Deck 2: Production possibilities and opportunity cost
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Production possibilities and opportunity cost
1
Which fundamental economic question requires society to choose the technological and resource mix used to produce goods?
A)The 'What to produce?' question.
B)The 'Why produce?' question.
C)The 'How to produce?' question.
D)The 'For whom to produce?' question.
A)The 'What to produce?' question.
B)The 'Why produce?' question.
C)The 'How to produce?' question.
D)The 'For whom to produce?' question.
C
2
Marginal analysis is the effect of:
A)scarcity.
B)specialisation.
C)trade.
D)efficiency.
E)opportunity cost.
A)scarcity.
B)specialisation.
C)trade.
D)efficiency.
E)opportunity cost.
E
3
The production possibilities frontier shows that:
A)scarcity can be eliminated.
B)all output combinations are possible.
C)an economy that is operating efficiently can have more of one good without giving up some of another good.
D)some of one good must be given up to get more of another good in an economy that is operating efficiently.
A)scarcity can be eliminated.
B)all output combinations are possible.
C)an economy that is operating efficiently can have more of one good without giving up some of another good.
D)some of one good must be given up to get more of another good in an economy that is operating efficiently.
D
4
One of the assumptions underlying the production possibilities frontier or curve for any given economy is that:
A)the state of technology changes.
B)there is an unlimited supply of resources.
C)there is full employment of resources when the economy is on the curve.
D)goods can be produced outside the curve.
A)the state of technology changes.
B)there is an unlimited supply of resources.
C)there is full employment of resources when the economy is on the curve.
D)goods can be produced outside the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If Bruce pays $2000 in tuition fees to the college,what is his opportunity cost?
A)$2000 minus the income the student forgoes by attending school rather than working.
B)$2000.
C)the income the student forgoes by attending school rather than working plus his tuition fees.
D)there is no opportunity cost since Bruce chose to study rather than working.
A)$2000 minus the income the student forgoes by attending school rather than working.
B)$2000.
C)the income the student forgoes by attending school rather than working plus his tuition fees.
D)there is no opportunity cost since Bruce chose to study rather than working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A farmer is deciding whether or not to add fertiliser to his or her crops.If the farmer adds 1 kilogram of fertiliser per hectare,the value of the resulting crops rises from $80 to $100 per hectare.According to marginal analysis,the farmer should add fertiliser if it costs less than:
A)$12.50 per kilogram.
B)$20 per kilogram.
C)$80 per kilogram.
D)$100 per kilogram.
A)$12.50 per kilogram.
B)$20 per kilogram.
C)$80 per kilogram.
D)$100 per kilogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Bill has $10 that he can spend on a Superman action figure,a Batman graphic novel or an X-Men T-shirt.Bill decides to buy the action figure,even though the graphic novel was a close second choice.What is the opportunity cost of buying the action figure?
A)The amount he spends: $10.
B)Nothing, since he got his preferred choice.
C)The Batman graphic novel.
D)The X-Men T-shirt.
A)The amount he spends: $10.
B)Nothing, since he got his preferred choice.
C)The Batman graphic novel.
D)The X-Men T-shirt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The opportunity cost to a city for using local tax revenues to construct a new park is the:
A)best alternative foregone by building the park.
B)dollar cost of constructing the new park.
C)dollar cost of the old park.
D)increased taxes necessary to pay for maintenance of the new park.
A)best alternative foregone by building the park.
B)dollar cost of constructing the new park.
C)dollar cost of the old park.
D)increased taxes necessary to pay for maintenance of the new park.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The 'For whom to produce' question:
A)is irrelevant in economics.
B)means that society must ask whether government should override the market outcomes.
C)is the most important question in economics.
D)means that government should not intervene in market outcomes.
A)is irrelevant in economics.
B)means that society must ask whether government should override the market outcomes.
C)is the most important question in economics.
D)means that government should not intervene in market outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why must every nation answer the three fundamental economic questions?
A)Because of increased international trade and cooperation.
B)Because of the problem of scarcity.
C)Because rich nations must subsidise the development of poor nations.
D)Because some nations are more successful than others.
A)Because of increased international trade and cooperation.
B)Because of the problem of scarcity.
C)Because rich nations must subsidise the development of poor nations.
D)Because some nations are more successful than others.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following does not illustrate opportunity cost?
A)If I study, I must give up going to the movies.
B)If I buy a computer, I must do without an iPod.
C)The more I spend now means the more I spend in the future.
D)If I spend more on books, I must spend less on jewellery.
A)If I study, I must give up going to the movies.
B)If I buy a computer, I must do without an iPod.
C)The more I spend now means the more I spend in the future.
D)If I spend more on books, I must spend less on jewellery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The opportunity cost of watching television is:
A)the cost of not watching all other programs that appear on other stations.
B)unable to be estimated because there is no money expenditure involved.
C)the next best alternative you do instead of watching the program.
D)zero if it benefits you.
A)the cost of not watching all other programs that appear on other stations.
B)unable to be estimated because there is no money expenditure involved.
C)the next best alternative you do instead of watching the program.
D)zero if it benefits you.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All points along the production possibilities frontier are:
A)unattainable combinations of two goods.
B)minimum possible combinations of two goods.
C)efficient maximum possible combinations of two goods.
D)a combination of two goods given that not all available resources are used.
A)unattainable combinations of two goods.
B)minimum possible combinations of two goods.
C)efficient maximum possible combinations of two goods.
D)a combination of two goods given that not all available resources are used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The opportunity cost of watching a movie is the:
A)dollar cost of a movie ticket plus enjoyment from watching a movie.
B)dollar cost of a movie ticket.
C)alternatives foregone such as studying and fishing.
D)best alternative foregone such as studying.
A)dollar cost of a movie ticket plus enjoyment from watching a movie.
B)dollar cost of a movie ticket.
C)alternatives foregone such as studying and fishing.
D)best alternative foregone such as studying.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Mikki decides to work five hours the night before her economics exam.She earns an extra $75,but her exam score is 10 points lower than it would have been had she stayed home and studied.Her opportunity cost of working more is the:
A)five hours she worked.
B)$75 she earned.
C)10 points she lost on her exam.
D)time she could have spent watching television.
E)guilt she feels about neglecting her economics studies.
A)five hours she worked.
B)$75 she earned.
C)10 points she lost on her exam.
D)time she could have spent watching television.
E)guilt she feels about neglecting her economics studies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Production possibilities frontier analysis allows us to identify:
A)minimum possible combinations of goods and services.
B)ways to eliminate scarcity.
C)total benefits of production.
D)inefficient production.
A)minimum possible combinations of goods and services.
B)ways to eliminate scarcity.
C)total benefits of production.
D)inefficient production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would be most likely to cause the production possibilities frontier for trucks and movies to shift outward?
A)A choice of more trucks and less movies.
B)A choice of more movies and fewer trucks.
C)A reduction in the labour force.
D)An increase in the quantity of resources.
A)A choice of more trucks and less movies.
B)A choice of more movies and fewer trucks.
C)A reduction in the labour force.
D)An increase in the quantity of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 2-1 Production possibilities frontier data
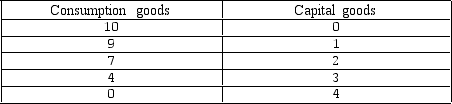
In Exhibit 2-1,the opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of capital goods is:
A)zero.
B)1 unit of consumption goods.
C)2 units of consumption goods.
D)4 units of consumption goods.
E)not determinable from the information given.

