Deck 21: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
1
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is made up of
A) 12 elected commercial bankers.
B) five elected presidents of Federal Reserve banks and seven commercial bankers appointed by the president of the United States.
C) seven people appointed by the president of the United States.
D) the 12 district presidents of the Federal Reserve System.
E) the treasurer of the United States, a member of the House and Senate Banking Committee, three commercial bankers, and two Federal Reserve Bank presidents.
A) 12 elected commercial bankers.
B) five elected presidents of Federal Reserve banks and seven commercial bankers appointed by the president of the United States.
C) seven people appointed by the president of the United States.
D) the 12 district presidents of the Federal Reserve System.
E) the treasurer of the United States, a member of the House and Senate Banking Committee, three commercial bankers, and two Federal Reserve Bank presidents.
C
2
Government management of the banking system's reserves is known as ________ policy.
A) fiscal
B) incomes
C) trade
D) commercial
E) monetary
A) fiscal
B) incomes
C) trade
D) commercial
E) monetary
E
3
The term of office for a member of the Federal Reserve Board is
A) two years.
B) four years.
C) seven years.
D) 14 years.
E) life.
A) two years.
B) four years.
C) seven years.
D) 14 years.
E) life.
D
4
Economic stabilization activity,which is the responsibility of the executive and legislative branches of the U.S.government,is called ________,while that presided over by the U.S.central bank is called ________.
A) deficit financing; functional finance
B) supply-side economics; liquidity preference
C) incomes policy; commercial policy
D) fiscal policy; monetary policy
E) positive economics; normative economics
A) deficit financing; functional finance
B) supply-side economics; liquidity preference
C) incomes policy; commercial policy
D) fiscal policy; monetary policy
E) positive economics; normative economics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If monetary authorities ease credit or money,________ will rise.
A) interest rates
B) unemployment
C) tax rates
D) the money supply
E) the gold supply
A) interest rates
B) unemployment
C) tax rates
D) the money supply
E) the gold supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The major indicators of monetary tightness or ease are the
A) discount rate and the prime rate of interest.
B) level of interest rates and the rate of growth of the money supply.
C) government deficit and the tax rate.
D) size and composition of the money supply.
E) level of real output and the level of interest.
A) discount rate and the prime rate of interest.
B) level of interest rates and the rate of growth of the money supply.
C) government deficit and the tax rate.
D) size and composition of the money supply.
E) level of real output and the level of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Monetary policy is carried out primarily through actions taken by the
A) president of the United States.
B) large member banks of the Federal Reserve System.
C) Treasury Department on advice from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
D) Federal Reserve Board and Federal Open Market Committee.
E) chairperson of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
A) president of the United States.
B) large member banks of the Federal Reserve System.
C) Treasury Department on advice from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.
D) Federal Reserve Board and Federal Open Market Committee.
E) chairperson of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the long run,increases or decreases in the money supply
A) cause real potential output to rise and fall.
B) must ultimately be approved by Congress.
C) may increase or decrease aggregate supply but not aggregate demand.
D) are tied to increases and decreases in the U.S. government holdings of gold.
E) raise and lower the price level but have no effect on real GDP.
A) cause real potential output to rise and fall.
B) must ultimately be approved by Congress.
C) may increase or decrease aggregate supply but not aggregate demand.
D) are tied to increases and decreases in the U.S. government holdings of gold.
E) raise and lower the price level but have no effect on real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The chief spokesperson for U.S.monetary policy is the
A) president of the United States.
B) secretary of the Treasury.
C) chairperson of the Council of Economic Advisers.
D) chairperson of the Joint Economic Committee of Congress.
E) chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
A) president of the United States.
B) secretary of the Treasury.
C) chairperson of the Council of Economic Advisers.
D) chairperson of the Joint Economic Committee of Congress.
E) chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Federal Reserve influences the money supply by managing
A) personal and corporate tax rates.
B) government spending programs.
C) the foreign trade balance.
D) the reserves of the banking system.
E) the number of financial intermediaries.
