Deck 15: National Income and Product
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: National Income and Product
1
Social Security payments by the government are NOT included in GDP because
A) Social Security was not yet in place when procedures for calculating GDP were devised.
B) Social Security is counted as an economic cost and subtracted from output in determining GDP.
C) income received through Social Security is not directly related to contributions to production.
D) income received through Social Security is too small to affect GDP.
E) these payments are in current dollars and GDP is measured in constant dollars.
A) Social Security was not yet in place when procedures for calculating GDP were devised.
B) Social Security is counted as an economic cost and subtracted from output in determining GDP.
C) income received through Social Security is not directly related to contributions to production.
D) income received through Social Security is too small to affect GDP.
E) these payments are in current dollars and GDP is measured in constant dollars.
C
2
The new chain-weighted estimate of GDP has the disadvantage that
A) real GDP is different in amount than GDP measured in current dollars.
B) it reflects only changes in current prices, not changes in the prices of previous years.
C) it is calculated on the basis of fewer goods and services than fixed-weight estimates.
D) the components of GDP do not precisely add up to total GDP.
E) it results in some double counting in the value of GDP.
A) real GDP is different in amount than GDP measured in current dollars.
B) it reflects only changes in current prices, not changes in the prices of previous years.
C) it is calculated on the basis of fewer goods and services than fixed-weight estimates.
D) the components of GDP do not precisely add up to total GDP.
E) it results in some double counting in the value of GDP.
D
3
Gross domestic product (GDP)
A) equals the total wages paid in a year.
B) is a measure of government output.
C) equals the total value of final goods and services produced in a year.
D) is the sum of all goods, both final and intermediate.
E) is an obsolete economic indicator of inflation.
A) equals the total wages paid in a year.
B) is a measure of government output.
C) equals the total value of final goods and services produced in a year.
D) is the sum of all goods, both final and intermediate.
E) is an obsolete economic indicator of inflation.
C
4
Printed circuits used in the production of computers are an example of a(n)
A) transfer payment.
B) base transaction.
C) secondhand good.
D) intermediate good.
E) nonmarket transaction.
A) transfer payment.
B) base transaction.
C) secondhand good.
D) intermediate good.
E) nonmarket transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
GDP expressed in constant dollars is called
A) capital accumulation.
B) the net national product.
C) permanent income.
D) real GDP.
E) a price index.
A) capital accumulation.
B) the net national product.
C) permanent income.
D) real GDP.
E) a price index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
As of 1999,software purchases by businesses are
A) counted as a business transfer in GDP.
B) counted as a production input in GDP.
C) counted as consumer nondurables in GDP.
D) counted as a business investment in GDP.
E) not explicitly counted in GDP.
A) counted as a business transfer in GDP.
B) counted as a production input in GDP.
C) counted as consumer nondurables in GDP.
D) counted as a business investment in GDP.
E) not explicitly counted in GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Expressing GDP in constant dollars is an attempt to adjust for changes in
A) the money supply.
B) population.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) quality improvements.
E) prices.
A) the money supply.
B) population.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) quality improvements.
E) prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The measurement of GDP is useful to business executives because it
A) aids in forecasting the future health of their firms.
B) represents the dollar value of all their economic transactions for the year.
C) enables businesses to estimate depreciation.
D) illustrates the social costs that arise from the production of private goods and services.
E) discourages businesses from cheating on their income taxes.
A) aids in forecasting the future health of their firms.
B) represents the dollar value of all their economic transactions for the year.
C) enables businesses to estimate depreciation.
D) illustrates the social costs that arise from the production of private goods and services.
E) discourages businesses from cheating on their income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Comparisons of year-to-year changes in the current dollar value of output can be misleading because
A) nonmarket transactions are included.
B) intermediate goods are excluded.
C) nonproductive transactions are added to changes in production costs.
D) secondhand goods are excluded.
E) they reflect changes in both prices and output.
A) nonmarket transactions are included.
B) intermediate goods are excluded.
C) nonproductive transactions are added to changes in production costs.
D) secondhand goods are excluded.
E) they reflect changes in both prices and output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When measuring GDP,we double count if we include the value of
A) government expenditures.
B) intermediate goods.
C) nonmarket transactions.
D) nonproductive transactions.
E) net exports.
A) government expenditures.
B) intermediate goods.
C) nonmarket transactions.
D) nonproductive transactions.
E) net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Double counting takes place if GDP includes
A) sales of secondhand goods.
B) nonmarket transactions.
C) nonproductive transactions.
D) final goods measured in constant dollars.
E) the services performed by government officials.
A) sales of secondhand goods.
B) nonmarket transactions.
C) nonproductive transactions.
D) final goods measured in constant dollars.
E) the services performed by government officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Productive activities typically excluded from GDP include
A) government and private transfer payments.
B) sales of secondhand goods.
C) services performed by government.
D) nonmarket transactions.
E) sales and purchases of securities.
A) government and private transfer payments.
B) sales of secondhand goods.
C) services performed by government.
D) nonmarket transactions.
