Deck 36: The Cold War Begins,1945-1952
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/145
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 36: The Cold War Begins,1945-1952
1
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Richard M.Nixon
Richard M.Nixon
Student answers will vary.
2
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Mao Zedong (Mao Tse-tung)
Mao Zedong (Mao Tse-tung)
Student answers will vary.
3
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Benjamin Spock
Benjamin Spock
Student answers will vary.
4
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Henry Wallace
Henry Wallace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Sunbelt
Sunbelt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
George F.Kennan
George F.Kennan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Reinhold Niebuhr
Reinhold Niebuhr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Servicemen's Readjustment Act (GI Bill)
Servicemen's Readjustment Act (GI Bill)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Frostbelt
Frostbelt

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Dean Acheson
Dean Acheson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-shek)
Jiang Jieshi (Chiang Kai-shek)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Joseph McCarthy
Joseph McCarthy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Harry S.Truman
Harry S.Truman

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
J.Robert Oppenheimer
J.Robert Oppenheimer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Thomas Dewey
Thomas Dewey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Taft-Hartley Act
Taft-Hartley Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Cold War
Cold War

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Yalta Conference
Yalta Conference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Berlin airlift
Berlin airlift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Fair Deal
Fair Deal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
H-Bomb
H-Bomb

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Truman Doctrine
Truman Doctrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
North Atlantic Treaty Organization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
United Nations
United Nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
"containment doctrine"
"containment doctrine"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Progressive party
Progressive party

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
iron curtain
iron curtain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
McCarran Act
McCarran Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Point Four
Point Four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Dixiecrats
Dixiecrats

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
baby boom
baby boom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
U.N.Security Council
U.N.Security Council

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
House Committee on Un-American Activities
House Committee on Un-American Activities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
NSC-68
NSC-68

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Nuremberg trials
Nuremberg trials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
National Security Act
National Security Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Marshall Plan
Marshall Plan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
UNESCO
UNESCO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Albania
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Albania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Lithuania
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Lithuania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Many Americans feared that the end of World War II would bring
A) heightened racial tensions.
B) a return of the Great Depression.
C) moral and religious decline.
D) continued fascist resistance in Germany.
E) a new war with the Soviet Union.
A) heightened racial tensions.
B) a return of the Great Depression.
C) moral and religious decline.
D) continued fascist resistance in Germany.
E) a new war with the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Taft-Hartley Act delivered a major blow to labor by
A) outlawing strikes by public employees.
B) creating a serious inflationary spiral.
C) banning labor's political action committees.
D) outlawing closed (all-union) shops.
E) forbidding union organizers to enter workplaces.
A) outlawing strikes by public employees.
B) creating a serious inflationary spiral.
C) banning labor's political action committees.
D) outlawing closed (all-union) shops.
E) forbidding union organizers to enter workplaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Estonia
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Estonia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The passage of the Servicemen's Readjustment Act (GI Bill of Rights)was partly motivated by
A) fear of postwar veterans' protests.
B) memories of the mistreatment of the veterans' Bonus Army in the 1930s.
C) fear that the labor markets could not absorb millions of discharged veterans.
D) a desire to expand the social diversity of American colleges and universities.
E) the need of American business for a more highly educated workforce.
A) fear of postwar veterans' protests.
B) memories of the mistreatment of the veterans' Bonus Army in the 1930s.
C) fear that the labor markets could not absorb millions of discharged veterans.
D) a desire to expand the social diversity of American colleges and universities.
E) the need of American business for a more highly educated workforce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
thirty-eighth parallel
thirty-eighth parallel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
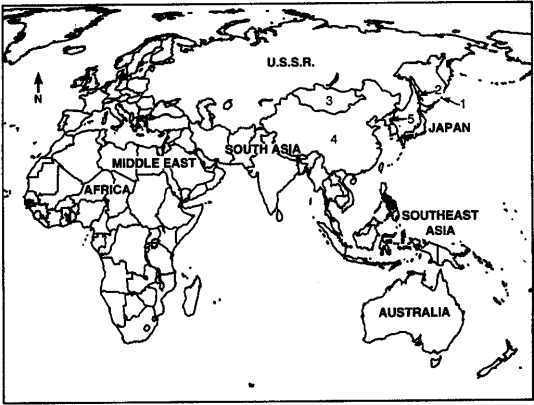
____ South Sakhalin Island

____ South Sakhalin Island

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ China

____ China

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Mongolia

____ Mongolia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Poland
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Poland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Bulgaria
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Bulgaria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Kuril Islands

