Deck 4: Speciation and Phylogeny
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Speciation and Phylogeny
1
________ occurs when members of a given group of organisms do NOT successfully mate with organisms of the same species outside of their group.
A) Monogamy
B) Gene flow
C) Reproductive isolation
D) Microevolution
A) Monogamy
B) Gene flow
C) Reproductive isolation
D) Microevolution
C
2
The existence of asexual species provides evidence that
A) species can be maintained through the biological species concept.
B) species can be maintained through the ecological species concept.
C) macroevolution is a stronger force than microevolution.
D) microevolution is a stronger force than macroevolution.
A) species can be maintained through the biological species concept.
B) species can be maintained through the ecological species concept.
C) macroevolution is a stronger force than microevolution.
D) microevolution is a stronger force than macroevolution.
B
3
Allopatric speciation occurs when
A) gene flow is maintained between two subgroups of a mother population.
B) two morphologically different subgroups of a species share the same habitat.
C) gene flow prevents genetic variants from being exchanged between subgroups.
D) a subgroup is physically isolated from the mother population and gene flow can no longer occur.
A) gene flow is maintained between two subgroups of a mother population.
B) two morphologically different subgroups of a species share the same habitat.
C) gene flow prevents genetic variants from being exchanged between subgroups.
D) a subgroup is physically isolated from the mother population and gene flow can no longer occur.
D
4
Imagine a scenario where a lake dries up enough to become two separate lakes, dividing a population of fish into two daughter populations. This is an example of
A) allopatric speciation.
B) sympatric speciation.
C) both allopatric and sympatric speciation.
D) neither allopatric or sympatric speciation.
A) allopatric speciation.
B) sympatric speciation.
C) both allopatric and sympatric speciation.
D) neither allopatric or sympatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Sympatric speciation occurs when two populations
A) experience different mutations.
B) living in the same location experience different selection pressures.
C) form fertile hybrids.
D) are physically separated from each other.
A) experience different mutations.
B) living in the same location experience different selection pressures.
C) form fertile hybrids.
D) are physically separated from each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The biological species concept emphasizes
A) genetic drift within populations.
B) gene flow between populations.
C) the importance of mutations.
D) that the amount of genetic information that is exchanged within a population rarely changes.
A) genetic drift within populations.
B) gene flow between populations.
C) the importance of mutations.
D) that the amount of genetic information that is exchanged within a population rarely changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is NOT a reason that reproductive isolation occurs?
A) An increase in a population's size
B) Variation in a species' courtship behavior
C) Restriction in a population's habitat
D) Variation in individual's activity patterns
A) An increase in a population's size
B) Variation in a species' courtship behavior
C) Restriction in a population's habitat
D) Variation in individual's activity patterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following does the ecological species concept emphasize?
A) The importance of allopatry between species
B) The importance of gene flow within species
C) The importance of sympatry within species
D) The importance of selection pressures
A) The importance of allopatry between species
B) The importance of gene flow within species
C) The importance of sympatry within species
D) The importance of selection pressures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
According to the biological species concept, a species is a group of organisms that
A) share morphology.
B) share the same geographical and environmental circumstances.
C) are reproductively isolated from other like groups.
D) share genetic information.
A) share morphology.
B) share the same geographical and environmental circumstances.
C) are reproductively isolated from other like groups.
D) share genetic information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Allopatric speciation can involve
A) recolonization without reproductive isolation.
B) gene flow.
C) genetic drift.
D) sharing habitat.
A) recolonization without reproductive isolation.
B) gene flow.
C) genetic drift.
D) sharing habitat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Character displacement is a process
A) that occurs when the morphology of two populations diverges.
B) of speciation involving gene flow.
C) of speciation involving genetic drift.
D) that can occur when hybrids are formed.
A) that occurs when the morphology of two populations diverges.
B) of speciation involving gene flow.
C) of speciation involving genetic drift.
D) that can occur when hybrids are formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Why are biologists uncertain about how a species should be defined?
A) Biologists have not incorporated behavior into species' definitions.
B) Biologists do not know how reproductive isolation happens.
C) Biologists are uncertain of how new species arise and how established species are maintained.
D) Biologists have not figured out how to use DNA data to determine species' status.
A) Biologists have not incorporated behavior into species' definitions.
B) Biologists do not know how reproductive isolation happens.
C) Biologists are uncertain of how new species arise and how established species are maintained.
D) Biologists have not figured out how to use DNA data to determine species' status.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On the Galápagos Islands, natural selection pressures maintain the boundaries between three species even though there is substantial gene flow between them. This example provides evidence that
A) neither the biological nor the ecological species concept applies to all situations.