E) sales and purchases of securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To correct for changes in the price level,output values are expressed in terms of
A) current dollars.
B) base-year prices.
C) residuals.
D) inflationary expectations.
E) relative deviations.
A) current dollars.
B) base-year prices.
C) residuals.
D) inflationary expectations.
E) relative deviations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is excluded from GDP?
A) gasoline purchased for the family car
B) services performed by municipal law enforcement officials
C) the purchase of cloth by a homemaker to make draperies for the bedroom
D) steel sold to a refrigerator manufacturer
E) goods and services sold to foreigners
A) gasoline purchased for the family car
B) services performed by municipal law enforcement officials
C) the purchase of cloth by a homemaker to make draperies for the bedroom
D) steel sold to a refrigerator manufacturer
E) goods and services sold to foreigners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A case of wine costs $10 to produce and sells for $40.A bottle of prescription pills costs $5 to produce and sells for $10.On the basis of this information,we can conclude that the
A) pills contribute more to GDP, but it is impossible to say how much more.
B) pills contribute twice as much as the wine to GDP.
C) wine contributes twice as much as the pills to GDP.
D) wine contributes four times as much as the pills to GDP.
E) wine contributes six times as much as the pills to GDP.
A) pills contribute more to GDP, but it is impossible to say how much more.
B) pills contribute twice as much as the wine to GDP.
C) wine contributes twice as much as the pills to GDP.
D) wine contributes four times as much as the pills to GDP.
E) wine contributes six times as much as the pills to GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Gross domestic product is a measure of the country's
A) leisure.
B) price level.
C) quantity of money in circulation.
D) population.
E) output.
A) leisure.
B) price level.
C) quantity of money in circulation.
D) population.
E) output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
U.S.gross domestic product measured in current dollars is
A) growing more slowly than GDP measured in constant dollars.
B) measured in terms of 1996 dollars.
C) the same in the base year as GDP measured in constant dollars.
D) not affected by changes in the price level.
E) also known as real GDP.
A) growing more slowly than GDP measured in constant dollars.
B) measured in terms of 1996 dollars.
C) the same in the base year as GDP measured in constant dollars.
D) not affected by changes in the price level.
E) also known as real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Gross domestic product is
A) a measure of the value of all goods and services produced in a given year.
B) a measure of the value of all goods and services produced by the private sector in a given year.
C) measured, when possible, using the prices of goods and services as a measure of value.
D) equal to the total wage bill.
E) a measure of the total value of all market transactions in a given year.
A) a measure of the value of all goods and services produced in a given year.
B) a measure of the value of all goods and services produced by the private sector in a given year.
C) measured, when possible, using the prices of goods and services as a measure of value.
D) equal to the total wage bill.
E) a measure of the total value of all market transactions in a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Transfer payments are payments
A) by individuals of taxes to the government.
B) for newly produced goods and services.
C) to individuals who do not contribute to production in exchange for them.
D) for intermediate goods and services.
E) for government services.
A) by individuals of taxes to the government.
B) for newly produced goods and services.
C) to individuals who do not contribute to production in exchange for them.
D) for intermediate goods and services.
E) for government services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In an economy as complex as ours,the only way to achieve a meaningful estimate of what we produce is to
A) reduce everything to a common denominator: money.
B) consider the number of hours of labor involved in production.
C) calculate the ultimate value of each product to our social welfare.
D) count only tangible products, not intangible services.
E) aggregate all financial transactions for a given year.
A) reduce everything to a common denominator: money.
B) consider the number of hours of labor involved in production.
C) calculate the ultimate value of each product to our social welfare.
D) count only tangible products, not intangible services.
E) aggregate all financial transactions for a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The total of the value added by all U.S.industries equals the
A) net exports.
B) gross business profits.
C) total business sales.
D) gross private domestic investment.
E) gross domestic product.
A) net exports.
B) gross business profits.
C) total business sales.
D) gross private domestic investment.
E) gross domestic product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To compute value added in an industry,we must
A) add indirect taxes.
B) subtract the cost of intermediate goods from the value of sales.
C) add the cost of intermediate goods to the value of output.
D) divide by the rate of inflation.
E) add depreciation.
A) add indirect taxes.
B) subtract the cost of intermediate goods from the value of sales.
C) add the cost of intermediate goods to the value of output.
D) divide by the rate of inflation.
E) add depreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A measure of the extent of production taking place in a particular firm is called
A) value added.
B) double counting.
C) a nonmarket transaction.
D) a transfer payment.
E) opportunity cost.
A) value added.
B) double counting.
C) a nonmarket transaction.
D) a transfer payment.
E) opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The value added by an industry is the value of the goods and services produced minus
A) depreciation.
B) taxes.
C) wages.
D) inflation.
E) the cost of intermediate goods.
A) depreciation.
B) taxes.
C) wages.
D) inflation.
E) the cost of intermediate goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the estimated current dollar output is $3,535 billion and the relevant price index is 2.21,the constant dollar output is ________ billion.
A) $1,600
B) $2,921
C) $3,314
D) $3,756
E) $7,812
A) $1,600
B) $2,921
C) $3,314
D) $3,756
E) $7,812

