Deck 6: Production costs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Production costs
1
Which of the following are implicit costs for a typical firm?
A)Insurance costs.
B)Electricity costs.
C)Opportunity costs of capital owned and used by the firm.
D)Cost of labour hired by the firm.
E)The cost of raw materials.
A)Insurance costs.
B)Electricity costs.
C)Opportunity costs of capital owned and used by the firm.
D)Cost of labour hired by the firm.
E)The cost of raw materials.
C
2
Implicit costs are best thought of as:
A)variable costs.
B)marginal costs.
C)accounting costs.
D)opportunity costs.
E)sunk costs.
A)variable costs.
B)marginal costs.
C)accounting costs.
D)opportunity costs.
E)sunk costs.
D
3
Implicit costs are:
A)labour costs to the firm.
B)the opportunity costs of using someone else's resources.
C)payments from owners of a firm for labour.
D)the opportunity costs of using resources owned by the firm.
E)payments to non-owners of a firm for their resources.
A)labour costs to the firm.
B)the opportunity costs of using someone else's resources.
C)payments from owners of a firm for labour.
D)the opportunity costs of using resources owned by the firm.
E)payments to non-owners of a firm for their resources.
D
4
An economist left her $100 000-a-year teaching position to work full-time in her own consulting business.In the first year,she had total revenue of $200 000 and business expenses of $100 000.She made a/an:
A)economic profit.
B)economic loss.
C)implicit profit.
D)accounting loss but not an economic loss.
E)zero economic profit.
A)economic profit.
B)economic loss.
C)implicit profit.
D)accounting loss but not an economic loss.
E)zero economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a firm has total revenue of $200 million,explicit costs of $190 million and implicit costs of $10 million,its economic profit is:
A)$200 million.
B)$70 million.
C)$10 million.
D)$0 million.
E)-$10 million.
A)$200 million.
B)$70 million.
C)$10 million.
D)$0 million.
E)-$10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A farm can produce 10 000 bushels of wheat per year with five workers and 12 000 bushels with six workers.The marginal product of the sixth worker for this farm is:
A)10 000 bushels.
B)2000 bushels.
C)500 bushels.
D)23 000 bushels.
A)10 000 bushels.
B)2000 bushels.
C)500 bushels.
D)23 000 bushels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the long run,total fixed cost:
A)falls.
B)does not exist.
C)is constant.
D)increases.
A)falls.
B)does not exist.
C)is constant.
D)increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explicit costs would include:
A)rent.
B)the interest loss of the business owner on money withdrawn from his/her saving account and invested in the business.
C)the loss of rent on a building the business owner owns and uses in his/her business.
D)the opportunity costs of the business owner's time.
E)the use of tools owned by the business owner and dedicated to the business.
A)rent.
B)the interest loss of the business owner on money withdrawn from his/her saving account and invested in the business.
C)the loss of rent on a building the business owner owns and uses in his/her business.
D)the opportunity costs of the business owner's time.
E)the use of tools owned by the business owner and dedicated to the business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Economic profit is:
A)always zero.
B)always less than accounting profit.
C)always more than accounting profit.
D)only sometimes less than accounting profit.
A)always zero.
B)always less than accounting profit.
C)always more than accounting profit.
D)only sometimes less than accounting profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Economic profit equals accounting profit plus implicit costs.
B)The short run is any period of time in which there is at least one fixed input.
C)A fixed input is any resource for which the quantity can change during the period under consideration.
D)In the long run there are no implicit costs.
A)Economic profit equals accounting profit plus implicit costs.
B)The short run is any period of time in which there is at least one fixed input.
C)A fixed input is any resource for which the quantity can change during the period under consideration.
D)In the long run there are no implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
During the course of a week,McDonalds has enough time to hire or lay-off workers,but it does not have enough time to expand its kitchen or add an additional seating area.In this situation,McDonald's:
