Deck 11: Surveying the Stars
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/129
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Surveying the Stars
1
The spectral sequence, in order of decreasing temperature, is
A) OFBAGKM.
B) OBAGFKM.
C) OBAFGKM.
D) ABFGKMO.
E) BAGFKMO.
A) OFBAGKM.
B) OBAGFKM.
C) OBAFGKM.
D) ABFGKMO.
E) BAGFKMO.
C
2
Which of the following correctly states the relationship between the apparent brightness, luminosity, and distance of a star?
A) luminosity =
B) apparent brightness =
C) apparent brightness = luminosity × 4π × (distance) ²
D) distance =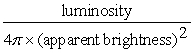
A) luminosity =

B) apparent brightness =

C) apparent brightness = luminosity × 4π × (distance) ²
D) distance =
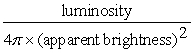
B
3
Which o the following stars are brightest at ultraviolet wavelengths?
A) O and B stars
B) A and F stars
C) G and K stars
D) M stars
E) none, all stars are brightest at optical wavelengths
A) O and B stars
B) A and F stars
C) G and K stars
D) M stars
E) none, all stars are brightest at optical wavelengths
A
4
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find stars that are cool and dim?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the standard units for apparent brightness?
A) Watts
B) Joules
C) Newtons
D) Watts per second
E) Watts per square meter
A) Watts
B) Joules
C) Newtons
D) Watts per second
E) Watts per square meter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
You see two main-sequence stars with the same spectral type. Star 1 is dimmer in apparent brightness than Star 2 by a factor of 100. What can you conclude, assuming there is no absorption of either star's light by interstellar gas or dust?
A) Without first knowing the distances to these stars, you cannot draw any conclusions about how their true luminosities compare to each other.
B) The luminosity of Star 1 is a factor of 100 less than the luminosity of Star 2.
C) Star 1 is 100 times more distant than Star 2.
D) Star 1 is 100 times nearer than Star 2.
E) Star 1 is 10 times more distant than Star 2.
A) Without first knowing the distances to these stars, you cannot draw any conclusions about how their true luminosities compare to each other.
B) The luminosity of Star 1 is a factor of 100 less than the luminosity of Star 2.
C) Star 1 is 100 times more distant than Star 2.
D) Star 1 is 100 times nearer than Star 2.
E) Star 1 is 10 times more distant than Star 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements about apparent and absolute magnitudes is true?
A) The magnitude system that we use now is based on a system used by the ancient Greeks over 2,000 years ago that classified stars by how bright they appeared.
B) A star with an apparent magnitude of 1 appears brighter than a star with an apparent magnitude of 2.
C) The absolute magnitude of a star is another measure of its luminosity.
D) A star's absolute magnitude is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were at a distance of 10 parsecs from Earth.
E) All of the above are true.
A) The magnitude system that we use now is based on a system used by the ancient Greeks over 2,000 years ago that classified stars by how bright they appeared.
B) A star with an apparent magnitude of 1 appears brighter than a star with an apparent magnitude of 2.
C) The absolute magnitude of a star is another measure of its luminosity.
D) A star's absolute magnitude is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were at a distance of 10 parsecs from Earth.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
You measure the parallax angle for a star to be 0.5 arcseconds. The distance to this star is
A) 0.5 light-year.
B) 0.5 parsec.
C) 5 light-years.
D) 5 parsecs.
E) 2 parsecs.
A) 0.5 light-year.
B) 0.5 parsec.
C) 5 light-years.
D) 5 parsecs.
E) 2 parsecs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What are the standard units for luminosity?
A) Watts
B) Joules
C) Newtons
D) kilograms
E) Watts per second
A) Watts
B) Joules
C) Newtons
D) kilograms
E) Watts per second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements about spectral types of stars is true?
A) The spectral type of a star can be used to determine its surface temperature.
B) The spectral type of a star can be used to determine its color.
C) A star with spectral type A is cooler than a star with spectral type B.
D) A star with spectral type F2 is hotter than a star with spectral type F3.
E) All of the above are true.
A) The spectral type of a star can be used to determine its surface temperature.
B) The spectral type of a star can be used to determine its color.
C) A star with spectral type A is cooler than a star with spectral type B.
D) A star with spectral type F2 is hotter than a star with spectral type F3.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A star's luminosity is the
A) apparent brightness of the star in our sky.
B) surface temperature of the star.
C) lifetime of the star.
D) total amount of energy that the star will radiate over its entire lifetime.
E) total amount of energy that the star radiates each second.