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Converting values expressed in current dollars to values expressed in constant dollars is called
A) double counting.
B) deflating.
C) depleting.
D) depreciating.
E) devaluing.
A) double counting.
B) deflating.
C) depleting.
D) depreciating.
E) devaluing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The dollar value of business sales minus the cost of intermediate products purchased from other firms equals the
A) depreciation.
B) personal income.
C) direct and indirect tax liabilities.
D) value added.
E) profit.
A) depreciation.
B) personal income.
C) direct and indirect tax liabilities.
D) value added.
E) profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A price index is computed by
A) calculating the ratio of the percentage change in price to the percentage change in output.
B) multiplying average prices in the base year by 100.
C) subtracting GDP in the base year from the current GDP.
D) adding values expressed in base-year terms to current values.
E) dividing the current cost of a set of goods by the cost of the same goods in the base year.
A) calculating the ratio of the percentage change in price to the percentage change in output.
B) multiplying average prices in the base year by 100.
C) subtracting GDP in the base year from the current GDP.
D) adding values expressed in base-year terms to current values.
E) dividing the current cost of a set of goods by the cost of the same goods in the base year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a limitation of real GDP as a measure of economic well-being?
A) Little is revealed about the distribution or composition of output.
B) Output is overstated because intermediate production is included.
C) It fails to account for the consumption of a country's productive capacity.
D) It measures only a country's expenditures, not its income.
E) It fails to account for expenditures by the public sector.
A) Little is revealed about the distribution or composition of output.
B) Output is overstated because intermediate production is included.
C) It fails to account for the consumption of a country's productive capacity.
D) It measures only a country's expenditures, not its income.
E) It fails to account for expenditures by the public sector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
One important element of our well-being that does NOT show up in GDP is our consumption of
A) new automobiles.
B) imported consumer goods.
C) nondurable goods.
D) medical services.
E) leisure time.
A) new automobiles.
B) imported consumer goods.
C) nondurable goods.
D) medical services.
E) leisure time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the estimated current dollar output is $3,535 billion and the relevant price index is 2.21,current prices must on average be what percentage of base-year prices?
A) 2.21 percent
B) 22.1 percent
C) 121 percent
D) 221 percent
E) 321 percent
A) 2.21 percent
B) 22.1 percent
C) 121 percent
D) 221 percent
E) 321 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
GDP is improved as a measure of economic well-being when
A) stated in per capita terms.
B) computed by the expenditures approach.
C) exports are excluded.
D) depreciation is added to it.
E) government and private transfer payments are equal.
A) stated in per capita terms.
B) computed by the expenditures approach.
C) exports are excluded.
D) depreciation is added to it.
E) government and private transfer payments are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following question is based on the following table:
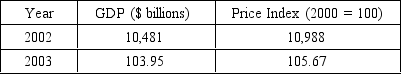
According to the data in the table,from 2002 to 2003,GDP in constant dollars rose by ________ percent.
A) 6.5
B) 5.7
C) 4.8
D) 3.1
E) 1.7