____ Kuril Islands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Hungary
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Hungary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Romania
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Romania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Yugoslavia
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Yugoslavia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ German Democratic Republic (East Germany)
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ German Democratic Republic (East Germany)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Latvia
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Latvia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ North Korea

____ North Korea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
COMPLETION
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Czechoslovakia
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:

____ Czechoslovakia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following did not contribute to the rapid rise of suburbia in post-World War II America?
A) The baby boom
B) Government mortgage guarantees
C) New federally funded highways
D) White flight
E) Urban environmental problems
A) The baby boom
B) Government mortgage guarantees
C) New federally funded highways
D) White flight
E) Urban environmental problems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
All of the following encouraged many post-1945 Americans to move to the suburbs except
A) development of fuel-efficient automobiles.
B) home-loan guarantees from the Federal Housing Authority and the Veterans' Administration.
C) government-built highways.
D) tax deductions for interest payments on home mortgages.
E) white flight from racial change.
A) development of fuel-efficient automobiles.
B) home-loan guarantees from the Federal Housing Authority and the Veterans' Administration.
C) government-built highways.
D) tax deductions for interest payments on home mortgages.
E) white flight from racial change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Much of the Sunbelt's new prosperity was based on its
A) tremendous influx of money from the federal government.
B) policy of high state taxes.
C) regulated economic growth.
D) cooperative effort rather than unbridled individualism.
E) attention to environmental issues.
A) tremendous influx of money from the federal government.
B) policy of high state taxes.
C) regulated economic growth.
D) cooperative effort rather than unbridled individualism.
E) attention to environmental issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The post-World War II prosperity in the United States was most beneficial to
A) African Americans.
B) labor unions.
C) women.
D) Hispanics.
E) farmers.
A) African Americans.
B) labor unions.
C) women.
D) Hispanics.
E) farmers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The dramatically reduced number of American farms and farmers in the postwar era was accompanied by
A) growing poverty in rural America.
B) increasing shortages of American-grown food and fiber.
C) radical protests by farmers and farm laborers.
D) a romantic "back to the land" movement among city dwellers.
E) spectacular gains in American agricultural productivity and food growing.
A) growing poverty in rural America.
B) increasing shortages of American-grown food and fiber.
C) radical protests by farmers and farm laborers.
D) a romantic "back to the land" movement among city dwellers.
E) spectacular gains in American agricultural productivity and food growing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
One sign of the stress that the widespread post-World War II geographic mobility placed on American families was the
A) redistribution of income.
B) popularity of advice books on child-rearing.
C) increasing reliance on television as a baby sitter.
D) increased number of long-distance telephone calls.
E) dramatic rise in divorces.
A) redistribution of income.
B) popularity of advice books on child-rearing.
C) increasing reliance on television as a baby sitter.
D) increased number of long-distance telephone calls.
E) dramatic rise in divorces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The long economic boom from World War II to about 1970 was especially fueled by
A) low energy costs.
B) reduced military expenditures.
C) low inflation.
D) low taxes.
E) a more highly educated work force.
A) low energy costs.
B) reduced military expenditures.
C) low inflation.
D) low taxes.
E) a more highly educated work force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
By 1960,the proportion of Americans who lived in areas classified as metropolitan suburbs was approximately
A) three out of four (75 percent).
B) one out of four (25 percent).
C) half (50 percent).
D) one out of ten (10 percent).
E) four out of ten (40 percent).
A) three out of four (75 percent).
B) one out of four (25 percent).
C) half (50 percent).
D) one out of ten (10 percent).
E) four out of ten (40 percent).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Population distribution after World War II followed a pattern of
A) movement into the Northeast and out of the South.
B) mass migration of blacks from the West to the Midwest.
C) movement from the Southwest to Appalachia.
D) movement out of the cities and into small towns.
E) an urban-suburban segregation of blacks and whites in major metropolitan areas.
A) movement into the Northeast and out of the South.
B) mass migration of blacks from the West to the Midwest.
C) movement from the Southwest to Appalachia.
D) movement out of the cities and into small towns.
E) an urban-suburban segregation of blacks and whites in major metropolitan areas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The continued growth of the suburbs led to
A) increased school integration.
B) better entertainment opportunities in the cities.
C) an increase in urban poverty.
D) a decrease in urban crime.
E) more efficient transportation.
A) increased school integration.
B) better entertainment opportunities in the cities.
C) an increase in urban poverty.
D) a decrease in urban crime.
