Deck 6: Economic Efficiency,market Supply,and Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Economic Efficiency,market Supply,and Perfect Competition
1
Which set of characteristics best identifies a monopolistically competitive market?
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition
D
2
Which of the following characteristics would be inappropriate when describing a perfectly competitive market?
A) many firms
B) homogeneous product
C) some power over price
D) low barriers to entry
E) no form of nonprice competition practices
A) many firms
B) homogeneous product
C) some power over price
D) low barriers to entry
E) no form of nonprice competition practices
C
3
Profit-maximizing firms should increase output to the point where
A) total revenue is largest.
B) total revenue just exceeds total cost.
C) an increase in revenue is just offset by an increase in cost.
D) fixed costs are covered.
E) total cost is minimized.
A) total revenue is largest.
B) total revenue just exceeds total cost.
C) an increase in revenue is just offset by an increase in cost.
D) fixed costs are covered.
E) total cost is minimized.
C
4
Which set of characteristics best identifies a pure monopoly?
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The shape of the total revenue curve of a perfectly competitive firm is a(n)
A) horizontal line.
B) vertical line.
C) downward-sloping straight line.
D) upward-sloping straight line.
E) parabolic line, rising at first and then falling.
A) horizontal line.
B) vertical line.
C) downward-sloping straight line.
D) upward-sloping straight line.
E) parabolic line, rising at first and then falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The following questions are based on the following graph:
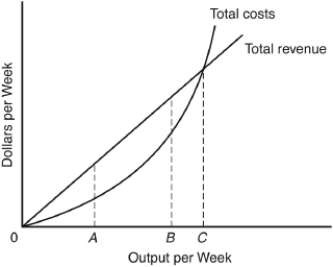
The Golden Rule of Output Determination for a perfectly competitive firm is to
A) choose the output rate at which price is greatest.
B) choose the output rate at which price equals marginal cost.
C) produce to the point of diminishing marginal returns.
D) produce until total revenue exceeds total cost.
E) choose the output rate at which total cost is the lowest.

The Golden Rule of Output Determination for a perfectly competitive firm is to
A) choose the output rate at which price is greatest.
B) choose the output rate at which price equals marginal cost.
C) produce to the point of diminishing marginal returns.
D) produce until total revenue exceeds total cost.
E) choose the output rate at which total cost is the lowest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A market consisting of many firms,low barriers to entry,some control over price but considerable nonprice competition is characteristic of
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) dictatorship.
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) dictatorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which set of characteristics best identifies an oligopoly market?
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition
A) many firms, homogeneous product, significant barriers to entry, significant nonprice competition, and considerable power over price
B) few firms, differentiated product, no barriers to entry, the absence of nonprice competition, and considerable advertising
C) one firm producing a product with no close substitutes, significant barriers to entry, and considerable power over price
D) many firms, differentiated product, few barriers to entry, and nonprice competition
E) few firms, differentiated product, significant barriers to entry, and significant amounts of nonprice competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The perfectly competitive firm
A) strives to produce at the lowest total cost possible.
B) is forced to respond to price actions of rival producers.
C) cannot affect the price of its product because of government regulation.
D) is a price maker.
E) is able to sell all it can produce at the prevailing price.
A) strives to produce at the lowest total cost possible.
B) is forced to respond to price actions of rival producers.
C) cannot affect the price of its product because of government regulation.
D) is a price maker.
E) is able to sell all it can produce at the prevailing price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve that is
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) greater than the market price.
D) equal to the total costs of production for each level of output.
E) nonexistent.
A) downward sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) greater than the market price.
D) equal to the total costs of production for each level of output.
E) nonexistent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following would be excluded from the key characteristics used to classify a market structure?
A) number of firms
B) type of product
C) level of technology
D) barriers to entry
E) power of firm over price
A) number of firms
B) type of product
C) level of technology
D) barriers to entry
E) power of firm over price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The legal,technical,and financial difficulties a firm must overcome to participate in a particular market are called
A) implicit costs.
B) open market operations.
C) crowding-out conditions.
D) external economies and diseconomies.
E) barriers to entry.
A) implicit costs.
B) open market operations.
C) crowding-out conditions.
D) external economies and diseconomies.
E) barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following questions are based on the following cost and revenue schedule for the Presto Piano Company:
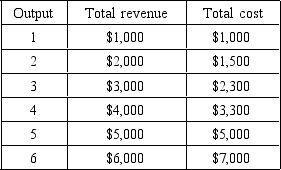
To maximize profits,the firm should produce between ________ units per period.
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6

