Deck 20: Stellar Evolution: The Life and Death of a Star
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/107
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Stellar Evolution: The Life and Death of a Star
1
While none yet exist,in the very distant future,black dwarfs will comprise the majority of the "normal matter" of the universe.
True
2
Eventually,all low mass stars will become white,then black,dwarfs.
True
3
Evolution of a star off the main sequence is caused by the loss of mass from hydrogen fusion by the star while a main sequence star.
False
4
The shell ejection in making a planetary is spherical and symmetrical in all cases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The matter in white dwarfs is about a million times denser than matter around you,since you have packed the mass of the Sun into the volume of our Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Modern astronomers have observed the complete life cycle for many stars,making stellar evolution one of the best-tested astronomical theories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Every red dwarf star that ever joined the main sequence is still there today.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
There is no helium flash for a high mass star; for them,it is just one more step toward the heaviest element formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The age of a star cluster can be determined by the luminosity of the main sequence turnoff into the giant stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For binary star systems where the stars are separated by more than 1000 stellar radii,mass transfer is not an issue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a star becomes a red giant,its core expands to a roughly proportional larger size too.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All planetary nebulae are slowly-expanding spherical disks ejected by red giants,while their exposed cores appear as white dwarfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A star cluster of age 100 million years contains no type O stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The Sun will get brighter in the next 4 to 5 billion years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Low mass stars should produce white dwarfs,while high mass stars will produce more compact end products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A ten billion year old globular cluster has every star evolved into a giant,with no main sequence stars left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For our Sun,the production of carbon will be the end of its nucleosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As a star begins to evolve away from the main sequence,it gets larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
While more massive than most of its neighbors,the Sun is still technically a low mass star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When helium fusion begins in a one solar mass main star,it begins gradually,with this rate slowly increasing over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A star is on the horizontal branch of the H-R diagram.Which statement is true?
A) It is burning both hydrogen and helium.
B) It is about to experience the helium flash.
C) It is burning only helium.
D) The star is contracting.
E) The star is about to return to the main sequence.
A) It is burning both hydrogen and helium.
B) It is about to experience the helium flash.
C) It is burning only helium.
D) The star is contracting.
E) The star is about to return to the main sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
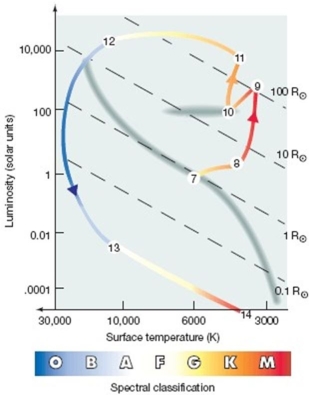
Refer to the figure above.What is the name of the path between the points labeled 10 and 11?
A) planetary nebula
B) red giant branch
C) horizontal branch
D) asymptotic giant branch
E) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What are black dwarfs?
A) the lowest mass main sequence stars
B) the end result of massive star evolution
C) objects that are not quite massive enough to be stars
D) pulsars that have slowed down and stopped spinning
E) cooled off white dwarfs that no longer glow visibly
A) the lowest mass main sequence stars
B) the end result of massive star evolution
C) objects that are not quite massive enough to be stars
D) pulsars that have slowed down and stopped spinning
E) cooled off white dwarfs that no longer glow visibly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
During the hydrogen shell burning phase:
A) the star grows more luminous.
B) the star becomes less luminous.
C) helium is burning in the core.
D) the core is expanding.
E) hydrogen is burning in the central core.
A) the star grows more luminous.
B) the star becomes less luminous.
C) helium is burning in the core.
D) the core is expanding.
E) hydrogen is burning in the central core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The "helium flash" occurs at what stage in stellar evolution?
