Deck 13: Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Economic Growth
1
Significant government involvement in stimulating economic growth became more common
A) before the Civil War.
B) between the Civil War and World War I.
C) during the 1920s.
D) during the 1930s.
E) after World War II.
A) before the Civil War.
B) between the Civil War and World War I.
C) during the 1920s.
D) during the 1930s.
E) after World War II.
E
2
Small differences in the annual rate of economic growth can make substantial differences in living standards a few decades later because
A) each year the increase in output is added to a larger base, thus compounding its impact.
B) increases in output create surplus labor, keeping costs low.
C) the more rapid the rate of growth, the higher the rate of inflation.
D) increases in output lead to greater increases in population, lowering overall standards of living.
E) expanding economies use up national resources at a rapid rate and create substantial amounts of pollution.
A) each year the increase in output is added to a larger base, thus compounding its impact.
B) increases in output create surplus labor, keeping costs low.
C) the more rapid the rate of growth, the higher the rate of inflation.
D) increases in output lead to greater increases in population, lowering overall standards of living.
E) expanding economies use up national resources at a rapid rate and create substantial amounts of pollution.
A
3
The next question is based on the following table:
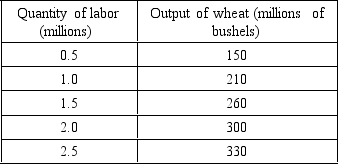
According to Malthus,if subsistence is 150 bushels of wheat per worker,the equilibrium labor force would be ________ million.
A) 0.5
B) 1.0
C) 1.5
D) 2.0
E) 2.5

According to Malthus,if subsistence is 150 bushels of wheat per worker,the equilibrium labor force would be ________ million.
A) 0.5
B) 1.0
C) 1.5
D) 2.0
E) 2.5
D
4
Two common measures of the rate of economic growth are the rates of growth of
A) real GDP and real per capita GDP.
B) income and consumption.
C) full-time unemployment and prices.
D) the money supply and income.
E) real population and full-time employment.
A) real GDP and real per capita GDP.
B) income and consumption.
C) full-time unemployment and prices.
D) the money supply and income.
E) real population and full-time employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following questions are based on the following diagram:
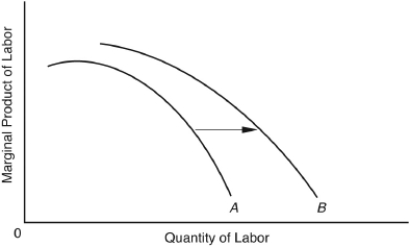
If,with this shift,the amount of labor does NOT change,
A) total output will not change.
B) total output will fall.
C) total output will rise.
D) marginal product of labor will not change.
E) unemployment must result.

If,with this shift,the amount of labor does NOT change,
A) total output will not change.
B) total output will fall.
C) total output will rise.
D) marginal product of labor will not change.
E) unemployment must result.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An element of economic welfare that is NOT effectively captured in growth measurement of real per capita GDP is
A) population growth.
B) output growth.
C) the rate of inflation.
D) income distribution.
E) a change in the price level.
A) population growth.
B) output growth.
C) the rate of inflation.
D) income distribution.
E) a change in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A subsistence standard of living coupled with periods of starvation was the prospect for humanity according to the views of
A) Adam Smith.
B) David Ricardo.
C) Joseph Schumpeter.
D) Karl Marx.
E) Thomas Malthus.
A) Adam Smith.
B) David Ricardo.
C) Joseph Schumpeter.
D) Karl Marx.
E) Thomas Malthus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Malthusian model seems particularly relevant for the
A) agricultural sector.
B) less-developed countries.
C) industrialized nations.
D) countries of eastern Europe.
E) western world.
A) agricultural sector.
B) less-developed countries.
C) industrialized nations.
D) countries of eastern Europe.
E) western world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An element of economic welfare that is NOT effectively captured in growth measurements of real per capita GDP is
A) the rate of inflation.
B) new products and improvements in the quality of goods and services.
C) population growth.
D) a change in the price level.
E) a change in the growth of output.