In Exhibit 2-1,the opportunity cost of producing the fourth unit of capital goods is:
A)zero.
B)1 unit of consumption goods.
C)2 units of consumption goods.
D)4 units of consumption goods.
E)not determinable from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 2-1 Production possibilities frontier data

In Exhibit 2-1,according to the information,the opportunity cost of producing 3 units of capital goods is:
A)3 units of consumption goods.
B)4 units of consumption goods.
C)6 units of consumption goods.
D)7 units of consumption goods.

In Exhibit 2-1,according to the information,the opportunity cost of producing 3 units of capital goods is:
A)3 units of consumption goods.
B)4 units of consumption goods.
C)6 units of consumption goods.
D)7 units of consumption goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Marginal analysis:
A)compares some benefits of a change with all the costs of the change.
B)compares total benefits of a change with total costs of the change.
C)examines the impact of changes from a current situation.
D)examines only the non-important issues.
A)compares some benefits of a change with all the costs of the change.
B)compares total benefits of a change with total costs of the change.
C)examines the impact of changes from a current situation.
D)examines only the non-important issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Efficient production means producing:
A)less than feasible output for a given amount of resources.
B)more than feasible output for a given amount of resources.
C)less than what is needed.
D)the maximum feasible output for a given amount of resources.
E)in excess of what is needed.
A)less than feasible output for a given amount of resources.
B)more than feasible output for a given amount of resources.
C)less than what is needed.
D)the maximum feasible output for a given amount of resources.
E)in excess of what is needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the opportunity cost of producing laptops increases as more laptops are produced,then:
A)no more laptops will be produced.
B)resources are equally suited to the production of laptops and to other goods.
C)the production possibilities frontier is a straight line.
D)the production possibilities frontier becomes positively sloped.
E)the law of increasing costs is present.
A)no more laptops will be produced.
B)resources are equally suited to the production of laptops and to other goods.
C)the production possibilities frontier is a straight line.
D)the production possibilities frontier becomes positively sloped.
E)the law of increasing costs is present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A production possibility graph slopes down because of:
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)non-homogeneous resources.
C)inefficiency.
D)an improper output mix.
E)unemployment.
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)non-homogeneous resources.
C)inefficiency.
D)an improper output mix.
E)unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If an economy is producing at full employment,it means that:
A)there are idle resources in this economy.
B)production is not efficient.
C)the economy is operating at maximum technical and economic efficiency at this point of time.
D)the economy is producing at a point that is to the left of the production possibilities curve.
E)the economy is producing at a point that is to the right of the production possibilities curve.
A)there are idle resources in this economy.
B)production is not efficient.
C)the economy is operating at maximum technical and economic efficiency at this point of time.
D)the economy is producing at a point that is to the left of the production possibilities curve.
E)the economy is producing at a point that is to the right of the production possibilities curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A point outside a production possibilities curve reflects:
A)efficiency.
B)specialisation.
C)inefficiency.
D)unemployment.
E)an impossible choice.
A)efficiency.
B)specialisation.
C)inefficiency.
D)unemployment.
E)an impossible choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 2-2 Production possibilities frontier
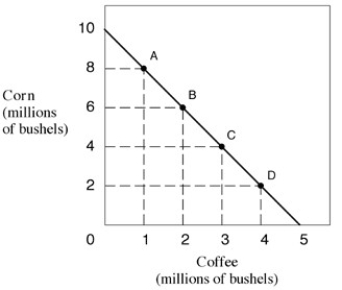
In Exhibit 2-2,the opportunity cost of coffee when moving from A to B is:
A)2 million bushels of corn.
B)6 million bushels of corn.
C)8 million bushels of corn.
D)14 million bushels of corn.
E)not possible to determine.