A) when the T Tauri bipolar jets shoot out
B) in the middle of the main sequence stage
C) red giant
D) horizontal branch
E) planetary nebula
A) when the T Tauri bipolar jets shoot out
B) in the middle of the main sequence stage
C) red giant
D) horizontal branch
E) planetary nebula

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

Refer to the figure above.At what numbered point on the graph above does the helium flash occur?
A) 7
B) 8
C) 9
D) 10
E) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What spectral type of star that is still around formed longest ago?
A) O
B) A
C) F
D) K
E) M
A) O
B) A
C) F
D) K
E) M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Mass transfer will almost always occur for spectroscopic and eclipsing binaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What temperature is needed to fuse helium into carbon?
A) 5,800 K
B) 100,000 K
C) 15 million K
D) 100 million K
E) one billion K
A) 5,800 K
B) 100,000 K
C) 15 million K
D) 100 million K
E) one billion K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a star's inward gravity and outward pressure are balanced,the star is said to be:
A) in gravitational collapse.
B) in thermal expansion.
C) in rotational equilibrium.
D) in hydrostatic equilibrium.
E) a stage 2 protostar.
A) in gravitational collapse.
B) in thermal expansion.
C) in rotational equilibrium.
D) in hydrostatic equilibrium.
E) a stage 2 protostar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following elements contained in your body is NOT formed in the cores of stars during thermonuclear fusion?
A) hydrogen
B) carbon
C) calcium
D) iron
E) aluminum
A) hydrogen
B) carbon
C) calcium
D) iron
E) aluminum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A solar mass star will evolve off the main sequence when:
A) it completely runs out of hydrogen.
B) it expels a planetary nebula to cool off and release radiation.
C) it explodes as a violent nova.
D) it builds up a core of inert helium.
E) it loses all its neutrinos, so fusion must cease.
A) it completely runs out of hydrogen.
B) it expels a planetary nebula to cool off and release radiation.
C) it explodes as a violent nova.
D) it builds up a core of inert helium.
E) it loses all its neutrinos, so fusion must cease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A star (no matter what its mass)spends most of its life:
A) as a protostar.
B) as a main sequence star.
C) as a planetary nebula.
D) as a red giant or supergiant.
E) as a T Tauri variable star.
A) as a protostar.
B) as a main sequence star.
C) as a planetary nebula.
D) as a red giant or supergiant.
E) as a T Tauri variable star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What inevitably forces a star like the Sun to evolve away from being a main sequence star?
A) The core begins fusing iron.
B) The star uses up all its supply of hydrogen.
C) The carbon detonation explodes it as a type I supernova.
D) Helium builds up in the core, while the hydrogen burning shell expands.
E) The core loses all its neutrinos, so all fusion ceases.
A) The core begins fusing iron.
B) The star uses up all its supply of hydrogen.
C) The carbon detonation explodes it as a type I supernova.
D) Helium builds up in the core, while the hydrogen burning shell expands.
E) The core loses all its neutrinos, so all fusion ceases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

Refer to the figure above.What is the name of the star labeled 10?
A) planetary nebula
B) red giant branch
C) horizontal branch
D) asymptotic giant branch
E) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

Refer to the figure above.What is the name of the path between the points labeled 8 and 9?
A) planetary nebula
B) red giant branch
C) horizontal branch
D) asymptotic giant branch
E) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
At which stage in a Sun-like star's life is its core the least dense?
A) Main Sequence
B) Subgiant Branch
C) Helium Fusion
D) Planetary Nebula
E) White Dwarf
A) Main Sequence
B) Subgiant Branch
C) Helium Fusion
D) Planetary Nebula
E) White Dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Just as a low-mass main sequence star runs out of fuel in its core,it actually becomes brighter.How is this possible?
A) Helium fusion gives more energy than hydrogen fusion does, based on masses.
B) Its outer envelope is stripped away and we see the brilliant core.
C) The core contracts, raising the temperature and increasing the size of the region of hydrogen shell-burning.
D) It explodes.
E) It immediately starts to fuse helium.
A) Helium fusion gives more energy than hydrogen fusion does, based on masses.
