Deck 21: Some Almost Assumption-Free Tests
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Some Almost Assumption-Free Tests
1
We wish to determine if two strains of laboratory rats differ in maze-running ability. Random samples of naive (never been experimented on) rats are selected from each strain, and each rat is run through a test maze until it can negotiate the maze with no errors on two consecutive trials. The following results are obtained (number of trials to learn):
 Apply the Mann-Whitney test. Use
Apply the Mann-Whitney test. Use
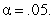
Interpret the outcome using appropriate descriptive statistics.
 Apply the Mann-Whitney test. Use
Apply the Mann-Whitney test. Use 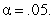
Interpret the outcome using appropriate descriptive statistics.
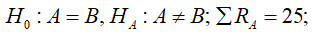
critical values (.05): 11 and 29; retain
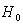 ; no significant difference between medians.
; no significant difference between medians. 2
Dr. Smith wishes to compare three widely used sleeping pills with regard to possible "hangover" effects. Twelve volunteers are given a problem-solving test at 9:00 a.m. after having been administered the standard recommended dose of one of the preparations (according to random assignment) the night before. The results are given below.
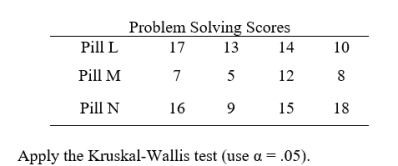

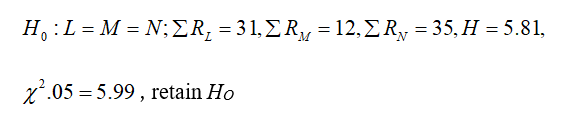
3
Your casual observations suggest that sons, upon maturity, are in general taller than their fathers. A friend, on the other hand, argues that the opposite is true. In order to check this out, you measure the heights of a sample of nine father-son pairs. The following are the results (to the nearest inch):
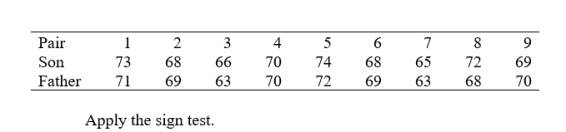

(a) - (b)If + represents a taller son, there are 5 pluses and 3 minuses and one tie; with the tie eliminated, the effective sample size is 8;
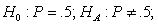
critical regions: 0 or 8; retain
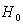 .
.
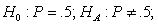
critical regions: 0 or 8; retain
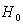 .
. 4
The most important reason for using assumption-freer statistical tests has to do with
A) matters of computation
B) statistical assumptions
C) power and Type II error
D) random sampling
A) matters of computation
B) statistical assumptions
C) power and Type II error
D) random sampling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compared to z, t, and F, assumption-freer statistical tests become increasingly attractive when
A) normality of distribution can be assumed
B) sample size is large
C) homogeneity of variance is the rule
D) sample size is small
A) normality of distribution can be assumed
B) sample size is large
C) homogeneity of variance is the rule
D) sample size is small

