Deck 18: The Resurgence of Conservatism 1980-1992
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/120
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: The Resurgence of Conservatism 1980-1992
1
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Boris Yeltsin
Boris Yeltsin
Answers will vary.
2
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Perestroika
Perestroika
Answers will vary.
3
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Sandra Day O'Connor
Sandra Day O'Connor
Answers will vary.
4
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
George Herbert Walker Bush
George Herbert Walker Bush

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Walter Mondale
Walter Mondale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Clarence Thomas
Clarence Thomas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Michael Dukakis
Michael Dukakis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Geraldine Ferraro
Geraldine Ferraro

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Jimmy Carter
Jimmy Carter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
"supply-side" economics
"supply-side" economics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Jesse Jackson
Jesse Jackson

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Manuel Noriega
Manuel Noriega

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Edward Kennedy
Edward Kennedy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Jerry Falwell
Jerry Falwell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Thatcher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Anita Hill
Anita Hill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
contras
contras

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
ethnic cleansing
ethnic cleansing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
"ABC" movement
"ABC" movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Reaganomics
Reaganomics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
identity politics
identity politics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Strategic Defense Initiative ("Star Wars")
Strategic Defense Initiative ("Star Wars")

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Intermediate-Range Nuclear Force (INF)
Intermediate-Range Nuclear Force (INF)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
"boll weevils"
"boll weevils"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Planned Parenthood v. Casey
Planned Parenthood v. Casey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
yuppies
yuppies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
rainbow coalition
rainbow coalition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Iran-Contra Affair
Iran-Contra Affair

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
New Right
New Right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Moral Majority
Moral Majority

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Religious Right
Religious Right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Sandinistas
Sandinistas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
pro-choice/pro-life
pro-choice/pro-life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Grenada
Grenada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Chappaquiddick
Chappaquiddick

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Glasnost
Glasnost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Solidarity Movement
Solidarity Movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The New Right movement that helped to elect Ronald Reagan was spearheaded by
A) fiscal conservatives.
B) evangelical Christians.
C) gold-standard advocates.
D) midwesterners.
E) neoconservatives.
A) fiscal conservatives.
B) evangelical Christians.
C) gold-standard advocates.
D) midwesterners.
E) neoconservatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Democrats who opposed the reelection of President Carter complained that he
A) had failed to control double-digit inflation.
B) negotiated the Panama Canal Treaty.
C) had not aggressively pursued civil rights.
D) failed to rescue the hostages in Iran.
E) had removed regulatory controls from major industries.
A) had failed to control double-digit inflation.
B) negotiated the Panama Canal Treaty.
C) had not aggressively pursued civil rights.
D) failed to rescue the hostages in Iran.
E) had removed regulatory controls from major industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991
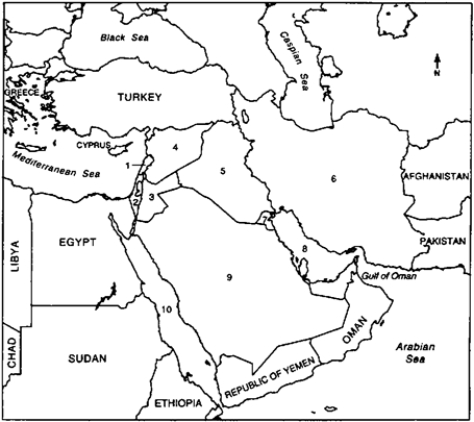
____ Red Sea
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Red Sea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Roe v. Wade
Roe v. Wade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Lebanon
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Lebanon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Iran
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Iran

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Persian Gulf
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Persian Gulf

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Americans With Disabilities Act
Americans With Disabilities Act

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Syria
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Syria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Saudi Arabia
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Saudi Arabia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Operation Desert Storm
Operation Desert Storm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Israel
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Israel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
Webster v. Reproductive Health Services
Webster v. Reproductive Health Services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Jordan
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Jordan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Kuwait
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Kuwait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Identify and state the historical significance of the following:
"gender gap"
"gender gap"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the 1980 national elections
A) Edward Kennedy challenged incumbent President Carter for the nomination of the Democratic party.
B) although Ronald Reagan won the presidency, both houses of Congress still had Democratic party majorities.
C) third-party candidate John Anderson won three states and seventeen Electoral College votes.
D) Ronald Reagan won the presidency by the closest margin since the Kennedy-Nixon election of 1960.
E) Reagan led Republicans to majorities in both houses of Congress.
A) Edward Kennedy challenged incumbent President Carter for the nomination of the Democratic party.
B) although Ronald Reagan won the presidency, both houses of Congress still had Democratic party majorities.
C) third-party candidate John Anderson won three states and seventeen Electoral College votes.
D) Ronald Reagan won the presidency by the closest margin since the Kennedy-Nixon election of 1960.
E) Reagan led Republicans to majorities in both houses of Congress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Edward Kennedy's campaign to take the presidential nomination away from Jimmy Carter in 1980 was handicapped by
A) his poor performance as a senator.
B) a growing dislike for the Kennedys.
C) Carter's popularity.
D) lingering suspicions about his involvement in an automobile accident in which a young woman was killed.
E) his inability to reach beyond New England.
A) his poor performance as a senator.
B) a growing dislike for the Kennedys.
C) Carter's popularity.
D) lingering suspicions about his involvement in an automobile accident in which a young woman was killed.
E) his inability to reach beyond New England.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Locate the following places by reference number on the map:
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Iraq
The Middle East During the Persian Gulf Crisis, 1990-1991