A) personal and corporate tax rates.
B) government spending programs.
C) the foreign trade balance.
D) the reserves of the banking system.
E) the number of financial intermediaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Reducing bank reserves would be an appropriate measure
A) during a recession.
B) to balance the government budget.
C) to contain strong inflationary pressures.
D) to promote an increased level of business borrowing.
E) to increase the M1 money supply.
A) during a recession.
B) to balance the government budget.
C) to contain strong inflationary pressures.
D) to promote an increased level of business borrowing.
E) to increase the M1 money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Increasing bank reserves would be an appropriate measure
A) during a recession.
B) to balance the government budget.
C) to contain strong inflationary pressures.
D) to promote an increased level of business borrowing.
E) to increase the M1 money supply.
A) during a recession.
B) to balance the government budget.
C) to contain strong inflationary pressures.
D) to promote an increased level of business borrowing.
E) to increase the M1 money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Under normal conditions the president may appoint a member to the Federal Reserve Board every
A) year.
B) two years.
C) four years.
D) seven years.
E) 14 years.
A) year.
B) two years.
C) four years.
D) seven years.
E) 14 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If monetary authorities tighten credit or money,________ will rise.
A) the price level
B) interest rates
C) the money supply
D) aggregate demand
E) excess reserves
A) the price level
B) interest rates
C) the money supply
D) aggregate demand
E) excess reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the United States today,which of the following functions as the central bank?
A) the Federal Reserve System
B) the IMF
C) the Bank of America
D) the treasurer of the United States
E) There is no central bank in the United States.
A) the Federal Reserve System
B) the IMF
C) the Bank of America
D) the treasurer of the United States
E) There is no central bank in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Federal Reserve Bank's exercising control over the quantity of money and interest rates is called
A) fiscal policy.
B) commercial banking.
C) monetary policy.
D) functional finance.
E) incomes policy.
A) fiscal policy.
B) commercial banking.
C) monetary policy.
D) functional finance.
E) incomes policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The main reason for the length of the term of office on the Federal Reserve Board is that
A) this time period corresponds closely to the lag time between actions by the Fed and their impact on the economy.
B) this term gives the individual governors the same job security as their peers in private commercial banks.
C) many years of in-service education are required before board members can make substantive contributions.
D) given the stringent requirements for membership, it has proven difficult to fill positions any more frequently.
E) long appointments limit opportunities for political influence over the board.
A) this time period corresponds closely to the lag time between actions by the Fed and their impact on the economy.
B) this term gives the individual governors the same job security as their peers in private commercial banks.
C) many years of in-service education are required before board members can make substantive contributions.
D) given the stringent requirements for membership, it has proven difficult to fill positions any more frequently.
E) long appointments limit opportunities for political influence over the board.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When monetary authorities decrease the money supply and push up interest rates,they are pursuing a(n)________ money policy.
A) easy
B) tight
C) selective
D) fiscal
E) open
A) easy
B) tight
C) selective
D) fiscal
E) open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When monetary authorities increase the money supply and push down interest rates,they are pursuing a(n)________ money policy.
A) easy
B) tight
C) selective
D) fiscal
E) open
A) easy
B) tight
C) selective
D) fiscal
E) open

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Federal Open Market Committee is made up of
A) five of the seven Federal Reserve Board governors.
B) the Board of Governors plus five of the presidents of the 12 Federal Reserve banks.
C) 12 members of the Federal Advisory Council plus the chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the president of the United States, the secretary of the Treasury, and the members of the Federal Reserve Board.
E) 12 commercial bank presidents chosen by the president of the United States.
A) five of the seven Federal Reserve Board governors.
B) the Board of Governors plus five of the presidents of the 12 Federal Reserve banks.
C) 12 members of the Federal Advisory Council plus the chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the president of the United States, the secretary of the Treasury, and the members of the Federal Reserve Board.
E) 12 commercial bank presidents chosen by the president of the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Virtually all economists agree that the key to the Fed's power lies in its ability to
A) control the reserves of the banking system.