According to the data in the table,from 2002 to 2003,GDP in constant dollars rose by ________ percent.
A) 6.5
B) 5.7
C) 4.8
D) 3.1
E) 1.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Changes in the quality of a good
A) are not reflected in GDP unless the price of the good reflects the improvement.
B) increase the national income and lower GDP.
C) are reflected in GDP when GDP is deflated.
D) are one reason the dollar value of output exceeds the dollar value of income.
E) explain why we must avoid double counting.
A) are not reflected in GDP unless the price of the good reflects the improvement.
B) increase the national income and lower GDP.
C) are reflected in GDP when GDP is deflated.
D) are one reason the dollar value of output exceeds the dollar value of income.
E) explain why we must avoid double counting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To deflate,one must
A) multiply the price ratio by 100.
B) divide the current dollar values by the price index.
C) subtract the constant dollar values from the current dollar values.
D) add the price index in the current year to the price index in the base year.
E) find the difference between the values of two different sets of goods in a given year.
A) multiply the price ratio by 100.
B) divide the current dollar values by the price index.
C) subtract the constant dollar values from the current dollar values.
D) add the price index in the current year to the price index in the base year.
E) find the difference between the values of two different sets of goods in a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
GDP overestimates our true economic welfare because
A) goods are not valued at their market prices.
B) costs associated with environmental damage are not deducted.
C) it includes consumer expenditures on nondurables.
D) government economists are responsible for its computation.
E) intermediate goods are excluded.
A) goods are not valued at their market prices.
B) costs associated with environmental damage are not deducted.
C) it includes consumer expenditures on nondurables.
D) government economists are responsible for its computation.
E) intermediate goods are excluded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The concept of value added
A) is not applicable to intermediate goods.
B) represents a firm's or industry's contribution to production.
C) is the same as a firm's profits.
D) refers to the nonmarketed goods and services not included in GDP.
E) helps distinguish between current dollar GDP and real GDP.
A) is not applicable to intermediate goods.
B) represents a firm's or industry's contribution to production.
C) is the same as a firm's profits.
D) refers to the nonmarketed goods and services not included in GDP.
E) helps distinguish between current dollar GDP and real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the estimated current dollar GDP is $5,616 billion while real GDP is $4,129 billion,then the prices of goods and services have risen by what percentage from their base-year levels?
A) 26 percent
B) 36 percent
C) 44 percent
D) 74 percent
E) impossible to determine from the information given
A) 26 percent
B) 36 percent
C) 44 percent
D) 74 percent
E) impossible to determine from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the ratio of the value of a set of goods expressed in current dollars to their value expressed in constant dollars is 1.54,prices on average must have risen by ________ percent.
A) 154
B) 100
C) 54
D) 46
E) 1.54
A) 154
B) 100
C) 54
D) 46
E) 1.54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Fixed-weight price indexes are less reliable when there have been changes in
A) relative prices.
B) current dollar output.
C) the amount of nonproductive transactions.
D) the date of the base year.
E) population.
A) relative prices.
B) current dollar output.
C) the amount of nonproductive transactions.
D) the date of the base year.
E) population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To measure the value of all final goods produced in a given year,we must include the value of
A) used goods that are resold.
B) intermediate goods.
C) government and private transfer payments.
D) all financial transactions.
E) changes in total inventories.
A) used goods that are resold.
B) intermediate goods.
C) government and private transfer payments.
D) all financial transactions.
E) changes in total inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The following questions are based on the following information about a hypothetical economy:
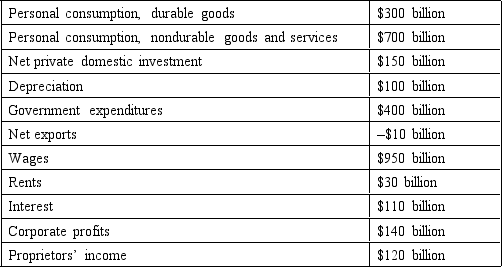
Indirect taxes are
A) $110 billion.
B) $190 billion.
C) $290 billion.
D) $410 billion.
E) impossible to calculate from the information given.