B) multiple genes influence beak size.
C) these three species should be classified as a single species.
D) the medium ground finch (Geospiza fortis) has the optimal beak size.
A) neither the biological nor the ecological species concept applies to all situations.
B) multiple genes influence beak size.
C) these three species should be classified as a single species.
D) the medium ground finch (Geospiza fortis) has the optimal beak size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
During allopatric speciation, ________ may amplify the initial differences between populations and lead to two new species.
A) microevolution and asexual reproduction
B) reinforcement and character displacement
C) blending and macroevolution
D) phylogeny and disequilibrium
A) microevolution and asexual reproduction
B) reinforcement and character displacement
C) blending and macroevolution
D) phylogeny and disequilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
According to the ecological species concept, a species is a group of organisms that
A) share morphology.
B) are reproductively isolated from other like groups.
C) share genetic information.
D) share the same geographical and environmental circumstances.
A) share morphology.
B) are reproductively isolated from other like groups.
C) share genetic information.
D) share the same geographical and environmental circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Macroevolution is
A) the formation of new species.
B) the death of individuals.
C) evolutionary change within a species.
D) the extinction of a species.
A) the formation of new species.
B) the death of individuals.
C) evolutionary change within a species.
D) the extinction of a species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Microevolution is
A) the formation of new species.
B) the extinction of a species.
C) evolutionary change within a species.
D) the death of individuals.
A) the formation of new species.
B) the extinction of a species.
C) evolutionary change within a species.
D) the death of individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
According to the biological species concept, species remain the same because
A) new mutations are usually maladaptive.
B) environments change slowly.
C) gene flow keeps individuals similar to each other.
D) natural selection is a powerful process.
A) new mutations are usually maladaptive.
B) environments change slowly.
C) gene flow keeps individuals similar to each other.
D) natural selection is a powerful process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the ecological species concept, individuals within a species remain similar to each other because
A) individuals in the same environment experience similar natural selection pressures.
B) lack of gene flow prevents the mixing of genes.
C) individuals in the same population share DNA.
D) individuals in the same environment sometimes experience different selection pressures.
A) individuals in the same environment experience similar natural selection pressures.
B) lack of gene flow prevents the mixing of genes.
C) individuals in the same population share DNA.
D) individuals in the same environment sometimes experience different selection pressures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Sympatric speciation involves
A) natural selection.
B) lack of gene flow.
C) a mother population divided into two physically separated populations.
D) genetic drift.
A) natural selection.
B) lack of gene flow.
C) a mother population divided into two physically separated populations.
D) genetic drift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Parapatric speciation occurs when
A) selection causes a single species to develop different adaptations to a similar environment.
B) a population is divided into two reproductively isolated subgroups that form separate species.
C) a single species experiences a gradient of environmental differences within its geographic range, which result in reproductive isolation.
D) a formerly isolated subpopulation recolonizes its home range and mates with the remaining individuals.
A) selection causes a single species to develop different adaptations to a similar environment.
B) a population is divided into two reproductively isolated subgroups that form separate species.
C) a single species experiences a gradient of environmental differences within its geographic range, which result in reproductive isolation.
D) a formerly isolated subpopulation recolonizes its home range and mates with the remaining individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
________ speciation occurs when selection causes a single species to develop different adaptations to a similar environment.
A) Allopatric
B) Sympatric
C) Parapatric
D) Peripatric
A) Allopatric
B) Sympatric
C) Parapatric
D) Peripatric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Homologous characters are similar because of
A) convergent evolution.
B) similar selection pressures acting on unrelated species.
C) common ancestry.
D) similar environments in different parts of the world.
A) convergent evolution.
B) similar selection pressures acting on unrelated species.
C) common ancestry.
D) similar environments in different parts of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Adaptive radiation occurs when
A) a mutation caused by solar radiation produces adaptations.
B) a population expands across a uniform habitat.
C) multiple new species are produced because subpopulations adapt to new environments.
D) a species loses adaptations through mutation.
A) a mutation caused by solar radiation produces adaptations.
B) a population expands across a uniform habitat.
C) multiple new species are produced because subpopulations adapt to new environments.
D) a species loses adaptations through mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When scientists use phylogenies to name species and classify them into hierarchical categories, they create
A) systematics.
B) taxonomies.
C) macroevolution.
D) character displacement.
A) systematics.
B) taxonomies.
C) macroevolution.
