Deck 25: Growing a Green Thumb: Plant Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/66
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: Growing a Green Thumb: Plant Physiology
1
What is contained within the xylem sap of a plant?
A) water only
B) water and dissolved minerals only
C) water and sugars produced from photosynthesis only
D) water, dissolved minerals, and sugars
A) water only
B) water and dissolved minerals only
C) water and sugars produced from photosynthesis only
D) water, dissolved minerals, and sugars
B
2
Which adaptation is found in the leaves of cacti?
A) They store excess starch.
B) They are dropped during periods of drought.
C) They have been modified into spines.
D) They are very large to absorb plenty of sunlight.
A) They store excess starch.
B) They are dropped during periods of drought.
C) They have been modified into spines.
D) They are very large to absorb plenty of sunlight.
C
3
When can ice formation destroy plant cells?
A) as water flows into cells via osmosis as the temperature drops
B) as adhesion increases inside xylem tubes
C) as jagged ice crystals puncture cell membranes
D) as cells are poisoned by dissolved "antifreeze" solutes
A) as water flows into cells via osmosis as the temperature drops
B) as adhesion increases inside xylem tubes
C) as jagged ice crystals puncture cell membranes
D) as cells are poisoned by dissolved "antifreeze" solutes
C
4
Which action is most similar to the way in which water is moved through the xylem sap of a plant?
A) a person drinking through a straw
B) a vaccine being ejected out of a syringe
C) water gushing up from a fountain
D) a dart being blown out the end of a blowgun
A) a person drinking through a straw
B) a vaccine being ejected out of a syringe
C) water gushing up from a fountain
D) a dart being blown out the end of a blowgun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which type of plant would have the greatest rate of transpiration during the day?
A) a cactus
B) a plant with many large leaves
C) a plant with few and small leaves
D) a C₄ plant that grows in a hot, sunny, dry environment
A) a cactus
B) a plant with many large leaves
C) a plant with few and small leaves
D) a C₄ plant that grows in a hot, sunny, dry environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which plant performs C₄ photosynthesis?
A) pineapple
B) sugarcane
C) jade plant
D) oak tree
A) pineapple
B) sugarcane
C) jade plant
D) oak tree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which plant is best adapted to prevent an embolism in their xylem tubes?
A) a banana plant in a very warm climate
B) a spruce tree with narrow, tapering tracheids
C) a maple tree with wide, perforated vessel elements
D) a cattail in a marsh
A) a banana plant in a very warm climate
B) a spruce tree with narrow, tapering tracheids
C) a maple tree with wide, perforated vessel elements
D) a cattail in a marsh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which plants store CO₂ in the form of malic acid and close their stomata during the day?
A) C₃ plants
B) C₄ plants
C) CAM plants
D) hornworts and liverworts
A) C₃ plants
B) C₄ plants
C) CAM plants
D) hornworts and liverworts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the tendency of water molecules to stick together?
A) cohesion
B) adhesion
C) tension
D) transpiration
A) cohesion
B) adhesion
C) tension
D) transpiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What type of force moves water up a tree, from its roots to its leaves?
A) pushing
B) pulling
C) pumping
D) positive pressure
A) pushing
B) pulling
C) pumping
D) positive pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How can plants change rates of transpiration?
A) by changing the size of stomata openings
B) by making a cellulose plug in the xylem tubes
C) by promoting flowering
D) by reducing cohesion
A) by changing the size of stomata openings
B) by making a cellulose plug in the xylem tubes
C) by promoting flowering
D) by reducing cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What force is created by the negative water pressure resulting from water evaporating from the stomata of a leaf?