B) Its outer envelope is stripped away and we see the brilliant core.
C) The core contracts, raising the temperature and increasing the size of the region of hydrogen shell-burning.
D) It explodes.
E) It immediately starts to fuse helium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What spectral type of star that is still around formed most recently?
A) O
B) A
C) F
D) K
E) M
A) O
B) A
C) F
D) K
E) M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is a planetary nebula?
A) the bipolar jets ejected by a T Tauri variable
B) a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas
C) the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a solar system
D) the ejected envelope, often bipolar, of a red giant surrounding a stellar core remnant
E) a type of young, medium mass star
A) the bipolar jets ejected by a T Tauri variable
B) a planet surrounded by a glowing shell of gas
C) the disk of gas and dust surrounding a young star that will soon form a solar system
D) the ejected envelope, often bipolar, of a red giant surrounding a stellar core remnant
E) a type of young, medium mass star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the evolution of massive stars,what is the significance of the temperature 600 million K?
A) It is the temperature at which helium fuses into carbon.
B) It is the temperature needed for carbon fusing into heavier elements.
C) It is the main sequence core temperature which makes massive stars so bright.
D) It is the temperature needed for helium burning into boron.
E) It is the final temperature reached during their evolution.
A) It is the temperature at which helium fuses into carbon.
B) It is the temperature needed for carbon fusing into heavier elements.
C) It is the main sequence core temperature which makes massive stars so bright.
D) It is the temperature needed for helium burning into boron.
E) It is the final temperature reached during their evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of these will the Sun probably become in the very distant future?
A) hypernova
B) supernova
C) pulsar
D) planetary nebula
E) nova
A) hypernova
B) supernova
C) pulsar
D) planetary nebula
E) nova

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A high-mass star dies more violently than a low-mass star because:
A) it must always end up as a black hole.
B) it generates more heat and its core eventually collapses very suddenly.
C) it cannot fuse elements heavier than carbon.
D) gravity is weakened by its high luminosity.
E) it is most often found as part of a binary system.
A) it must always end up as a black hole.
B) it generates more heat and its core eventually collapses very suddenly.
C) it cannot fuse elements heavier than carbon.
D) gravity is weakened by its high luminosity.
E) it is most often found as part of a binary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is true regarding planetary nebulae?
A) Some are spherical, but most have bipolar structure.
B) They are the result of the mass loss during the main sequence stage of the most massive stars.
C) They are the rings of material surrounding newly formed stars that will eventually form the planetary systems.
D) They are the ejected envelopes of highly evolved brown dwarf stars.
E) They are the coronas surrounding most blue stragglers.
A) Some are spherical, but most have bipolar structure.
B) They are the result of the mass loss during the main sequence stage of the most massive stars.
C) They are the rings of material surrounding newly formed stars that will eventually form the planetary systems.
D) They are the ejected envelopes of highly evolved brown dwarf stars.
E) They are the coronas surrounding most blue stragglers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
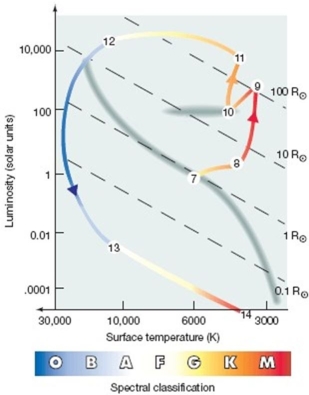
Refer to the figure above.What is the name of the path between the points labeled 13 and 14?
A) planetary nebula
B) red giant branch
C) horizontal branch
D) asymptotic giant branch
E) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
As a 4-10 solar mass star leaves the main sequence on its way to becoming a red supergiant,its luminosity:
A) decreases.
B) first decreases, then increases.
C) increases.
D) remains roughly constant.
E) first increases, then decreases.
A) decreases.
B) first decreases, then increases.
C) increases.