A) apparent brightness of the star in our sky.
B) surface temperature of the star.
C) lifetime of the star.
D) total amount of energy that the star will radiate over its entire lifetime.
E) total amount of energy that the star radiates each second.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The spectral sequence sorts stars according to
A) mass.
B) surface temperature.
C) luminosity.
D) core temperature.
E) radius.
A) mass.
B) surface temperature.
C) luminosity.
D) core temperature.
E) radius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which stellar spectral type has strong molecular absorption lines in its optical spectrum?
A) O
B) B
C) G
D) K
E) M
A) O
B) B
C) G
D) K
E) M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most distant stars we can measure stellar parallax for are approximately
A) 5 parsecs away.
B) 100 parsecs away.
C) 10,000 parsecs away.
D) halfway across the Milky Way Galaxy.
E) in the Andromeda Galaxy.
A) 5 parsecs away.
B) 100 parsecs away.
C) 10,000 parsecs away.
D) halfway across the Milky Way Galaxy.
E) in the Andromeda Galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
You measure the parallax angle for a star to be 0.1 arcseconds. The distance to this star is
A) 10 light-years.
B) 10 parsecs.
C) 0.1 light-year.
D) 0.1 parsec.
E) impossible to determine.
A) 10 light-years.
B) 10 parsecs.
C) 0.1 light-year.
D) 0.1 parsec.
E) impossible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Since all stars begin their lives with the same basic composition, what characteristic most determines how they will differ?
A) location where they are formed
B) time they are formed
C) luminosity they are formed with
D) mass they are formed with
E) color they are formed with
A) location where they are formed
B) time they are formed
C) luminosity they are formed with
D) mass they are formed with
E) color they are formed with

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following terms is given to a pair of stars that appear to change position in the sky, indicating that they are orbiting one another?
A) visual binary
B) eclipsing binary
C) spectroscopic binary
D) double star
E) none of the above
A) visual binary
B) eclipsing binary
C) spectroscopic binary
D) double star
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following best describes the axes of a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram?
A) surface temperature on the horizontal axis and luminosity on the vertical axis
B) mass on the horizontal axis and luminosity on the vertical axis
C) surface temperature on the horizontal axis and radius on the vertical axis
D) mass on the horizontal axis and stellar age on the vertical axis
E) interior temperature on the horizontal axis and mass on the vertical axis
A) surface temperature on the horizontal axis and luminosity on the vertical axis
B) mass on the horizontal axis and luminosity on the vertical axis
C) surface temperature on the horizontal axis and radius on the vertical axis
D) mass on the horizontal axis and stellar age on the vertical axis
E) interior temperature on the horizontal axis and mass on the vertical axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the distance between us and a star is doubled, with everything else remaining the same, its luminosity
A) is decreased by a factor of four, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
B) is decreased by a factor of two, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
C) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
D) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
E) is decreased by a factor of four, but its apparent brightness remains the same.
A) is decreased by a factor of four, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
B) is decreased by a factor of two, and its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
C) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
D) remains the same, but its apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
E) is decreased by a factor of four, but its apparent brightness remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The faintest star visible to the naked eye has an apparent magnitude of about
A) 10.
B) 6.
C) 1.
D) 0.
E) 6.
A) 10.
B) 6.
C) 1.
D) 0.
E) 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A star of spectral type G lives approximately how long on the main sequence?
A) 1,000 years
B) 10,000 years
C) 10 million years
D) 1 billion years
E) 10 billion years
A) 1,000 years
B) 10,000 years
C) 10 million years
D) 1 billion years
E) 10 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is the most numerous type of main-sequence star?
A) an O star
B) an A star
C) an F star
D) a G star
E) an M star
A) an O star
B) an A star
C) an F star
D) a G star
E) an M star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
You observe a star cluster with a main-sequence turn-off point at spectral type G2 (the same spectral type as the Sun). What is the age of this star cluster?
A) 10,000 years.
B) 4.6 billion years.
C) 10 billion years.
D) 100 billion years.
E) You also need to know the luminosity class of the turn-off point to determine the age.
A) 10,000 years.
B) 4.6 billion years.
C) 10 billion years.
D) 100 billion years.
E) You also need to know the luminosity class of the turn-off point to determine the age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find stars that have the largest radii?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find white dwarfs?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The more distant a star, the smaller its parallax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The age of stars in a cluster can be determined by
A) fitting the position of the main sequence to the Sun.
B) determining the main sequence turnoff point.
C) finding pulsating variable stars in the cluster.