B) change the discount rate whenever it wants to.
C) issue Federal Reserve notes.
D) persuade Congress to change fiscal policy.
E) raise or lower taxes.
A) control the reserves of the banking system.
B) change the discount rate whenever it wants to.
C) issue Federal Reserve notes.
D) persuade Congress to change fiscal policy.
E) raise or lower taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The Federal Reserve System
A) is an outgrowth of the Bank of the United States.
B) is directly controlled by Congress.
C) was established by Congress in 1913 after a severe financial panic six years earlier.
D) controls the minting of coins.
E) includes by law all of this country's financial institutions.
A) is an outgrowth of the Bank of the United States.
B) is directly controlled by Congress.
C) was established by Congress in 1913 after a severe financial panic six years earlier.
D) controls the minting of coins.
E) includes by law all of this country's financial institutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The major liability of the Federal Reserve System is
A) gold certificates.
B) government securities.
C) loans to commercial banks.
D) Federal Reserve notes.
E) treasury deposits.
A) gold certificates.
B) government securities.
C) loans to commercial banks.
D) Federal Reserve notes.
E) treasury deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If one pictures the Federal Reserve System as a pyramid,the apex (top peak)of the pyramid represents
A) the president.
B) Congress.
C) the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the Federal Open Market Committee.
E) the presidents of large commercial banks.
A) the president.
B) Congress.
C) the Federal Reserve Board.
D) the Federal Open Market Committee.
E) the presidents of large commercial banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The major asset of the Federal Reserve System is
A) gold certificates.
B) government securities.
C) loans to commercial banks.
D) Federal Reserve notes.
E) treasury deposits.
A) gold certificates.
B) government securities.
C) loans to commercial banks.
D) Federal Reserve notes.
E) treasury deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The 12 Federal Reserve banks
A) hold the deposits of member banks and make loans to them.
B) are all located in Washington, DC, but serve different districts throughout the country.
C) are all headed by members of the Federal Open Market Committee.
D) carry out policies dictated by the Treasury Department.
E) hold about 73 percent of the nation's demand deposits.
A) hold the deposits of member banks and make loans to them.
B) are all located in Washington, DC, but serve different districts throughout the country.
C) are all headed by members of the Federal Open Market Committee.
D) carry out policies dictated by the Treasury Department.
E) hold about 73 percent of the nation's demand deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Gold certificates held by the Federal Reserve are
A) legal tender.
B) warehouse receipts issued by the Treasury for gold bullion.
C) the assets for backing our paper money.
D) deposits used by the Treasury to pay its bills.
E) I.O.U.s that reflect the gold we owe those countries that export more to us than we export to them.
A) legal tender.
B) warehouse receipts issued by the Treasury for gold bullion.
C) the assets for backing our paper money.
D) deposits used by the Treasury to pay its bills.
E) I.O.U.s that reflect the gold we owe those countries that export more to us than we export to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When the Fed buys government securities on the open market
A) the national debt increases.
B) bank deposits decrease.
C) the Treasury Department realizes a profit.
D) interest rates rise.
E) bank reserves increase.
A) the national debt increases.
B) bank deposits decrease.
C) the Treasury Department realizes a profit.
D) interest rates rise.
E) bank reserves increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Federal Reserve Bank holdings of securities consist mainly of
A) foreign currencies.
B) corporate stocks and bonds.
C) securities representing U.S. loans to foreign nations.
D) funds the Federal Reserve has borrowed from the Treasury.
E) U.S. government bonds, notes, and bills.
A) foreign currencies.
B) corporate stocks and bonds.
C) securities representing U.S. loans to foreign nations.
D) funds the Federal Reserve has borrowed from the Treasury.
E) U.S. government bonds, notes, and bills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The paper currency we use in the United States is
A) issued and controlled by the Treasury Department.
B) backed by gold certificates.
C) issued by commercial banks.
D) composed almost entirely of silver certificates.
E) a debt of the Federal Reserve System.
