Deck 4: Hypothesis Tests
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Hypothesis Tests
1
The p-value is
A) the probability that the null hypothesis is true.
B) the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true.
C) the probability, when the null hypothesis is true, of obtaining a sample as extreme as (or more extreme than) the observed sample.
D) the probability, when the alternative hypothesis is true, of obtaining a sample as extreme as (or more extreme than) the observed sample.
A) the probability that the null hypothesis is true.
B) the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true.
C) the probability, when the null hypothesis is true, of obtaining a sample as extreme as (or more extreme than) the observed sample.
D) the probability, when the alternative hypothesis is true, of obtaining a sample as extreme as (or more extreme than) the observed sample.
the probability, when the null hypothesis is true, of obtaining a sample as extreme as (or more extreme than) the observed sample.
2
A Type I error occurs by
A) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
B) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
C) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
D) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
A) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
B) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
C) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
D) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
3
A Type II error occurs by
A) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
B) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
C) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
D) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
A) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
B) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
C) rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
D) not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true.
not rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is false.
4
An article published in the Canadian Journal of Zoology presented a method for estimating the body fat percentage of North American porcupines; the method was illustrated with a sample of n = 25 porcupines. Based on this sample, a 95% bootstrap confidence interval for the average body fat percentage of porcupines is 17.4% to 25.8%. Which of the following null hypotheses would be rejected based on this confidence interval?
A)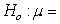 18.6%
18.6%
B)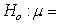 26.6%
26.6%
C)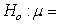 20.0%
20.0%
D)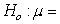 22.9%
22.9%
A)
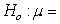 18.6%
18.6%B)
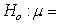 26.6%
26.6%C)
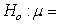 20.0%
20.0%D)
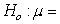 22.9%
22.9%
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
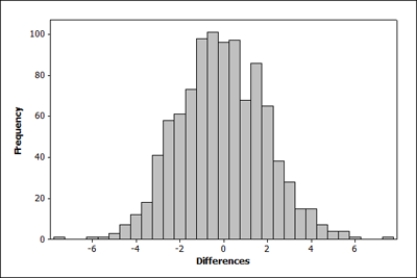
The following figure shows a randomization distribution for the hypotheses 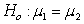 versus
versus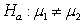 . The statistic used for each sample is
. The statistic used for each sample is 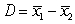 . Which of the two possible sample results provides the most evidence against Ho?
. Which of the two possible sample results provides the most evidence against Ho?
A)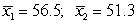
B)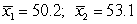
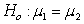 versus
versus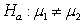 . The statistic used for each sample is
. The statistic used for each sample is 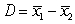 . Which of the two possible sample results provides the most evidence against Ho?
. Which of the two possible sample results provides the most evidence against Ho?
A)
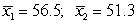
B)
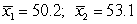

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Of the two p-values, which provides more evidence against Ho?
A) p-value = 0.41
B) p-value = 0.045
A) p-value = 0.41
B) p-value = 0.045

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
It is of interest to test the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.8 versus Ha: p < 0.8. The sample outcome, based on n = 10 observations, is = 0.7, and the randomization statistic to be calculated is . The p-value for this test was found to be 0.322. If the test was performed correctly, where should the randomization distribution be centered?
A) 0.7
B) 10
C) 0.8
D) 0.322
A) 0.7
B) 10
C) 0.8
D) 0.322

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The average SAT-Critical Reading score for college bound students taking the exam in the 2009-2010 academic year was 501. A highly selective university wants to know if their 2010 incoming class had an average SAT-Critical Reading score that was higher than the national average. Which of the following possible samples provides the most evidence for this claim?
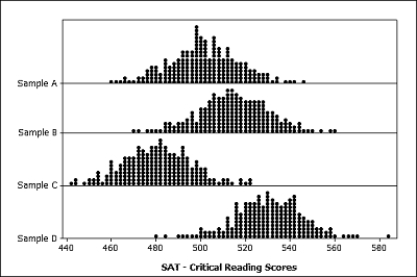
A) Sample A
B) Sample B
C) Sample C
D) Sample D