To maximize profits,the firm should produce between ________ units per period.
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A market consisting of a few firms producing similar products with significant barriers to entry is characteristic of
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) libertarianism.
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) libertarianism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The following questions are based on the following cost and revenue schedule for the Presto Piano Company:

If the firm finds that the market price per unit of output is $800,it should produce between ________ units per period.
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6

If the firm finds that the market price per unit of output is $800,it should produce between ________ units per period.
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 4 and 5
E) 5 and 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The following questions are based on the following cost and revenue schedule for the Presto Piano Company:

The profit-maximizing rate of output for the perfectly competitive firm occurs where marginal cost equals
A) output.
B) average cost.
C) total cost.
D) total revenue.
E) price.

The profit-maximizing rate of output for the perfectly competitive firm occurs where marginal cost equals
A) output.
B) average cost.
C) total cost.
D) total revenue.
E) price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The following questions are based on the following graph:

Profits are maximized at an output
A) between 0 and A.
B) between A and B.
C) between B and C.
D) at C.
E) greater than output C.

Profits are maximized at an output
A) between 0 and A.
B) between A and B.
C) between B and C.
D) at C.
E) greater than output C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The following questions are based on the following graph:

Which of the following is implied by the graph?
A) Output rate B is more profitable than output rate A.
B) Any positive output rate less than C is profitable.
C) Output rate A maximizes profits.
D) After output rate B, total cost increases more slowly than total revenue.
E) All output rates greater than C are profitable.

Which of the following is implied by the graph?
A) Output rate B is more profitable than output rate A.
B) Any positive output rate less than C is profitable.
C) Output rate A maximizes profits.
D) After output rate B, total cost increases more slowly than total revenue.
E) All output rates greater than C are profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A market consisting of many firms producing a homogeneous product,having complete knowledge of relevant information,having no power over the product's market price,and having low barriers to entry is characteristic of
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) a Robinson Crusoe economy.
A) perfect competition.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) oligopoly.
E) a Robinson Crusoe economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The model of perfect competition is useful because
A) most firms in the real world are perfectly competitive.
B) perfectly competitive firms exert significant pricing power.
C) government regulation is designed to eliminate perfect competition.
D) it is a model of an ideal world that sheds much light on a market's effect on resource allocation.
E) advertising agencies depend heavily on the advertising dollars of perfectly competitive firms.
A) most firms in the real world are perfectly competitive.
B) perfectly competitive firms exert significant pricing power.
C) government regulation is designed to eliminate perfect competition.
D) it is a model of an ideal world that sheds much light on a market's effect on resource allocation.
E) advertising agencies depend heavily on the advertising dollars of perfectly competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The following questions are based on the following diagram of a perfectly competitive firm:
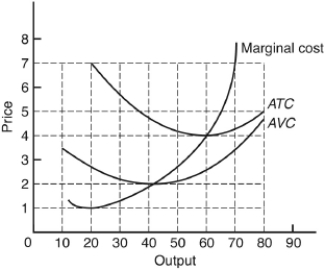
What is the minimum output that the firm would produce in the short run?
A) 20 units
B) 30 units
C) 40 units
D) 50 units
E) 60 units

What is the minimum output that the firm would produce in the short run?
A) 20 units
B) 30 units
C) 40 units
D) 50 units
E) 60 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If a perfectly competitive firm in the short run can sell its output at $2.50 per bushel and it has an average variable cost of $2.75 per bushel and a marginal cost of $2.50 per bushel,it should
A) expand output.
B) raise its price.
C) cut output to zero.
D) advertise.
E) do nothing at all; it is currently maximizing profits.
A) expand output.
B) raise its price.
C) cut output to zero.
D) advertise.
E) do nothing at all; it is currently maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The following questions are based on the following diagram showing the short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm:
At what price per unit would the firm find it no more profitable to operate than NOT to operate?
A) $1
B) $2
C) $3
D) $4
E) $5