A) issued and controlled by the Treasury Department.
B) backed by gold certificates.
C) issued by commercial banks.
D) composed almost entirely of silver certificates.
E) a debt of the Federal Reserve System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The most important function of a central bank is to
A) set interest rates.
B) make loans to the Federal Reserve System.
C) hold time and demand deposits.
D) control the quantity of money.
E) lend out money to large corporations.
A) set interest rates.
B) make loans to the Federal Reserve System.
C) hold time and demand deposits.
D) control the quantity of money.
E) lend out money to large corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System do NOT include which of the following?
A) collecting federal taxes
B) supplying the public with currency
C) acting as fiscal agents for the federal government
D) providing facilities for check collection
E) supervising the operation of the member commercial banks
A) collecting federal taxes
B) supplying the public with currency
C) acting as fiscal agents for the federal government
D) providing facilities for check collection
E) supervising the operation of the member commercial banks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If one pictures the Federal Reserve System as a pyramid,the bottom of the pyramid represents
A) the 12 Regional Reserve banks.
B) the U.S. consumers.
C) the Federal Advisory Council and other economic advisers.
D) commercial banks.
E) Congress.
A) the 12 Regional Reserve banks.
B) the U.S. consumers.
C) the Federal Advisory Council and other economic advisers.
D) commercial banks.
E) Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In addition to controlling the money supply,the Federal Reserve System also
A) holds deposits for the public.
B) acts as fiscal agents for the federal government.
C) regulates the market for corporate securities.
D) governs the International Monetary Fund.
E) insures most commercial bank accounts through the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
A) holds deposits for the public.
B) acts as fiscal agents for the federal government.
C) regulates the market for corporate securities.
D) governs the International Monetary Fund.
E) insures most commercial bank accounts through the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an example of a government security?
A) treasury bills
B) Federal Reserve notes
C) gold certificates
D) treasury deposits
E) member bank reserves
A) treasury bills
B) Federal Reserve notes
C) gold certificates
D) treasury deposits
E) member bank reserves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The number of Federal Reserve banks is
A) one.
B) seven.
C) 12.
D) 50.
E) 6,000.
A) one.
B) seven.
C) 12.
D) 50.
E) 6,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Federal Reserve System was established by Congress in
A) 1887.
B) 1907.
C) 1913.
D) 1929.
E) 1934.
A) 1887.
B) 1907.
C) 1913.
D) 1929.
E) 1934.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Federal Reserve's most important tool for controlling the amount of reserves in the banking system is
A) changing the discount rate.
B) moral suasion.
C) establishing margin requirements.
D) open market operations.
E) buying and selling gold certificates.
A) changing the discount rate.
B) moral suasion.
C) establishing margin requirements.
D) open market operations.
E) buying and selling gold certificates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Each Federal Reserve Bank is a corporation owned by
A) the Board of Governors.
B) state governments.
C) the U.S. Treasury.
D) central banks.
E) commercial banks.
A) the Board of Governors.
B) state governments.
C) the U.S. Treasury.
D) central banks.
E) commercial banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Our nation's currency is
A) created by the commercial banks in the Federal Reserve System.
B) created by both the commercial banking system and the Federal Reserve System.
C) issued by the Federal Reserve System.
D) a fractional-reserve currency.
E) issued by the Treasury.
A) created by the commercial banks in the Federal Reserve System.
B) created by both the commercial banking system and the Federal Reserve System.
C) issued by the Federal Reserve System.
D) a fractional-reserve currency.
E) issued by the Treasury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The table below shows the net effect of an open market operation undertaken by the Fed. Use it to answer the following question.
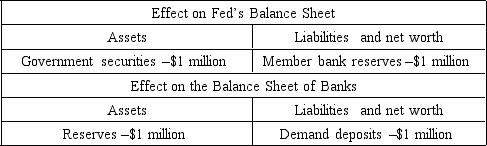
The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.

The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Over the 2001-03 period,the Fed steadily reduced the discount rate to 2 percent.These moves suggest that monetary policy was
A) selective.