A) Sample A
B) Sample B
C) Sample C
D) Sample D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Using a significance level of 5%, the appropriate conclusion for a test with a p-value of 0.0421 would be:
A) Reject Ho
B) Do not Reject HO
A) Reject Ho
B) Do not Reject HO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
It is believed that about 37% of college students binge drink (5 or more drinks for men, and 4 or more drinks for women, in two hours). Administrators at a small university of 6,000 students want to do a study to determine if the proportion of their students who binge drink differs from 37%. They select a sample of 98 students enrolled at the university to survey about their drinking behavior. When generating the randomization distribution for this test, how large should each individual randomization sample be?
A) 98 because that is the size of the original sample
B) 1,000 to get an accurate randomization distribution
C) 6,000 because that is the size of the university
D) 2,220 because that is 37% of the students at the university
A) 98 because that is the size of the original sample
B) 1,000 to get an accurate randomization distribution
C) 6,000 because that is the size of the university
D) 2,220 because that is 37% of the students at the university

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose that a 95% confidence interval for 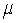 is (54.8, 60.8). Which of the following is most likely the p-value for the test of
is (54.8, 60.8). Which of the following is most likely the p-value for the test of 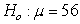 versus ?
versus ?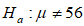 ?
?
A) 0.031
B) 0.001
C) 0.016
D) 0.231
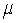 is (54.8, 60.8). Which of the following is most likely the p-value for the test of
is (54.8, 60.8). Which of the following is most likely the p-value for the test of 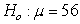 versus ?
versus ?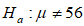 ?
?A) 0.031
B) 0.001
C) 0.016
D) 0.231

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The significance level, 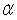 , represents the tolerable probability of making a Type II error.
, represents the tolerable probability of making a Type II error.
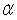 , represents the tolerable probability of making a Type II error.
, represents the tolerable probability of making a Type II error.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A statistical test uses data from a sample to assess a claim about a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When generating a randomization sample, the sample should be consistent with the ________________ hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The evidence against the null and in favor of the alternative is very strong.
A) 0.0001
B) 0.0735
C) 0.6082
D) 0.0361
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The evidence against the null and in favor of the alternative is very strong.
A) 0.0001
B) 0.0735
C) 0.6082
D) 0.0361

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The result is significant at the 5% level but not at a 1% level."
A) 0.0002
B) 0.0736
C) 0.6083
D) 0.0362
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The result is significant at the 5% level but not at a 1% level."
A) 0.0002
B) 0.0736
C) 0.6083
D) 0.0362

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the following
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "There is really no evidence supporting the alternative hypothesis."
A) 0.0003
B) 0.0737
C) 0.6084
D) 0.0363
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "There is really no evidence supporting the alternative hypothesis."
A) 0.0003
B) 0.0737
C) 0.6084
D) 0.0363

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Use the following
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The evidence against the null is significant, but only at the 10% level."
A) 0.0004
B) 0.0738
C) 0.6085
D) 0.0364
Match each p-value to the most appropriate conclusion.
-________ "The evidence against the null is significant, but only at the 10% level."
A) 0.0004
B) 0.0738
C) 0.6085
D) 0.0364

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify the error in the following hypotheses: 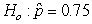 versus
versus 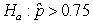 .
.
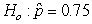 versus
versus 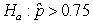 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify the error in the following hypotheses: 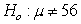 versus
versus 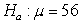 .
.
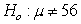 versus
versus 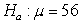 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify the error in the following hypotheses: Ho: p = 30 versus Ha: p > 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The null and alternative hypotheses for a test are Ho: p = 0.6 vs. Ha: p > 0.6. Give the notation for a sample statistic we might record for each simulated sample to create the randomization distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the following
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.72
A)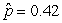
B)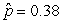
C)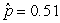
D)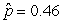
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.72
A)
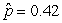
B)
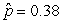
C)
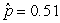
D)
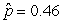

