Deck 12: Business cycles and economic growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/124
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Business cycles and economic growth
1
A phase in the business cycle in which the decline in the economy's real GDP persists for at least half a year is known as:
A)a depression.
B)a recession.
C)a downtick.
D)disequilibrium.
E)limited demand.
A)a depression.
B)a recession.
C)a downtick.
D)disequilibrium.
E)limited demand.
B
2
A business cycle is the period of time in which:
A)a business is established and ceases operations.
B)there are three phases, which are: peak, depression and recovery.
C)real GDP declines.
D)expansion and contraction of economic activity are alternated.
A)a business is established and ceases operations.
B)there are three phases, which are: peak, depression and recovery.
C)real GDP declines.
D)expansion and contraction of economic activity are alternated.
D
3
Suppose the index of leading economic indicators begins to decline for several months.Which of the following economic events will likely follow?
A)A recession.
B)Severe inflation.
C)Greater employment.
D)Higher investment.
A)A recession.
B)Severe inflation.
C)Greater employment.
D)Higher investment.
A
4
Economic indicators (e.g.unemployment claims and the average working week),which change before real GDP changes,are called:
A)leading.
B)lagging.
C)coincident.
D)structural.
A)leading.
B)lagging.
C)coincident.
D)structural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Retail sales data is an example of a:
A)leading indicator.
B)lagging indicator.
C)coincident indicator.
D)goal of macroeconomic policy.
E)countercyclical indicator.
A)leading indicator.
B)lagging indicator.
C)coincident indicator.
D)goal of macroeconomic policy.
E)countercyclical indicator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not a variable in the index of leading indicators?
A)Average working week.
B)Duration of unemployment.
C)Unemployment claims.
D)New businesses.
A)Average working week.
B)Duration of unemployment.
C)Unemployment claims.
D)New businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The period during which real output falls during a business cycle is called:
A)peak.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.
E)growth.
A)peak.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.
E)growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a coincident indicator?
A)CPI data.
B)Industrial production.
C)Building approvals.
D)Retail sales.
A)CPI data.
B)Industrial production.
C)Building approvals.
D)Retail sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The point at which real output reaches a maximum during a business cycle is called the:
A)depression.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.
E)peak.
A)depression.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.
E)peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a coincident indicator?
A)Average work week.
B)New building approvals.
C)Stock prices.
D)Household income.
A)Average work week.
B)New building approvals.
C)Stock prices.
D)Household income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A recession is a decline in real GDP lasting at least:
A)one year.
B)six months.
C)three months.
D)one month.
A)one year.
B)six months.
C)three months.
D)one month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not a lagging indicator?
A)Outstanding commercial loans.
B)Duration of unemployment.
C)Prime rate.
D)Stock prices.
A)Outstanding commercial loans.
B)Duration of unemployment.
C)Prime rate.
D)Stock prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Economic growth is measured by the annual percentage increase in a nation's level of:
A)nominal GDP.
B)real GDP.
C)real GDP deflator.
D)economic indicators.
A)nominal GDP.
B)real GDP.
C)real GDP deflator.
D)economic indicators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What stage of the business cycle immediately follows the trough?
A)Peak.
B)Recovery.
C)Recession.
D)Depression.
A)Peak.
B)Recovery.
C)Recession.
D)Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If you look for a job for 18 months after graduation,but fail to generate an offer,even after lowering your expectations,the economy is probably in the business cycle phase called:
A)recession.
B)peak.
C)boom.
D)recovery.
E)trough.
A)recession.
B)peak.
C)boom.
D)recovery.
E)trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a lagging indicator?
A)Material prices.
B)Changes in inventories.
C)Industrial production.
D)Retail sales.
A)Material prices.
B)Changes in inventories.
C)Industrial production.
D)Retail sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A business cycle is:
A)the period of time in which the expansion and contraction of economic activity are equal.
B)the period of time in which there are three phases, which are: peak, depression and recovery.
C)the recurring growth and decline in real GDP.
D)the period of time in which a business is established and ceases operations.