A) the rate of inflation.
B) new products and improvements in the quality of goods and services.
C) population growth.
D) a change in the price level.
E) a change in the growth of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Economic growth is an increase in
A) population.
B) price levels.
C) unemployment.
D) real output.
E) consumption.
A) population.
B) price levels.
C) unemployment.
D) real output.
E) consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Who wrote the classic work on the effect of population growth on the rate of economic growth?
A) David Ricardo
B) Adam Smith
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Thomas Malthus
E) Karl Marx
A) David Ricardo
B) Adam Smith
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Thomas Malthus
E) Karl Marx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The term marginal product of labor refers to the
A) change in the average product of labor as output increases.
B) decreasing value of labor's total output.
C) additional output that could be produced at full employment.
D) subsistence output per worker.
E) additional output resulting from an extra unit of labor.
A) change in the average product of labor as output increases.
B) decreasing value of labor's total output.
C) additional output that could be produced at full employment.
D) subsistence output per worker.
E) additional output resulting from an extra unit of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The rate of growth in real per capita GDP is deficient as a measure of the rate of economic growth because
A) it does not account for the rate of inflation.
B) per capita GDP has no relation to per capita income.
C) the rate of increase of per capita GDP does not measure the degree of inequality in output distribution.
D) large differences in the rate of increase of current per capita GDP make little difference in living standards in the future.
E) it underestimates the rate of growth in real GDP.
A) it does not account for the rate of inflation.
B) per capita GDP has no relation to per capita income.
C) the rate of increase of per capita GDP does not measure the degree of inequality in output distribution.
D) large differences in the rate of increase of current per capita GDP make little difference in living standards in the future.
E) it underestimates the rate of growth in real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to Malthus,the human race in the long run would
A) enjoy increasing levels of affluence.
B) disappear entirely.
C) be forced to endure subsistence levels of living.
D) have a standard of living above subsistence but remaining constant, neither improving nor worsening.
E) on average produce more goods and services, but these would become distributed more and more unevenly.
A) enjoy increasing levels of affluence.
B) disappear entirely.
C) be forced to endure subsistence levels of living.
D) have a standard of living above subsistence but remaining constant, neither improving nor worsening.
E) on average produce more goods and services, but these would become distributed more and more unevenly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An element of economic welfare that is NOT effectively captured in measurements of real per capita GDP is
A) population growth.
B) output.
C) income.
D) inflation.
E) leisure.
A) population growth.
B) output.
C) income.
D) inflation.
E) leisure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The law of diminishing marginal returns does NOT apply to cases where
A) at least one input is fixed in quantity.
B) there is only one variable input.
C) technology changes.
D) average product is falling.
E) total product is rising.
A) at least one input is fixed in quantity.
B) there is only one variable input.
C) technology changes.
D) average product is falling.
E) total product is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A more rapid rate of growth can often be achieved only if
A) consumers are willing to forego current consumption.
B) the government runs a budget deficit in perpetuity.
C) the level of current investment is diminished.
D) government involvement is eliminated.
E) private saving is discouraged.
A) consumers are willing to forego current consumption.
B) the government runs a budget deficit in perpetuity.
C) the level of current investment is diminished.
D) government involvement is eliminated.
E) private saving is discouraged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Malthus believed that maintaining or improving humanity's standard of living would be possible only with
A) technological change.
B) war, famine, or the universal adoption of birth control measures.
C) the introduction of widespread public assistance programs.
D) an expansion of the Corn Laws limiting imports.
E) an accumulation of capital.
A) technological change.
B) war, famine, or the universal adoption of birth control measures.
C) the introduction of widespread public assistance programs.
D) an expansion of the Corn Laws limiting imports.
E) an accumulation of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Thomas Malthus felt the human population was in danger of outrunning its food supply because
A) he thought population would increase at a geometric rate while land remained essentially fixed in supply.
B) environmental pollution would eventually decrease the efficiency of agriculture.
C) the expected standard of living grows over time.
D) profits were insufficient to induce farmers to use their land properly.
E) the production possibilities curve shifts inward as population increases.