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.293
A)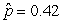
B)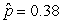
C)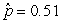
D)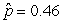
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.293
A)
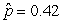
B)
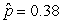
C)
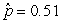
D)
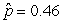

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the following
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.138
A)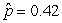
B)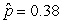
C)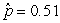
D)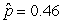
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.138
A)
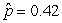
B)
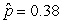
C)
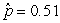
D)
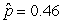

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the following
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.019
A)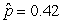
B)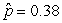
C)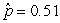
D)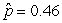
Consider testing the hypotheses Ho: p = 0.4 versus Ha: p > 0.4. Four possible sample statistics, along with four possible p-values, are given. Match the statistics to their p-values.
-________ p-value = 0.019
A)
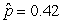
B)
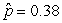
C)
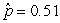
D)
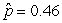

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
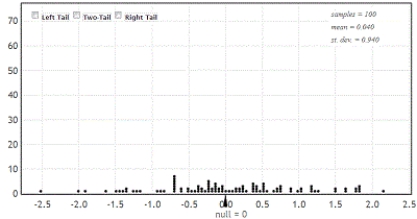
The randomization distribution for testing the hypotheses 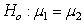 versus
versus 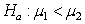 is provided. The sample statistic is
is provided. The sample statistic is 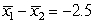 . Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this test.
. Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this test.
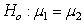 versus
versus 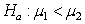 is provided. The sample statistic is
is provided. The sample statistic is 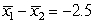 . Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this test.
. Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this test.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The provided figure displays the randomization distribution for testing 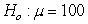 versus
versus 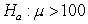 .
.
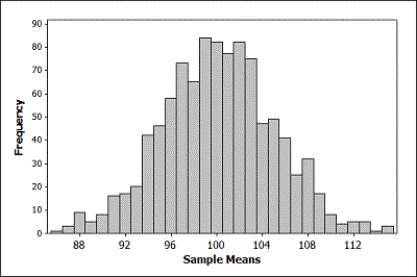
The p-value for the sample mean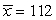 is closest to
is closest to
A) 0.01
B) 0.25
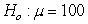 versus
versus 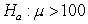 .
.
The p-value for the sample mean
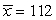 is closest to
is closest toA) 0.01
B) 0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Briefly explain the difference between a "bootstrap distribution" and a "randomization distribution".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Decreasing the significance level of a hypothesis test (say, from 5% to 1%) will cause the p-value of an observed test statistic to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following samples provides the most evidence that the amount of time spent studying for an exam and the grade on the exam are positively correlated? 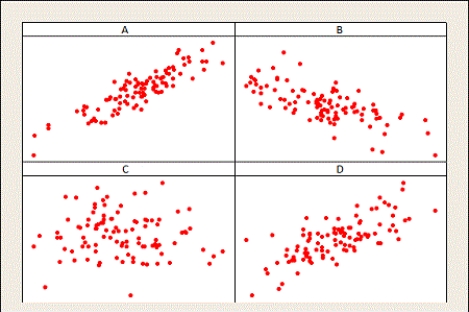
A) Sample A
B) Sample B
C) Sample C
D) Sample D