A)the period of time in which the expansion and contraction of economic activity are equal.
B)the period of time in which there are three phases, which are: peak, depression and recovery.
C)the recurring growth and decline in real GDP.
D)the period of time in which a business is established and ceases operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The phase of the business cycle that follows a recession is known as the:
A)peak.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.
A)peak.
B)recession.
C)recovery.
D)trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The phase in the business cycle in which real GDP declines is called a:
A)trendline.
B)peak.
C)recession.
D)recovery.
E)trough.
A)trendline.
B)peak.
C)recession.
D)recovery.
E)trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Variables that change before real GDP changes are measured by the:
A)personal income index.
B)real GDP index.
C)forecasting gauge.
D)index of leading indicators.
A)personal income index.
B)real GDP index.
C)forecasting gauge.
D)index of leading indicators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exhibit 12-1 Business cycle
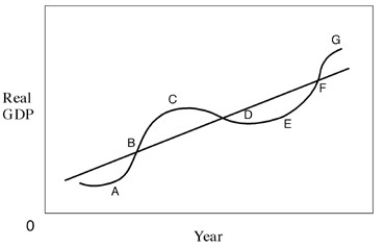
In Exhibit 12-1,point E represents a:
A)recession and a trough.
B)peak and a trough.
C)recession and a trough.
D)recession and a peak.
E)recovery and a peak.

In Exhibit 12-1,point E represents a:
A)recession and a trough.
B)peak and a trough.
C)recession and a trough.
D)recession and a peak.
E)recovery and a peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true?
A)The business cycle is a maximum period of economic growth.
B)The rise and fall in nominal GDP is a significant indicator of the business cycle.
C)Employment growth indicates a downturn in the business cycle.
D)Increase in employment indicates a phase of economic growth.
A)The business cycle is a maximum period of economic growth.
B)The rise and fall in nominal GDP is a significant indicator of the business cycle.
C)Employment growth indicates a downturn in the business cycle.
D)Increase in employment indicates a phase of economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not a part of the business cycle?
A)Peak.
B)Trough.
C)Existence.
D)Recession.
A)Peak.
B)Trough.
C)Existence.
D)Recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The cost of cyclical unemployment is also called:
A)real GDP.
B)the GDP surplus.
C)the inflation gap.
D)potential output minus actual output.
A)real GDP.
B)the GDP surplus.
C)the inflation gap.
D)potential output minus actual output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The trough is good news because:
A)it is the middle of the expansion phase of the business cycle.
B)production is at the highest level.
C)unemployment is low.
D)it is the starting point to improve economic conditions.
A)it is the middle of the expansion phase of the business cycle.
B)production is at the highest level.
C)unemployment is low.
D)it is the starting point to improve economic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The GDP gap is the difference between:
A)full-employment real GDP and nominal GDP chain price index.
B)unemployment rate and real GDP chain price index.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)discouraged workers and actual real GDP.
A)full-employment real GDP and nominal GDP chain price index.
B)unemployment rate and real GDP chain price index.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)discouraged workers and actual real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the GDP gap is zero,we can conclude that:
A)unemployment is zero.
B)we are below our potential output level.
C)cyclical unemployment is zero.
D)we are above our potential output level.
A)unemployment is zero.
B)we are below our potential output level.
C)cyclical unemployment is zero.
D)we are above our potential output level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The GDP gap is the difference between:
A)full-employment nominal GDP and actual real GDP.
B)full-employment real GDP and nominal real GDP.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)full unemployment and actual nominal GDP.
A)full-employment nominal GDP and actual real GDP.
B)full-employment real GDP and nominal real GDP.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)full unemployment and actual nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 12-1 Business cycle

In Exhibit 12-1,the recovery phase of the business cycle can be represented by points:
A)A and C
B)B and F
C)B and D
D) C and G.
E) E and G.

In Exhibit 12-1,the recovery phase of the business cycle can be represented by points:
A)A and C
B)B and F
C)B and D
D) C and G.