D) remains roughly constant.
E) first increases, then decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which type of star has the strongest stellar winds?
A) giant K- and M-type stars
B) white dwarfs
C) dwarf K- and M-type stars
D) main sequence O- and B-type stars
E) T Tauri stars
A) giant K- and M-type stars
B) white dwarfs
C) dwarf K- and M-type stars
D) main sequence O- and B-type stars
E) T Tauri stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Virtually all the carbon-rich dust in the plane of the galaxy originated in:
A) low-mass stars.
B) high-mass stars.
C) planetary nebulae.
D) white dwarfs.
E) brown dwarfs.
A) low-mass stars.
B) high-mass stars.
C) planetary nebulae.
D) white dwarfs.
E) brown dwarfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The brightest stars in a young open cluster will be:
A) massive blue stars at the top left on the H-R diagram.
B) red T-tauri stars still heading for the main sequence.
C) red giants that are fusing helium into carbon.
D) yellow giants like our Sun, but much larger.
E) the core stars of planetary nebulae.
A) massive blue stars at the top left on the H-R diagram.
B) red T-tauri stars still heading for the main sequence.
C) red giants that are fusing helium into carbon.
D) yellow giants like our Sun, but much larger.
E) the core stars of planetary nebulae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following best describes the evolutionary track followed on the H-R diagram for the most massive stars?
A) vertically upward, along the left edge of the diagram
B) diagonally to lower right, then vertical, then horizontally left
C) horizontally right, diagonally to lower left, then horizontally right
D) horizontally right
E) horizontally right, then forms a clockwise loop
A) vertically upward, along the left edge of the diagram
B) diagonally to lower right, then vertical, then horizontally left
C) horizontally right, diagonally to lower left, then horizontally right
D) horizontally right
E) horizontally right, then forms a clockwise loop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following best describes the evolutionary track of the most massive stars?
A) diagonally to lower right, then vertical, then horizontal left
B) horizontally right, diagonal to lower left, then horizontal right
C) horizontal right, then a clockwise loop
D) horizontal right
E) vertically left, then straight down
A) diagonally to lower right, then vertical, then horizontal left
B) horizontally right, diagonal to lower left, then horizontal right
C) horizontal right, then a clockwise loop
D) horizontal right
E) vertically left, then straight down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Some globular clusters have three main sequence tracks.This indicates:
A) three different stellar compositions.
B) three episodes of star formation, separated by billions of years.
C) stars evolve through three different mechanisms.
D) the stars were observed from three different telescopes.
A) three different stellar compositions.
B) three episodes of star formation, separated by billions of years.
C) stars evolve through three different mechanisms.
D) the stars were observed from three different telescopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The brightest stars of a young open cluster will be:
A) Cepheid variables.
B) massive blue main sequence stars.
C) red giants.
D) yellow main sequence stars like the Sun.
E) T Tauri variables.
A) Cepheid variables.
B) massive blue main sequence stars.
C) red giants.
D) yellow main sequence stars like the Sun.
E) T Tauri variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Compared to our Sun,a typical white dwarf has:
A) about the same mass and density.
B) about the same mass and a million times higher density.
C) a larger mass and a 100 times lower density.
D) a smaller mass and half the density.
E) a smaller mass and twice the density.
A) about the same mass and density.
B) about the same mass and a million times higher density.
C) a larger mass and a 100 times lower density.
D) a smaller mass and half the density.
E) a smaller mass and twice the density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the typical age for a globular cluster associated with our Milky Way?
A) a few million years
B) 200 million years
C) a billion years
D) 10-12 billion years
E) 45 billion years
A) a few million years
B) 200 million years
C) a billion years
D) 10-12 billion years
E) 45 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The order of evolutionary stages of a star like the Sun would be Main Sequence,giant,planetary nebula,and finally:
A) hypernova.
B) neutron star.
C) white dwarf.
D) nova.
E) black hole.
A) hypernova.