In Exhibit 2-2,the opportunity cost of coffee when moving from A to B is:
A)2 million bushels of corn.
B)6 million bushels of corn.
C)8 million bushels of corn.
D)14 million bushels of corn.
E)not possible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is true about a production possibilities curve? The curve:
A)indicates which production point will be chosen.
B)indicates only the efficient production points.
C)indicates how to eliminate scarcity.
D)indicates the feasible and non-feasible production points.
A)indicates which production point will be chosen.
B)indicates only the efficient production points.
C)indicates how to eliminate scarcity.
D)indicates the feasible and non-feasible production points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Along a production possibilities curve showing capital and consumption goods production,which of the following pairs are being held fixed?
A)Unemployment and capital goods production.
B)Number of resources and consumption goods production.
C)Composition of the economy's output and number of resources.
D)Capital and consumption goods production.
E)Technology and number of resources.
A)Unemployment and capital goods production.
B)Number of resources and consumption goods production.
C)Composition of the economy's output and number of resources.
D)Capital and consumption goods production.
E)Technology and number of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When an economy's resources are not fully employed,then it must be true that the:
A)production point is located outside and to the right of the production possibilities frontier.
B)production point is located along the production possibilities frontier.
C)production point is located inside and to the left of the production possibilities frontier.
D)production possibilities frontier shifts to the right.
E)production possibilities frontier shifts to the left.
A)production point is located outside and to the right of the production possibilities frontier.
B)production point is located along the production possibilities frontier.
C)production point is located inside and to the left of the production possibilities frontier.
D)production possibilities frontier shifts to the right.
E)production possibilities frontier shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The law of increasing costs indicates that the opportunity cost of producing a good:
A)is proportional to the production of the good.
B)is constant to the production of the good.
C)increases as more of the good is produced.
D)decreases as more of the good is produced.
E)increases as less of the good is produced.
A)is proportional to the production of the good.
B)is constant to the production of the good.
C)increases as more of the good is produced.
D)decreases as more of the good is produced.
E)increases as less of the good is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A production possibilities frontier shows the various:
A)combinations of resources the economy has the capacity to produce.
B)prices that can be charged for capital and consumption goods.
C)combinations of prices and outputs that can be produced.
D)combinations of goods the economy has the capacity to produce.
E)combinations of resources and prices that the economy can produce.
A)combinations of resources the economy has the capacity to produce.
B)prices that can be charged for capital and consumption goods.
C)combinations of prices and outputs that can be produced.
D)combinations of goods the economy has the capacity to produce.
E)combinations of resources and prices that the economy can produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not true about a production possibilities curve? The curve:
A)indicates the combinations of goods and services that can be produced with given technology.
B)indicates the efficient production points.
C)indicates the non-efficient production points.
D)indicates the feasible and non-feasible production points.
E)indicates which production point will be chosen.
A)indicates the combinations of goods and services that can be produced with given technology.
B)indicates the efficient production points.
C)indicates the non-efficient production points.
D)indicates the feasible and non-feasible production points.
E)indicates which production point will be chosen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A point outside a production possibilities curve reflects:
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)future technological innovation.
C)less than full use of resources and technology.
D)economic efficiency.
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)future technological innovation.
C)less than full use of resources and technology.
D)economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 2-2 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-2,the opportunity cost of coffee when moving from B to C is:
A)2 million bushels of corn.
B)6 million bushels of corn.
C)8 million bushels of corn.
D)14 million bushels of corn.
E)not possible to determine.