E) E and G.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If real GDP is currently $500 billion,there is 3 per cent cyclical unemployment and the potential nominal GDP is $600 billion,we can conclude with certainty that:
A)the GDP gap is $100 billion.
B)there is no GDP gap.
C)there is a GDP gap.
D)the economy is operating above full employment.
A)the GDP gap is $100 billion.
B)there is no GDP gap.
C)there is a GDP gap.
D)the economy is operating above full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The GDP gap is the difference between:
A)seasonal unemployment and actual real GDP.
B)the unemployment rate and real GDP deflator.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)full-employment real GDP and real GDP deflator.
A)seasonal unemployment and actual real GDP.
B)the unemployment rate and real GDP deflator.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)full-employment real GDP and real GDP deflator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Over time,real GDP tends to:
A)fluctuate.
B)trend upward.
C)slow down.
D)trend downward.
A)fluctuate.
B)trend upward.
C)slow down.
D)trend downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is true?
A)The GDP gap is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
B)Economic growth is a difference between last year's CPI and this year's CPI.
C)Economic growth is measured by the annual amount increase in a nation's real GDP.
D)Discouraged workers are not fully accounted for in the unemployment rate.
A)The GDP gap is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
B)Economic growth is a difference between last year's CPI and this year's CPI.
C)Economic growth is measured by the annual amount increase in a nation's real GDP.
D)Discouraged workers are not fully accounted for in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A coincident indicator:
A)highlights future changes in economic growth.
B)highlights previous changes in economic growth.
C)highlights current changes in economic growth.
D)always runs countercyclically to the business cycle.
E)highlights future inflation.
A)highlights future changes in economic growth.
B)highlights previous changes in economic growth.
C)highlights current changes in economic growth.
D)always runs countercyclically to the business cycle.
E)highlights future inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What stage of the business cycle immediately follows the peak?
A)Peak.
B)Recovery.
C)Recession.
D)Depression.
A)Peak.
B)Recovery.
C)Recession.
D)Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Exhibit 12-1 Business cycle

In Exhibit 12-1,the recession phase of the business cycle can be represented by:
A)D
B) B and D.
C) F.
D) C.
E) A and E.

In Exhibit 12-1,the recession phase of the business cycle can be represented by:
A)D
B) B and D.
C) F.
D) C.
E) A and E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The business cycle is the:
A)succession of long-run fluctuations around the long-term trend.
B)succession of short-run fluctuations around the long-term trend.
C)erratic movements around the long-term trend.
D)straight line.
A)succession of long-run fluctuations around the long-term trend.
B)succession of short-run fluctuations around the long-term trend.
C)erratic movements around the long-term trend.
D)straight line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The trough is the point:
A)at which the economy reaches its maximum.
B)at which unemployment is at the lowest level relative to recent years.
C)where the level of real GDP is at a maximum.
D)at which employment is at the lowest level relative to the recent years.
A)at which the economy reaches its maximum.
B)at which unemployment is at the lowest level relative to recent years.
C)where the level of real GDP is at a maximum.
D)at which employment is at the lowest level relative to the recent years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Total spending influences the business cycle because:
A)increases in spending flow through to higher output, employment and income.
B)it allows GDP to increase well beyond the full-employment level of output.
C)decreases in spending will increase inflation, which then reduces real GDP.
D)increases in spending will decrease inflation, which then increases real GDP.
A)increases in spending flow through to higher output, employment and income.
B)it allows GDP to increase well beyond the full-employment level of output.
C)decreases in spending will increase inflation, which then reduces real GDP.
D)increases in spending will decrease inflation, which then increases real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The business cycle occurs from:
A)changes in industry demand.
B)changes in local supply and taxes.
C)changes in weather.
D)changes in the costs of production and in total spending.
A)changes in industry demand.
B)changes in local supply and taxes.
C)changes in weather.
D)changes in the costs of production and in total spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The GDP gap is the difference between:
A)full-employment real GDP and nominal GDP.
B)the full employment rate and real GDP chain price index.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)seasonal unemployment and nominal GDP.
A)full-employment real GDP and nominal GDP.