A)has no fixed costs.
B)is in the short run.
C)suffers an economic loss.
D)earns a large profit.
A)has no fixed costs.
B)is in the short run.
C)suffers an economic loss.
D)earns a large profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Marginal product measures the change in:
A)total cost brought about by changing production by one unit.
B)product price brought about by changing production by one unit.
C)a firm's revenue brought about by changing production by one unit.
D)the firm's output brought about by employing one additional unit of input.
E)the firm's profit brought about by employing one more input.
A)total cost brought about by changing production by one unit.
B)product price brought about by changing production by one unit.
C)a firm's revenue brought about by changing production by one unit.
D)the firm's output brought about by employing one additional unit of input.
E)the firm's profit brought about by employing one more input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The long run is a period of time:
A)that is too short to change the size of a firm's plant.
B)that is long enough to permit changes in all the firm's inputs, both fixed and variable.
C)in which production occurs beyond one year.
D)in which production occurs beyond five years.
A)that is too short to change the size of a firm's plant.
B)that is long enough to permit changes in all the firm's inputs, both fixed and variable.
C)in which production occurs beyond one year.
D)in which production occurs beyond five years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Economic profit equals total revenue minus:
A)total explicit costs.
B)implicit costs.
C)total opportunity costs.
D)variable costs.
A)total explicit costs.
B)implicit costs.
C)total opportunity costs.
D)variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar.To do so,he would have to quit his current job,which pays $20 000 a year,and take over a store building that he owns and currently rents to his brother for $6000 a year.His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50 000 for food and $2000 for gas and electricity.What are his explicit costs?
A)$26 000.
B)$66 000.
C)$78 000.
D)$52 000.
E)$72 000.
A)$26 000.
B)$66 000.
C)$78 000.
D)$52 000.
E)$72 000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Suppose a firm has total revenue of $500 million,explicit costs of $200 million and implicit costs of $100 million.This firm's economic profit is:
A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$700 million.
D)-$200 million.
A)$200 million.
B)$300 million.
C)$700 million.
D)-$200 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A firm can produce 450 litres of milk per day with four workers and 500 litres per day with five workers.The marginal product of the fifth worker expressed in gallons per worker per day,is:
A)35.
B)50.
C)70.
D)350.
A)35.
B)50.
C)70.
D)350.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The short run is a period of time:
A)in which a firm uses at least one fixed input.
B)that is long enough to permit changes in the firm's plant size.
C)in which production occurs within one year.
D)in which production occurs within six months.
A)in which a firm uses at least one fixed input.
B)that is long enough to permit changes in the firm's plant size.
C)in which production occurs within one year.
D)in which production occurs within six months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar.To do so,he would have to quit his current job,which pays $20 000 a year,and take over a store building that he owns and currently rents to his brother for $6000 a year.His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50 000,for food and $2000 for gas and electricity.What are his implicit costs?
A)$26 000.
B)$66 000.
C)$78 000.
D)$52 000.
E)$72 000.
A)$26 000.
B)$66 000.
C)$78 000.
D)$52 000.
E)$72 000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a firm has total revenue of $300 million,explicit costs of $200 million and implicit costs of $30 million,its accounting profit is:
A)$200 million.
B)$100 million.
C)$70 million.
D)-$10 million.
E)-$20 million.
A)$200 million.
B)$100 million.
C)$70 million.
D)-$10 million.
E)-$20 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 6-2 Production of pizza data
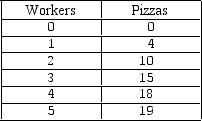
Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the second employee equals:
A)4.
B)10.
C)14.
D)6.
E)15.

Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the second employee equals:
A)4.
B)10.
C)14.
D)6.
E)15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 6-1: The production function
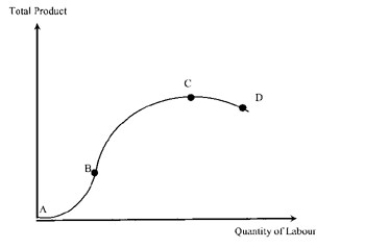
In Exhibit 6-1,total output increases from A to C because:
A)workers receive higher wages.
B)of technological progress in industries.
C)the law of diminishing marginal returns sets in.
D)of specialisation and therefore the increasing returns.

In Exhibit 6-1,total output increases from A to C because:
A)workers receive higher wages.
B)of technological progress in industries.
C)the law of diminishing marginal returns sets in.
D)of specialisation and therefore the increasing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Exhibit 6-3 A marginal product curve
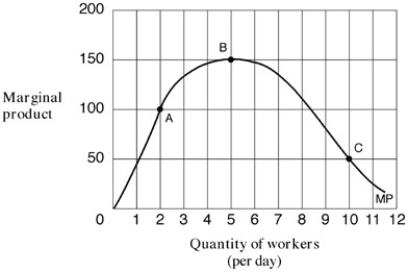
As shown in Exhibit 6-3,what was the marginal product of labour when only one worker was hired?
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,what was the marginal product of labour when only one worker was hired?
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Due to fixed resources, an additional unit of labour always adds more to production.
B)The marginal product of labour always increases when an additional unit of labour is employed.
C)Diminishing returns is a rare situation that occurs only when all inputs are not fixed.
D)The law of diminishing returns indicates that addition of an extra unit of a variable factor will decrease the marginal product.
A)Due to fixed resources, an additional unit of labour always adds more to production.
B)The marginal product of labour always increases when an additional unit of labour is employed.
C)Diminishing returns is a rare situation that occurs only when all inputs are not fixed.
D)The law of diminishing returns indicates that addition of an extra unit of a variable factor will decrease the marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Exhibit 6-4 Workers and output data
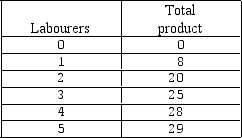
In Exhibit 6-4,the marginal returns are largest when the _____ worker is hired.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

In Exhibit 6-4,the marginal returns are largest when the _____ worker is hired.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The main reason why the slope of the production function decreases is because of:
A)increasing returns to the variable factor.
B)constant returns to an increasing factor.
C)diminishing returns to the variable factor.
D)diseconomies of scale.
E)the fact that all factors are variable.
A)increasing returns to the variable factor.
B)constant returns to an increasing factor.
C)diminishing returns to the variable factor.
D)diseconomies of scale.
E)the fact that all factors are variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The short-run production function is based on the assumption that:
A)employees have different skills.
B)employees are paid different wage rates.
C)all factors of production can be changed.
D)technology is constant.
A)employees have different skills.
B)employees are paid different wage rates.
C)all factors of production can be changed.
D)technology is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 6-2 Production of pizza data

Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the fifth worker is.
A)0
B)1
C)4
D)6
E)10

Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the fifth worker is.
A)0
B)1
C)4
D)6
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 6-1: The production function

In Exhibit 6-1,the marginal product of labour is equal to zero at point:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

In Exhibit 6-1,the marginal product of labour is equal to zero at point:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The law of diminishing returns applies to which of the following segments of the marginal product of labour curve?
A)The entire curve.
B)The downward-sloping segment only.
C)The upward-sloping segment only.
D)The point where labour input is zero.
A)The entire curve.
B)The downward-sloping segment only.
C)The upward-sloping segment only.
D)The point where labour input is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The marginal product curve reflects the change in:
A)output because the productivity is constant.
B)price because an introduction of competition leads to reduction in prices.
C)wages of workers that are increasing over time.
D)the total output curve because marginal product is the slope of the total output curve.
A)output because the productivity is constant.
B)price because an introduction of competition leads to reduction in prices.
C)wages of workers that are increasing over time.
D)the total output curve because marginal product is the slope of the total output curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Exhibit 6-2 Production of pizza data

Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the labour input begins to fall with the employment of the _____ worker.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

Exhibit 6-2 shows the change in the production of pizzas as more workers are hired.The marginal product of the labour input begins to fall with the employment of the _____ worker.
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The _____ is the situation in which the marginal product of labour is greater than zero and declining as more labour is hired.
A)law of demand
B)law of diminishing supply
C)law of diminishing returns
D)law of returns to scale
A)law of demand
B)law of diminishing supply
C)law of diminishing returns
D)law of returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
One season is a short run because:
A)production occurs within one short season.
B)a firm's plant size can be changed.
C)a firm uses at least one fixed input.
D)one season is less than three seasons.
A)production occurs within one short season.
B)a firm's plant size can be changed.
C)a firm uses at least one fixed input.
D)one season is less than three seasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The situation in which the marginal product of labour is greater than zero and declining as more labour is hired is called the law of:
A)negative returns to scale.
B)diminishing returns.
C)inverse return to labour.
D)demand.
A)negative returns to scale.
B)diminishing returns.
C)inverse return to labour.
D)demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exhibit 6-3 A marginal product curve

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,the marginal product of labour when 5 additional workers are employed per day is (points from B to C):
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,the marginal product of labour when 5 additional workers are employed per day is (points from B to C):
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Exhibit 6-3 A marginal product curve

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,the law of diminishing returns applies where there are:
A)more than 5 workers per day.
B)more than 4 workers per day.
C)more than 3 workers per day.
D)between zero and 5 workers per day.