In Exhibit 2-2,the opportunity cost of coffee when moving from B to C is:
A)2 million bushels of corn.
B)6 million bushels of corn.
C)8 million bushels of corn.
D)14 million bushels of corn.
E)not possible to determine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Exhibit 2-2 Production possibilities frontier

The production possibilities in Exhibit 2-2 indicates that the opportunity cost of corn is:
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)does not change.
D)zero.
E)indeterminate.

The production possibilities in Exhibit 2-2 indicates that the opportunity cost of corn is:
A)increasing.
B)decreasing.
C)does not change.
D)zero.
E)indeterminate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The production possibilities frontier illustrates all of the following concepts except:
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)unlimited wants.
C)scarcity.
D)opportunity cost.
E)availability of resources.
A)the law of increasing costs.
B)unlimited wants.
C)scarcity.
D)opportunity cost.
E)availability of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The production possibilities frontier shows different combinations of two goods:
A)that are able to be produced at a particular point of time with underemployment.
B)that are able to be produced at a particular point of time with resources available.
C)that are able to be produced with technology available in the future.
D)that will be produced at a particular point of time with or without full employment .
A)that are able to be produced at a particular point of time with underemployment.
B)that are able to be produced at a particular point of time with resources available.
C)that are able to be produced with technology available in the future.
D)that will be produced at a particular point of time with or without full employment .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The production possibilities frontier demonstrates the basic economic principle that:
A)market-based economies are more efficient.
B)supply will determine demand in the economy.
C)the production of more capital goods this year will cause the economy to produce fewer consumption goods next year.
D)to produce more of any one thing, assuming full employment, the economy must produce less of something else.
E)to produce more consumption goods this year requires the production of more capital goods this year.
A)market-based economies are more efficient.
B)supply will determine demand in the economy.
C)the production of more capital goods this year will cause the economy to produce fewer consumption goods next year.
D)to produce more of any one thing, assuming full employment, the economy must produce less of something else.
E)to produce more consumption goods this year requires the production of more capital goods this year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Inefficient production occurs:
A)at any point inside the production possibilities curve.
B)at any point along the production possibilities curve.
C)at any point outside the production possibilities curve.
D)at a point that cannot be determined.
A)at any point inside the production possibilities curve.
B)at any point along the production possibilities curve.
C)at any point outside the production possibilities curve.
D)at a point that cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Exhibit 2-2 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-2,what is the maximum possible production of coffee if production of corn has decreased from 4 to 2 million bushels:
A)0 millions of bushels.
B)2 millions of bushels.
C)5 millions of bushels.
D)4 millions of bushels.

In Exhibit 2-2,what is the maximum possible production of coffee if production of corn has decreased from 4 to 2 million bushels:
A)0 millions of bushels.
B)2 millions of bushels.
C)5 millions of bushels.
D)4 millions of bushels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Exhibit 2-6 Production possibilities frontier data
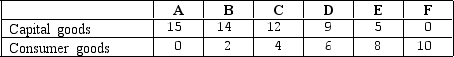
As shown in Exhibit 2-6,a total output of zero units of capital goods and 10 units of consumer goods is:
A)the maximum rate of output for this economy.
B)an inefficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)the result of maximum use of the economy's labour force.
D)unobtainable in this economy.

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,a total output of zero units of capital goods and 10 units of consumer goods is:
A)the maximum rate of output for this economy.
B)an inefficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)the result of maximum use of the economy's labour force.
D)unobtainable in this economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 2-3 Production possibilities curve data
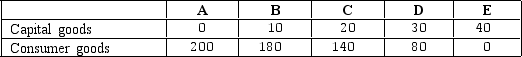
According to the data in Exhibit 2-3,a total output of 140 units of consumer goods and 10 units of capital goods would:
A)be unobtainable in this economy.
B)be an efficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)result in the maximum use of the economy's labour force.
D)result in underemployment.

According to the data in Exhibit 2-3,a total output of 140 units of consumer goods and 10 units of capital goods would:
A)be unobtainable in this economy.
B)be an efficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)result in the maximum use of the economy's labour force.
D)result in underemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The production possibility curve is bowed outward from the origin because of:
A)the law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)the finite nature of the resource base.
C)inefficiency.
D)an improper output mix.
E)unemployment.
A)the law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)the finite nature of the resource base.
C)inefficiency.
D)an improper output mix.
E)unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The production possibilities curve is:
A)convex to the origin and bowed inwards.
B)concave to the origin and bowed outwards.
C)concave to the origin and bowed inwards.
D)convex to the origin and bowed outwards.
A)convex to the origin and bowed inwards.
B)concave to the origin and bowed outwards.
C)concave to the origin and bowed inwards.
D)convex to the origin and bowed outwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 2-3 Production possibilities curve data

According to the data given in Exhibit 2-3,the production of 140 units of consumer goods and 30 units of capital goods:
A)is possible but would be inefficient.
B)may be a result of unemployment.
C)may be a result of unused natural resources.
D)is impossible.