B)the full employment rate and real GDP chain price index.
C)full-employment real GDP and actual real GDP.
D)seasonal unemployment and nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The 'golden rule',steady-state in the Solow growth model occurs when:
A)the level at which the economy will be made no better off by additional saving.
B)the level of output per person is maximised.
C)the level of savings per person is minimised.
D)the level of consumption per person is maximised.
A)the level at which the economy will be made no better off by additional saving.
B)the level of output per person is maximised.
C)the level of savings per person is minimised.
D)the level of consumption per person is maximised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the Solow growth model,investment is only possible if:
A)consumption equals output.
B)consumption is greater than output.
C)output is greater than consumption.
D)firms borrow from overseas.
E)savings are greater than consumption.
A)consumption equals output.
B)consumption is greater than output.
C)output is greater than consumption.
D)firms borrow from overseas.
E)savings are greater than consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The GDP gap measures:
A)the value of non-market goods.
B)the cost of additional labour.
C)total value of final goods and services.
D)the value of all goods and services.
E)the cost of cyclical unemployment.
A)the value of non-market goods.
B)the cost of additional labour.
C)total value of final goods and services.
D)the value of all goods and services.
E)the cost of cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The 1987 the Nobel Laureate,awarded for his contribution to growth theory,was:
A)John Maynard Keynes.
B)Milton Friedman.
C)Robert Solow.
D)Gregory Mankiw.
E)Adam Smith.
A)John Maynard Keynes.
B)Milton Friedman.
C)Robert Solow.
D)Gregory Mankiw.
E)Adam Smith.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The level of GDP that could be produced at full employment is:
A)aggregated GDP.
B)desirable nominal GDP.
C)potential real GDP.
D)unattainable.
E)potential nominal GDP.
A)aggregated GDP.
B)desirable nominal GDP.
C)potential real GDP.
D)unattainable.
E)potential nominal GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The 'golden rule',steady-state level of capital per worker in the Solow model is where:
A)the savings rate equals zero.
B)the savings rate equals the consumption rate.
C)the savings rate results in the maximum level of output per worker.
D)the savings rate results in the maximum level of consumption per worker.
A)the savings rate equals zero.
B)the savings rate equals the consumption rate.
C)the savings rate results in the maximum level of output per worker.
D)the savings rate results in the maximum level of consumption per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If an increase in labour and capital of 10 per cent leads to output increasing by 10 per cent then,ceteris paribus,the economy is operating with:
A)increasing returns to scale.
B)decreasing returns to scale.
C)constant returns to scale.
D)economies of scale.
E)diseconomies of scale.
A)increasing returns to scale.
B)decreasing returns to scale.
C)constant returns to scale.
D)economies of scale.
E)diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the simple Solow growth model,with constant technology and constant returns to scale,GDP per capita can only increase if:
A)capital increases at the same rate as labour increases.
B)capital increases at a slower rate than labour.
C)capital increases at a faster rate than labour.
D)increasing marginal returns to capital exists.
A)capital increases at the same rate as labour increases.
B)capital increases at a slower rate than labour.
C)capital increases at a faster rate than labour.
D)increasing marginal returns to capital exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is true?
A)The GDP gap is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
B)Economic growth is needed because it reduces the nation's standard of living.
C)Economic growth is measured by the annual percentage increase in a nation's real GDP.
D)Economic growth is required to reduce the value of net exports.
A)The GDP gap is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
B)Economic growth is needed because it reduces the nation's standard of living.
C)Economic growth is measured by the annual percentage increase in a nation's real GDP.
D)Economic growth is required to reduce the value of net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
According to the Solow model,with constant technology,an increase in capital per worker will lead to a smaller increase in GDP per capita.This is explained by:
A)constant returns to scale.
B)the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C)the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D)decreasing returns to scale.
A)constant returns to scale.
B)the law of diminishing marginal returns.
C)the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D)decreasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the simple Solow growth model,investment depends crucially on:
A)the capital stock.
B)the supply of labour.
C)household savings.
D)diminishing returns to capital.