B) neutron star.
C) white dwarf.
D) nova.
E) black hole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the source of the large dust shells seen around some red giants and red supergiants?
A) leftover material from their formation
B) debris left behind by a supernova
C) material from winds from these same stars
D) debris left behind by passing comets
E) star-forming molecular clouds
A) leftover material from their formation
B) debris left behind by a supernova
C) material from winds from these same stars
D) debris left behind by passing comets
E) star-forming molecular clouds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age?
A) the ratio of main sequence to white dwarfs stars
B) the number of red giants
C) the faintest stars seen in the cluster
D) the main sequence turnoff
E) the total number of stars in the cluster
A) the ratio of main sequence to white dwarfs stars
B) the number of red giants
C) the faintest stars seen in the cluster
D) the main sequence turnoff
E) the total number of stars in the cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

Refer to the figure above.What is the name of the path between the points labeled 11 and 12?
A) planetary nebula
B) red giant branch
C) horizontal branch
D) asymptotic giant branch
E) white dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Isolated main-sequence stars as massive as 10 to 12 times the mass of the Sun may still manage to avoid going supernova.Why?
A) because they can also have strong stellar winds
B) because about half that mass will be contained in the carbon core
C) because they would be classified as brown dwarfs
D) because these stars will eject at least 4 solar masses in the planetary nebula stage
E) because their masses will decrease as they fuse heavy elements into lighter elements in their cores
A) because they can also have strong stellar winds
B) because about half that mass will be contained in the carbon core
C) because they would be classified as brown dwarfs
D) because these stars will eject at least 4 solar masses in the planetary nebula stage
E) because their masses will decrease as they fuse heavy elements into lighter elements in their cores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which stars in globular clusters are believed to be examples of mergers?
A) eclipsing binaries
B) blue supergiants
C) blue stragglers
D) brown dwarfs
E) planetary nebulae cores
A) eclipsing binaries
B) blue supergiants
C) blue stragglers
D) brown dwarfs
E) planetary nebulae cores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
That brighter Sirius A weighs 3 solar masses,but the white dwarf Sirius B is only about one solar mass implies:
A) that white dwarfs evolve slower than main sequence stars.
B) that the collapsed companion transferred mass to Sirius A.
C) that there should be a planetary nebula around the Sirius system.
D) that Sirius A will be stable three times longer than Sirius B.
E) the Sirius A will end up as a black hole, not a white dwarf like its companion.
A) that white dwarfs evolve slower than main sequence stars.
B) that the collapsed companion transferred mass to Sirius A.
C) that there should be a planetary nebula around the Sirius system.
D) that Sirius A will be stable three times longer than Sirius B.
E) the Sirius A will end up as a black hole, not a white dwarf like its companion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Noting the turnoff mass in a star cluster allows you to determine its:
A) distance.
B) radial velocity.
C) age.
D) total mass.
E) number of stars.
A) distance.
B) radial velocity.
C) age.
D) total mass.
E) number of stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The Main Sequence is the first stellar stage in which energy produced by ________ balances the energy lost by radiation from the surface of the star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Mass transfer in binaries occurs when one giant swells to reach the:
A) Chandrasekhar Limit.
B) Cassini Division.
C) Hayashi Track.
D) Roche Lobe.
E) Herbig-Haro Limit.
A) Chandrasekhar Limit.
B) Cassini Division.
C) Hayashi Track.
D) Roche Lobe.
E) Herbig-Haro Limit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The thermonuclear process in solar and less massive stars which produces one atom of helium from four of hydrogen is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
You observe a low-mass helium white dwarf.What can you conclude?
A) It is over 100 billion years old.
B) It will soon be a planetary nebula.
C) It is part of a binary star system.
D) Its core is mostly carbon.
E) It was once a blue supergiant.
A) It is over 100 billion years old.
B) It will soon be a planetary nebula.
C) It is part of a binary star system.
D) Its core is mostly carbon.