At what price per unit would the firm find it no more profitable to operate than NOT to operate?
A) $1
B) $2
C) $3
D) $4
E) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost curve above the minimum value of average variable cost is equivalent to the
A) industry demand curve.
B) long-run average cost curve.
C) firm's production function.
D) production possibilities curve.
E) firm's supply curve.
A) industry demand curve.
B) long-run average cost curve.
C) firm's production function.
D) production possibilities curve.
E) firm's supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the profit-maximizing level of output for a perfectly competitive firm with the following cost and revenue information?
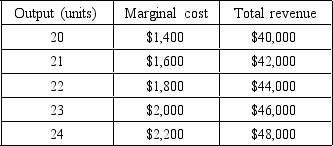
A) 20 units
B) 21 units
C) 22 units
D) 23 units
E) 24 units

A) 20 units
B) 21 units
C) 22 units
D) 23 units
E) 24 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
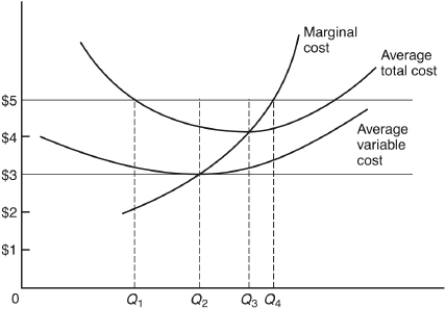
The following questions are based on the following diagram of a perfectly competitive firm:

At which price will the firm earn zero economic profits if it follows the Golden Rule of Output Determination?
A) $1
B) $2
C) $3
D) $4
E) $5

At which price will the firm earn zero economic profits if it follows the Golden Rule of Output Determination?
A) $1
B) $2
C) $3
D) $4
E) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following questions are based on the following diagram of a perfectly competitive firm:

If the price is $7 per unit,the firm will produce ________ units.
A) 20
B) 40
C) 60
D) 70
E) 80