E)increasing returns to capital.
A)the capital stock.
B)the supply of labour.
C)household savings.
D)diminishing returns to capital.
E)increasing returns to capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The Solow growth model attempts to explain:
A)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technology combine to determine long-term economic growth.
B)how technology is endogenous to economic growth.
C)how government spending, saving, capital, labour and technology combine to determine long-term economic growth.
D)how capital and labour combine to determine short-term economic growth.
A)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technology combine to determine long-term economic growth.
B)how technology is endogenous to economic growth.
C)how government spending, saving, capital, labour and technology combine to determine long-term economic growth.
D)how capital and labour combine to determine short-term economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
According to the Solow model,with a constant amount of labour and constant technology,increases in the quantity of capital will lead to output per worker:
A)increasing at an increasing rate.
B)increasing at a decreasing rate.
C)remaining constant.
D)declining at an increasing rate.
E)declining at a decreasing rate.
A)increasing at an increasing rate.
B)increasing at a decreasing rate.
C)remaining constant.
D)declining at an increasing rate.
E)declining at a decreasing rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The 'golden rule' level of capital per worker in the Solow model implies:
A)governments should consistently follow the same monetary policy rule regardless of the economy's stage in the business cycle.
B)consumption will be maximised when capital per worker is at its maximum.
C)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise investment.
D)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise consumption.
E)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise output.
A)governments should consistently follow the same monetary policy rule regardless of the economy's stage in the business cycle.
B)consumption will be maximised when capital per worker is at its maximum.
C)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise investment.
D)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise consumption.
E)there is an optimal rate of saving that will maximise output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the Solow model,technological change:
A)is not included in the model.
B)is assumed to be endogenous.
C)is assumed not to exist.
D)is assumed to be exogenous.
A)is not included in the model.
B)is assumed to be endogenous.
C)is assumed not to exist.
D)is assumed to be exogenous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
According to the Solow growth model,technological progress:
A)was thought to occur within the economic system.
B)was thought to occur independently of the economic growth process.
C)was thought not to exist.
D)was thought to exist but only inside the economic system.
A)was thought to occur within the economic system.
B)was thought to occur independently of the economic growth process.
C)was thought not to exist.
D)was thought to exist but only inside the economic system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The law of diminishing returns in the Solow model implies that for sustained long-term economic growth to occur,a country needs to:
A)continually increase the quantity of capital.
B)continually increase the proportion of savings.
C)continually increase consumption.
D)have technological progress.
A)continually increase the quantity of capital.
B)continually increase the proportion of savings.
C)continually increase consumption.
D)have technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If an increase in labour and capital of 10 per cent leads to output increasing by 20 per cent then,ceteris paribus,the economy is operating with:
A)diseconomies of scale.
B)decreasing returns to scale.
C)constant returns to scale.
D)increasing returns to scale.
E)diminishing returns to output.
A)diseconomies of scale.
B)decreasing returns to scale.
C)constant returns to scale.
D)increasing returns to scale.
E)diminishing returns to output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Over the past century,virtually all countries have experienced long-term growth of:
A)zero per cent.
B)2 per cent.
C)3 per cent.
D)various rates.
A)zero per cent.
B)2 per cent.
C)3 per cent.
D)various rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An implication of the Solow growth model is that:
A)economies will automatically move from the optimal saving rate.
B)there may be a role for governments to play in moving the economy to its steady state.
C)output per worker will be maximised at the steady-state level.
D)it is impossible for a country to save 'too much'.
A)economies will automatically move from the optimal saving rate.
B)there may be a role for governments to play in moving the economy to its steady state.
C)output per worker will be maximised at the steady-state level.
D)it is impossible for a country to save 'too much'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
According to the Solow growth model,the only way for a country to enjoy long-term economic growth is through:
A)increasing saving to the optimal steady-state level.
B)maximising consumption per worker.
C)technological progress.
D)increasing the quantity of capital per worker.
A)increasing saving to the optimal steady-state level.
B)maximising consumption per worker.