Indirect taxes are
A) $110 billion.
B) $190 billion.
C) $290 billion.
D) $410 billion.
E) impossible to calculate from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following questions are based on the following information:
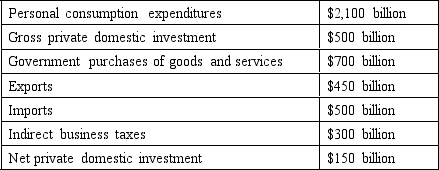
Gross domestic product equals ________ billion.
A) $3,050
B) $3,250
C) $3,350
D) $3,750
E) $4,250

Gross domestic product equals ________ billion.
A) $3,050
B) $3,250
C) $3,350
D) $3,750
E) $4,250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Government transfer payments are NOT included when computing GDP via the expenditures approach because they are
A) included when computing GDP via the income approach.
B) payments to foreigners for the goods we import.
C) expressed in current rather than constant dollar terms.
D) not payments for current production.
E) incapable of affecting the economic well-being of households.
A) included when computing GDP via the income approach.
B) payments to foreigners for the goods we import.
C) expressed in current rather than constant dollar terms.
D) not payments for current production.
E) incapable of affecting the economic well-being of households.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The following questions are based on the following information:

Depreciation equals ________ billion.
A) $50
B) $150
C) $350
D) $850
E) $1,350

Depreciation equals ________ billion.
A) $50
B) $150
C) $350
D) $850
E) $1,350

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following questions are based on the following information about a hypothetical economy:

In this economy
A) the stock of capital goods fell during the year.
B) the government balanced its budget.
C) value added exceeded the income.
D) output exceeded GDP.
E) imports exceeded exports.

In this economy
A) the stock of capital goods fell during the year.
B) the government balanced its budget.
C) value added exceeded the income.
D) output exceeded GDP.
E) imports exceeded exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The following questions are based on the following information about a hypothetical economy:

GDP is ________ billion.
A) $1,240
B) $1,250
C) $1,340
D) $1,640
E) $2,590

GDP is ________ billion.
A) $1,240
B) $1,250
C) $1,340
D) $1,640
E) $2,590

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The best example of a consumer nondurable counted in this year's GDP is a
A) haircut.
B) refrigerator.
C) pizza.
D) concert.
E) used car.
A) haircut.
B) refrigerator.
C) pizza.
D) concert.
E) used car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The purchase of a new living room sofa from a major furniture store would be explicitly counted when computing the gross domestic product by the ________ approach.
A) income
B) expenditures
C) surplus value
D) intermediate product
E) standard of living
A) income
B) expenditures
C) surplus value
D) intermediate product
E) standard of living

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Income generated in the production of this year's output is measured by summing transactions in ________ markets.
A) foreign
B) resource
C) commodity
D) stock
E) black
A) foreign
B) resource
C) commodity
D) stock
E) black