If the price is $7 per unit,the firm will produce ________ units.
A) 20
B) 40
C) 60
D) 70
E) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a perfectly competitive firm in the short run can sell its output at $2.50 per bushel and it has an average variable cost of $1.75 per bushel and a marginal cost of $0.85 per bushel,it should
A) expand output.
B) raise its price.
C) cut output to zero.
D) advertise.
E) do nothing at all; it is currently maximizing profits.
A) expand output.
B) raise its price.
C) cut output to zero.
D) advertise.
E) do nothing at all; it is currently maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The perfectly competitive firm's supply curve is exactly the same as
A) the supply curve of all other firms in the industry.
B) the average variable cost curve, since the firm will not produce if price is less than average variable cost.
C) the firm's marginal cost curve for all prices above the minimum value of average variable cost.
D) its fully allocated costs.
E) the price faced by the firm.
A) the supply curve of all other firms in the industry.
B) the average variable cost curve, since the firm will not produce if price is less than average variable cost.
C) the firm's marginal cost curve for all prices above the minimum value of average variable cost.
D) its fully allocated costs.
E) the price faced by the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Even if a perfectly competitive firm produces at a loss in the short run,continued production is preferable to shutting down as long as
A) price is below marginal cost.
B) total losses are less than total fixed cost.
C) average variable cost exceeds price.
D) total revenue exceeds total fixed cost.
E) total variable cost exceeds total revenue.
A) price is below marginal cost.
B) total losses are less than total fixed cost.
C) average variable cost exceeds price.
D) total revenue exceeds total fixed cost.
E) total variable cost exceeds total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
It would NOT pay a firm to produce anything in the short run if price were
A) above average total cost.
B) equal to marginal cost and above average variable cost.
C) equal to total revenue divided by output.
D) below average variable cost.
E) below marginal average cost.
A) above average total cost.
B) equal to marginal cost and above average variable cost.
C) equal to total revenue divided by output.
D) below average variable cost.
E) below marginal average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If input prices increase with industry expansion
A) the short-run market supply curve will become more elastic.
B) profits will decline.
C) industry costs will fall.
D) the firm's marginal cost curves will not shift.
E) the market supply curve is not the horizontal summation of the firm's supply curves.
A) the short-run market supply curve will become more elastic.
B) profits will decline.
C) industry costs will fall.
D) the firm's marginal cost curves will not shift.
E) the market supply curve is not the horizontal summation of the firm's supply curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Choosing an output rate at which price equals marginal cost maximizes profits for the perfectly competitive firm because further increases in the output rate would
A) increase total cost.
B) decrease total revenue.
C) add more to total cost than it would to total revenue.
D) result in a price decline.
E) increase average fixed cost more than average variable cost.
A) increase total cost.
B) decrease total revenue.
C) add more to total cost than it would to total revenue.
D) result in a price decline.
E) increase average fixed cost more than average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following conditions would indicate that a perfectly competitive firm should expand its output to increase its profit?
A) Marginal cost equals average cost.
B) Total cost exceeds marginal cost.
C) Price exceeds marginal cost.
D) Total revenue exceeds total cost.
E) Total revenue equals price.
A) Marginal cost equals average cost.
B) Total cost exceeds marginal cost.
C) Price exceeds marginal cost.
D) Total revenue exceeds total cost.
E) Total revenue equals price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the short run the perfectly competitive firm will produce at a loss rather than discontinue production if
A) there is an output rate at which price exceeds average variable cost.
B) total losses exceed total fixed cost.
C) there is an output rate at which price equals marginal cost.
D) the firm's supply curve is upward sloping.
E) total revenue can be increased by producing more.
A) there is an output rate at which price exceeds average variable cost.
B) total losses exceed total fixed cost.
C) there is an output rate at which price equals marginal cost.
D) the firm's supply curve is upward sloping.
E) total revenue can be increased by producing more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the marginal cost for a perfectly competitive,profit-maximizing firm currently exceeds the price of its output,the firm should
A) expand its output and lower its price.
B) continue to produce at the same output rate and raise its price.
C) contract output.
D) increase its nonprice competition.
E) do nothing; it is currently maximizing profits.
A) expand its output and lower its price.
B) continue to produce at the same output rate and raise its price.
C) contract output.
D) increase its nonprice competition.
E) do nothing; it is currently maximizing profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The following questions are based on the following graph:

A perfectly competitive firm has the following cost schedule:
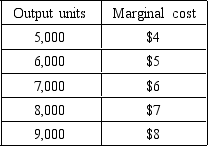
If the firm is a profit-maximizing firm and it can sell its output for $5 each,it should produce ________ units.
A) 5,000
B) 6,000
C) 7,000
D) 8,000
E) 9,000

A perfectly competitive firm has the following cost schedule:

If the firm is a profit-maximizing firm and it can sell its output for $5 each,it should produce ________ units.
A) 5,000
B) 6,000
C) 7,000
D) 8,000
E) 9,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The relevant cost for making short-run production decisions is the ________ cost.
A) variable
B) fixed
C) sunk
D) reproduction
E) historic
A) variable
B) fixed
C) sunk
D) reproduction
E) historic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The following questions are based on the following diagram showing the short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm:

If the price is $5 per unit,the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) zero.
B) 0Q1.
C) 0Q2.
D) 0Q3.
E) 0Q4.

If the price is $5 per unit,the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) zero.
B) 0Q1.
C) 0Q2.
D) 0Q3.
E) 0Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The following questions are based on the following diagram showing the short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm:

If the price is $2 per unit,the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) zero.
B) 0Q1.
C) 0Q2.
D) 0Q3.
E) 0Q4.