B) redundant.
C) tight.
D) autonomous.
E) easy.
A) selective.
B) redundant.
C) tight.
D) autonomous.
E) easy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following policy tools will have the greatest effect on bank reserves?
A) maintaining the existing legal reserve ratio
B) advising Congress on budget policy
C) decreasing the discount rate
D) encouraging banks to be more cautious
E) buying U.S. government securities
A) maintaining the existing legal reserve ratio
B) advising Congress on budget policy
C) decreasing the discount rate
D) encouraging banks to be more cautious
E) buying U.S. government securities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The interest rate charged by the Fed for loans to commercial banks is called the
A) prime rate.
B) required reserve ratio.
C) discount rate.
D) Q rate.
E) T-bill rate.
A) prime rate.
B) required reserve ratio.
C) discount rate.
D) Q rate.
E) T-bill rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The power to decide on the amount of government securities the Fed should buy or sell at any given time rests with the
A) Federal Open Market Committee.
B) president of the United States.
C) chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
D) secretary of the Treasury.
E) Council of Economic Advisers.
A) Federal Open Market Committee.
B) president of the United States.
C) chairperson of the Federal Reserve Board.
D) secretary of the Treasury.
E) Council of Economic Advisers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If this same bank has its legal reserve requirement raised to 18 percent,it
A) need not do anything since it still has sufficient legal reserves to meet this new requirement.
B) must take steps to increase its demand deposits by making new loans from its reserves.
C) should discourage new demand deposit accounts until its legal reserves are increased.
D) must either sell securities or not renew loans as they come due.
E) should buy government securities to increase the money supply.
A) need not do anything since it still has sufficient legal reserves to meet this new requirement.
B) must take steps to increase its demand deposits by making new loans from its reserves.
C) should discourage new demand deposit accounts until its legal reserves are increased.
D) must either sell securities or not renew loans as they come due.
E) should buy government securities to increase the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The next question is based on this table.
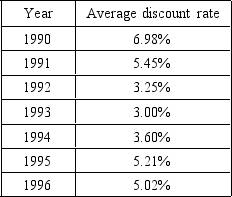
In December 1991,the Fed cut the discount rate by a full percentage point to 3.5 percent,the lowest discount rate in 27 years.This move clearly reflects the Fed's
A) concern that inflation was getting out of control.
B) desire to reduce bank reserves.
C) effort to eliminate the large government budget deficit.
D) need to borrow more money from abroad.
E) attempt to send a clear signal to the banking system that it was time to expand credit.

In December 1991,the Fed cut the discount rate by a full percentage point to 3.5 percent,the lowest discount rate in 27 years.This move clearly reflects the Fed's
A) concern that inflation was getting out of control.
B) desire to reduce bank reserves.
C) effort to eliminate the large government budget deficit.
D) need to borrow more money from abroad.
E) attempt to send a clear signal to the banking system that it was time to expand credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The next question is based on this table.

The information in the table suggests that the Fed was pursuing a more restrictive monetary policy during the period from
A) 1990 to 1996.
B) 1990 to 1993.
C) 1993 to 1995.
D) 1995 to 1996.
E) January to December 1993.

The information in the table suggests that the Fed was pursuing a more restrictive monetary policy during the period from
A) 1990 to 1996.
B) 1990 to 1993.
C) 1993 to 1995.
D) 1995 to 1996.
E) January to December 1993.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If commercial banks have no excess reserves and the Fed sells government securities
A) the money supply will expand and interest rates will fall.
B) total demand deposits in the banking system will fall by some multiple of the bond sale.
C) the size of the money supply will not change but its composition will.
D) the required reserve ratio will increase.
E) banks will gain excess reserves equal to the amount of bonds sold.
A) the money supply will expand and interest rates will fall.
B) total demand deposits in the banking system will fall by some multiple of the bond sale.
C) the size of the money supply will not change but its composition will.
D) the required reserve ratio will increase.