D) finding spectroscopic binaries in the cluster.
E) counting the number of stars in each spectral class.
A) fitting the position of the main sequence to the Sun.
B) determining the main sequence turnoff point.
C) finding pulsating variable stars in the cluster.
D) finding spectroscopic binaries in the cluster.
E) counting the number of stars in each spectral class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find red giant stars?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
On the main sequence, stars obtain their energy
A) from chemical reactions.
B) from gravitational contraction.
C) by converting hydrogen to helium.
D) by converting helium to carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen.
E) from nuclear fission.
A) from chemical reactions.
B) from gravitational contraction.
C) by converting hydrogen to helium.
D) by converting helium to carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen.
E) from nuclear fission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following stellar properties has the greatest range in values?
A) mass
B) radius
C) core temperature
D) surface temperature
E) luminosity
A) mass
B) radius
C) core temperature
D) surface temperature
E) luminosity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A star of spectral type B with a mass of 10 times the mass of the Sun lives approximately how long on the main sequence?
A) 1,000 years
B) 10,000 years
C) 10 million years
D) 1 billion years
E) 10 billion years
A) 1,000 years
B) 10,000 years
C) 10 million years
D) 1 billion years
E) 10 billion years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The apparent brightness of a star depends only on its luminosity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the distance between us and a star is doubled, its apparent brightness will decrease by a factor of four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where would you find stars that are cool and luminous?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
On a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, where on the main sequence would you find stars that have the greatest mass?
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left
A) upper right
B) lower right
C) upper left
D) lower left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following statements about globular clusters is true?
A) All stars in the cluster are approximately at the same stage in their evolution.
B) Most of the stars in the cluster are younger than 10 billion years.
C) Most stars in the cluster are yellow or reddish in color.
D) All stars in the cluster have approximately the same mass.
E) There is an approximately equal number of all types of stars in the cluster.
A) All stars in the cluster are approximately at the same stage in their evolution.
B) Most of the stars in the cluster are younger than 10 billion years.
C) Most stars in the cluster are yellow or reddish in color.
D) All stars in the cluster have approximately the same mass.
E) There is an approximately equal number of all types of stars in the cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following luminosity classes refers to stars on the main sequence?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
We can measure the parallax of most stars in our galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following comparisons between low-mass stars and high-mass stars is true?
A) Low-mass stars are cooler and less luminous than high-mass stars.
B) Low-mass stars are hotter and more luminous than high-mass stars.
C) Low-mass stars are cooler but more luminous than high-mass stars.
D) Low-mass stars are hotter but less luminous than high-mass stars.
E) Low-mass stars have the same temperature and luminosity as high-mass stars.
A) Low-mass stars are cooler and less luminous than high-mass stars.
B) Low-mass stars are hotter and more luminous than high-mass stars.
C) Low-mass stars are cooler but more luminous than high-mass stars.
D) Low-mass stars are hotter but less luminous than high-mass stars.
E) Low-mass stars have the same temperature and luminosity as high-mass stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements about open clusters is true?
A) All stars in the cluster are approximately the same color.
B) All stars in the cluster are approximately the same age.
C) All stars in the cluster have approximately the same mass.
D) All stars in the cluster will evolve similarly.
E) There is an approximately equal number of all types of stars in the cluster.
A) All stars in the cluster are approximately the same color.
B) All stars in the cluster are approximately the same age.
C) All stars in the cluster have approximately the same mass.
D) All stars in the cluster will evolve similarly.
