B) creditor
C) owner
D) Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Marian bought $3,000 in stock and held it for one year. She paid $50 per share in cash, received no dividends, and sold the shares for $55 per share one year later. Ignoring transaction costs, what was her return on investment?
A) 3%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 30%
A) 3%
B) 5%
C) 10%
D) 30%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Debt financing is typically _______ for a company than equity financing.
A) more expensive
B) less expensive
C) the same cost
D) exorbitant
A) more expensive
B) less expensive
C) the same cost
D) exorbitant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following are reasons that a company might prefer to sell bonds than issue stock?
A) It typically costs less to issue bonds than to issue stock.
B) Interest payments on bonds are tax-deductible for the firm, whereas dividend payments are not.
C) When a firm issues bonds, the percentage ownership of existing shareholders is not reduced.
D) All of the above are reasons that a company might prefer issuing bonds over issuing stock.
A) It typically costs less to issue bonds than to issue stock.
B) Interest payments on bonds are tax-deductible for the firm, whereas dividend payments are not.
C) When a firm issues bonds, the percentage ownership of existing shareholders is not reduced.
D) All of the above are reasons that a company might prefer issuing bonds over issuing stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Increasing the amount of debt financing used by a company will usually _______ the return to the stockholders.
A) decrease
B) increase
C) have no effect on
D) have a negative effect on
A) decrease
B) increase
C) have no effect on
D) have a negative effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Favorable leverage occurs when the
A) interest rate on debt financing is less than the rate of return earned by the firm.
B) dividend rate on a stock is less than the interest rate a on bond.
C) interest rate on debt financing is less than the dividend yield on a stock.
D) rate of return earned by the firm is less than the interest rate on its debt financing.
A) interest rate on debt financing is less than the rate of return earned by the firm.
B) dividend rate on a stock is less than the interest rate a on bond.
C) interest rate on debt financing is less than the dividend yield on a stock.
D) rate of return earned by the firm is less than the interest rate on its debt financing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Corporate bonds are typically issued in denominations of
A) $25.
B) $100.
C) $1,000.
D) $10,000.
A) $25.
B) $100.
C) $1,000.
D) $10,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following types of bonds has the lowest liquidity risk?
A) Treasury bonds
B) corporate bonds
C) municipal bonds
D) All have equal liquidity risk.
A) Treasury bonds
B) corporate bonds
C) municipal bonds
D) All have equal liquidity risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A U.S. government security that has an original maturity of one year or less is called a
A) Treasury bond.
B) Treasury note.
C) Treasury bill.
D) municipal bond.
A) Treasury bond.
B) Treasury note.
C) Treasury bill.
D) municipal bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The interest paid on municipal bonds is always exempt from
A) federal income tax.
B) all state income tax.
C) federal and all state income taxes.
D) federal and state income tax of residency.
A) federal income tax.
B) all state income tax.
C) federal and all state income taxes.
D) federal and state income tax of residency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A municipal bond that is repaid from normal operating cash flows is a(n)
A) general obligation bond.
B) secured bond.
C) revenue bond.
D) operational bond.
A) general obligation bond.
B) secured bond.
C) revenue bond.
D) operational bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Agency issues are issued in _______ denominations than Treasury issues and are more commonly bought by _______ investors than are Treasury securities.
A) larger; individual
B) larger; institutional
C) smaller; individual
D) smaller; institutional
A) larger; individual
B) larger; institutional
C) smaller; individual
D) smaller; institutional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The most common arrangement for bond coupon payments is
A) fixed-rate interest paid in semiannual payments.
B) floating-rate interest paid in annual payments.
C) zero-coupon payments.
D) indexed-rate payments.
A) fixed-rate interest paid in semiannual payments.
B) floating-rate interest paid in annual payments.
C) zero-coupon payments.
D) indexed-rate payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A bond that has its interest payments tied to current market interest rates is called a
A) market rate bond.
B) floating-rate bond.
C) fixed-rate bond.
D) zero-coupon bond.
A) market rate bond.
B) floating-rate bond.
C) fixed-rate bond.
D) zero-coupon bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is an advantage of floating-rate bonds?
A) No risk of being called
B) Greater resale value
C) Higher interest rates
D) Increased marketability
A) No risk of being called
B) Greater resale value
C) Higher interest rates
D) Increased marketability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The annual rate of return on a zero-coupon bond investment comes from the
A) interest yield.