A) he thought population would increase at a geometric rate while land remained essentially fixed in supply.
B) environmental pollution would eventually decrease the efficiency of agriculture.
C) the expected standard of living grows over time.
D) profits were insufficient to induce farmers to use their land properly.
E) the production possibilities curve shifts inward as population increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An advantage in increasing the per capita annual rate of growth,however slightly,is that it will
A) shift the production possibilities curve inward.
B) lead to a more rapid increase in population.
C) lead to a substantially higher level of real output two or three decades later.
D) ensure the elimination of the business cycle.
E) eliminate the problem of relative scarcity.
A) shift the production possibilities curve inward.
B) lead to a more rapid increase in population.
C) lead to a substantially higher level of real output two or three decades later.
D) ensure the elimination of the business cycle.
E) eliminate the problem of relative scarcity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The essence of Ricardo's argument against the Corn Laws was that
A) each country should specialize in those products it is relatively most efficient at producing.
B) an increase in the tariff on grain would be profitable for industrialists.
C) population tends to increase to the subsistence point.
D) a repeal of the Corn Laws would improve the climate for agricultural landlords.
E) industrialists are more deserving than workers.
A) each country should specialize in those products it is relatively most efficient at producing.
B) an increase in the tariff on grain would be profitable for industrialists.
C) population tends to increase to the subsistence point.
D) a repeal of the Corn Laws would improve the climate for agricultural landlords.
E) industrialists are more deserving than workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The law of diminishing marginal returns
A) requires that all inputs be varied proportionately.
B) states that as an input is increased (all other inputs held constant), total output falls after some point.
C) is relevant only when there is significant unemployment in the economy.
D) states that if more and more of a resource is used (the quantities of other resources being held constant), after some point, the average, marginal, and total products all become equal.
E) states that as a variable input is increased (with other inputs remaining constant), beyond some point the marginal product of the variable input falls.
A) requires that all inputs be varied proportionately.
B) states that as an input is increased (all other inputs held constant), total output falls after some point.
C) is relevant only when there is significant unemployment in the economy.
D) states that if more and more of a resource is used (the quantities of other resources being held constant), after some point, the average, marginal, and total products all become equal.
E) states that as a variable input is increased (with other inputs remaining constant), beyond some point the marginal product of the variable input falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
One popular measure of the rate of technological change is the rate
A) of profit from research and development.
B) of increase in the capital-output ratio.
C) of investment in human capital.
D) at which the gap between actual and potential output is narrowed.
E) of growth in output per worker.
A) of profit from research and development.
B) of increase in the capital-output ratio.
C) of investment in human capital.
D) at which the gap between actual and potential output is narrowed.
E) of growth in output per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Keeping the marginal productivity of capital constant while investment in plant and equipment expands requires
A) a slowdown in the growth rate.
B) a decrease (shift to the left) in the marginal productivity of capital schedule.
C) a falling rate of return on investment.
D) that the productivity of existing technology be exhausted before investing in something new.
E) continued development of new technologies, products, and processes.
A) a slowdown in the growth rate.
B) a decrease (shift to the left) in the marginal productivity of capital schedule.
C) a falling rate of return on investment.
D) that the productivity of existing technology be exhausted before investing in something new.
E) continued development of new technologies, products, and processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In essence,the Corn Laws
A) lowered the profits of landlords.
B) imposed high tariffs on grain.
C) were designed to benefit industrialists by ensuring low agricultural prices.
D) were written to encourage the substitution of British corn for U.S. and Canadian wheat.
E) provided poor people in England with free grain.
A) lowered the profits of landlords.
B) imposed high tariffs on grain.
C) were designed to benefit industrialists by ensuring low agricultural prices.
D) were written to encourage the substitution of British corn for U.S. and Canadian wheat.
E) provided poor people in England with free grain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The standard of living in the industrialized nations has improved dramatically over the past two centuries despite Malthus's dismal predictions.Malthus's most important mistake was to
A) underestimate the extent of technological change.
B) ignore the benefits of free trade between nations, as witnessed by his advocacy of the Corn Laws.