If the price is $2 per unit,the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) zero.
B) 0Q1.
C) 0Q2.
D) 0Q3.
E) 0Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The following questions are based on the following table showing the supply curves of the five individual firms constituting the rutabaga market in a small community. Assume that simultaneous changes in output by all firms do NOT affect input prices.
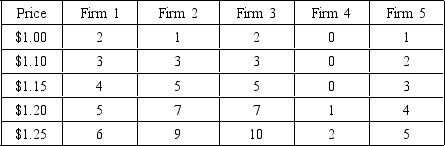
If the price is $1.00 per unit,the quantity supplied will be
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.
E) 8.

If the price is $1.00 per unit,the quantity supplied will be
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.
E) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose all firms in an industry in long-run equilibrium have U-shaped average cost curves.If the market demand increases,the resulting increase in price in the short run
A) rations out the current production.
B) rations out the current production and results in higher profits to producers.
C) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, and prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input.
D) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input, and causes a short-run increase in industry capacity by drawing new producers into the market.
E) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input, and causes a short-run increase in industry capacity by drawing new producers into the market, all while existing firms increase capacity by expanding plant size.
A) rations out the current production.
B) rations out the current production and results in higher profits to producers.
C) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, and prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input.
D) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input, and causes a short-run increase in industry capacity by drawing new producers into the market.
E) rations out the current production, results in higher profits to producers, prompts existing firms to increase output by hiring more variable input, and causes a short-run increase in industry capacity by drawing new producers into the market, all while existing firms increase capacity by expanding plant size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following questions are based on the following graph, showing short-run supply and demand curves for a perfectly competitive market. The initial supply curve is labeled "Supply" and the initial demand curve is labeled "Demand." Price 0A and output rate 0X represent the initial equilibrium price and output.
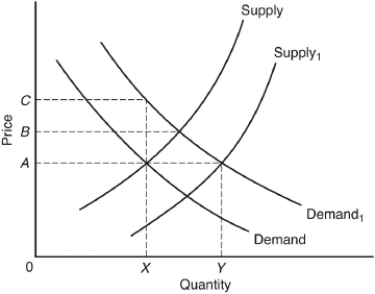
For a typical producer in this market
A) marginal cost equals 0A.
B) average total cost is less than 0A.
C) average total cost is greater than 0A.
D) long-run average cost equals the supply curve.
E) average total cost equals the supply curve.

For a typical producer in this market
A) marginal cost equals 0A.
B) average total cost is less than 0A.
C) average total cost is greater than 0A.
D) long-run average cost equals the supply curve.
E) average total cost equals the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The following questions are based on the following table showing the supply curves of the five individual firms constituting the rutabaga market in a small community. Assume that simultaneous changes in output by all firms do NOT affect input prices.

In the short run,what adjustments take place when a perfectly competitive market in long-run equilibrium experiences an increase in demand?
A) Price and profits fall, causing new firms to enter and existing firms to expand.
B) Price and output remain fixed.
C) Price rises but output remains unchanged.
D) Price rises and firms expand output by using existing capacity more intensively.
E) New firms enter and existing firms expand capacity, leading to an increase in supply and a decline in price.