B) capital gain yield.
C) interest yield and the capital gain yield.
D) tax savings.
A) interest yield.
B) capital gain yield.
C) interest yield and the capital gain yield.
D) tax savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is false regarding zero-coupon bonds?
A) They make regular semiannual coupon payments.
B) Both corporations and governments issue them.
C) Their entire yield comes from capital gains.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) They make regular semiannual coupon payments.
B) Both corporations and governments issue them.
C) Their entire yield comes from capital gains.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you own a TIPS bond that promises an inflation-adjusted rate of return of 2.5 percent, and annual inflation is 3 percent in a given year,
A) you will be paid a higher rate of interest on the bond the following year.
B) your bond's face value in the following year will be increased by the inflation rate, resulting in an increase in the amount of interest paid.
C) the dollar amount of interest you receive will go down in the following year to compensate for inflation.
D) both the bond face value and the coupon rate will be increased by 3 percent the following year.
A) you will be paid a higher rate of interest on the bond the following year.
B) your bond's face value in the following year will be increased by the inflation rate, resulting in an increase in the amount of interest paid.
C) the dollar amount of interest you receive will go down in the following year to compensate for inflation.
D) both the bond face value and the coupon rate will be increased by 3 percent the following year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If Standard & Poor's Ratings Services lowers its corporate credit rating on a particular company's bonds from B+ to BB-, the new rating informs investors that the bonds are
A) very high quality.
B) high quality.
C) speculative.
D) in default.
A) very high quality.
B) high quality.
C) speculative.
D) in default.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Bonds that are rated BBB or better by Standard & Poor's are referred to as
A) investment-grade bonds.
B) risk-free bonds.
C) junk bonds.
D) recession-proof bonds.
A) investment-grade bonds.
B) risk-free bonds.
C) junk bonds.
D) recession-proof bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Bond rating agencies grade the lowest risk bonds as
A) junk bonds.
B) speculative-grade bonds.
C) low-yield bonds.
D) investment-grade bonds.
A) junk bonds.
B) speculative-grade bonds.
C) low-yield bonds.
D) investment-grade bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A trustee of a bond issue is usually
A) the investment bank that sold the issue.
B) the issuer's commercial bank.
C) the Federal Reserve.
D) a bank trust company.
A) the investment bank that sold the issue.
B) the issuer's commercial bank.
C) the Federal Reserve.
D) a bank trust company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How does the typical bond pay down principal?
A) Amortized monthly over the life of the issue
B) Amortized at coupon dates
C) Amortized annually
D) Payable at maturity
A) Amortized monthly over the life of the issue
B) Amortized at coupon dates
C) Amortized annually
D) Payable at maturity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The annual rate of interest on a bond is known as the
A) face value.
B) coupon rate.
C) call provision.
D) dividend.
A) face value.
B) coupon rate.
C) call provision.
D) dividend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The coupon rate is the fixed interest rate on the bond and is quoted as a percentage of
A) face value.
B) current value.
C) market value
D) callable value.
A) face value.
B) current value.
C) market value
D) callable value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A corporate bond has a 9.4% annual coupon rate. The bond has a $1,000 face value and is currently selling at $900. The annual coupon payment on this bond is
A) $84.60.
B) $94.00.
C) $97.83.
D) $108.70.
A) $84.60.
B) $94.00.
C) $97.83.
D) $108.70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What amount of interest is paid per year on a 20-year, 7% coupon corporate bond with a $1,000 face value and semiannual interest payments?
A) $35
B) $70
C) $1,000
D) $1,070
A) $35
B) $70
C) $1,000
D) $1,070

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Corporate bonds often have a _________, a contractual term that allows the firm to repay the bond before the maturity date.
A) convertible provision
B) call provision
C) bearer provision
D) maturity date provision
A) convertible provision
B) call provision
C) bearer provision
D) maturity date provision

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The price of a convertible bond is more likely to rise when the underlying stock price
A) declines.
B) rises.
C) declares a dividend.
D) pays a dividend.
A) declines.
B) rises.
C) declares a dividend.
D) pays a dividend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The value of a bond is the discounted present value of
A) the interest to be received.
B) the par value of the bond.
C) both the interest to be received and the par value of the bond.
D) both the interest to be received and the market value of the bond.
A) the interest to be received.
B) the par value of the bond.
C) both the interest to be received and the par value of the bond.