C) believe that the capital stock would remain at a constant level due to a lack of incentives for expansion.
D) ignore the potential for expanding actual output to the level of full-employment output.
E) ignore the effects of population increase.
A) underestimate the extent of technological change.
B) ignore the benefits of free trade between nations, as witnessed by his advocacy of the Corn Laws.
C) believe that the capital stock would remain at a constant level due to a lack of incentives for expansion.
D) ignore the potential for expanding actual output to the level of full-employment output.
E) ignore the effects of population increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The number of dollars of investment required to produce an extra dollar of goods or services is called the
A) multiplier.
B) rate of innovation.
C) marginal efficiency of investment.
D) capital-output ratio.
E) rate of return.
A) multiplier.
B) rate of innovation.
C) marginal efficiency of investment.
D) capital-output ratio.
E) rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Empirical evidence from industrialized countries on the relationship between population growth and output
A) clearly supports the Malthusian conclusions.
B) suggests little or no relationship between the rates of population growth and output per person per year.
C) refutes the law of diminishing returns.
D) indicates that labor-intensive production techniques are more efficient.
E) suggests that technology has had a minimal impact on economic growth.
A) clearly supports the Malthusian conclusions.
B) suggests little or no relationship between the rates of population growth and output per person per year.
C) refutes the law of diminishing returns.
D) indicates that labor-intensive production techniques are more efficient.
E) suggests that technology has had a minimal impact on economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The dire predictions of the 1974 Club of Rome's The Limits of Growth report are in part discredited because
A) the United States' mineral resources are infinite in supply.
B) growing populations do not consume resources at higher rates.
C) the U.S. economy has significantly reduced its overall consumption of resources because of its affluence.
D) as minerals become scarce and increase in price, it becomes cost effective for users to find substitutes.
E) they assumed the developing countries would industrialize more rapidly than they have.
A) the United States' mineral resources are infinite in supply.
B) growing populations do not consume resources at higher rates.
C) the U.S. economy has significantly reduced its overall consumption of resources because of its affluence.
D) as minerals become scarce and increase in price, it becomes cost effective for users to find substitutes.
E) they assumed the developing countries would industrialize more rapidly than they have.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The marginal product of capital decreases because of
A) increases in population growth that decrease the average product of labor.
B) the law of diminishing returns.
C) technological advances.
D) rising capital productivity.
E) growing investment opportunities.
A) increases in population growth that decrease the average product of labor.
B) the law of diminishing returns.
C) technological advances.
D) rising capital productivity.
E) growing investment opportunities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The purpose of the British Corn Laws was to
A) maintain the high profits of the British landlords.
B) prevent British farmers from exporting corn to other nations.
C) prevent British farmers from growing grain.
D) encourage grain imports from France and Germany.
E) encourage the British to substitute corn for meat.
A) maintain the high profits of the British landlords.
B) prevent British farmers from exporting corn to other nations.
C) prevent British farmers from growing grain.
D) encourage grain imports from France and Germany.
E) encourage the British to substitute corn for meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a society attempts to increase output by increasing the amount of labor used,holding land and capital fixed,it will experience diminishing marginal
A) cost.
B) utility.
C) propensity.
D) employment.
E) returns.
A) cost.
B) utility.
C) propensity.
D) employment.
E) returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The shift in the marginal product of labor curve shown in the diagram might be caused by
A) population growth.
B) an increase in the price of food.
C) a declining average product of labor.
D) technological change.
E) a decreasing total product of labor.
A) population growth.
B) an increase in the price of food.
C) a declining average product of labor.
D) technological change.
E) a decreasing total product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Both Malthus and Ricardo erred in expecting an eventual termination of economic growth by
A) neglecting the potential for population control.
B) believing that the law of diminishing marginal returns applies solely to land.
C) assuming a constant marginal productivity of labor.
D) neglecting the role of the credit system.
E) underestimating the extent and impact of technological change.
A) neglecting the potential for population control.
B) believing that the law of diminishing marginal returns applies solely to land.
C) assuming a constant marginal productivity of labor.