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,the law of diminishing returns applies where there are:
A)more than 5 workers per day.
B)more than 4 workers per day.
C)more than 3 workers per day.
D)between zero and 5 workers per day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Exhibit 6-3 A marginal product curve

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,what was the marginal product of labour when the second worker was hired?
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

As shown in Exhibit 6-3,what was the marginal product of labour when the second worker was hired?
A)50.
B)100.
C)150.
D)175.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Marginal product can be:
A)positive, zero or negative
B)only positive
C)only negative
D)positive or zero
A)positive, zero or negative
B)only positive
C)only negative
D)positive or zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A fixed input is any resource for which the quantity can:
A)change any time.
B)change during a specific time.
C)not change at all.
D)not change during a specific time.
A)change any time.
B)change during a specific time.
C)not change at all.
D)not change during a specific time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Total variable cost:
A)is added to the total fixed cost.
B)consists of costs that are never zero.
C)only relates to the costs of variable inputs.
D)does not change.
A)is added to the total fixed cost.
B)consists of costs that are never zero.
C)only relates to the costs of variable inputs.
D)does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is true if the total variable cost curve is rising?
A)Average fixed cost is increasing.
B)Marginal cost is decreasing.
C)Marginal cost is increasing.
D)Average fixed cost is constant.
A)Average fixed cost is increasing.
B)Marginal cost is decreasing.
C)Marginal cost is increasing.
D)Average fixed cost is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Marginal cost is:
A)change in total cost divided by change in quantity.
B)change in total fixed cost divided by change in quantity.
C)change in average variable cost divided by change in quantity.
D)change in average fixed cost divided by change in quantity.
A)change in total cost divided by change in quantity.
B)change in total fixed cost divided by change in quantity.
C)change in average variable cost divided by change in quantity.
D)change in average fixed cost divided by change in quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The vertical distance between the TC and TVC is:
A)AVC.
B)MC.
C)TFC.
D)ATC.
E)TMC.
A)AVC.
B)MC.
C)TFC.
D)ATC.
E)TMC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The marginal cost is the change in:
A)average variable cost as the quantity changes by two units.
B)total cost as the quantity changes by a number of units.
C)total variable cost as the quantity changes by one unit.
D)total fixed cost as the quantity changes by one unit.
A)average variable cost as the quantity changes by two units.
B)total cost as the quantity changes by a number of units.
C)total variable cost as the quantity changes by one unit.
D)total fixed cost as the quantity changes by one unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose the cost to produce an additional unit of output is $20.What is the change in total variable cost?
A)$10.
B)$20.
C)$30.
D)$40.
A)$10.
B)$20.
C)$30.
D)$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Total fixed costs:
A)vary as output varies.
B)are zero when the output is zero.
C)are the costs that do not vary with the output.
D)are the costs that increase with output.
A)vary as output varies.
B)are zero when the output is zero.
C)are the costs that do not vary with the output.
D)are the costs that increase with output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Marginal cost is defined as the increase in total cost resulting from an increase in:
A)1 unit of output.
B)output of 100 units.
C)a firm's plant size.
D)1 unit of labour.
A)1 unit of output.
B)output of 100 units.
C)a firm's plant size.
D)1 unit of labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements is true?
A)TC = TFC - TVC.
B)AVC = TC/Q.
C)TFC = TC - TVC.
D)MC equals the change in ATC divided by the change in Q.
A)TC = TFC - TVC.
B)AVC = TC/Q.
C)TFC = TC - TVC.
D)MC equals the change in ATC divided by the change in Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When the cost curves have U-shapes,at the point where marginal cost equals average total cost:
A)average variable cost is constant.
B)fixed cost is declining.
C)average total cost is at its maximum and the marginal cost is falling.
D)average total cost is at its minimum and the marginal cost is rising.
A)average variable cost is constant.
B)fixed cost is declining.
C)average total cost is at its maximum and the marginal cost is falling.
D)average total cost is at its minimum and the marginal cost is rising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
As a firm expands its output from zero:
A)marginal wage of labour increases.
B)it suffers from the diseconomies of scale.
C)it has to pay wages, rent and electricity to cover the variable costs.
D)no change in the cost is occurring.
A)marginal wage of labour increases.
B)it suffers from the diseconomies of scale.
C)it has to pay wages, rent and electricity to cover the variable costs.
D)no change in the cost is occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The minimum point on the marginal cost curve corresponds to the:
A)maximum point on the total cost curve.
B)minimum point on the total cost curve.
C)minimum point on the average variable cost curve.
D)midpoint of the total cost curve.
A)maximum point on the total cost curve.
B)minimum point on the total cost curve.
C)minimum point on the average variable cost curve.
D)midpoint of the total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 6-4 Workers and output data

In Exhibit 6-4,the marginal product of the third worker is:
A)0.
B)5.
C)10.
D)12.
E)20.