E) banks will gain excess reserves equal to the amount of bonds sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If a commercial bank has $8 million in demand deposits and $1.4 million in legal reserves and the legal reserve requirement is 16 percent,then the bank has excess reserves of
A) $0.
B) $120,000.
C) $224,000.
D) $1,176,000.
E) $1,280,000.
A) $0.
B) $120,000.
C) $224,000.
D) $1,176,000.
E) $1,280,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An important characteristic of the discount rate is that it
A) has a powerful effect on the money supply.
B) has a direct impact on bank reserves without changing the money supply.
C) can be changed frequently and substantially.
D) structurally alters bank credit creation.
E) has no effect on financial markets.
A) has a powerful effect on the money supply.
B) has a direct impact on bank reserves without changing the money supply.
C) can be changed frequently and substantially.
D) structurally alters bank credit creation.
E) has no effect on financial markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The table below shows the net effect of an open market operation undertaken by the Fed. Use it to answer the following question.

The Fed can decrease the money supply by
A) selling government securities.
B) raising taxes.
C) lowering reserve requirements.
D) lowering discount rates.
E) decreasing government spending.

The Fed can decrease the money supply by
A) selling government securities.
B) raising taxes.
C) lowering reserve requirements.
D) lowering discount rates.
E) decreasing government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When the Fed sells government securities on the open market
A) bank reserves decline.
B) the Fed is following an easy money policy.
C) government bond prices rise.
D) bank reserves and interest rates both rise.
E) interest rates fall.
A) bank reserves decline.
B) the Fed is following an easy money policy.
C) government bond prices rise.
D) bank reserves and interest rates both rise.
E) interest rates fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Fed seldom exercises its power to change the legal reserve requirements because
A) it lacks the authority to do so without prior congressional approval.
B) such changes are limited to no more than one per year.
C) this policy tool has a minimal effect on bank reserves because the limits are quite low.
D) most commercial banks manage their reserves responsibly without the Fed's intervention.
E) it is a drastic way to change bank reserves compared to open market operations.
A) it lacks the authority to do so without prior congressional approval.
B) such changes are limited to no more than one per year.
C) this policy tool has a minimal effect on bank reserves because the limits are quite low.
D) most commercial banks manage their reserves responsibly without the Fed's intervention.
E) it is a drastic way to change bank reserves compared to open market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Increases in the discount rate tend to tighten the money supply by
A) making it more expensive for member banks to augment their reserves by borrowing from the Fed.
B) forcing member banks to recall loans.
C) inducing banks to sell government securities.
D) reducing the amount of demand deposits that a given amount of reserves can legally support.
E) increasing the interest rate banks are legally allowed to pay depositors.
A) making it more expensive for member banks to augment their reserves by borrowing from the Fed.
B) forcing member banks to recall loans.
C) inducing banks to sell government securities.
D) reducing the amount of demand deposits that a given amount of reserves can legally support.
E) increasing the interest rate banks are legally allowed to pay depositors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In 1975 Congress passed a resolution that the Fed must publish its targets for growth in the money supply.The general effect of that resolution has been to
A) noticeably restrict the Fed's power.
B) curb the Fed's power over monetary policy but enhance its power over fiscal policy.
C) give the Fed the right to set a ceiling on commercial banks' interest rates for the first time.
D) force the Fed to rely more heavily on changes in the reserve ratio.
E) have some impact; however, it has been difficult to measure just how much or at what cost.
A) noticeably restrict the Fed's power.
B) curb the Fed's power over monetary policy but enhance its power over fiscal policy.
C) give the Fed the right to set a ceiling on commercial banks' interest rates for the first time.
D) force the Fed to rely more heavily on changes in the reserve ratio.
E) have some impact; however, it has been difficult to measure just how much or at what cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The table above shows the net effect of an open market operation undertaken by the Fed. Use it to answer the following question.
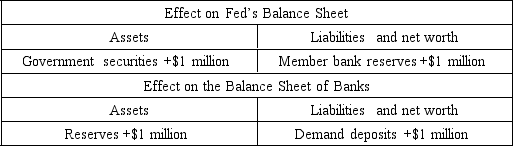
The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.