____ Iraq

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
President Ronald Reagan and the new British prime minister, Margaret Thatcher, shared all of the following goals except
A) limiting the role of government, especially in regulating business.
B) shrinking the power of labor unions.
C) strengthening the Anglo-American alliance.
D) enhancing the role of religion in public life.
E) promoting a muscular foreign policy, especially against the Soviet Union.
A) limiting the role of government, especially in regulating business.
B) shrinking the power of labor unions.
C) strengthening the Anglo-American alliance.
D) enhancing the role of religion in public life.
E) promoting a muscular foreign policy, especially against the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Ronald Reagan's essential domestic goal as president was to
A) cut back on military expenditures.
B) remove government interference in people's private lives in such areas as abortion and pornography.
C) dismantle the welfare state and shrink the size of the federal government.
D) transfer welfare programs to the states.
E) reform public education.
A) cut back on military expenditures.
B) remove government interference in people's private lives in such areas as abortion and pornography.
C) dismantle the welfare state and shrink the size of the federal government.
D) transfer welfare programs to the states.
E) reform public education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the 1980s, for the first time in the twentieth century
A) income gaps widened between the richest and the poorest Americans.
B) middle-class incomes rose.
C) the poor made economic gains.
D) the economy was uniformly healthy.
E) the majority of Americans were middle class.
A) income gaps widened between the richest and the poorest Americans.
B) middle-class incomes rose.
C) the poor made economic gains.
D) the economy was uniformly healthy.
E) the majority of Americans were middle class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Conservative Democrats who helped Ronald Reagan to pass his budget and tax-cutting legislation were called
A) blue dogs.
B) sagebrush rebels.
C) scalawags.
D) neoconservatives.
E) boll weevils.
A) blue dogs.
B) sagebrush rebels.
C) scalawags.
D) neoconservatives.
E) boll weevils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of these is NOT a true statement about yuppies?
A) "Yuppies" was a nickname for young, urban professionals in the 1980s.
B) Yuppies symbolized the new income stratification in America.
C) Yuppies were known for their materialism and conspicuous consumption.
D) Yuppies showcased the pursuit of wealth that symbolized the 1980s.
E) Yuppies represented the largest group of working Americans in the 1980s.
A) "Yuppies" was a nickname for young, urban professionals in the 1980s.
B) Yuppies symbolized the new income stratification in America.
C) Yuppies were known for their materialism and conspicuous consumption.
D) Yuppies showcased the pursuit of wealth that symbolized the 1980s.
E) Yuppies represented the largest group of working Americans in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
To President Reagan, "the focus of evil in the modern world" was
A) anti-American terrorists.
B) the federal bureaucracy.
C) political liberalism.
D) the Soviet Union.
E) communist China.
A) anti-American terrorists.
B) the federal bureaucracy.
C) political liberalism.
D) the Soviet Union.
E) communist China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Before being elected president, Ronald Reagan's experience in elected public office had been as
A) senator from California.
B) governor of California.
C) Orange County, California, supervisor.
D) governor of Nevada.
E) U.S. representative from California.
A) senator from California.
B) governor of California.
C) Orange County, California, supervisor.
D) governor of Nevada.
E) U.S. representative from California.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Ronald Reagan was similar to Franklin D. Roosevelt in that both men
A) disliked big business.
B) championed the common man against vast, impersonal menaces.
C) were raised in wealthy families.
D) favored social engineering by the government.
E) had run for vice president before being elected president.
A) disliked big business.
B) championed the common man against vast, impersonal menaces.
C) were raised in wealthy families.
D) favored social engineering by the government.
E) had run for vice president before being elected president.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For the Soviet Union's new policies of Glasnost (openness) and Perestroika (restructuring) to work, it was essential that the
A) Soviets keep control of Eastern Europe.
B) Communist Party engage in democratic competition.
C) United States and Western Europe sign free trade agreements with the Soviet Union.
D) United States send economic and food aid to the Soviet Union.
E) Cold War end.
A) Soviets keep control of Eastern Europe.
B) Communist Party engage in democratic competition.
C) United States and Western Europe sign free trade agreements with the Soviet Union.
D) United States send economic and food aid to the Soviet Union.
E) Cold War end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The only two places not swept by Ronald Reagan in his 1984 electoral landslide over former vice president Walter Mondale were