A) cohesion
B) adhesion
C) tension
D) pressure flow
A) cohesion
B) adhesion
C) tension
D) pressure flow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
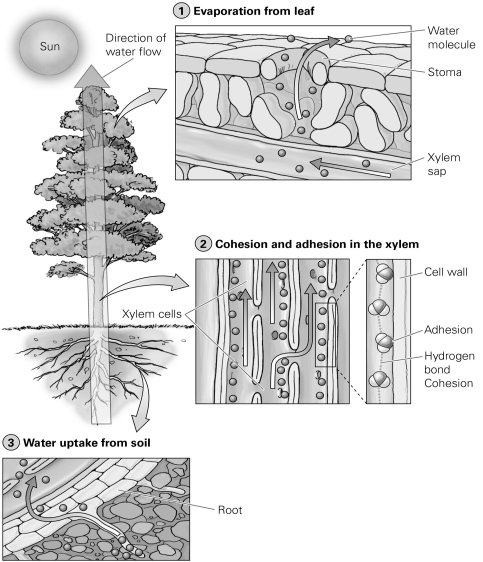
What is the overall process illustrated by this diagram?
A) C₄ adaptations
B) CAM adaptations
C) apical dominance
D) transpiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the cold tolerance of a plant called?
A) photoperiodism
B) persistence
C) hardiness
D) apical dominance
A) photoperiodism
B) persistence
C) hardiness
D) apical dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What will happen to a houseplant that's overwatered?
A) The leaves will burst.
B) The leaves will wilt.
C) The flowers will leak excess water.
D) It will grow faster than usual.
A) The leaves will burst.
B) The leaves will wilt.
C) The flowers will leak excess water.
D) It will grow faster than usual.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which plants drop their leaves on an annual basis?
A) annuals
B) perennials
C) deciduous
D) biennials
A) annuals
B) perennials
C) deciduous
D) biennials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which action allows a plant to conserve water?
A) increasing photosynthesis during the day
B) opening stomata only at night
C) possessing large leaves
D) developing wide vessel elements
A) increasing photosynthesis during the day
B) opening stomata only at night
C) possessing large leaves
D) developing wide vessel elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What process is responsible for the flow of water through a plant, from the soil to the leaves?
A) translocation
B) transpiration
C) respiration
D) internal pumping
A) translocation
B) transpiration
C) respiration
D) internal pumping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
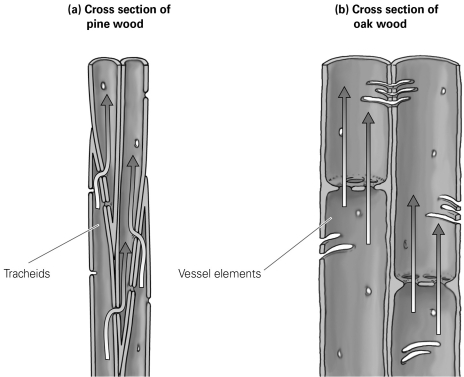
Whereas vessel elements produce ________ friction on the flow of water than tracheids, they result in ________.
A) more; a reduced risk of an embolism
B) less; a greater risk of an embolism
C) more; reduced rates of water loss from leaves during a drought
D) less; the prevention of water loss from leaves during a drought

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why DON'T water molecules located within a column of xylem sap move apart?
A) Cohesion holds the water molecules to each other; adhesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
B) Adhesion holds the water molecules to each other; tension holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
C) Tension holds the water molecules to each other; cohesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
D) Adhesion holds the water molecules to each other; cohesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
A) Cohesion holds the water molecules to each other; adhesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
B) Adhesion holds the water molecules to each other; tension holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
C) Tension holds the water molecules to each other; cohesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.
D) Adhesion holds the water molecules to each other; cohesion holds water molecules to the cellulose in plant cell walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When might cytosol leak into plant cell vacuoles?
A) if water freezes outside a plant cell
B) if water freezes inside a plant cell
C) if severe drought conditions shut down normal rates of transpiration
D) if the critical night length isn't met
A) if water freezes outside a plant cell
B) if water freezes inside a plant cell
C) if severe drought conditions shut down normal rates of transpiration
D) if the critical night length isn't met

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What do both the C₄ and CAM pathways of photosynthesis allow plants to do?