D) neglecting the role of the credit system.
E) underestimating the extent and impact of technological change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Ricardo,in his work on income distribution,emphasized the struggle between
A) workers and industrialists.
B) landowners and the aristocracy.
C) England and Spain.
D) farmers and workers.
E) industrialists and landowners.
A) workers and industrialists.
B) landowners and the aristocracy.
C) England and Spain.
D) farmers and workers.
E) industrialists and landowners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Club of Rome study was concerned primarily with the ________ growth.
A) benefits of
B) costs of
C) sources of
D) limits to
E) rates of
A) benefits of
B) costs of
C) sources of
D) limits to
E) rates of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Holding technology constant,increases in investment in plant and equipment
A) raise the rate of return.
B) reduce the ratio of capital to output.
C) raise the average product of capital.
D) reduce the marginal product of capital.
E) raise the profitability of investment.
A) raise the rate of return.
B) reduce the ratio of capital to output.
C) raise the average product of capital.
D) reduce the marginal product of capital.
E) raise the profitability of investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Improvements in agricultural technology will
A) raise the price of food.
B) lower the total product of labor.
C) raise the marginal product of labor.
D) lower the output of food.
E) raise the rate of starvation.
A) raise the price of food.
B) lower the total product of labor.
C) raise the marginal product of labor.
D) lower the output of food.
E) raise the rate of starvation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Malthusian forecast that population growth would outrun the food supply can be explained in terms of
A) Say's law.
B) the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) the law of the jungle.
D) the law of demand.
E) Gresham's law.
A) Say's law.
B) the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C) the law of the jungle.
D) the law of demand.
E) Gresham's law.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
During the past century,the rate of return on investment in new plant equipment in the United States has
A) fluctuated around a fairly constant level.
B) steadily declined.
C) steadily increased.
D) increased as the marginal product of capital has declined.
E) decreased as the capital-output ratio has decreased.
A) fluctuated around a fairly constant level.
B) steadily declined.
C) steadily increased.
D) increased as the marginal product of capital has declined.
E) decreased as the capital-output ratio has decreased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The process by which the use of an innovation spreads from firm to firm and use to use is called the ________ process.
A) industrial
B) economic
C) diffusion
D) management
E) utilization
A) industrial
B) economic
C) diffusion
D) management
E) utilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
According to the Harrod-Domar growth model,an economy with a capital-output ratio of four that saves and invests 12 percent of its GDP will grow annually at a rate of ________ percent.
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
High rates of economic growth are clearly related to high rates of
A) unemployment.
B) consumption.
C) inflation.
D) technological change.
E) taxes on profits.
A) unemployment.
B) consumption.
C) inflation.
D) technological change.
E) taxes on profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Joseph Schumpeter's view of innovation and the diffusion process can be represented as
A) a continuous movement along the average product of capital curve.
B) a series of outward shifts of the marginal product curves of capital and labor.
C) a steady increase in the stock of human capital.
D) an increase over time in entrepreneurial ambitions.
E) the independent effects of workers and technology on production.
A) a continuous movement along the average product of capital curve.
B) a series of outward shifts of the marginal product curves of capital and labor.
C) a steady increase in the stock of human capital.
D) an increase over time in entrepreneurial ambitions.
E) the independent effects of workers and technology on production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In an economy with a GDP of $3,000 billion and a capital-output ratio of three,an increase in this year's full-employment GDP of $30 billion means that last year's intended investment must have increased by ________ billion.
A) $10
B) $30
C) $90
D) $100
E) $1,000
A) $10
B) $30
C) $90
D) $100
E) $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Between 1980 and 2000,empirical estimates of the "education premium" rose from ________ percent.
A) 3 to 5
B) 10 to 40
C) 20 to 40
D) 40 to 80
E) 80 to 100
A) 3 to 5
B) 10 to 40
C) 20 to 40
D) 40 to 80
E) 80 to 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Expenditures on education and training that raise per capita output are viewed as
A) conspicuous consumption.
B) public and private transfer payments.
C) investments in human capital.
D) consumer surplus.