In the short run,what adjustments take place when a perfectly competitive market in long-run equilibrium experiences an increase in demand?
A) Price and profits fall, causing new firms to enter and existing firms to expand.
B) Price and output remain fixed.
C) Price rises but output remains unchanged.
D) Price rises and firms expand output by using existing capacity more intensively.
E) New firms enter and existing firms expand capacity, leading to an increase in supply and a decline in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Compared to its initial position,a typical firm in new short-run equilibrium
A) finds its average fixed cost higher.
B) increases its plant size.
C) finds its marginal cost higher.
D) makes less profit.
E) reduces average variable cost.
A) finds its average fixed cost higher.
B) increases its plant size.
C) finds its marginal cost higher.
D) makes less profit.
E) reduces average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is a principal determinant of the market supply curve?
A) consumer preferences
B) the level of input prices
C) the price elasticity of demand
D) the number of buyers in the market
E) the level of expenditures in the market
A) consumer preferences
B) the level of input prices
C) the price elasticity of demand
D) the number of buyers in the market
E) the level of expenditures in the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the long run,in a perfectly competitive industry,________ are zero.
A) economic profits
B) costs of production
C) average total costs
D) prices
E) variable costs
A) economic profits
B) costs of production
C) average total costs
D) prices
E) variable costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In the long run,perfectly competitive industries experiencing decreases in demand
A) gain firms.
B) lose resources.
C) require price controls.
D) become monopolies.
E) remain unaffected.
A) gain firms.
B) lose resources.
C) require price controls.
D) become monopolies.
E) remain unaffected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the long-run response of this industry to a shift in the demand schedule to Demand₁ is to increase supply out to Supply₁,then compared to its initial position,a typical firm in long-run equilibrium
A) makes more profit.
B) reduces its long-run average cost.
C) finds its marginal cost higher.
D) finds its average cost unchanged.
E) finds that the price for its product has risen.
A) makes more profit.
B) reduces its long-run average cost.
C) finds its marginal cost higher.
D) finds its average cost unchanged.
E) finds that the price for its product has risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If demand for the product increases to Demand₁,the market achieves its short-run equilibrium position where the
A) market price is 0A.
B) market price is 0B.
C) market price is 0C.
D) industry output rate is 0X.
E) industry output rate is 0Y.
A) market price is 0A.
B) market price is 0B.
C) market price is 0C.
D) industry output rate is 0X.
E) industry output rate is 0Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
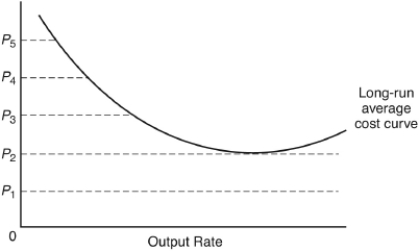
If the perfectly competitive firm pictured is in long-run equilibrium,the price must be
A) 0P₁.
B) 0P₂.
C) 0P₃.
D) 0P₄.
E) 0P₅.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The basic distinction between the short run and the long run in a perfectly competitive industry is that in the long run,firms
A) earn economic profits.
B) are free to enter or exit.
C) face vertical demand curves.
D) have zero marginal costs.
E) produce the highest possible output rates.
A) earn economic profits.
B) are free to enter or exit.
C) face vertical demand curves.
D) have zero marginal costs.
E) produce the highest possible output rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following questions are based on the following table showing the supply curves of the five individual firms constituting the rutabaga market in a small community. Assume that simultaneous changes in output by all firms do NOT affect input prices.

A price increase from $1.20 to $1.25 would cause the quantity supplied to increase by
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.
E) 8.

A price increase from $1.20 to $1.25 would cause the quantity supplied to increase by
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 7.
E) 8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Perfectly competitive firms have zero economic profits in the long run because
A) they all produce slightly different products.
B) of nonprice competition.
C) of freedom of entry and exit.
D) of the outgrowth of advertising expenditures.
E) of the law of diminishing marginal utility.
A) they all produce slightly different products.
B) of nonprice competition.
C) of freedom of entry and exit.
D) of the outgrowth of advertising expenditures.
E) of the law of diminishing marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the long run,what adjustments take place when a perfectly competitive market in long-run equilibrium experiences an increase in demand?
A) Price and profits fall, causing new firms to enter and existing firms to expand.
B) Price and output remain fixed.
C) Price rises but output remains unchanged.
D) Price rises and firms expand output by using existing capacity more intensively.
E) New firms enter and existing firms expand capacity, leading to an increase in supply and a decline in price.
A) Price and profits fall, causing new firms to enter and existing firms to expand.
B) Price and output remain fixed.
C) Price rises but output remains unchanged.
D) Price rises and firms expand output by using existing capacity more intensively.
E) New firms enter and existing firms expand capacity, leading to an increase in supply and a decline in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following questions are based on the following graph, showing short-run supply and demand curves for a perfectly competitive market. The initial supply curve is labeled "Supply" and the initial demand curve is labeled "Demand." Price 0A and output rate 0X represent the initial equilibrium price and output.

The typical producer in this market
A) faces a demand curve less elastic than the one shown.
B) minimizes total cost.
C) produces a tiny fraction of output 0X.
D) must produce at least 0Y.
E) must increase price to break even.