A) to perform photosynthesis in the absence of carbon dioxide
B) to outcompete C₃ plants in cool, dry conditions
C) to keep stomata partially or completely closed during the hottest parts of the day
D) to take up carbon dioxide at night and then store it as an acid until the day
A) to perform photosynthesis in the absence of carbon dioxide
B) to outcompete C₃ plants in cool, dry conditions
C) to keep stomata partially or completely closed during the hottest parts of the day
D) to take up carbon dioxide at night and then store it as an acid until the day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why do florists and horticulturists often cut stems while they're holding a plant underwater?
A) to avoid transpiration
B) to prevent dormancy
C) to disrupt apical dominance
D) to avoid formation of an embolism
A) to avoid transpiration
B) to prevent dormancy
C) to disrupt apical dominance
D) to avoid formation of an embolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the negative water pressure in the xylem of a plant?
A) torsion
B) cohesion
C) adhesion
D) tension
A) torsion
B) cohesion
C) adhesion
D) tension

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What are the narrow, tapering cells found in the xylem tubes of drought-adapted plant species?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the purpose for the process of deadheading?
A) It decreases the duration of flowering in an annual plant.
B) It removes fruits and seeds from plants when they're mature.
C) It allows the plant to produce and support more flowers than normal.
D) It reduces the amount of water needed by the plant.
A) It decreases the duration of flowering in an annual plant.
B) It removes fruits and seeds from plants when they're mature.
C) It allows the plant to produce and support more flowers than normal.
D) It reduces the amount of water needed by the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In what direction do the sugars in a peach tree move?
A) only toward the fruit
B) only toward the sugar source
C) only toward a sugar sink
D) either toward or away from sugar sources
A) only toward the fruit
B) only toward the sugar source
C) only toward a sugar sink
D) either toward or away from sugar sources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Where would you expect a plant with the largest leaves to grow?
A) in sunny conditions
B) in shady sites
C) in dry conditions
D) in very sandy soils
A) in sunny conditions
B) in shady sites
C) in dry conditions
D) in very sandy soils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which phenomena drives transpiration in a terrestrial woody plant?
A) evaporation
B) gravitropism
C) translocation
D) photoperiodism
A) evaporation
B) gravitropism
C) translocation
D) photoperiodism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which structures are the water-conducting cells in mosses?
A) xylem cells
B) vessel elements
C) tracheids
D) hydroids
A) xylem cells
B) vessel elements
C) tracheids
D) hydroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which plant has the greatest hardiness (can tolerate the lowest temperature)?
A) a tomato plant
B) a cabbage plant
C) an apple tree
D) a houseplant that evolved in the tropics
A) a tomato plant
B) a cabbage plant
C) an apple tree
D) a houseplant that evolved in the tropics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which plant closes its stomata during the day and conducts photosynthesis using chemically stored carbon?
A) moss
B) Kentucky bluegrass
C) jade plant
D) oak tree
A) moss
B) Kentucky bluegrass
C) jade plant
D) oak tree

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When have many deciduous plants adapted to drop their leaves?
A) when overwatered
B) during summer
C) during droughts
D) whenever daylight cycles shorten
A) when overwatered
B) during summer
C) during droughts
D) whenever daylight cycles shorten

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the time from the final frost in the spring to the first frost in the fall?
A) transpiration
B) hardiness
C) a growing season
D) translocation
A) transpiration
B) hardiness
C) a growing season
D) translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which is an example of a CAM plant?
A) sugarcane
B) corn
C) crabgrass
D) aloe plant
A) sugarcane
B) corn
C) crabgrass
D) aloe plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Plants that have undergone a gradual cooling period and are able to resist cold environmental temperatures are referred to as ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What would plants living in areas with moist soils be most likely to have?