A) Sample A
B) Sample B
C) Sample C
D) Sample D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.
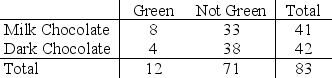
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to test if this sample provides evidence that the proportion of candies that are green differs for the two types of M&M's. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
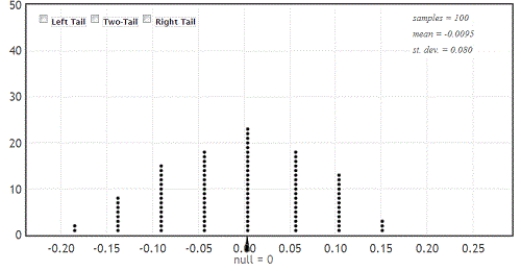
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to test if this sample provides evidence that the proportion of candies that are green differs for the two types of M&M's. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use technology and the provided data to test if this sample provides evidence that the proportion of candies that are green differs for the two types of M&M's. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use technology and the provided data to test if this sample provides evidence that the proportion of candies that are green differs for the two types of M&M's. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.
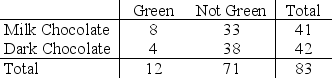
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if the proportion of green M&M's differs for milk chocolate and dark chocolate M&M's.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if the proportion of green M&M's differs for milk chocolate and dark chocolate M&M's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.
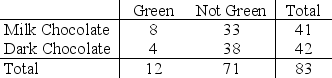
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if the proportion of green M&M's differs for milk chocolate and dark chocolate M&M's.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if the proportion of green M&M's differs for milk chocolate and dark chocolate M&M's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.
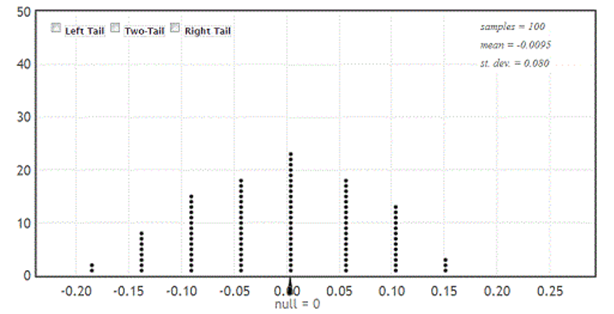
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
A student in an introductory statistics course investigated if there is evidence that the proportion of milk chocolate M&M's that are green differs from the proportion of dark chocolate M&M's that are green. She purchased a bag of each variety, and her data are summarized in the following table.

-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Describe how you could generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Describe how you could generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 1,000 samples) to test if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
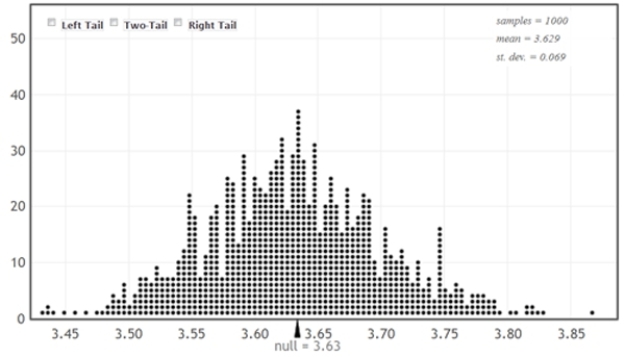
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 1,000 samples) to test if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use technology and the provided data to test if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use technology and the provided data to test if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.