A) Washington State and Hawaii.
B) Minnesota and Wisconsin.
C) Massachusetts and Vermont.
D) Minnesota and the District of Columbia.
E) New York and New Jersey.
A) Washington State and Hawaii.
B) Minnesota and Wisconsin.
C) Massachusetts and Vermont.
D) Minnesota and the District of Columbia.
E) New York and New Jersey.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
One consequence of the record-high deficits and high interest rates of the 1980s was
A) lower energy costs.
B) growing productivity in manufacturing.
C) a soaring value for the dollar.
D) a general demand to raise taxes.
E) new capital investment.
A) lower energy costs.
B) growing productivity in manufacturing.
C) a soaring value for the dollar.
D) a general demand to raise taxes.
E) new capital investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Ronald Reagan's supply side economic advisers assured him that the combination of budgetary discipline and tax reduction would do all of the following except
A) stimulate new investment.
B) deplete overall tax revenues for the federal government.
C) boost productivity.
D) foster dramatic economic growth.
E) reduce the federal budget deficit.
A) stimulate new investment.
B) deplete overall tax revenues for the federal government.
C) boost productivity.
D) foster dramatic economic growth.
E) reduce the federal budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Despite his failure in the White House, President Jimmy Carter earned widespread admiration in his post-presidential years for his
A) foreign policy speeches.
B) political influence in the Democratic party.
C) humanitarian and human rights activities.
D) advocacy of women's rights.
E) refusal to comment critically on political matters involving his presidential successors.
A) foreign policy speeches.
B) political influence in the Democratic party.
C) humanitarian and human rights activities.
D) advocacy of women's rights.
E) refusal to comment critically on political matters involving his presidential successors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The strong tax revolt against extensive government programs and spending was spurred by the passage of Proposition 13 that severely limited property taxes in
A) Arizona.
B) Wisconsin.
C) New Hampshire.
D) California.
E) Oregon.
A) Arizona.
B) Wisconsin.
C) New Hampshire.
D) California.
E) Oregon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Besides cutting the federal budget, Reagan's other main domestic initiative when he took office was
A) developing new programs to aid business.
B) expanding federally funded social programs.
C) making substantial reductions in marginal tax rates over a period of three years.
D) privatizing the Social Security system.
E) eliminating government regulation of food and drugs.
A) developing new programs to aid business.
B) expanding federally funded social programs.
C) making substantial reductions in marginal tax rates over a period of three years.
D) privatizing the Social Security system.
E) eliminating government regulation of food and drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The first woman to receive the vice-presidential nomination of a major political party was
A) Elizabeth Dole.
B) Sandra Day O'Connor.
C) Jeanne Kirkpatrick.
D) Geraldine Ferraro.
E) Janet Reno.
A) Elizabeth Dole.
B) Sandra Day O'Connor.
C) Jeanne Kirkpatrick.
D) Geraldine Ferraro.
E) Janet Reno.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The first results of Reagan's supply-side economics in 1982 were a(n)
A) sharp recession and rise in unemployment.
B) reduced federal deficit.
C) expansion of international trade.
D) economic boom.
E) wave of new business investment.
A) sharp recession and rise in unemployment.
B) reduced federal deficit.
C) expansion of international trade.
D) economic boom.
E) wave of new business investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Ronald Reagan began to abandon his liberal New Deal political philosophy and to espouse a conservative, anti-government line
A) after being elected governor of California.
B) during World War II.
C) when he discovered communist infiltration in Hollywood.
D) when he decided to challenge President Gerald Ford for the Republican presidential nomination in 1976.
E) when he became a spokesman for General Electric.
A) after being elected governor of California.
B) during World War II.
C) when he discovered communist infiltration in Hollywood.
D) when he decided to challenge President Gerald Ford for the Republican presidential nomination in 1976.
E) when he became a spokesman for General Electric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the these social issues was not an important concern that the New Right hoped to constrict or eliminate through legal action?
A) Divorce
B) Pornography
C) Homosexuality
D) Abortion
E) Affirmative action
A) Divorce
B) Pornography
C) Homosexuality
D) Abortion
E) Affirmative action

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In contrast to the Old Right, many New Right activists of the 1980s were most concerned about
A) cultural and social issues.
B) laissez-faire economics.
C) foreign policy.
D) the environment.
E) health care.
A) cultural and social issues.
B) laissez-faire economics.
C) foreign policy.
D) the environment.
E) health care.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 120 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