E) normative expenditures.
A) conspicuous consumption.
B) public and private transfer payments.
C) investments in human capital.
D) consumer surplus.
E) normative expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Human capital formation refers to
A) expenditures by society on formal education, on-the-job training, and health programs.
B) acquiring machines that do not displace existing workers.
C) maintaining a full-employment level of GDP.
D) the development of humanlike robots (androids).
E) cloning humans.
A) expenditures by society on formal education, on-the-job training, and health programs.
B) acquiring machines that do not displace existing workers.
C) maintaining a full-employment level of GDP.
D) the development of humanlike robots (androids).
E) cloning humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The firm or individual that first applies a new technology is called a(n)
A) consumer.
B) monopolist.
C) Keynesian.
D) innovator.
E) financier.
A) consumer.
B) monopolist.
C) Keynesian.
D) innovator.
E) financier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the best example of an innovation?
A) Boeing introduces computer-assisted design and manufacturing to the aircraft industry.
B) GM brings out its version of a minivan to compete with Chrysler's.
C) Exxon introduces a higher-octane grade of unleaded gas.
D) McDonald's increases the size of its hamburger.
E) Microsoft updates its Windows operating system.
A) Boeing introduces computer-assisted design and manufacturing to the aircraft industry.
B) GM brings out its version of a minivan to compete with Chrysler's.
C) Exxon introduces a higher-octane grade of unleaded gas.
D) McDonald's increases the size of its hamburger.
E) Microsoft updates its Windows operating system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The major determinant of the rapidity with which an innovation spreads is its
A) durability.
B) complexity.
C) sex appeal.
D) exclusiveness.
E) profitability.
A) durability.
B) complexity.
C) sex appeal.
D) exclusiveness.
E) profitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Innovation is
A) the application of a new technology for the first time.
B) another name for technological change.
C) the application of existing technologies to low-risk projects.
D) the reward for risk taking.
E) a basic managerial technique necessary at all levels of management.
A) the application of a new technology for the first time.
B) another name for technological change.
C) the application of existing technologies to low-risk projects.
D) the reward for risk taking.
E) a basic managerial technique necessary at all levels of management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Educational expenditures may be viewed as an investment process when
A) the money spent increases the current income to teachers and other related professionals.
B) college tuition expenses are tax deductible.
C) future gains in productivity follow from the sacrifice of current production and consumption.
D) intellectual depreciation is counted as part of GDP.
E) such expenditures represent a noticeable share of our GDP.
A) the money spent increases the current income to teachers and other related professionals.
B) college tuition expenses are tax deductible.
C) future gains in productivity follow from the sacrifice of current production and consumption.
D) intellectual depreciation is counted as part of GDP.
E) such expenditures represent a noticeable share of our GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
________ stressed the importance of innovation in the process of economic growth.
A) Joseph Schumpeter
B) Karl Marx
C) Thomas Malthus
D) David Ricardo
E) Adam Smith
A) Joseph Schumpeter
B) Karl Marx
C) Thomas Malthus
D) David Ricardo
E) Adam Smith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Harrod-Domar growth model
A) expresses the growth rate of GDP as a function of the proportion of GDP saved, divided by the capital-output ratio.
B) indicates that full-employment GDP will grow faster as the capital-output ratio in the economy rises.
C) requires the capital-output ratio to grow if the economy is to increase to its full-employment GDP.
D) expresses the rate of growth of GDP as an inverse function of the savings rate.
E) indicates that full-employment GDP will grow only if the savings rate declines while the capital-output ratio increases.
A) expresses the growth rate of GDP as a function of the proportion of GDP saved, divided by the capital-output ratio.
B) indicates that full-employment GDP will grow faster as the capital-output ratio in the economy rises.
C) requires the capital-output ratio to grow if the economy is to increase to its full-employment GDP.
D) expresses the rate of growth of GDP as an inverse function of the savings rate.
E) indicates that full-employment GDP will grow only if the savings rate declines while the capital-output ratio increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the capital-output ratio is three,the full-employment GDP is $5,100 billion,and intended investment is $750 billion,then a $60 billion increase in intended investment will increase full-employment GDP by ________ billion.