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following would be explicitly counted when computing the gross domestic product by the expenditures approach?
A) the purchase of a used car by a college student
B) the salary of the CEO of Gillette Corporation
C) the purchase of fuel injectors by Ford
D) Social Security payments to retired persons
E) the purchase of a microwave oven by newlyweds
A) the purchase of a used car by a college student
B) the salary of the CEO of Gillette Corporation
C) the purchase of fuel injectors by Ford
D) Social Security payments to retired persons
E) the purchase of a microwave oven by newlyweds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The two methods of measuring the value of GDP are the ________ approaches.
A) input and output
B) direct and residual
C) business and household
D) domestic and foreign
E) income and expenditures
A) input and output
B) direct and residual
C) business and household
D) domestic and foreign
E) income and expenditures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Negative net private domestic investment means that
A) intermediate goods are being double counted.
B) gross investment is smaller than depreciation.
C) imports are greater than exports.
D) indirect business taxes are rising.
E) a country's stock of capital goods is rising.
A) intermediate goods are being double counted.
B) gross investment is smaller than depreciation.
C) imports are greater than exports.
D) indirect business taxes are rising.
E) a country's stock of capital goods is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The greatest amount of consumer spending in the economy is on
A) durable goods.
B) nondurable goods.
C) services.
D) plants and equipment.
E) residential structures.
A) durable goods.
B) nondurable goods.
C) services.
D) plants and equipment.
E) residential structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The change in a country's stock of capital goods is indicated by its net
A) exports.
B) output.
C) profit.
D) income.
E) investment.
A) exports.
B) output.
C) profit.
D) income.
E) investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following would be included in GDP when computed by the expenditures approach?
A) fertilizer purchased by a farmer
B) flour purchased by a bakery
C) bread purchased by a restaurant
D) purchases of shares of common stock in a bakery
E) new production machinery purchased by a bakery
A) fertilizer purchased by a farmer
B) flour purchased by a bakery
C) bread purchased by a restaurant
D) purchases of shares of common stock in a bakery
E) new production machinery purchased by a bakery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When computing GDP,services performed by the government are
A) excluded.
B) considered nonproductive transactions.
C) valued at their cost to the taxpayer.
D) given values estimated from similar activities in the private sector.
E) added to government transfer payments.
A) excluded.
B) considered nonproductive transactions.
C) valued at their cost to the taxpayer.
D) given values estimated from similar activities in the private sector.
E) added to government transfer payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
When computing GDP via the income approach,we must include
A) exports minus imports.
B) gross investment.
C) depreciation and indirect business taxes.
D) household savings and consumption.
E) government purchases of goods and services.
A) exports minus imports.
B) gross investment.
C) depreciation and indirect business taxes.
D) household savings and consumption.
E) government purchases of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The components of gross private domestic investment include
A) net exports.
B) consumer durable goods.
C) the net change in total inventories.
D) government purchases of goods and services.
E) corporate income taxes.
A) net exports.
B) consumer durable goods.
C) the net change in total inventories.
D) government purchases of goods and services.
E) corporate income taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Government services are valued in GDP at cost rather than at their market prices because
A) price changes occur frequently as a result of inflation, which distorts the measurement of GDP.
B) it is necessary to avoid counting intermediate goods in GDP.
C) otherwise government and private transfer payments would end up being counted in GDP.
D) most government services produced are not purchased by their users.
E) the price of a service is not always a measure of the worth of a service.
A) price changes occur frequently as a result of inflation, which distorts the measurement of GDP.
B) it is necessary to avoid counting intermediate goods in GDP.
C) otherwise government and private transfer payments would end up being counted in GDP.
D) most government services produced are not purchased by their users.
E) the price of a service is not always a measure of the worth of a service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
According to economist Richard Gill,the source of our economy's real income is
A) profits.
B) the goods we produce.
C) the resourcefulness and skill of our people.
D) impossible to identify.
E) the amount of money in circulation.
A) profits.
B) the goods we produce.
C) the resourcefulness and skill of our people.
D) impossible to identify.
E) the amount of money in circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Prior to the Great Depression,estimates of the level of economic well-being in the United States were based on
A) measures of GDP, the same as it is now.
B) the measured economic welfare scale of Nordhaus and Tobin.
C) government statistics based on census and average net income.
D) consumers' personal sense of well-being.
E) deflating after-tax incomes received by households.
A) measures of GDP, the same as it is now.
B) the measured economic welfare scale of Nordhaus and Tobin.
C) government statistics based on census and average net income.
D) consumers' personal sense of well-being.
E) deflating after-tax incomes received by households.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What effect did the U.S.contribution to the war effort during World War II have on GNP?
A) It boosted GNP dramatically.
B) It boosted GNP slightly.
C) GNP fell to its lowest level in years as resources were depleted.
D) Since resources were only transferred from one kind of production to another, there was virtually no effect.
E) It made GNP difficult to estimate accurately, since output was being diverted to the government.
A) It boosted GNP dramatically.
B) It boosted GNP slightly.
C) GNP fell to its lowest level in years as resources were depleted.
D) Since resources were only transferred from one kind of production to another, there was virtually no effect.
E) It made GNP difficult to estimate accurately, since output was being diverted to the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Kuznets was honored for his contribution to economics with the Nobel Prize,largely on the basis of his contributions to the GNP measure.In particular,Kuznets was cited for
A) quantifying a measure that had previously been largely impressionistic.
B) recognizing that products have a higher economic value than services.
C) revealing that the nation's GNP was higher, even during the Depression, than anyone had supposed.
D) finding a way to include child care and other domestic services in the measure of GNP.
E) traffic violations, bootlegging, and tax evasion.
A) quantifying a measure that had previously been largely impressionistic.
B) recognizing that products have a higher economic value than services.
C) revealing that the nation's GNP was higher, even during the Depression, than anyone had supposed.
D) finding a way to include child care and other domestic services in the measure of GNP.
E) traffic violations, bootlegging, and tax evasion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The next question is based on the following information:
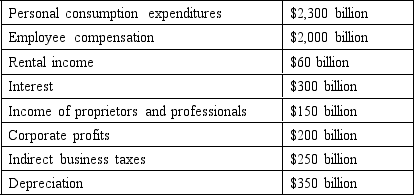
GDP is ________ billion.
A) $2,710
B) $2,960
C) $3,310
D) $3,610
E) $5,610