E) It was once a blue supergiant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The longest stage in the life cycle of a star is as a(n)________ star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The brightest stars in aging globular clusters will be:
A) core stars of planetary nebulae.
B) massive blue main sequence stars like Spica.
C) blue stragglers.
D) red supergiants like Betelguese and Antares.
E) blue supergiants like Rigel and Deneb.
A) core stars of planetary nebulae.
B) massive blue main sequence stars like Spica.
C) blue stragglers.
D) red supergiants like Betelguese and Antares.
E) blue supergiants like Rigel and Deneb.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compared to a cluster containing type O and B stars,a cluster with only type F and cooler stars will be:
A) younger.
B) older.
C) further away.
D) more obscured by dust.
E) less obscured by dust.
A) younger.
B) older.
C) further away.
D) more obscured by dust.
E) less obscured by dust.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which is used observationally to determine the age of a star cluster?
A) the total number of main sequence stars
B) the ratio of giants to supergiants
C) the luminosity of the main sequence turn-off point
D) the number of white dwarfs
E) the amount of dust that lies around the cluster
A) the total number of main sequence stars
B) the ratio of giants to supergiants
C) the luminosity of the main sequence turn-off point
D) the number of white dwarfs
E) the amount of dust that lies around the cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a fairly young star cluster,if the most massive stars are swelling up into giants,the least massive stars are:
A) also evolving off the main sequence as well.
B) continuing to shine as stable main sequence stars.
C) blowing off shells as planetary nebula instead.
D) collapsing directly to white dwarfs.
E) still evolving toward their ZAMS positions.
A) also evolving off the main sequence as well.
B) continuing to shine as stable main sequence stars.
C) blowing off shells as planetary nebula instead.
D) collapsing directly to white dwarfs.
E) still evolving toward their ZAMS positions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The region in the H-R Diagram where evolved,low mass stars are converting helium to carbon in their cores is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is a typical age for a globular cluster?
A) 10 million years
B) 200 million years
C) one billion years
D) 4.8 billion years
E) 12 billion years
A) 10 million years
B) 200 million years
C) one billion years
D) 4.8 billion years
E) 12 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The most famous case of a more massive hot star orbiting with a more evolved but presently less massive red giant is the eclipsing binary:
A) Aldeberan.
B) Antares.
C) Algol.
D) Alberio.
E) Altair.
A) Aldeberan.
B) Antares.
C) Algol.
D) Alberio.
E) Altair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the unusual result of mass transfer in the Algol binary system?
A) a helium white dwarf
B) a carbon white dwarf
C) a black dwarf
D) a red dwarf
E) a brown dwarf
A) a helium white dwarf
B) a carbon white dwarf
C) a black dwarf
D) a red dwarf
E) a brown dwarf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Roche lobe of a star in a binary star system:
A) resembles the ear of Edouard Roche, a French mathematician.
B) is, in terms of the star's gravity, its "zone of influence."
C) is the part of a rapidly rotating star that will eventually spin away to form planets.
D) is the accretion disk around the companion star.
E) leads to formation of rings, like around the jovian planets.
A) resembles the ear of Edouard Roche, a French mathematician.
B) is, in terms of the star's gravity, its "zone of influence."
C) is the part of a rapidly rotating star that will eventually spin away to form planets.
D) is the accretion disk around the companion star.
E) leads to formation of rings, like around the jovian planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In globular clusters,the brightest stars will be:
A) massive blue main sequence stars.
B) red supergiants.
C) T Tauri stars.
D) blue stragglers.
E) planetary nebulae.
A) massive blue main sequence stars.
B) red supergiants.
C) T Tauri stars.
D) blue stragglers.
E) planetary nebulae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The thermonuclear process in high mass stars that produces one atom of helium from four of hydrogen is the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In an H-R Diagram,the path showing changes in a star's luminosity and surface temperature as a function of time is called its ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 107 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