D) both the interest to be received and the market value of the bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not a major risk of investing in bonds?
A) Tax risk
B) Default risk
C) reinvestment risk
D) Inflation risk
A) Tax risk
B) Default risk
C) reinvestment risk
D) Inflation risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Investors who buy bonds often do so because bonds
A) have a higher return potential than stocks.
B) provide a predictable income stream.
C) have a higher risk than stocks.
D) are risk-free.
A) have a higher return potential than stocks.
B) provide a predictable income stream.
C) have a higher risk than stocks.
D) are risk-free.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Bond prices go up and down over time in response to changes in
A) the consumer price index.
B) the stock market.
C) market interest rates.
D) housing prices.
A) the consumer price index.
B) the stock market.
C) market interest rates.
D) housing prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements regarding bonds and inflation risk is true?
A) Bond investors will require higher yields on bonds if inflation rises.
B) Rising inflation will generally cause bond prices to also rise.
C) Bonds are less influenced by inflation risk than are common stocks.
D) Long-term bonds have less inflation risk than short-term bonds.
A) Bond investors will require higher yields on bonds if inflation rises.
B) Rising inflation will generally cause bond prices to also rise.
C) Bonds are less influenced by inflation risk than are common stocks.
D) Long-term bonds have less inflation risk than short-term bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following statements regarding bond price and interest rates is true?
A) The longer the time to maturity, the greater the percentage decline in bond value for a given rise in interest rates
B) The longer the time to maturity, the greater the percentage decline in bond value for a given decline in interest rates
C) The longer the time to maturity, the smaller the percentage decline in bond value for a given rise in interest rates
D) The longer the time to maturity, the smaller the percentage rise in bond value for a given rise in interest rates
A) The longer the time to maturity, the greater the percentage decline in bond value for a given rise in interest rates
B) The longer the time to maturity, the greater the percentage decline in bond value for a given decline in interest rates
C) The longer the time to maturity, the smaller the percentage decline in bond value for a given rise in interest rates
D) The longer the time to maturity, the smaller the percentage rise in bond value for a given rise in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Yield to maturity is a popular measure because it tells an investor
A) the annualized yield they will earn if they hold the bond to maturity.
B) the yield they will earn if they sell the bond today.
C) how much annual interest they will receive.
D) None of the above.
A) the annualized yield they will earn if they hold the bond to maturity.
B) the yield they will earn if they sell the bond today.
C) how much annual interest they will receive.
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A 7.8% coupon bond that pays interest semiannually is selling at $872, has a face value of $1,000, and matures in 12 years. What is the bond's yield to maturity?
A) 3.90%
B) 4.81%
C) 7.80%
D) 9.62%
A) 3.90%
B) 4.81%
C) 7.80%
D) 9.62%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Preferred stock usually pays a _______ dividend based on a fixed percentage of its par value.
A) monthly
B) quarterly
C) semiannual
D) annual
A) monthly
B) quarterly
C) semiannual
D) annual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Callable preferred stock generally
A) pays a higher dividend than comparable noncallable preferred stock.
B) pays a lower dividend than comparable noncallable preferred stock.
C) does not pay a dividend.
D) pays the same dividend as a noncallable preferred stock.
A) pays a higher dividend than comparable noncallable preferred stock.
B) pays a lower dividend than comparable noncallable preferred stock.
C) does not pay a dividend.
D) pays the same dividend as a noncallable preferred stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Convertible preferred stock allows the stockholder to convert into
A) common stock of the company.
B) bonds of the company.
C) either common stock or bonds of the company.
D) bonds and common stock of the company.
A) common stock of the company.
B) bonds of the company.
C) either common stock or bonds of the company.
D) bonds and common stock of the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
You would expect ______ stock to carry a higher dividend rate than comparable ______ stock.
A) convertible preferred; nonconvertible preferred
B) nonconvertible preferred; convertible preferred
C) convertible preferred; common
D) common; nonconvertible preferred
A) convertible preferred; nonconvertible preferred
B) nonconvertible preferred; convertible preferred
C) convertible preferred; common
D) common; nonconvertible preferred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Preferred stock values, like ____, generally ________ when interest rates fall.
A) bonds; move down
B) bonds, move up
C) common stock; remain the same
D) bonds; remain the same
A) bonds; move down
B) bonds, move up
C) common stock; remain the same
D) bonds; remain the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