E) There is an approximately equal number of all types of stars in the cluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The Earth is about 150 million km from the Sun, and the apparent brightness of the Sun in our sky is about 1,300 watts per square meter. Determine the apparent brightness we would measure for the Sun if we were located five times the earth's distance from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Two stars have the same spectral type. Star X is in luminosity class III, while Star Y is in luminosity class V. Star X must be larger in radius than Star Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
We can measure the radii of stars in eclipsing binary systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Two stars have the same luminosity. Star X is spectral type F, while Star Y is spectral type K. Star X must be larger in radius than Star Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Earth is about 150 million km from the Sun, and the apparent brightness of the Sun in our sky is about 1,300 watts per square meter. Determine the apparent brightness we would measure for the Sun if we were located one-third of the earth's distance from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Observing Stellar Evolution: Stars evolve on timescales of millions to billions of years, making it impossible for astronomers to follow the life-cycle of any individual star. Explain how astronomers overcome this limitation. Be sure to discuss the important role that observations of star clusters play in revealing the evolution of stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The faintest visible stars to the naked eye have an apparent magnitude of about 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
It is impossible for a star to have a negative apparent magnitude, such as -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Confusing Terminology in Science: Scientists' love of jargon and acronyms often confounds the public and makes it impossible for them to read scientific literature. Use the example of spectral types introduced in this chapter (i.e. the Sun is a "G2" star) as a case study in jargon. What is the historical origin of the spectral types? Why are the letters in a confusing, non-alphabetical order? Why do you think astronomers persist in using spectral types? Do you think astronomers should drop this notation, and, if so, what should replace it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A star with an apparent magnitude of 10 appears fainter than a star with an apparent magnitude of 9.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Two stars both lie on the main sequence. Star X is spectral type A, while Star Y is spectral type G. Star X must be more massive than Star Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Some stars are cool enough to have molecules in their atmosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
All stars spend approximately the same amount of time on the main sequence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The size of the Earth's orbit is doubled. This will allow the parallaxes of more distant stars to be measured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The Earth is about 150 million km from the Sun, and the apparent brightness of the Sun in our sky is about 1,300 watts per square meter. Determine the apparent brightness we would measure for the Sun if we were located half the earth's distance from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Spectral type, surface temperature, and color all describe the same basic characteristic of a star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Blue stars are always more luminous than red stars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Our Sun, An Average Star: Often in science it is helpful to talk about a representative example of the objects or phenomena being studied. However, you must always keep in mind that the average case is not always representative. For example, our Sun is often described as an "average" star in the Milky Way. In what sense is this statement true? In what sense is this statement seriously misleading? Do you think it is useful to characterize the stars in the Milky Way by simply citing our "average" Sun?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A 10 solar mass star is about ten times more luminous than a 1 solar mass star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Most stars on the main sequence fuse hydrogen into helium in their cores, but some do not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Two stars, Fred and Barney, are of the same size. Fred has spectral type F, while Barney has spectral type B. Which one is more luminous?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which cluster is 10 billion years old?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which group includes the Sun?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which group represents stars that are hot but dim?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which group represents stars that are hot and very bright?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following stars has a spectrum that peaks at the highest frequency?
A) A yellow star
B) A red star
C) A blue star
A) A yellow star
B) A red star
C) A blue star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which group includes stars that are burning elements besides hydrogen in their cores?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which group represents hydrogen-burning stars with the shortest lifetimes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Two stars, Betty and Wilma, are both on the main sequence. Betty is more luminous than Wilma. Which one has a hotter surface temperature? Which one is more massive? Which one is bigger? If they both formed at the same time, which one will evolve off the main sequence first?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which group includes stars that are burning helium in their cores?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which star cluster is the youngest star cluster? The one where the brightest main sequence stars are . . .
A) O stars.
B) A stars.
C) G stars.
D) M stars.
E) B stars.
A) O stars.
B) A stars.
C) G stars.
D) M stars.
E) B stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Two stars, Tom and Jerry, have the same spectral type. Tom is luminosity class V and Jerry is luminosity class I. Which star is bigger? Which star is more luminous? Which star has a hotter surface temperature? Explain your answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which star is the hottest star?
A) G
B) A
C) O
D) M
E) Can't tell from information provided.
A) G
B) A
C) O
D) M
E) Can't tell from information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Explain why stars more massive than the Sun live shorter main sequence lives than stars less massive than the Sun, despite having more fuel available for nuclear reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain why stars displaying spectral lines of molecules must be relatively cool.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which is brighter in our sky, a star with apparent magnitude 2 or a star with apparent magnitude 7?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which group represents stars of the smallest radii?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A scientist claims that all red main sequence stars are 1 billion years old. Which of the following, if true, would prove that this claim is false?
A) The discovery of a red main sequence star in a star cluster where all the other stars are red giants or red supergiants.
B) Stellar evolution theory predicts that the main sequence lifetime of red stars can be as long as 100 billion years.
C) The minimum lifespan of a red main sequence star is estimated to be 10 billion years.
D) The discovery of a red main sequence star in a star cluster where the main sequence turnoff is about that of the Sun.
A) The discovery of a red main sequence star in a star cluster where all the other stars are red giants or red supergiants.
B) Stellar evolution theory predicts that the main sequence lifetime of red stars can be as long as 100 billion years.
C) The minimum lifespan of a red main sequence star is estimated to be 10 billion years.
D) The discovery of a red main sequence star in a star cluster where the main sequence turnoff is about that of the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which cluster is the youngest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which cluster is the oldest?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