D) character displacement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Closely related species are similar to each other because they
A) share a recent common ancestor.
B) have converged on some functional characteristic, such as flight.
C) live in close proximity to one another.
D) live in similar environments all over the world.
A) share a recent common ancestor.
B) have converged on some functional characteristic, such as flight.
C) live in close proximity to one another.
D) live in similar environments all over the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Scientists use ________ to construct phylogenies.
A) systematics
B) taphonomy
C) macroevolution
D) character displacement
A) systematics
B) taphonomy
C) macroevolution
D) character displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Analogous characters are similar because of
A) similar DNA.
B) similar selection pressures acting on unrelated species.
C) common ancestry.
D) similar mutations.
A) similar DNA.
B) similar selection pressures acting on unrelated species.
C) common ancestry.
D) similar mutations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A phylogeny
A) reflects developmental stages.
B) can only be used for closely related species.
C) reflects the evolutionary history of living species.
D) does not help us understand evolutionary events.
A) reflects developmental stages.
B) can only be used for closely related species.
C) reflects the evolutionary history of living species.
D) does not help us understand evolutionary events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Consider species A, B, and C, who share a knuckle-walking common ancestor. Species A and B are bipedal. Species C is a knuckle walker. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
A) A and B are more closely related to each other than to C.
B) A and C are more closely related to each other than to B.
C) C and B are more closely related to each other than to A.
D) There is not enough information to determine the most likely relationship.
A) A and B are more closely related to each other than to C.
B) A and C are more closely related to each other than to B.
C) C and B are more closely related to each other than to A.
D) There is not enough information to determine the most likely relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Different species of baboons live all over Africa in very diverse habitats. This is an example of ________ speciation.
A) non-Darwinian
B) parapatric
C) sympatric
D) allopatric
A) non-Darwinian
B) parapatric
C) sympatric
D) allopatric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A hybrid zone
A) provides evidence for allopatric speciation.
B) sometimes contains individuals that are less fit than those outside of hybrid zones.
C) sometimes contains adaptive radiations.
D) provides evidence for the ecological species concept.
A) provides evidence for allopatric speciation.
B) sometimes contains individuals that are less fit than those outside of hybrid zones.
C) sometimes contains adaptive radiations.
D) provides evidence for the ecological species concept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Ancestral characters are traits that
A) characterize the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
B) evolved after the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
C) are less well suited to the environment than derived characters.
D) are less specialized than derived characters.
A) characterize the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
B) evolved after the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
C) are less well suited to the environment than derived characters.
D) are less specialized than derived characters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In order to conduct a meaningful comparative analysis, a researcher must
A) not take phylogeny into account.
B) only compare behavioral features.
C) only use independently evolved features.
D) compare absolutely everything about two taxa.
A) not take phylogeny into account.
B) only compare behavioral features.
C) only use independently evolved features.
D) compare absolutely everything about two taxa.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Adaptive radiations are associated with
A) macroevolution.
B) microevolution.
C) taxonomy.
D) systematics.
A) macroevolution.
B) microevolution.
C) taxonomy.
D) systematics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Closely related species are more similar to each other than they are to distantly related species for all of the following reasons EXCEPT
A) they share a more recent common ancestor than distantly related species.
B) distantly related species have had interrupted gene flow for a longer period of time.
C) distantly related species have had a longer time for independent evolution.
D) they have experienced more similar selection pressures than distantly related species.
A) they share a more recent common ancestor than distantly related species.
B) distantly related species have had interrupted gene flow for a longer period of time.
C) distantly related species have had a longer time for independent evolution.
D) they have experienced more similar selection pressures than distantly related species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
At the end of the Cretaceous era, mammals diversified to fill a broad range of ecological niches. This is an example of
A) reinforcement.
B) hybrid zones.
C) phylogeny.
D) adaptive radiation.
A) reinforcement.
B) hybrid zones.
C) phylogeny.
D) adaptive radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Derived characters are traits that
A) characterize the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
B) evolved after the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
C) are less well suited to the environment than ancestral characters.
D) are more complicated than ancestral characters.
A) characterize the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
B) evolved after the last common ancestor that a particular collection of species share.
C) are less well suited to the environment than ancestral characters.
D) are more complicated than ancestral characters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following amino acid sequence for three different species, A, B, and C. Each number is a different amino acid. The letter in each cell depicts the nitrogenous base that is associated with each amino acid. Which two species are most closely related based on this part of the genome? 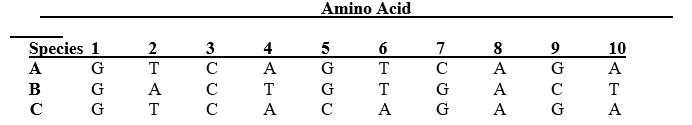
A) Species A and C are most closely related.