It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average gas price in Illinois exceeds the national average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 1,000 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.
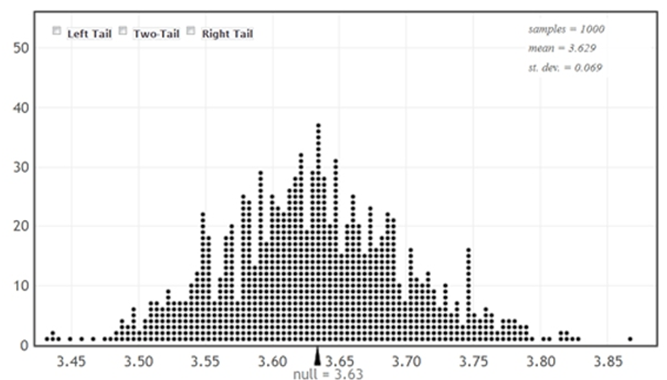
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 1,000 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.
As of August 8, 2012, the national average price for a gallon of regular unleaded gasoline was $3.63. The prices for a sample of n = 10 gas stations in the state of Illinois are provided.
 It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.
It is of interest to use this sample to compare the average gas price in Illinois to the national average.-Use your p-value to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem. Include an assessment of the strength of your evidence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What conclusion would the authors have made at the 10% significance level?
A) Tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
B) Tracking accuracy was not significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
C) Not enough information
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What conclusion would the authors have made at the 10% significance level?
A) Tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
B) Tracking accuracy was not significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
C) Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What conclusion would the authors have made at the 1% significance level?
A) Tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
B) Tracking accuracy was not significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
C) Not enough information
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What conclusion would the authors have made at the 1% significance level?
A) Tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
B) Tracking accuracy was not significantly worse in the dual-task condition.
C) Not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Use the following
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What does the phrase "significantly worse" mean in this context?
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-What does the phrase "significantly worse" mean in this context?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Use the following
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-Which type of error, Type I or Type II, could have occurred in this situation? Briefly justify your answer.
A study recently described in Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics investigated the impacts of mult-tasking on people who play video games and those who don't. Participants in the study were asked to perform three visually demanding tasks with (dual-task) and without (single-task) answering unrelated questions over the phone. One of the tasks involved tracking multiple circles moving around on a computer monitor. At the 5% significance level, the authors of the study concluded "tracking accuracy was significantly worse in the dual-task condition"
for both people who play video games and those who do not.
-Which type of error, Type I or Type II, could have occurred in this situation? Briefly justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following
In 2012 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that in a sample of 4,349 African Americans 31% were Vitamin D deficient. A 90% confidence interval based on this sample is (0.30, 0.32). It is believed that among the general population of Americans 8% suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
-Define the appropriate parameter and state the appropriate hypotheses for testing the claim that, among African Americans, Vitamin D deficiency occurs at a rate other than 8%.
In 2012 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that in a sample of 4,349 African Americans 31% were Vitamin D deficient. A 90% confidence interval based on this sample is (0.30, 0.32). It is believed that among the general population of Americans 8% suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
-Define the appropriate parameter and state the appropriate hypotheses for testing the claim that, among African Americans, Vitamin D deficiency occurs at a rate other than 8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following
In 2012 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that in a sample of 4,349 African Americans 31% were Vitamin D deficient. A 90% confidence interval based on this sample is (0.30, 0.32). It is believed that among the general population of Americans 8% suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
-Does this confidence interval provide evidence that among African Americans Vitamin D deficiency occurs at a rate other than 8%? What significance level is being used to make this decision? Briefly justify your answer.
In 2012 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that in a sample of 4,349 African Americans 31% were Vitamin D deficient. A 90% confidence interval based on this sample is (0.30, 0.32). It is believed that among the general population of Americans 8% suffer from Vitamin D deficiency.
-Does this confidence interval provide evidence that among African Americans Vitamin D deficiency occurs at a rate other than 8%? What significance level is being used to make this decision? Briefly justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The provided histogram displays the prices (in thousands of dollars) of 17 homes sold between November 2011 and February 2012 in a Midwestern city.
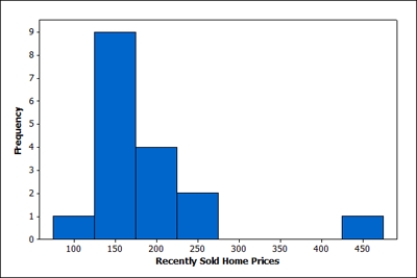
In general this shape, right skewed with some unusually high values, is common for describing home values in many cities. For this reason, the median home value for a city is a useful parameter. This sample of recently sold homes had a median price (value) of $166,500. Someone considering moving to this city is interested in knowing if the median home value is more than $150,000.
Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate from the sample.