In Exhibit 6-4,the marginal product of the third worker is:
A)0.
B)5.
C)10.
D)12.
E)20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is considered to be a fixed cost of operating a hairdressing salon?
A)Wages.
B)Insurance.
C)Cost of receipt books.
D)Cost of shampoos.
A)Wages.
B)Insurance.
C)Cost of receipt books.
D)Cost of shampoos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If ATC = $10,AVC = $8,AFC = $2 and MC = $12,then:
A)the firm must be operating on the downward-sloping section of its ATC curve.
B)the firm must be operating on the upward-sloping section of its AFC curve.
C)the firm must be operating on the upward-sloping section of its ATC curve.
D)it is uncertain from the figures given where the firm is operating.
E)the firm must be operating on the downward-sloping section of its AVC curve.
A)the firm must be operating on the downward-sloping section of its ATC curve.
B)the firm must be operating on the upward-sloping section of its AFC curve.
C)the firm must be operating on the upward-sloping section of its ATC curve.
D)it is uncertain from the figures given where the firm is operating.
E)the firm must be operating on the downward-sloping section of its AVC curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Average total cost is:
A)average fixed cost added to average total cost.
B)total fixed cost divided by wages.
C)total variable cost divided by quantity.
D)average fixed cost added to average variable cost.
A)average fixed cost added to average total cost.
B)total fixed cost divided by wages.
C)total variable cost divided by quantity.
D)average fixed cost added to average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As output increases:
A)ATC rises at first and then falls.
B)AFC falls at first and then rises.
C)AVC cuts ATC when MC is at its minimum.
D)AFC declines and the gap between ATC and AVC declines.
A)ATC rises at first and then falls.
B)AFC falls at first and then rises.
C)AVC cuts ATC when MC is at its minimum.
D)AFC declines and the gap between ATC and AVC declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If ATC = $10,AVC = $6,AFC = $3 and MC = $5,then if output increased by one unit:
A)MC will increase.
B)MC will decrease.
C)ATC will increase.
D)MC may be increasing or decreasing.
E)AFC will increase.
A)MC will increase.
B)MC will decrease.
C)ATC will increase.
D)MC may be increasing or decreasing.
E)AFC will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The shape of the total cost curve is:
A)it completely follows the shape of TFC.
B)always upwards sloping.
C)intersecting the TVC at its minimum.
D)it mimics the shape of the TVC.
A)it completely follows the shape of TFC.
B)always upwards sloping.
C)intersecting the TVC at its minimum.
D)it mimics the shape of the TVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
ATC can be calculated as follows:
A)AFC*AVC or TC*Q
B)AFC-AVC or TC/Q
C)AFC+AVC or TC*Q
D)AFC+AVC or TC/Q
A)AFC*AVC or TC*Q
B)AFC-AVC or TC/Q
C)AFC+AVC or TC*Q
D)AFC+AVC or TC/Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas
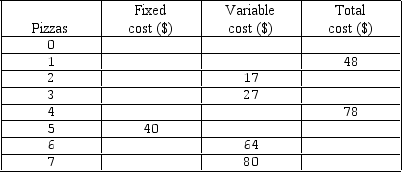
By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the ATC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the ATC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The law of diminishing returns states that beyond some point the marginal product of a variable resource continues to rise.
B)The marginal product is the change in total output by adding one additional unit of a fixed input.
C)Fixed costs are costs which vary with the output level.
D)When marginal productivity of a variable input is falling, then marginal costs of production must be rising.
E)When marginal cost is below average cost, average cost rises; when marginal cost is above average cost, average cost falls.
A)The law of diminishing returns states that beyond some point the marginal product of a variable resource continues to rise.
B)The marginal product is the change in total output by adding one additional unit of a fixed input.
C)Fixed costs are costs which vary with the output level.
D)When marginal productivity of a variable input is falling, then marginal costs of production must be rising.
E)When marginal cost is below average cost, average cost rises; when marginal cost is above average cost, average cost falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the ATC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the ATC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AFC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AFC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements is not true?
A)TC = TFC * Q.
B)AVC = TVC/Q.
C)TFC = AFC * Q.
D)MC =ATC /Q.
A)TC = TFC * Q.
B)AVC = TVC/Q.
C)TFC = AFC * Q.
D)MC =ATC /Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Exhibit 6-7 Short-run cost curves schedule for a pizzeria's hourly production
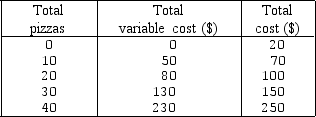
In Exhibit 6-7,the pizzeria's fixed cost is equal to:
A)$0.
B)$20.
C)$50.
D)$70.
E)$100.
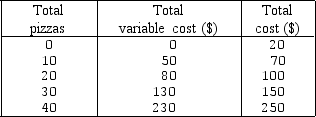
In Exhibit 6-7,the pizzeria's fixed cost is equal to:
A)$0.
B)$20.
C)$50.
D)$70.
E)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 6-6 Cost schedule for firm X
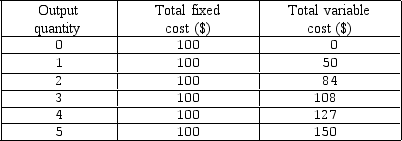
As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the marginal cost of producing the fourth unit is:
A)$0.
B)$19.
C)$27.
D)$100.