A) many narrow, tapering tracheids
B) lots of wide, perforated vessel elements
C) frequent embolisms and loss of tension
D) reduced transpiration rates
A) many narrow, tapering tracheids
B) lots of wide, perforated vessel elements
C) frequent embolisms and loss of tension
D) reduced transpiration rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In plants, what are embolisms?
A) toxic acids produced when stomata are closed and it's sunny
B) formations of ice crystals when a plant is subjected to below-freezing temperatures
C) hormones that result in apical dominance
D) air bubbles that form within xylem
A) toxic acids produced when stomata are closed and it's sunny
B) formations of ice crystals when a plant is subjected to below-freezing temperatures
C) hormones that result in apical dominance
D) air bubbles that form within xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What might result from the overwatering of houseplants and garden plants?
A) an increase in chlorophyll within the leaves
B) decreased rates of transpiration
C) dormancy due to loss of leaves
D) the formation of hydroids
A) an increase in chlorophyll within the leaves
B) decreased rates of transpiration
C) dormancy due to loss of leaves
D) the formation of hydroids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What causes the "pulling" of a water column from the soil to the leaves?
A) hydrogen bonds
B) gravity
C) hardiness
D) active transport
A) hydrogen bonds
B) gravity
C) hardiness
D) active transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is dormancy?
A) the ability of a plant to produce fruits
B) a plant's annual rest period
C) the period of time between flowering and fruiting
D) another term for translocation
A) the ability of a plant to produce fruits
B) a plant's annual rest period
C) the period of time between flowering and fruiting
D) another term for translocation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What effect does pruning flowers have on a plant?
A) The plant will make more flowers than normal.
B) The new flowers that grow will be larger.
C) The plant will produce more leaves.
D) The plant will produce fruits instead of flowers.
A) The plant will make more flowers than normal.
B) The new flowers that grow will be larger.
C) The plant will produce more leaves.
D) The plant will produce fruits instead of flowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In which direction would translocation occur in a pine tree?
A) from the roots to the needles
B) from pinecones to the roots
C) from the sugar source to the sink
D) from the sugar sink to the source
A) from the roots to the needles
B) from pinecones to the roots
C) from the sugar source to the sink
D) from the sugar sink to the source

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What type of plants live for one year?
A) annuals
B) biennials
C) perennials
D) woody plants
A) annuals
B) biennials
C) perennials
D) woody plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the tendency of a plant's uppermost bud to limit the growth of lower buds? (two words)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the purpose of plant hormones?
A) They are produced in small amounts but have great effects.
B) They break down quickly after they are produced.
C) They act only at the location where they are produced.
D) They generally have one limited effect on the plant.
A) They are produced in small amounts but have great effects.
B) They break down quickly after they are produced.
C) They act only at the location where they are produced.
D) They generally have one limited effect on the plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which chemical is photosensitive and allows plants to "measure" day length?
A) abscisic acid
B) malic acid
C) cytokinin
D) phytochrome
A) abscisic acid
B) malic acid
C) cytokinin
D) phytochrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What do the roots emerging from germinating seeds exhibit?
A) positive gravitropism
B) negative gravitropism
C) positive phototropism
D) negative phototropism
A) positive gravitropism
B) negative gravitropism
C) positive phototropism
D) negative phototropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In plants, how are the sugars produced from photosynthesis moved around?
A) via phloem sap
B) via xylem sap
C) via stomata
D) via embolisms
A) via phloem sap
B) via xylem sap
C) via stomata
D) via embolisms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A greenhouse manager wants to encourage long-term, productive flowering instead of short-term, rapid flowering in annual garden plants that are for sale. Which action would accomplish that goal?
A) pruning away early flowers
B) limiting water and fertilizer
C) moving the plants to the shadiest part of the greenhouse
D) allowing any flowers to become fruits and seeds
A) pruning away early flowers
B) limiting water and fertilizer
C) moving the plants to the shadiest part of the greenhouse
D) allowing any flowers to become fruits and seeds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which process occurs when a grapevine wraps around a trellis or another supporting structure?