In general this shape, right skewed with some unusually high values, is common for describing home values in many cities. For this reason, the median home value for a city is a useful parameter. This sample of recently sold homes had a median price (value) of $166,500. Someone considering moving to this city is interested in knowing if the median home value is more than $150,000.
Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate from the sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Using the definition of a p-value, explain why the area in the tail of a randomization distribution is used to compute a p-value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In a test of the hypotheses 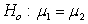 versus
versus 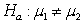 , the observed sample results in a p-value of 0.0256. Would you expect a 95% confidence interval for
, the observed sample results in a p-value of 0.0256. Would you expect a 95% confidence interval for 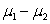 based on this sample to contain 0? Briefly explain why or why not.
based on this sample to contain 0? Briefly explain why or why not.
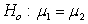 versus
versus 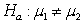 , the observed sample results in a p-value of 0.0256. Would you expect a 95% confidence interval for
, the observed sample results in a p-value of 0.0256. Would you expect a 95% confidence interval for 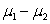 based on this sample to contain 0? Briefly explain why or why not.
based on this sample to contain 0? Briefly explain why or why not.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In August 2012 Gallup reported the results from a survey of 177,663 U.S. adults from January - June 2012 for the Gallup-Healthways Well-Being Index. Based on self-reported height and weight data, they found that 62.8% of U.S. adults are overweight or obese. A 95% confidence interval for the proportion of U.S. adults that are overweight or obese is (0.626, 0.63). Does this interval support the claim that "two-thirds of Americans are overweight or obese"? Briefly justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Briefly explain what a Type II error would mean in this situation.
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Briefly explain what a Type II error would mean in this situation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Suppose they find that the average rating for the shirts cleaned with the new formula was 8.2 and the average rating for the shirts cleaned with the old formula is 8.0 (p-value = 0.046). Do you think these results are practically significant? Briefly explain.
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Suppose they find that the average rating for the shirts cleaned with the new formula was 8.2 and the average rating for the shirts cleaned with the old formula is 8.0 (p-value = 0.046). Do you think these results are practically significant? Briefly explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Suppose, at the 5% significance level, they find that the new formula cleaned the shirts significantly better than the old formula, with a p-value of 0.046. Interpret the p-value, in terms of the probability of the results happening by random chance, in this context.
The makers of a popular brand of laundry detergent have discovered a new secret ingredient that they believe will boost the cleaning power of their detergent. The new ingredient is expensive, and if they use it, they would have to increase the retail price of the detergent (and they worry that the price increase will cause them to lose customers). However, they believe that if the improved detergent gets clothes drastically cleaner, customers will recognize that it is worth the extra cost. They conduct an experiment to compare the performance of the new and old formulas at removing grass stains, red wine, and chocolate from white t-shirts. Each cleaned shirt was rated on a scale from 1 (stain did not get removed) to 10 (no evidence of the stain) by trained experts. They compared the average rating for the new and old formulas.
-Suppose, at the 5% significance level, they find that the new formula cleaned the shirts significantly better than the old formula, with a p-value of 0.046. Interpret the p-value, in terms of the probability of the results happening by random chance, in this context.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is about 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is about 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is about 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to determine if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years. Use a 5% significance level to make your conclusion.