B) Species A and B are most closely related.
C) Species B and C are most closely related.
D) All three species are equally related.

A) Species A and C are most closely related.
B) Species A and B are most closely related.
C) Species B and C are most closely related.
D) All three species are equally related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When daughter species first diverge from each other, they are most likely to differ in
A) morphological traits.
B) traits related to making a living or choosing mates.
C) features of their genome.
D) traits related to their life histories.
A) morphological traits.
B) traits related to making a living or choosing mates.
C) features of their genome.
D) traits related to their life histories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following can be used to determine whether a character is ancestral or derived?
A) The molecular clock
B) In-group comparison
C) The fossil record
D) Convergent characters
A) The molecular clock
B) In-group comparison
C) The fossil record
D) Convergent characters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Compare and contrast cladistic and evolutionary systematics. Illustrate your answer by discussing the phylogeny of apes and humans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Evolutionary taxonomy uses
A) only morphological similarity to classify organisms.
B) only descent to classify organisms.
C) both similarity and descent to classify organisms.
D) neither similarity nor descent to classify organisms.
A) only morphological similarity to classify organisms.
B) only descent to classify organisms.
C) both similarity and descent to classify organisms.
D) neither similarity nor descent to classify organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Give a hypothetical example of allopatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the biological species concept? Under what circumstances is this concept difficult to apply?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How do genetic distance measures work? How have genetic distance measurements been applied to the primate fossil record to reveal information about the divergence of primate groups?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Proponents of the neutral theory
A) believe that most changes in DNA sequences produce clocklike change because they are controlled by drift and mutation.
B) think the molecular clock is a result of natural selection.
C) are not sure if we can accurately calculate how long ago two lineages diverged.
D) use only derived traits in their analysis.
A) believe that most changes in DNA sequences produce clocklike change because they are controlled by drift and mutation.
B) think the molecular clock is a result of natural selection.
C) are not sure if we can accurately calculate how long ago two lineages diverged.
D) use only derived traits in their analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain why shared ancestral characters do not yield good information about relationships between species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain the difference between ancestral and derived characters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the ecological species concept? Is it applicable to asexual species?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Give a hypothetical example of parapatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Cladistic systematics uses
A) only morphological similarity to classify organisms.
B) only descent to classify organisms.
C) both similarity and descent to classify organisms.
D) neither similarity nor descent to classify organisms.
A) only morphological similarity to classify organisms.
B) only descent to classify organisms.
C) both similarity and descent to classify organisms.
D) neither similarity nor descent to classify organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The observation that chickens and humans are bipedal but not part of the same taxonomic group is an example of
A) gene flow.
B) ancestry.
C) systematics.
D) convergent evolution.
A) gene flow.
B) ancestry.
C) systematics.
D) convergent evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Genetic distance data reveals that ________ are more genetically distant from humans than any of the other great apes.
A) gorillas
B) orangutans
C) chimpanzees
D) bonobos
A) gorillas
B) orangutans
C) chimpanzees
D) bonobos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How does speciation occur? After a speciation event, by what mechanisms do new species remain distinct?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain the difference between homologous and analogous characters. Which of these should be used in phylogenetic analysis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The limbs of all mammals contain three bones. This is an example of a(n) ________ trait.
A) analogous
B) derived
C) homologous
D) convergent
A) analogous
B) derived
C) homologous
D) convergent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Scientists should only use derived traits to construct phylogenies because
A) many fossil species retain only derived traits.
B) derived traits are under greater genetic control than are analogous and homologous traits.
C) all organisms have homologous traits.
D) analogous and homologous traits do not tell us anything about close phylogenetic relationships.
A) many fossil species retain only derived traits.
B) derived traits are under greater genetic control than are analogous and homologous traits.
C) all organisms have homologous traits.
D) analogous and homologous traits do not tell us anything about close phylogenetic relationships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider all three species of the genus Happy: the Eastern Mugwump, the Western Mugwump, and the Middle Mugwump. All of these species evolved from a six-legged common ancestor. The Eastern and Middle Mugwumps have six legs, and the Western Mugwumps have eight legs. For the genus Happy, six-leggedness is
A) ancestral.
B) derived.
C) convergent.
D) a mutation.
A) ancestral.
B) derived.
C) convergent.
D) a mutation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