A) $250
B) $180
C) $60
D) $50
E) $20
A) $250
B) $180
C) $60
D) $50
E) $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The actual rate of growth of GDP is directly related to the percent of GDP devoted to
Investment if
A) the marginal product of labor equals one.
B) the stock of human capital expands at an exponential rate.
C) noninflationary full employment is sustained with a constant capital-output ratio.
D) consumption is an increasing percentage of GDP.
E) net inventory investment rises at an accelerating rate.
Investment if
A) the marginal product of labor equals one.
B) the stock of human capital expands at an exponential rate.
C) noninflationary full employment is sustained with a constant capital-output ratio.
D) consumption is an increasing percentage of GDP.
E) net inventory investment rises at an accelerating rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Investment in education enhances the rate of economic growth
A) because most of the important research and development is carried out in university laboratories.
B) by educating people about the evils of materialism and the need to redistribute income.
C) because the highest rates of labor-force productivity are found in educational institutions.
D) by training scientists, engineers, and industrial managers.
E) because of its tendency to use endowment funds to invest in new technologies.
A) because most of the important research and development is carried out in university laboratories.
B) by educating people about the evils of materialism and the need to redistribute income.
C) because the highest rates of labor-force productivity are found in educational institutions.
D) by training scientists, engineers, and industrial managers.
E) because of its tendency to use endowment funds to invest in new technologies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Intended investment in a given year
A) leads to stagflation in a subsequent year.
B) reduces the productivity of the labor force.
C) raises the following year's full-employment level of GDP.
D) reduces the amount of investment possible in a future year.
E) is higher when consumption represents a higher percentage of GDP.
A) leads to stagflation in a subsequent year.
B) reduces the productivity of the labor force.
C) raises the following year's full-employment level of GDP.
D) reduces the amount of investment possible in a future year.
E) is higher when consumption represents a higher percentage of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The rate of economic growth and the rate of technological change are linked by the
A) rate of substitution of labor for capital.
B) diminishing marginal product of labor that induces greater capital investment.
C) rate of inflation, since rapid price changes induce the application of new techniques.
D) gap between actual and potential output, since massive unemployment can induce labor-utilizing technological changes.
E) rate of innovation, since technological change must be applied to have an effect on economic growth.
A) rate of substitution of labor for capital.
B) diminishing marginal product of labor that induces greater capital investment.
C) rate of inflation, since rapid price changes induce the application of new techniques.
D) gap between actual and potential output, since massive unemployment can induce labor-utilizing technological changes.
E) rate of innovation, since technological change must be applied to have an effect on economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Combining monetary and fiscal policies to achieve full employment can lead to a one-shot improvement in economic growth by
A) decreasing the gap between actual and potential output.
B) shifting the production possibilities curve outward.
C) pushing to a new equilibrium where desired GDP exceeds actual GDP.
D) reducing government expenditures.
E) increasing nominal GDP faster than real GDP.
A) decreasing the gap between actual and potential output.
B) shifting the production possibilities curve outward.
C) pushing to a new equilibrium where desired GDP exceeds actual GDP.
D) reducing government expenditures.
E) increasing nominal GDP faster than real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An important endogenous factor influencing a country's rate of technological change is
A) the nature and extent of its scientific capabilities.
B) an absence of research and development.
C) a large gap between actual and potential output.
D) the presence of high levels of consumption with little or no household saving.
E) its capital-output ratio.
A) the nature and extent of its scientific capabilities.
B) an absence of research and development.
C) a large gap between actual and potential output.
D) the presence of high levels of consumption with little or no household saving.
E) its capital-output ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A country's economic,social,and political climate can increase its level of potential output and rate of growth by
A) deemphasizing the importance of material welfare in this world.
B) organizing a command economy with tight constraints on individual behavior.
C) capturing all the increased output for the ruling party's personal benefit.
D) encouraging competition and allowing economic and political freedom to foster the introduction of new ideas.
E) sponsoring feudalism.
A) deemphasizing the importance of material welfare in this world.