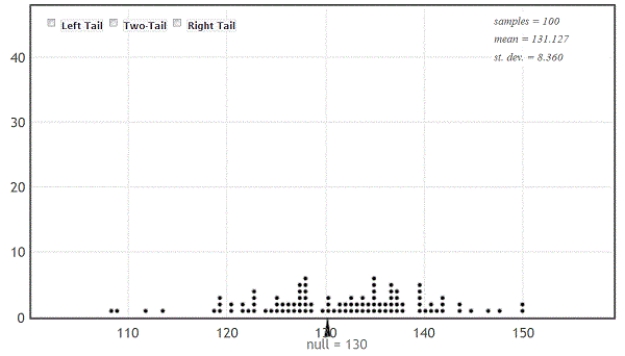
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is about 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to determine if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years. Use a 5% significance level to make your conclusion.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
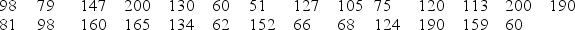
-Use technology and the provided data to determine if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years. Use a 5% significance level to make your conclusion.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
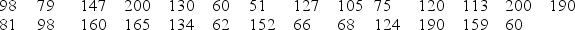
-Use technology and the provided data to determine if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years. Use a 5% significance level to make your conclusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify the statistic you would calculate for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.
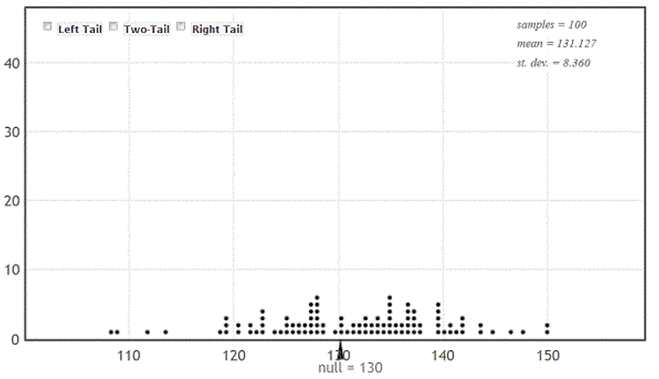
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use the provided randomization distribution (based on 100 samples) to estimate the p-value for this sample.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use your p-value and a 5% significance level to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-Use your p-value and a 5% significance level to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-What conclusion would you make at the 10% significance level?
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. The average age of the trees in the sample is approximately 120 years. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
-What conclusion would you make at the 10% significance level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
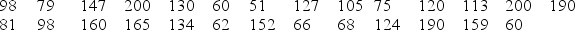
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
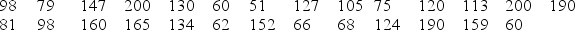
-Define the appropriate parameter(s) and state the hypotheses for testing if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood along this beach is less than 130 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
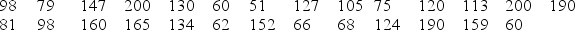
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
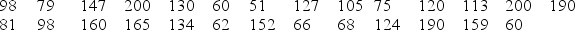
-Describe how you would generate a single randomization sample in this situation, and identify (using the appropriate notation) the sample statistic you would record for each sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
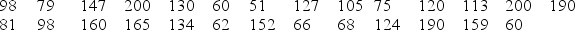
-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
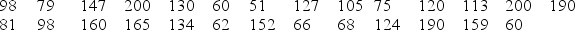
-Use technology to create a randomization distribution with at least 1,000 values for testing these hypotheses. Use your randomization distribution to estimate the p-value for this sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
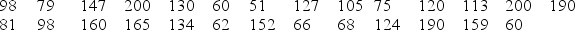
-Use your p-value and a 5% significance level to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem.
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
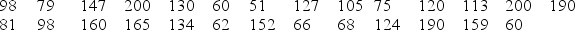
-Use your p-value and a 5% significance level to make a decision about these hypotheses. Be sure to word your decision in the context of the problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
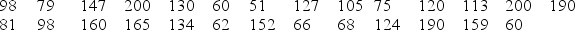
-What conclusion would you make at the 10% significance level?
A certain species of tree has an average life span of 130 years. A researcher has noticed a large number of trees of this species washing up along a beach as driftwood. She takes core samples from 27 of those trees to count the number of rings and measure the widths of the rings. Counting the rings allows the researcher to determine the age of each tree. Her data are displayed in the provided table. One of her interests is determining if this sample provides evidence that the average age of the driftwood is less than the 130 year life span expected for this type of tree. If the average age is less than 130 years it might suggest that the trees have died from unusual causes, such as invasive beetles or logging.
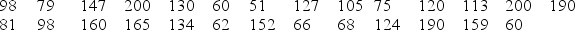
-What conclusion would you make at the 10% significance level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