According to the data given in Exhibit 2-3,the production of 140 units of consumer goods and 30 units of capital goods:
A)is possible but would be inefficient.
B)may be a result of unemployment.
C)may be a result of unused natural resources.
D)is impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Exhibit 2-6 Production possibilities frontier data

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,the concept of increasing opportunity costs is reflected in the fact that:
A)the quantity of consumer goods produced can never be zero.
B)the labour force in the economy is homogeneous.
C)greater amounts of capital goods must be sacrificed to produce an additional 2 units of consumer goods.
D)a graph of the production data is a downward-sloping straight line.

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,the concept of increasing opportunity costs is reflected in the fact that:
A)the quantity of consumer goods produced can never be zero.
B)the labour force in the economy is homogeneous.
C)greater amounts of capital goods must be sacrificed to produce an additional 2 units of consumer goods.
D)a graph of the production data is a downward-sloping straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 2-8 Production possibilities frontier data
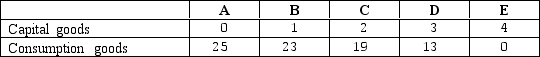
Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.As additional units of capital goods are being produced,the number of consumption goods produced must _____,because _____.
A)increase; the production possibility table shows only the maximum efficiency points
B)increase; of the law of increasing costs
C)decrease; of the law of decreasing costs
D)decrease; of the finite nature of the resource base
E)increase; capital goods will assist in the production of consumer goods

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.As additional units of capital goods are being produced,the number of consumption goods produced must _____,because _____.
A)increase; the production possibility table shows only the maximum efficiency points
B)increase; of the law of increasing costs
C)decrease; of the law of decreasing costs
D)decrease; of the finite nature of the resource base
E)increase; capital goods will assist in the production of consumer goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Exhibit 2-8 Production possibilities frontier data

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.The second unit of capital goods production will cost _____ units of consumption goods and the third unit of capital goods production will cost _____ units of consumption goods.
A)4; 6
B)25; 23
C)23; 19
D)1; 23
E)2; 19

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.The second unit of capital goods production will cost _____ units of consumption goods and the third unit of capital goods production will cost _____ units of consumption goods.
A)4; 6
B)25; 23
C)23; 19
D)1; 23
E)2; 19

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Exhibit 2-5 Production possibilities frontier
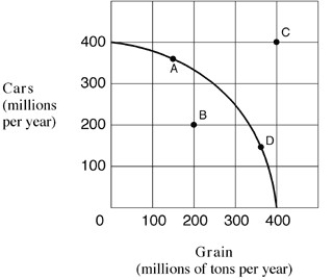
For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-5,which of the following is true when the economy is at point A?
A)Not enough grain is being produced.
B)There must be resources that are not being used fully.
C)If the economy reallocates resources from A to D, it has to sacrifice some car production.
D)Increased grain production would be impossible.

For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-5,which of the following is true when the economy is at point A?
A)Not enough grain is being produced.
B)There must be resources that are not being used fully.
C)If the economy reallocates resources from A to D, it has to sacrifice some car production.
D)Increased grain production would be impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 2-8 Production possibilities frontier data

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.The first unit of capital goods will cost the economy _____ units of consumption goods.
A)25
B)2
C)1
D)23
E)11

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.The first unit of capital goods will cost the economy _____ units of consumption goods.
A)25
B)2
C)1
D)23
E)11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The production possibility curve is bowed outward from the origin because of:
A)the law of decreasing opportunity costs.
B)the finite nature of the resource base.
C)inefficiency.
D)the changes in the opportunity cost due to different efficiencies of the same resource in different use.
E)unemployment.
A)the law of decreasing opportunity costs.
B)the finite nature of the resource base.
C)inefficiency.
D)the changes in the opportunity cost due to different efficiencies of the same resource in different use.
E)unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The law of increasing opportunity costs states that:
A)the opportunity cost cannot be determined when the economy operates on the production possibilities frontier.
B)people always prefer having more goods.
C)there is always full employment.
D)the opportunity cost increases as production of one output increases.
A)the opportunity cost cannot be determined when the economy operates on the production possibilities frontier.
B)people always prefer having more goods.
C)there is always full employment.
D)the opportunity cost increases as production of one output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 2-7 Production possibilities frontier
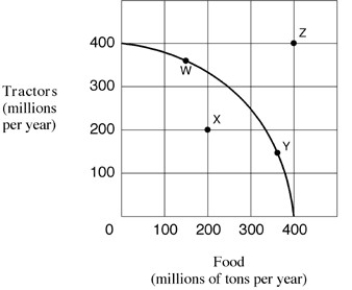
Which of the following moves from one point to another in Exhibit 2-7 would represent an increase in economic efficiency?
A)Z to W.
B)W to Y.
C)Z to X.
D)X to W.