The typical producer in this market
A) faces a demand curve less elastic than the one shown.
B) minimizes total cost.
C) produces a tiny fraction of output 0X.
D) must produce at least 0Y.
E) must increase price to break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The market supply curve for a perfectly competitive,constant cost industry is
A) identical with the supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm.
B) horizontal in the short run.
C) the numerical average of all the individual firms' supply curves.
D) likely to become perfectly inelastic as the length of time covered by the curve grows.
E) the horizontal summation of the marginal cost curves for all firms above the minimum average variable cost.
A) identical with the supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm.
B) horizontal in the short run.
C) the numerical average of all the individual firms' supply curves.
D) likely to become perfectly inelastic as the length of time covered by the curve grows.
E) the horizontal summation of the marginal cost curves for all firms above the minimum average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The following questions are based on the following table showing the supply curves of the five individual firms constituting the rutabaga market in a small community. Assume that simultaneous changes in output by all firms do NOT affect input prices.

The time period during which firms can raise output by using their fixed capacity more intensively is called the
A) market period.
B) short run.
C) long run.
D) infinite run.
E) flexible run.

The time period during which firms can raise output by using their fixed capacity more intensively is called the
A) market period.
B) short run.
C) long run.
D) infinite run.
E) flexible run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Under perfect competition,the existence of economic profits and losses
A) produces economic inefficiencies leading to the misallocation of resources in the long run.
B) generally causes output in the short run to fall in markets where economic profits are being made and to rise in markets where economic losses are being made.
C) creates hardships for producers, leading to industry concentration in the hands of relatively few producers.
D) ensures that output will not be produced at minimum unit cost in the long run.
E) causes firms to enter or leave markets and otherwise reallocate resources in the long run.
A) produces economic inefficiencies leading to the misallocation of resources in the long run.
B) generally causes output in the short run to fall in markets where economic profits are being made and to rise in markets where economic losses are being made.
C) creates hardships for producers, leading to industry concentration in the hands of relatively few producers.
D) ensures that output will not be produced at minimum unit cost in the long run.
E) causes firms to enter or leave markets and otherwise reallocate resources in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If price equals average total cost,economic profit will
A) become large.
B) equal marginal revenue.
C) equal total cost.
D) be zero.
E) exceed output.
A) become large.
B) equal marginal revenue.
C) equal total cost.
D) be zero.
E) exceed output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Shortages typically arise when there are
A) price floors.
B) equilibrium prices.
C) price ceilings.
D) fair prices.
E) scientific prices.
A) price floors.
B) equilibrium prices.
C) price ceilings.
D) fair prices.
E) scientific prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In a free market,a price ceiling
A) encourages sellers to produce more.
B) leads to a decrease in the market demand curve.
C) improves the ability of a market to adjust to changes in demand.
D) eliminates the need to ration.
E) creates shortages.
A) encourages sellers to produce more.
B) leads to a decrease in the market demand curve.
C) improves the ability of a market to adjust to changes in demand.
D) eliminates the need to ration.
E) creates shortages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Surpluses generally result from
A) price floors.
B) equilibrium prices.
C) price ceilings.
D) fair prices.
E) scientific prices.
A) price floors.
B) equilibrium prices.
C) price ceilings.
D) fair prices.
E) scientific prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The strategy used by the cattle ranchers in response to price ceilings imposed on beef by the Nixon administration was ineffective in the long run because of
A) shifting consumer demands in favor of horsemeat.
B) an unprecedented grain surplus.
C) the limited time in which to market a perishable product.
D) a surprising lack of consumer responsiveness to lower prices.
E) the increasing foreign demand for U.S. beef.
A) shifting consumer demands in favor of horsemeat.
B) an unprecedented grain surplus.
C) the limited time in which to market a perishable product.
D) a surprising lack of consumer responsiveness to lower prices.
E) the increasing foreign demand for U.S. beef.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Many observers feel that price controls imposed during World War II were generally more effective than those imposed in the 1970s because
A) there was more effective government enforcement.
B) the price ceilings were set below market equilibrium prices.