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The Mann-Whitney, Kruskal-Wallis, sign, and Wilcoxon signed-ranks tests are tests about
A) the difference between two (or more) means
B) the difference between two (or more) medians
C) the difference between two (or more) standard deviations
D) the difference between two (or more) distributions
A) the difference between two (or more) means
B) the difference between two (or more) medians
C) the difference between two (or more) standard deviations
D) the difference between two (or more) distributions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A randomization test compares the obtained sample results with
A) the sampling distribution of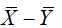
B) the theoretical distribution of 11efbba8_4689_a457_ad7c_172efb2abdfe_TB10832_00
C) all possible combinations of 11efbba8_4689_a457_ad7c_172efb2abdfe_TB10832_00 using the sample data
D) any of the above
A) the sampling distribution of
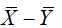
B) the theoretical distribution of 11efbba8_4689_a457_ad7c_172efb2abdfe_TB10832_00
C) all possible combinations of 11efbba8_4689_a457_ad7c_172efb2abdfe_TB10832_00 using the sample data
D) any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the following scores: 4, 2, 3, 6, 4, are placed in rank order, a score of 4 would be assigned a rank order of
A) 3
B) 4
C) 3.5
D) 4.5
A) 3
B) 4
C) 3.5
D) 4.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The sum of a set of ranks can be found from the formula:
A) n(n - 1)/2
B) n(n + 1)/2
C) n(n - 1)
D) (n1 - 1) + (n2 - 1)
A) n(n - 1)/2
B) n(n + 1)/2
C) n(n - 1)
D) (n1 - 1) + (n2 - 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Tests and measures involving rank order generally
A) will be unsatisfactory when there are ties in rank
B) will be reasonably satisfactory when there are ties in rank
C) will be reasonably satisfactory when there are not a lot of ties in rank
D) are satisfactory irrespective of the presence of ties in rank
A) will be unsatisfactory when there are ties in rank
B) will be reasonably satisfactory when there are ties in rank
C) will be reasonably satisfactory when there are not a lot of ties in rank
D) are satisfactory irrespective of the presence of ties in rank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The measure that seems most reasonable to examine upon obtaining significant results from a Mann-Whitney U test is the
A) median
B) mean
C) variance
D) standard deviation
A) median
B) mean
C) variance
D) standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A Mann-Whitney U test is performed and significant results are obtained. This indicates a population difference with regard to
A) central tendency
B) variability
C) shape
D) any or all of the above
A) central tendency
B) variability
C) shape
D) any or all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The basic data from which all other computations flow when performing a Mann-Whitney U test or a Kruskal-Wallis test are
A)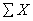 and
and 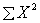 for each group separately
for each group separately
B) deviation scores based on combined groups
C) ranks within each group separately
D) ranks based on all groups combined
A)
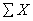 and
and 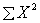 for each group separately
for each group separatelyB) deviation scores based on combined groups
C) ranks within each group separately
D) ranks based on all groups combined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Kruskal-Wallis test:Mann-Whitney U test as
A) t test for dependent means:one-way ANOVA
B) one-way ANOVA:two-way ANOVA
C) one-way ANOVA:t test for independent means
D) t test for dependent means:t test for independent means
A) t test for dependent means:one-way ANOVA
B) one-way ANOVA:two-way ANOVA
C) one-way ANOVA:t test for independent means
D) t test for dependent means:t test for independent means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The sign test could be considered as an alternative approach to the test of a hypothesis about
A) a single mean
B) the difference between two dependent means
C) the difference between two independent means
D) the difference among several independent means
A) a single mean
B) the difference between two dependent means
C) the difference between two independent means
D) the difference among several independent means

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The relative insensitivity of the sign test is derived in part from the fact that
A) it can only be used with small samples
B) it is not responsive to the question "how much?"
C) restrictive assumptions characterize it
D) all of the above are true
A) it can only be used with small samples
B) it is not responsive to the question "how much?"
C) restrictive assumptions characterize it
D) all of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Wilcoxon signed-ranks test is a particularly dubious choice if
A) population variances are unknown
B) n's are small
C) a difference of k score points means something different at various points in the scale
D) normality of distribution cannot be assumed
A) population variances are unknown
B) n's are small
C) a difference of k score points means something different at various points in the scale
D) normality of distribution cannot be assumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following loses most in efficiency relative to its counterpart test about means?
A) Mann-Whitney U test
B) sign-test
C) Kruskal-Wallis test
D) Wilcoxon signed-ranks test
A) Mann-Whitney U test
B) sign-test
C) Kruskal-Wallis test
D) Wilcoxon signed-ranks test

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which, if any, of the first three statements is false?
A) the Mann-Whitney U test is an alternative to the test of the difference between means of two independent samples
B) the sign test is an alternative to the test of the difference between means of two dependent samples
C) the Kruskal-Wallis test is an alternative to one-way analysis of variance
D) all of the above are true
A) the Mann-Whitney U test is an alternative to the test of the difference between means of two independent samples
B) the sign test is an alternative to the test of the difference between means of two dependent samples
C) the Kruskal-Wallis test is an alternative to one-way analysis of variance
D) all of the above are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