C)technological progress.
D)increasing the quantity of capital per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One of the long-term potential problems in getting an economy to increase its living standards in the Solow growth model is that:
A)current generations may not want to sacrifice investment for the benefit of future generations.
B)current generations may not want to sacrifice consumption for the benefit of future generations.
C)current generations may not want to sacrifice savings for the benefit of future generations.
D)future generations may not want to have to sacrifice consumption for the benefit of current generations.
E)future generations may not want to have to to sacrifice investment for the benefit of current generations.
A)current generations may not want to sacrifice investment for the benefit of future generations.
B)current generations may not want to sacrifice consumption for the benefit of future generations.
C)current generations may not want to sacrifice savings for the benefit of future generations.
D)future generations may not want to have to sacrifice consumption for the benefit of current generations.
E)future generations may not want to have to to sacrifice investment for the benefit of current generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The 'golden rule' of saving is:
A)the rate of saving that produces the minimum level of consumption per capita in the long-steady state.
B)the rate of saving that produces the maximum level of production per capita in the long-steady state.
C)the rate of saving that produces the maximum level of consumption per capita in the long-steady state.
D)The rate of saving that produces the minimum level of investment per capita in the long-steady state.
A)the rate of saving that produces the minimum level of consumption per capita in the long-steady state.
B)the rate of saving that produces the maximum level of production per capita in the long-steady state.
C)the rate of saving that produces the maximum level of consumption per capita in the long-steady state.
D)The rate of saving that produces the minimum level of investment per capita in the long-steady state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the Solow model,technological progress is assumed to be:
A)zero.
B)endogenous.
C)exogenous.
D)continually increasing.
E)continually decreasing.
A)zero.
B)endogenous.
C)exogenous.
D)continually increasing.
E)continually decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the Solow model,technological progress is assumed to occur:
A)systematically as part of capital accumulation.
B)randomly outside the system.
C)systematically as part of increases in output.
D)systematically as part of increases in investment.
A)systematically as part of capital accumulation.
B)randomly outside the system.
C)systematically as part of increases in output.
D)systematically as part of increases in investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not an example of technological progress?
A)Better training for workers.
B)Improvements in the quality of capital.
C)Improvements in management practices.
D)Increases in the quantity of capital.
E)More education for the population.
A)Better training for workers.
B)Improvements in the quality of capital.
C)Improvements in management practices.
D)Increases in the quantity of capital.
E)More education for the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Solow growth model explains:
A)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technological change combine in the short term to determine economic growth.
B)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technological change combine in the longer term to determine economic growth.
C)how history changes economic growth.
D)how net exports determine economic growth.
A)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technological change combine in the short term to determine economic growth.
B)how consumption, saving, capital, labour and technological change combine in the longer term to determine economic growth.
C)how history changes economic growth.
D)how net exports determine economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following statements is correct regarding the Solow growth model?
A)Increases in living standards will be achieved automatically in the long run.
B)An increase in the saving rate will always result in a higher level of output per person.
C)An increase in the saving rate will always result in a higher level of consumption per person.
D)The optimal saving rate will be achieved as the community is no better off by additional saving.
A)Increases in living standards will be achieved automatically in the long run.
B)An increase in the saving rate will always result in a higher level of output per person.
C)An increase in the saving rate will always result in a higher level of consumption per person.
D)The optimal saving rate will be achieved as the community is no better off by additional saving.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding the Solow growth model?
A)Increases in living standards are not necessarily guaranteed in an economy.
B)The optimal saving rate is achieved when saving per person is maximised.
C)The optimal saving rate is achieved when consumption per capita is maximised.
D)The optimal saving rate is derived under the assumption that technology is constant.
A)Increases in living standards are not necessarily guaranteed in an economy.
B)The optimal saving rate is achieved when saving per person is maximised.
C)The optimal saving rate is achieved when consumption per capita is maximised.
D)The optimal saving rate is derived under the assumption that technology is constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is an example of a government policy aimed at increasing the long-term living standards of Australians?
A)Increases in government spending.