GDP is ________ billion.
A) $2,710
B) $2,960
C) $3,310
D) $3,610
E) $5,610

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The largest income component of U.S.GDP is
A) corporate profits.
B) rental and interest income.
C) employee compensation.
D) personal and corporate taxes.
E) welfare payments.
A) corporate profits.
B) rental and interest income.
C) employee compensation.
D) personal and corporate taxes.
E) welfare payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When Simon Kuznets devised gross national product (GNP),he made the decision to exclude illegal activities like drug smuggling and gambling from his calculations.He based this decision mainly on the fact that
A) such activities, at that time, netted little national income.
B) he wanted to focus on activities that were "goods" and not "bads."
C) he could not obtain accurate information on income generated through such activities.
D) such activities generated income but few tangible products.
E) such activities were not bought and sold in markets.
A) such activities, at that time, netted little national income.
B) he wanted to focus on activities that were "goods" and not "bads."
C) he could not obtain accurate information on income generated through such activities.
D) such activities generated income but few tangible products.
E) such activities were not bought and sold in markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
According to the video,which of the following is the best assessment of the overall value of GNP measure?
A) Despite its statistical base, GNP is now considered an outmoded measure of productivity.
B) GNP is a highly accurate, remarkably precise measure of human welfare.
C) GNP is of interest to economists but offers no useful information to consumers or business people.
D) GNP is a universally useful estimate of our nation's productivity.
E) GNP is useful as a measure of annual output but not helpful in measuring economic growth over an extended period of time.
A) Despite its statistical base, GNP is now considered an outmoded measure of productivity.
B) GNP is a highly accurate, remarkably precise measure of human welfare.
C) GNP is of interest to economists but offers no useful information to consumers or business people.
D) GNP is a universally useful estimate of our nation's productivity.
E) GNP is useful as a measure of annual output but not helpful in measuring economic growth over an extended period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The best example of an indirect business tax is
A) an excise tax on alcoholic beverages.
B) the personal income tax.
C) depreciation.
D) the corporate income tax.
E) retained earnings.
A) an excise tax on alcoholic beverages.
B) the personal income tax.
C) depreciation.
D) the corporate income tax.
E) retained earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A leading pioneer in the efforts to provide the first estimates of U.S.income and output was
A) Alexander Hamilton.
B) David Schoenmacher.
C) Franklin D. Roosevelt.
D) John Maynard Keynes.
E) Simon Kuznets.
A) Alexander Hamilton.
B) David Schoenmacher.
C) Franklin D. Roosevelt.
D) John Maynard Keynes.
E) Simon Kuznets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Federal taxes on gasoline and cigarettes are examples of ________ taxes.
A) active
B) beneficial
C) cost of living
D) indirect business
E) exercise
A) active
B) beneficial
C) cost of living
D) indirect business
E) exercise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 71 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