Which of the following moves from one point to another in Exhibit 2-7 would represent an increase in economic efficiency?
A)Z to W.
B)W to Y.
C)Z to X.
D)X to W.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the production possibilities curve is bowed out,resources are:
A)equally well-suited to production of both goods.
B)not being used efficiently.
C)not equally suited to the production of both types of goods.
D)increasing as more of one good is produced.
E)of an inferior quality.
A)equally well-suited to production of both goods.
B)not being used efficiently.
C)not equally suited to the production of both types of goods.
D)increasing as more of one good is produced.
E)of an inferior quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 2-6 Production possibilities frontier data

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,if the economy reallocates resources from capital goods to consumer goods:
A)it gains extra units of capital goods due to technological progress.
B)it is an inefficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)it gains extra units of consumer goods but has to sacrifice units of capital goods.
D)it gains extra units of consumer goods without sacrificing units of capital goods.

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,if the economy reallocates resources from capital goods to consumer goods:
A)it gains extra units of capital goods due to technological progress.
B)it is an inefficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)it gains extra units of consumer goods but has to sacrifice units of capital goods.
D)it gains extra units of consumer goods without sacrificing units of capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 2-4 Production possibilities curve data
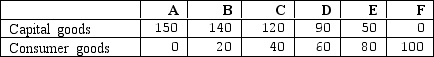
In Exhibit 2-4,the concept of increasing opportunity costs is represented by the fact that:
A)the quantity of capital goods produced must be less than 150.
B)the quantity of consumer goods is constant for each change in the quantity of capital goods produced.
C)greater amounts of capital goods must be sacrificed to produce each additional unit of consumer goods.
D)the amount of consumer goods produced must be greater than zero.

In Exhibit 2-4,the concept of increasing opportunity costs is represented by the fact that:
A)the quantity of capital goods produced must be less than 150.
B)the quantity of consumer goods is constant for each change in the quantity of capital goods produced.
C)greater amounts of capital goods must be sacrificed to produce each additional unit of consumer goods.
D)the amount of consumer goods produced must be greater than zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exhibit 2-7 Production possibilities frontier

Movement along the production possibilities curve shown in Exhibit 2-7 indicates:
A)The law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)The law of declining opportunity costs.
C)all inputs are homogeneous including labour.
D)that not all resources are utilised.

Movement along the production possibilities curve shown in Exhibit 2-7 indicates:
A)The law of increasing opportunity costs.
B)The law of declining opportunity costs.
C)all inputs are homogeneous including labour.
D)that not all resources are utilised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Exhibit 2-7 Production possibilities frontier

Unattainable combination Z shown in Exhibit 2-7:
A)may be achieved by investing in research and development.
B)can be achieved with using more of existing resources.
C)will never be achieved.
D)can easily be achieved by having full employment .

Unattainable combination Z shown in Exhibit 2-7:
A)may be achieved by investing in research and development.
B)can be achieved with using more of existing resources.
C)will never be achieved.
D)can easily be achieved by having full employment .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 2-5 Production possibilities frontier

For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-5 to operate at point C,it must:
A)be willing to lower the price of grain.
B)use its given resources more efficiently than it would at point A
C)experience underemployment.
D)experience an increase in its resources and/or an improvement in its technology.

For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-5 to operate at point C,it must:
A)be willing to lower the price of grain.
B)use its given resources more efficiently than it would at point A
C)experience underemployment.
D)experience an increase in its resources and/or an improvement in its technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Exhibit 2-6 Production possibilities frontier data

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,a total output of 6 units of consumer goods and 5 units of capital goods is:
A)the result of maximum use of the economy's labour force.
B)an efficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)unobtainable in this economy.
D)less than the maximum rate of output for this economy.