B) organizing a command economy with tight constraints on individual behavior.
C) capturing all the increased output for the ruling party's personal benefit.
D) encouraging competition and allowing economic and political freedom to foster the introduction of new ideas.
E) sponsoring feudalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The fear that continued growth at current rates will exhaust basic resources is diminished by
A) data contained in the Club of Rome's The Limits to Growth report.
B) the knowledge that amounts of the most basic resources are virtually unlimited.
C) the fact that the price system provides incentives to conserve and develop replacements for our resources.
D) the law of diminishing returns.
E) a slowdown in technological change that reduces the demand for these resources.
A) data contained in the Club of Rome's The Limits to Growth report.
B) the knowledge that amounts of the most basic resources are virtually unlimited.
C) the fact that the price system provides incentives to conserve and develop replacements for our resources.
D) the law of diminishing returns.
E) a slowdown in technological change that reduces the demand for these resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Once an economy is at full employment,further growth can occur only by
A) running a budget deficit.
B) expanding the money supply.
C) promoting slack in labor markets by reducing employment.
D) increasing the capital-output ratio above its full-employment values.
E) influencing factors that cause potential output to expand.
A) running a budget deficit.
B) expanding the money supply.
C) promoting slack in labor markets by reducing employment.
D) increasing the capital-output ratio above its full-employment values.
E) influencing factors that cause potential output to expand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
As compared to earlier years,the rate of growth of labor productivity in the United States during the late 1990s and early 2000s
A) remained constant.
B) slowed slightly.
C) slowed considerably.
D) increased significantly.
E) slowed in the late 1990s but rose in the early 2000s.
A) remained constant.
B) slowed slightly.
C) slowed considerably.
D) increased significantly.
E) slowed in the late 1990s but rose in the early 2000s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Successful innovations are generally imitated by others,causing the
A) production possibilities curve to shift to the left.
B) marginal product of capital curve to shift to the left.
C) profits of the innovator to decline.
D) output rate per worker to fall.
E) quality of output to fall.
A) production possibilities curve to shift to the left.
B) marginal product of capital curve to shift to the left.
C) profits of the innovator to decline.
D) output rate per worker to fall.
E) quality of output to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Many of the basic innovations introduced into the U.S.economy during the twentieth century are attributed to the fact that our culture has been able to nurture a great many
A) economists.
B) educators.
C) engineers.
D) entrepreneurs.
E) equestrians.
A) economists.
B) educators.
C) engineers.
D) entrepreneurs.
E) equestrians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A major reason why Henry Ford was able to sell the Model T for as little as $360 per car was
A) advertising.
B) an increase in the capital-labor ratio at Ford.
C) an expanded number of versions of the car (for example, convertible, hardtop, sedan, and so on).
D) cheap immigrant labor.
E) longer workdays.
A) advertising.
B) an increase in the capital-labor ratio at Ford.
C) an expanded number of versions of the car (for example, convertible, hardtop, sedan, and so on).
D) cheap immigrant labor.
E) longer workdays.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
One of the important elements for a successful technological innovation is that it
A) be relatively expensive to adapt to existing needs, creating monopoly profits.
B) reflect a comprehension of market realities and be encouraged by market forces.
C) is derived from technological development taking place outside the country.
D) lead to at least a doubling of an existing capital-output ratio.
E) lower output per person per hour, thus raising labor productivity.
A) be relatively expensive to adapt to existing needs, creating monopoly profits.
B) reflect a comprehension of market realities and be encouraged by market forces.
C) is derived from technological development taking place outside the country.
D) lead to at least a doubling of an existing capital-output ratio.
E) lower output per person per hour, thus raising labor productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
According to economist Edward Denison,about one-half of the growth in the U.S.output for the period 1929 to 1969 was the result of
A) increases in population.
B) increases in government spending.
C) surpluses in the balance of payments.
D) increased capital investment.
E) increased output per unit of input.
A) increases in population.
B) increases in government spending.
C) surpluses in the balance of payments.
D) increased capital investment.
E) increased output per unit of input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



