Deck 23: The Organic Chemistry of the Coenzymes,compounds Derived From Vitamins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: The Organic Chemistry of the Coenzymes,compounds Derived From Vitamins
1
Which of the following vitamins is not a water-soluble vitamin?
A) Vitamin A
B) Vitamin B1
C) Vitamin B6
D) Vitamin C
E) Vitamin H
A) Vitamin A
B) Vitamin B1
C) Vitamin B6
D) Vitamin C
E) Vitamin H
Vitamin A
2
Which of the following is not true of cofactors?
A) They assist in catalyzing a variety of reactions.
B) They can be metal ions.
C) They may be organic molecules that are then called coenzymes.
D) All vitamins function as precursors to coenzymes.
E) They may function as reducing or oxidizing agents.
A) They assist in catalyzing a variety of reactions.
B) They can be metal ions.
C) They may be organic molecules that are then called coenzymes.
D) All vitamins function as precursors to coenzymes.
E) They may function as reducing or oxidizing agents.
All vitamins function as precursors to coenzymes.
3
Which of the following is not true of pyridine nucleotide coenzymes?
A) NADH and NADPH are proton donors.
B) NAD+ and NADP+ are oxidizing agents.
C) NAD+ and NADH are generally coenzymes in catabolic reactions.
D) NADP+ and NADPH are generally coenzymes in anabolic reactions.
E) NADH and NADPH are reducing agents.
A) NADH and NADPH are proton donors.
B) NAD+ and NADP+ are oxidizing agents.
C) NAD+ and NADH are generally coenzymes in catabolic reactions.
D) NADP+ and NADPH are generally coenzymes in anabolic reactions.
E) NADH and NADPH are reducing agents.
NADH and NADPH are proton donors.
4
What enzyme catalyzes the following reaction? 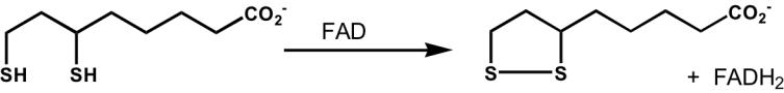
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) thiol dehydrogenase
D) amino acid oxidase
E) FADH2 dehydrogenase

A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
C) thiol dehydrogenase
D) amino acid oxidase
E) FADH2 dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not true of thiamine?
A) Thiamine is also known as vitamin B1.
B) Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) contains a positively charged nitrogen that promotes electrophilic attacks on carbonyl groups.
C) Thiamine is used to form the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.
D) TPP is an acyl transfer agent.
E) The positively charged nitrogen (thiazolium ring) of TPP is a very effective electron sink.
A) Thiamine is also known as vitamin B1.
B) Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) contains a positively charged nitrogen that promotes electrophilic attacks on carbonyl groups.
C) Thiamine is used to form the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.
D) TPP is an acyl transfer agent.
E) The positively charged nitrogen (thiazolium ring) of TPP is a very effective electron sink.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not true of biotin?
A) Biotin is a fat-soluble vitamin.
B) Biotin does not need to be included in a person's diet.
C) Biotin is required by enzymes that catalyze the carboxylation of an alpha-carbon.
D) Biotin-requiring enzymes also require bicarbonate, Mg2+ and ATP.
E) All biotin-requiring enzymes follow the same steps: activation of bicarbonate by ATP; reaction of biotin, with activated bicarbonate; and transfer of CO2 to the substrate.
A) Biotin is a fat-soluble vitamin.
B) Biotin does not need to be included in a person's diet.
C) Biotin is required by enzymes that catalyze the carboxylation of an alpha-carbon.
D) Biotin-requiring enzymes also require bicarbonate, Mg2+ and ATP.
E) All biotin-requiring enzymes follow the same steps: activation of bicarbonate by ATP; reaction of biotin, with activated bicarbonate; and transfer of CO2 to the substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) is required by enzymes that catalyze amino acid transformations, including
A) decarboxylation.
B) transamination.
C) racemization.
D) alpha- and beta-eliminations and cleavages.
E) all of the above.
A) decarboxylation.
B) transamination.
C) racemization.
D) alpha- and beta-eliminations and cleavages.
E) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not true of vitamin B12?
A) Enzymes that catalyze some isomerization reactions require coenzyme B12.
B) People must obtain vitamin B12 from their diets.
C) Coenzyme B12-requiring enzymes generally catalyze reactions through a cationic process.
D) Coenzyme B12 is required by enzymes that catalyze the exchange of a hydrogen bonded to one carbon with a group bonded to an adjacent carbon.
E) The chemistry of coenzyme B12 takes place at the bond joining the cobalt and the 5?-deoxyadenosyl group.
A) Enzymes that catalyze some isomerization reactions require coenzyme B12.
B) People must obtain vitamin B12 from their diets.
C) Coenzyme B12-requiring enzymes generally catalyze reactions through a cationic process.
D) Coenzyme B12 is required by enzymes that catalyze the exchange of a hydrogen bonded to one carbon with a group bonded to an adjacent carbon.
E) The chemistry of coenzyme B12 takes place at the bond joining the cobalt and the 5?-deoxyadenosyl group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following coenzymes is used in oxidation reactions?
A) THF
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) NAD+
E) all of the above
A) THF
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) NAD+
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following coenzymes is not used in reduction reactions?
A) dihydrolipoate
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) NADPH
E) none of the above; all are reducing agents
A) dihydrolipoate
B) FADH2
C) NADH
D) NADPH
E) none of the above; all are reducing agents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following enzymes is used in the transfer of a single carbon?
A) coenzyme B12
B) thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
C) tetrahydrofolate (THF)
D) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
E) flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
A) coenzyme B12
B) thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
C) tetrahydrofolate (THF)
D) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
E) flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