As shown in Exhibit 2-6,a total output of 6 units of consumer goods and 5 units of capital goods is:
A)the result of maximum use of the economy's labour force.
B)an efficient way of using the economy's scarce resources.
C)unobtainable in this economy.
D)less than the maximum rate of output for this economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Technological innovations will cause:
A)the production possibilities curve to stay the same.
B)the production possibilities curve to shift to the left.
C)the production possibilities curve to shift to the right.
D)an economy to operate below its production possibilities curve.
E)the production possibilities curve to increase or decrease.
A)the production possibilities curve to stay the same.
B)the production possibilities curve to shift to the left.
C)the production possibilities curve to shift to the right.
D)an economy to operate below its production possibilities curve.
E)the production possibilities curve to increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The production possibilities curve for the nation of Economania shifts to the right.This could have been caused by:
A)a decrease in Economania's capital stock.
B)a decrease in Economania's labour supply.
C)high unemployment in Economania for the previous time period.
D)Economania producing all consumer goods in the previous period.
E)improvement in the health and skill level of Economania's workforce.
A)a decrease in Economania's capital stock.
B)a decrease in Economania's labour supply.
C)high unemployment in Economania for the previous time period.
D)Economania producing all consumer goods in the previous period.
E)improvement in the health and skill level of Economania's workforce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Robinson Crusoe's decision to produce more capital goods and fewer consumer goods in a given period causes:
A)a decrease in the resources available in the economy.
B)a decrease in the ability to produce goods in the next period.
C)a decrease in economic growth in future periods.
D)no change in the availability of resources in the economy.
E)an increase in economic growth in future periods.
A)a decrease in the resources available in the economy.
B)a decrease in the ability to produce goods in the next period.
C)a decrease in economic growth in future periods.
D)no change in the availability of resources in the economy.
E)an increase in economic growth in future periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Law of increasing opportunity cost states:
A)that opportunity cost decreases as production of one output expands.
B)that the economy is operating at full employment.
C)that the stock of technology is increasing.
D)the production possibilities frontier bows inwards.
A)that opportunity cost decreases as production of one output expands.
B)that the economy is operating at full employment.
C)that the stock of technology is increasing.
D)the production possibilities frontier bows inwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 2-8 Production possibilities frontier data

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.As additional units of capital goods are produced,the opportunity cost in terms of sacrificed units of consumption goods _____ because of _____.
A)decreases; greater efficiency in production
B)increases; decreasing opportunity cost
C)increases; the law of increasing costs
D)increases; greater efficiency in production
E)decreases; the law of increasing costs

Suppose an economy is faced with the production possibilities table shown in Exhibit 2-8.As additional units of capital goods are produced,the opportunity cost in terms of sacrificed units of consumption goods _____ because of _____.
A)decreases; greater efficiency in production
B)increases; decreasing opportunity cost
C)increases; the law of increasing costs
D)increases; greater efficiency in production
E)decreases; the law of increasing costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Other things being equal,a decreased supply of natural resources would be represented on a production possibilities curve by a/an:
A)movement off the curve to a point inside the curve.
B)movement down along the curve.
C)movement up along the curve.
D)inward shift of the entire curve.
A)movement off the curve to a point inside the curve.
B)movement down along the curve.
C)movement up along the curve.
D)inward shift of the entire curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following would most likely cause the production possibilities curve for cars and bread to shift outward?
A)A choice of more bread and more cars.
B)A choice of more bread and fewer cars.
C)A choice of more cars and less bread.
D)An increase in the workforce level.
A)A choice of more bread and more cars.
B)A choice of more bread and fewer cars.
C)A choice of more cars and less bread.
D)An increase in the workforce level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 2-10 Production possibilities frontier
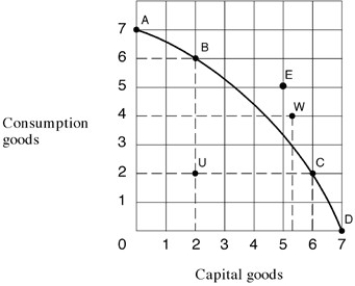
In Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are unattainable with the resources and technology currently available?
A)A, B, C, U.
B)A, B, C, D, U.
C)E and W.
D)B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, D.

In Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are unattainable with the resources and technology currently available?
A)A, B, C, U.
B)A, B, C, D, U.
C)E and W.
D)B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 2-10 Production possibilities frontier

From the information in Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are attainable with the resources and technology currently available?
A) A, B, C, E, U.
B) A, B, C, D, W.
C) E, U, W, C, A.
D) A,B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, D, E.

From the information in Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are attainable with the resources and technology currently available?
A) A, B, C, E, U.
B) A, B, C, D, W.
C) E, U, W, C, A.
D) A,B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, D, E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 2-10 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-10,to move from U to B,the opportunity cost:
A)would be 4 units of consumption goods.
B)would be 2 units of capital goods.
C)would be zero.
D)would be 5 units of capital goods.
E)cannot be estimated.

In Exhibit 2-10,to move from U to B,the opportunity cost:
A)would be 4 units of consumption goods.
B)would be 2 units of capital goods.
C)would be zero.
D)would be 5 units of capital goods.
E)cannot be estimated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 2-9 Production possibilities frontier
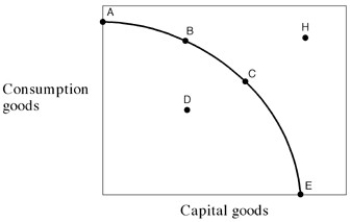
In Exhibit 2-9,which of the following is not true regarding point H? Point H:
A)cannot be achieved by this economy today.
B)could be achieved today only if the economy achieved full employment.
C)could be achieved in the future by an enlargement of the economy's resource base.
D)could be achieved in the future by an advancement in technology.
E)could be achieved in the future by growth in the economy.