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the marginal cost of producing the fourth unit is:
A)$0.
B)$19.
C)$27.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Exhibit 6-6 Cost schedule for firm X

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the average fixed cost of producing the fifth unit is:
A)$0.
B)$20.
C)$25.
D)$100.

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the average fixed cost of producing the fifth unit is:
A)$0.
B)$20.
C)$25.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 6-6 Cost schedule for firm X

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the total cost of producing 5 units is:
A)$0.
B)$227.
C)$250.
D)$100.

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the total cost of producing 5 units is:
A)$0.
B)$227.
C)$250.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exhibit 6-6 Cost schedule for firm X

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the average total cost of producing 5 units is:
A)$0.
B)$27.
C)$50.
D)$100.

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the average total cost of producing 5 units is:
A)$0.
B)$27.
C)$50.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 6-5 Cost schedule for a firm
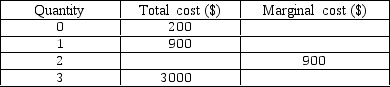
In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the fixed costs for the 2nd unit are
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$900.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the fixed costs for the 2nd unit are
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$900.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Exhibit 6-5 Cost schedule for a firm

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined the variable costs for the first unit is:
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$700.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined the variable costs for the first unit is:
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$700.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AVC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AVC of 3 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.00.
B)$10.00.
C)$13.33.
D)$22.33.
E)$40.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Exhibit 6-5 Cost schedule for a firm

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the total cost of the second unit of output is:
A)$0.
B)$700.
C)$1000.
D)$1200.
E)$1800.

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the total cost of the second unit of output is:
A)$0.
B)$700.
C)$1000.
D)$1200.
E)$1800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AVC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AVC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 6-5 Cost schedule for a firm

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the marginal cost of the third unit of output is:
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$700.
D)$1200.
E)$2000.

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the marginal cost of the third unit of output is:
A)$0.
B)$200.
C)$700.
D)$1200.
E)$2000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Exhibit 6-6 Cost schedule for firm X

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the total cost of producing 4 units is:
A)$0.
B)$227.
C)$250.
D)$100.

As shown in Exhibit 6-6,the total cost of producing 4 units is:
A)$0.
B)$227.
C)$250.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is true at the point where diminishing returns set in?
A)Both marginal product and marginal cost are at a maximum.
B)Both marginal product and marginal cost are at a minimum.
C)Marginal product is at a maximum and marginal cost at a minimum.
D)Marginal product is at a minimum and marginal cost at a maximum.
A)Both marginal product and marginal cost are at a maximum.
B)Both marginal product and marginal cost are at a minimum.
C)Marginal product is at a maximum and marginal cost at a minimum.
D)Marginal product is at a minimum and marginal cost at a maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Exhibit 6-8 Cost schedule for producing pizzas

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AFC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

By filling in the blanks in Exhibit 6-8,the AFC of 4 pizzas is shown to be equal to:
A)$9.50.
B)$10.00.
C)$19.50.
D)$40.00.
E)$78.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Exhibit 6-5 Cost schedule for a firm

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the marginal cost of the first unit of output is:
A)$200.
B)$700.
C)$900.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

In Exhibit 6-5,by filling in the blanks it can be determined that the marginal cost of the first unit of output is:
A)$200.
B)$700.
C)$900.
D)$1000.
E)$3000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