A) photoperiodism
B) thigmotropism
C) gravitropism
D) phototropism
A) photoperiodism
B) thigmotropism
C) gravitropism
D) phototropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the sugary phloem sap in a fruit tree is divided into many sugar sinks, then how will each individual fruit be affected?
A) The fruit will be small and sugary.
B) The fruit will be large and sugary.
C) The fruit will be small and diluted.
D) The fruit will be large and diluted.
A) The fruit will be small and sugary.
B) The fruit will be large and sugary.
C) The fruit will be small and diluted.
D) The fruit will be large and diluted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Photoperiodic plants react to a certain amount of darkness, referred to as ________ (three words).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What will happen after a gardener cuts off all the developing flowers on a tomato plant, with the exception of 12 of the flowers that have already been pollinated and set fruit?
A) The tomato plant will drop the 12 previously pollinated flowers.
B) The tomato plant will become dormant until next year and then 12 tomatoes will ripen.
C) The 12 tomatoes will develop fully on the plant, but they will be small and not very sweet.
D) The 12 tomatoes will develop, and they will be larger and sweeter than if the other flowers remained.
A) The tomato plant will drop the 12 previously pollinated flowers.
B) The tomato plant will become dormant until next year and then 12 tomatoes will ripen.
C) The 12 tomatoes will develop fully on the plant, but they will be small and not very sweet.
D) The 12 tomatoes will develop, and they will be larger and sweeter than if the other flowers remained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What type of plants flower only if day length is less than a critical value?
A) short-day plants
B) long-day plants
C) biennial plants
D) perennial plants
A) short-day plants
B) long-day plants
C) biennial plants
D) perennial plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Many garden plants that are grown for leaves or roots, such as parsley and carrots, produce vegetative growth the first year and reproductive structure growth the second year. Thus, what type of plants are parsley and carrots?
A) annuals
B) biennials
C) perennials
D) woody plants
A) annuals
B) biennials
C) perennials
D) woody plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which plant is a perennial?
A) peony
B) morning glory
C) petunia
D) pansy
A) peony
B) morning glory
C) petunia
D) pansy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is the first step in the pressure flow mechanism of translocation?
A) Sugar is loaded into the xylem at the source.
B) Sugar is loaded into the phloem at the source.
C) Water is loaded into the phloem at the source.
D) Water is loaded into the phloem at the sink.
A) Sugar is loaded into the xylem at the source.
B) Sugar is loaded into the phloem at the source.
C) Water is loaded into the phloem at the source.
D) Water is loaded into the phloem at the sink.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which plants live for many years and produce flowers every year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the response of a plant to the proportion of light and dark in a day?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Through what process do deciduous plants drop their leaves?
A) thigmotropism
B) gravitropism
C) abscission
D) photoperiodism
A) thigmotropism
B) gravitropism
C) abscission
D) photoperiodism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What can a person do to the topmost leaves and buds, resulting in reduced apical dominance in order to make a shrub bushier?
A) deadhead
B) harden
C) pinch back
D) translocate
A) deadhead
B) harden
C) pinch back
D) translocate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which hormone promotes the abscission of leaves and fruits?
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) cytokinin
D) gibberellin
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) cytokinin
D) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which plant hormone is responsible for apical dominance?
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) cytokinin
D) gibberellin
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) cytokinin
D) gibberellin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the tendency for plants that live on other plants (epiphytes) to send shoots upward while sending roots down toward the ground?
A) positive and negative gravitropism
B) positive and negative thigmotropism
C) negative and positive gravitropism
D) negative and positive thigmotropism
A) positive and negative gravitropism
B) positive and negative thigmotropism
C) negative and positive gravitropism
D) negative and positive thigmotropism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which hormone plays an "anti-abscission role" in plants?
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) gibberellin
D) cytokinin
A) auxin
B) ethylene
C) gibberellin
D) cytokinin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 66 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