In Exhibit 2-9,which of the following is not true regarding point H? Point H:
A)cannot be achieved by this economy today.
B)could be achieved today only if the economy achieved full employment.
C)could be achieved in the future by an enlargement of the economy's resource base.
D)could be achieved in the future by an advancement in technology.
E)could be achieved in the future by growth in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 2-10 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are full-employment production points?
A)A, B, C,
B)A, B, C, D, U.
C)E, U, W.
D)B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, U.

In Exhibit 2-10,which of the following points on the production possibilities curve are full-employment production points?
A)A, B, C,
B)A, B, C, D, U.
C)E, U, W.
D)B, C, D, U.
E) A, B, C, U.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Compare two economies A and B that start out with identical production possibilities curves.Economy A chooses an efficient point with 6 consumption goods and 3 capital goods,while economy B chooses an efficient point with 4 consumption goods and 5 capital goods.In the future we can predict:
A)economy A will operate inefficiently.
B)economy B will operate inefficiently.
C)economy A and economy B will grow equally fast.
D) economy A will grow faster than economy B.
E) economy B will grow faster than economy A.
A)economy A will operate inefficiently.
B)economy B will operate inefficiently.
C)economy A and economy B will grow equally fast.
D) economy A will grow faster than economy B.
E) economy B will grow faster than economy A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The economy experiences economic growth if:
A)the resource base decreases.
B)the production possibilities frontier shifts inwards.
C)the number of workers decreases.
D)the production possibilities frontier shifts outwards.
A)the resource base decreases.
B)the production possibilities frontier shifts inwards.
C)the number of workers decreases.
D)the production possibilities frontier shifts outwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
People in poor countries may have difficulties achieving economic growth because:
A)their production possibilities curves slope upward instead of downward.
B)they must cut back on current consumption to increase capital goods.
C)they have a solid consumption base already in place.
D)their resource bases are fully developed.
E)the law of increasing costs makes it hard to produce more goods.
A)their production possibilities curves slope upward instead of downward.
B)they must cut back on current consumption to increase capital goods.
C)they have a solid consumption base already in place.
D)their resource bases are fully developed.
E)the law of increasing costs makes it hard to produce more goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 2-9 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-9,if the economy decides to locate at point E,then:
A)this is the best choice for this economy.
B)the maximum number of consumption goods is being produced.
C)the economy has not achieved full employment.
D)the economy could not survive because no food is being produced.
E)the economy has not achieved maximum efficiency.

In Exhibit 2-9,if the economy decides to locate at point E,then:
A)this is the best choice for this economy.
B)the maximum number of consumption goods is being produced.
C)the economy has not achieved full employment.
D)the economy could not survive because no food is being produced.
E)the economy has not achieved maximum efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which would be least likely to cause the production possibilities curve to shift to the right?
A)An increase in the labour force.
B)Improved methods of production.
C)An increase in the education and training of the labour force.
D)A decrease in unemployment.
A)An increase in the labour force.
B)Improved methods of production.
C)An increase in the education and training of the labour force.
D)A decrease in unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Exhibit 2-9 Production possibilities frontier

In Exhibit 2-9,it can be inferred that:
A) point A is preferred to point B.
B) point A is preferred to point E.
C) point A is preferred to point D.
D) point B is preferred to point A.
E) point B is preferred to point C.

In Exhibit 2-9,it can be inferred that:
A) point A is preferred to point B.
B) point A is preferred to point E.
C) point A is preferred to point D.
D) point B is preferred to point A.
E) point B is preferred to point C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In order for an economy to shift its production possibilities curve rightward,it must:
A)utilise all existing resources.
B)reduce expenditure on research and development.
C)increase the unemployment rate.
D)experience an improvement in its technology.
A)utilise all existing resources.
B)reduce expenditure on research and development.
C)increase the unemployment rate.
D)experience an improvement in its technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An analysis of production possibilities curves indicates that the reason why underdeveloped nations have difficulties increasing their economic growth rates is because:
A)low population growth rates mean fewer workers to produce food and other necessities.
B)their production possibilities curves shift in when resources are increased.
C)their production possibilities curves are positively sloped, unlike those in more developed economies.
D)they must cut back their already meagre consumption levels to increase capital production.
E)the opportunity cost of shifting resources from consumption goods to capital goods is relatively low.
A)low population growth rates mean fewer workers to produce food and other necessities.
B)their production possibilities curves shift in when resources are increased.
C)their production possibilities curves are positively sloped, unlike those in more developed economies.
D)they must cut back their already meagre consumption levels to increase capital production.
E)the opportunity cost of shifting resources from consumption goods to capital goods is relatively low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