The Fed has
A) increased bank reserves, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
B) sold government securities, thereby decreasing the supply of money.
C) sold government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.
D) increased the national debt.
E) purchased government securities, thereby increasing the supply of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Changes in the legal reserve requirements
A) change the amount of Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance.
B) must be approved by Congress.
C) change the amount of demand deposits the banking system can support.
D) change the discount rate.
E) usually have no effect on the money supply.
A) change the amount of Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance.
B) must be approved by Congress.
C) change the amount of demand deposits the banking system can support.
D) change the discount rate.
E) usually have no effect on the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The discount rate is
A) the bonus the Fed credits to all banks that borrow from it.
B) a very inflexible policy tool, which the Fed rarely, if ever, uses.
C) the procedure the Fed uses when it issues treasury notes.
D) another name for the prime rate.
E) the interest rate charged by the Fed on its loans to banks.
A) the bonus the Fed credits to all banks that borrow from it.
B) a very inflexible policy tool, which the Fed rarely, if ever, uses.
C) the procedure the Fed uses when it issues treasury notes.
D) another name for the prime rate.
E) the interest rate charged by the Fed on its loans to banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Changes in the discount rate principally affect
A) expectations.
B) the ratio of reserves to deposits.
C) foreign exchange rates.
D) policy lags.
E) government spending levels.
A) expectations.
B) the ratio of reserves to deposits.
C) foreign exchange rates.
D) policy lags.
E) government spending levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In its reaction to financial crises in October 1987 and August 1998,the Fed
A) did nothing, allowing natural market forces to correct the conditions.
B) decreased the money supply while promoting an increase in demand to strengthen prices.
C) created and expanded the duties of the Long-Term Capital Management Corporation to oversee foreign lending.
D) ensured that adequate liquidity was available to minimize the real impact of these shocks.
E) raised interest rates to encourage more people to save rather than speculate with their money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In general,the discount rate is kept close to short-term market interest rates to
A) enable commercial banks to operate profitably.
B) reduce the government cost to borrow money.
C) discourage commercial banks from excessive use of the borrowing privilege.
D) avoid the possibility that monetary actions affect financial market expectations.
E) keep interest rates stable over long periods of time.
A) enable commercial banks to operate profitably.
B) reduce the government cost to borrow money.
C) discourage commercial banks from excessive use of the borrowing privilege.
D) avoid the possibility that monetary actions affect financial market expectations.
E) keep interest rates stable over long periods of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In 1965,President Johnson opposed a tax increase recommended by his economic advisers because
A) the war in Vietnam was drawing to a close and additional tax revenue was no longer needed.
B) he feared that a tax increase would bring the issue of the Vietnam War into sharp political focus.
C) he feared a tax increase would aggravate already high interest rates.
D) the Fed saw no immediate threat from inflation and Johnson elected to trust its judgment.
E) the United States had just had a significant increase in taxes to fund the Great Society.
A) the war in Vietnam was drawing to a close and additional tax revenue was no longer needed.
B) he feared that a tax increase would bring the issue of the Vietnam War into sharp political focus.
C) he feared a tax increase would aggravate already high interest rates.
D) the Fed saw no immediate threat from inflation and Johnson elected to trust its judgment.
E) the United States had just had a significant increase in taxes to fund the Great Society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Between 1929 and 1931,about 2,000 banks failed across the United States.A major reason for this was probably that the Fed
A) had little power since it was not created until mid-1931.
B) had no power to lend money to commercial banks.
C) felt its main obligation was to assist only those banks that were solvent.
D) was under the direction of the president and Congress and could act only at their specific request.
E) pursued a restrictive monetary policy to prevent the loss of gold reserves from the banking system.
A) had little power since it was not created until mid-1931.
B) had no power to lend money to commercial banks.
C) felt its main obligation was to assist only those banks that were solvent.
D) was under the direction of the president and Congress and could act only at their specific request.