E) more efficient transportation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of these is NOT a true statement about the GI Bill?
A) It included provisions to help veterans gain an education.
B) Benefits included $16 million in loans for veterans to buy farms, homes or businesses.
C) The GI Bill nurtured the nation's economic expansion in the postwar era.
D) Benefits were only available in the first three months after leaving the military.
E) Millions of veterans took advantage of the GI Bill programs.
A) It included provisions to help veterans gain an education.
B) Benefits included $16 million in loans for veterans to buy farms, homes or businesses.
C) The GI Bill nurtured the nation's economic expansion in the postwar era.
D) Benefits were only available in the first three months after leaving the military.
E) Millions of veterans took advantage of the GI Bill programs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Since 1945,population in the United States has grown most rapidly in the
A) Northeast.
B) Midwest.
C) Sunbelt.
D) Frostbelt.
E) Pacific Northwest.
A) Northeast.
B) Midwest.
C) Sunbelt.
D) Frostbelt.
E) Pacific Northwest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One striking consequence of the postwar economic boom was
A) the continued exclusion of most women from the workplace.
B) the growing split between urban and rural America.
C) the growing concentration of wealth at the top of society.
D) a vast expansion of the homeowning middle class.
E) the growth of blue-collar employment.
A) the continued exclusion of most women from the workplace.
B) the growing split between urban and rural America.
C) the growing concentration of wealth at the top of society.
D) a vast expansion of the homeowning middle class.
E) the growth of blue-collar employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The prosperity of the postwar decades paved the way for all of the following social transformations except
A) the civil rights movement.
B) new welfare programs like Medicare.
C) America's international leadership.
D) the migration of people to the North.
E) increased opportunity to move up economically.
A) the civil rights movement.
B) new welfare programs like Medicare.
C) America's international leadership.
D) the migration of people to the North.
E) increased opportunity to move up economically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
"Planned obsolescence" was a marketing tool invented in the postwar era that
A) pushed families to buy a second car, rather than owning just one.
B) encouraged manufacturers to make products that would break or wear out every two years.
C) meant changing the design of goods frequently enough so that customers would replace older versions with newer ones.
D) was the reason more and more mothers entered or re-entered the workforce.
E) barraged consumers with repetitive advertising campaigns designed to make them purchase more.
A) pushed families to buy a second car, rather than owning just one.
B) encouraged manufacturers to make products that would break or wear out every two years.
C) meant changing the design of goods frequently enough so that customers would replace older versions with newer ones.
D) was the reason more and more mothers entered or re-entered the workforce.
E) barraged consumers with repetitive advertising campaigns designed to make them purchase more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The refusal of the Federal Housing Authority to grant home loans to blacks contributed to
A) the growth of savings and loan institutions exclusively for blacks.
B) driving many blacks into public housing.
C) the development of exclusively black suburbs.
D) a decline in black migration to the cities.
E) All of these
A) the growth of savings and loan institutions exclusively for blacks.
B) driving many blacks into public housing.
C) the development of exclusively black suburbs.
D) a decline in black migration to the cities.
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The majority of the new jobs created in the postwar era went to
A) men.
B) women.
C) African Americans.
D) Hispanics.
E) New immigrants.
A) men.
B) women.
C) African Americans.
D) Hispanics.
E) New immigrants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The growth of organized labor in the post-World War II era was slowed by all of the following except the
A) Taft-Hartley Act.
B) rapidly growing number of service-sector workers.
C) failure of Operation Dixie.
D) reduced number of women in the work force.
E) growing number of part-time workers.
A) Taft-Hartley Act.
B) rapidly growing number of service-sector workers.
C) failure of Operation Dixie.
D) reduced number of women in the work force.
E) growing number of part-time workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Much of the prosperity of the 1950s and 1960s rested on the underpinnings of
A) foreign aid.
B) a rising stock market.
C) foreign trade.
D) a thriving automobile industry.
E) colossal military budgets.
A) foreign aid.
B) a rising stock market.
C) foreign trade.
D) a thriving automobile industry.
E) colossal military budgets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In an effort to forestall an economic downturn,the Truman administration did all of the following except
A) create the President's Council of Economic Advisers.
B) sell war factories and other government installations to private businesses at very low prices.
C) pass the Employment Act, which made it government policy to promote maximum employment.
D) pass the Servicemen's Readjustment Act, known as the GI Bill of Rights.
E) continue wartime wage and price controls.
A) create the President's Council of Economic Advisers.
B) sell war factories and other government installations to private businesses at very low prices.
C) pass the Employment Act, which made it government policy to promote maximum employment.
D) pass the Servicemen's Readjustment Act, known as the GI Bill of Rights.
E) continue wartime wage and price controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 145 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