B)Decreases in taxes.
C)Decreases in interest rates.
D)Compulsory superannuation.
E)Increases in interest rates.
A)Increases in government spending.
B)Decreases in taxes.
C)Decreases in interest rates.
D)Compulsory superannuation.
E)Increases in interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The Solow growth model was the first economic model to show that long-term increases in living standards depended crucially on:
A)increases in capital.
B)increases in labour.
C)increases in saving rates.
D)technological progress.
A)increases in capital.
B)increases in labour.
C)increases in saving rates.
D)technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
One country can have a higher level of output per worker because of:
A)an increase in the unemployment rate.
B)a reduction in its labour force.
C)improvement in its available production technologies.
D)a reduction in population.
A)an increase in the unemployment rate.
B)a reduction in its labour force.
C)improvement in its available production technologies.
D)a reduction in population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
One of the problems in a country achieving its steady-state level in the Solow model is that:
A)short-term saving must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
B)short-term consumption must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
C)short-term investment must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
D)future generations will need to cut back on consumption in the long term.
E)future generations will need to decrease savings in the long term.
A)short-term saving must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
B)short-term consumption must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
C)short-term investment must be sacrificed in order to increase living standards in the long term.
D)future generations will need to cut back on consumption in the long term.
E)future generations will need to decrease savings in the long term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In terms of the Solow growth model,the recent situation in Japan is perhaps an example of where a country has:
A)failed to increase its savings to the optimal rate.
B)been consistently able to achieve its optimal savings rate.
C)exceeded its optimal savings rate.
D)put too much emphasis on current consumption at the expense of future generations.
A)failed to increase its savings to the optimal rate.
B)been consistently able to achieve its optimal savings rate.
C)exceeded its optimal savings rate.
D)put too much emphasis on current consumption at the expense of future generations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A country can increase its real GDP per person by:
A)reducing the quantity of production factors.
B)increasing the number of holidays.
C)reducing its spending.
D)using more productive technology.
A)reducing the quantity of production factors.
B)increasing the number of holidays.
C)reducing its spending.
D)using more productive technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a country has no technological progress,the only way for it to have long-term increases in living standards is by:
A)continually increasing capital per worker.
B)continually increasing the saving rate.
C)continually increasing investment in research and development.
D)the government continually running budget surpluses to increase national savings.
A)continually increasing capital per worker.
B)continually increasing the saving rate.
C)continually increasing investment in research and development.
D)the government continually running budget surpluses to increase national savings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Without technological progress a country can never enjoy sustained increases in living standards because:
A)of diminishing marginal productivity.
B)of decreasing returns to scale.
C)an economy can never exceed its optimal rate of saving in the long run.
D)of increasing marginal productivity.
A)of diminishing marginal productivity.
B)of decreasing returns to scale.
C)an economy can never exceed its optimal rate of saving in the long run.
D)of increasing marginal productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For a given state of unchanging production technologies without the technological change:
A)no further growth in living standards can be achieved at some point in time.
B)further growth in living standards can be achieved if investment is higher than consumption.
C)further growth in living standards can be achieved at some point in time.
D)further growth in living standards can be achieved if saving is higher than investment.
A)no further growth in living standards can be achieved at some point in time.
B)further growth in living standards can be achieved if investment is higher than consumption.
C)further growth in living standards can be achieved at some point in time.
D)further growth in living standards can be achieved if saving is higher than investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following statements best represents the impact of technological progress in the Solow growth model?
A)There must be increases in the quality and quantity of consumption for long-term growth to be achieved.
B)Technological progress is necessary to achieve the steady-state level of consumption per worker.
C)There must be increases in the quality and quantity of capital for long-term growth to be achieved.
D)Technological progress allows for an increase in the saving rate.
A)There must be increases in the quality and quantity of consumption for long-term growth to be achieved.
B)Technological progress is necessary to achieve the steady-state level of consumption per worker.
C)There must be increases in the quality and quantity of capital for long-term growth to be achieved.
D)Technological progress allows for an increase in the saving rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 124 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