E) pursued a restrictive monetary policy to prevent the loss of gold reserves from the banking system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65

It has been estimated that the full economic effects of monetary policy are
A) realized almost immediately.
B) realized in slightly over one year.
C) realized in about one to three months.
D) unnoticed because money policy has little overall economic effect.
E) imperceptible because of the relatively minor nature of these policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The results of the Fed's efforts to help member banks in 1931 illustrate the general principle that
A) any action the Fed takes with regard to commercial banks causes an inevitable reaction in the economy as a whole.
B) any action taken by the Fed to help member banks has a negative impact on the economy as a whole.
C) actions taken by the Fed have far less impact on the overall economy than was once believed.
D) keeping member banks solvent is, in the long run, the single best way to stimulate a sluggish economy.
E) the nation's monetary system should be tied to the gold standard.
A) any action the Fed takes with regard to commercial banks causes an inevitable reaction in the economy as a whole.
B) any action taken by the Fed to help member banks has a negative impact on the economy as a whole.
C) actions taken by the Fed have far less impact on the overall economy than was once believed.
D) keeping member banks solvent is, in the long run, the single best way to stimulate a sluggish economy.
E) the nation's monetary system should be tied to the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
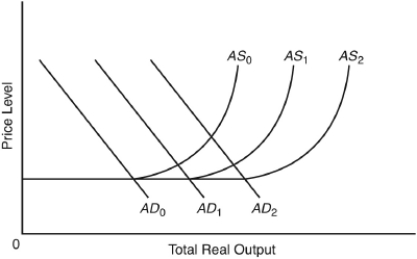
67

If the economy's aggregate demand and supply curves are AD₁ and AS₁,an increase in the money supply will:
A) lower total real output and raise the price level as aggregate supply shifts from AS₁ to AS₀.
B) lower total real output and leave the price level unchanged because AD₁ will shift to AD₀.
C) raise total real output but not the price level, for aggregate supply will shift from AS₁ to AS₂.
D) raise both total real output and the price level as aggregate demand shifts from AD₁ to AD₂.
E) raise the price level but leave total real output unchanged, as aggregate demand shifts from AD₁ to AD₂ and aggregate supply shifts from AS₁ to AS₀.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Fed's freedom to control the supply of money and interest rates unhampered by constraints of the U.S.Treasury was the principle result of the
A) Federal Reserve Act of 1913.
B) Full Employment Act of 1946.
C) Taft-Hartley Act of 1947.
D) Accord of 1951.
E) Humphrey-Hawkins Act of 1978.
A) Federal Reserve Act of 1913.
B) Full Employment Act of 1946.
C) Taft-Hartley Act of 1947.
D) Accord of 1951.
E) Humphrey-Hawkins Act of 1978.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A decrease in the money supply
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the left
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
E) affects neither the aggregate demand nor the aggregate supply curve, only interest rates.
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the left
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right.
E) affects neither the aggregate demand nor the aggregate supply curve, only interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An increase in the money supply
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the left.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right
E) affects neither the aggregate demand nor the aggregate supply curve, only interest rates.
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the left.
D) shifts the aggregate supply curve to the right
E) affects neither the aggregate demand nor the aggregate supply curve, only interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Banking Act of 1935 has been called the "single most important piece of banking legislation since the original Federal Reserve Act" because the act
A) guaranteed the solvency of member banks.
B) gave the Fed authority to take a leadership role in setting monetary policy.
C) made the Fed subservient to the Treasury, thus ensuring control of its power.
D) made the Fed a "reactive" agency, thus encouraging more sensitivity to political pressures of the times.
E) committed the U.S. government to continue backing its currency with gold.
A) guaranteed the solvency of member banks.
B) gave the Fed authority to take a leadership role in setting monetary policy.
C) made the Fed subservient to the Treasury, thus ensuring control of its power.
D) made the Fed a "reactive" agency, thus encouraging more sensitivity to political pressures of the times.
E) committed the U.S. government to continue backing its currency with gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