C) those imposed during the war tended to be more flexible than those in the 1970s.
D) they had the moral support of U.S. consumers.
E) the price freezes of the 1970s were short-run rather than long-run controls.
A) there was more effective government enforcement.
B) the price ceilings were set below market equilibrium prices.
C) those imposed during the war tended to be more flexible than those in the 1970s.
D) they had the moral support of U.S. consumers.
E) the price freezes of the 1970s were short-run rather than long-run controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Price supports are generally designed to
A) help consumers.
B) keep prices low.
C) increase sellers' incomes.
D) discourage production.
E) supplement rationing.
A) help consumers.
B) keep prices low.
C) increase sellers' incomes.
D) discourage production.
E) supplement rationing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Perhaps the biggest single criticism of price controls has been that they
A) encourage inefficient use of scarce resources.
B) tend to be harder on agriculture than on other segments of the economy.
C) invariably promote the very inflation they seek to quell.
D) are impossible to enforce in the short run.
E) have no effect on free markets.
A) encourage inefficient use of scarce resources.
B) tend to be harder on agriculture than on other segments of the economy.
C) invariably promote the very inflation they seek to quell.
D) are impossible to enforce in the short run.
E) have no effect on free markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
One of the major long-term effects of rent controls in New York City has been
A) an increase in the average size of an apartment.
B) the creation of above-average profits for landlords.
C) the creation of surpluses of affordable housing units.
D) a rapid increase in the rate of New York's population growth.
E) the abandonment of buildings, reducing the number of rental units available to consumers.
A) an increase in the average size of an apartment.
B) the creation of above-average profits for landlords.
C) the creation of surpluses of affordable housing units.
D) a rapid increase in the rate of New York's population growth.
E) the abandonment of buildings, reducing the number of rental units available to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The political dilemma facing the Eastern European countries as they attempted to reform their economies in the 1990s was
A) that they had to give up their domestic currency's convertibility for fixed exchange rates.
B) the falling price of bread, which was creating unrest among the masses.
C) reduced domestic consumption because their exports were greater than their imports.
D) the need to absorb the current pain associated with reforms whose benefits would be realized only much later.
E) that in many cases the state-owned enterprises were run much more efficiently than was possible under private ownership.
A) that they had to give up their domestic currency's convertibility for fixed exchange rates.
B) the falling price of bread, which was creating unrest among the masses.
C) reduced domestic consumption because their exports were greater than their imports.
D) the need to absorb the current pain associated with reforms whose benefits would be realized only much later.
E) that in many cases the state-owned enterprises were run much more efficiently than was possible under private ownership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When price ceilings on beef were imposed under the Nixon administration,cattle ranchers generally responded by
A) raising prices anyway.
B) creating a deliberate market shortage.
C) finding ways to hold demand down.
D) boycotting other inputs, like grain.
E) slaughtering their cattle.
A) raising prices anyway.
B) creating a deliberate market shortage.
C) finding ways to hold demand down.
D) boycotting other inputs, like grain.
E) slaughtering their cattle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
As Eastern European economies embraced capitalistic processes in the 1990s,they
A) dramatically reduced or eliminated price controls.
B) increased government ownership of factories.
C) immediately experienced rapidly increasing levels of output with no inflation.
D) began to rely even more heavily on central planning by government bureaucracies.
E) were able to eliminate poverty virtually overnight.
A) dramatically reduced or eliminated price controls.
B) increased government ownership of factories.
C) immediately experienced rapidly increasing levels of output with no inflation.
D) began to rely even more heavily on central planning by government bureaucracies.
E) were able to eliminate poverty virtually overnight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A price ceiling often necessitates that
A) the government buy up and store surplus production.
B) a formal system of rationing be established.
C) the government encourage producers to buy more at existing prices.
D) consumers be encouraged to buy more at existing prices.
E) producers be required to increase equilibrium prices.
A) the government buy up and store surplus production.
B) a formal system of rationing be established.
C) the government encourage producers to buy more at existing prices.
D) consumers be encouraged to buy more at existing prices.
E) producers be required to increase equilibrium prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



