Deck 1: The Night Sky
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/88
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: The Night Sky
1
At apogee, the Moon is at its farthest from the Earth and thus appears larger than normal. Because of this, it can produce total solar eclipses, but not annular solar eclipses.
True
2
The first quarter Moon will rise about noon, and set about midnight.
True
3
When the Moon passes directly between the Sun and the Earth, we see a lunar eclipse.
False
4
A light-year is a measurement of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the choices below correctly lists things in order from largest to smallest?
A) Sun, Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, Universe
B) Universe, Milky Way, Sun, Earth, Solar System
C) Solar System, Earth, Sun, Universe, Milky Way
D) Universe, Milky Way, Solar System, Sun, Earth
E) Milky Way, Universe, Solar System, Sun, Earth
A) Sun, Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, Universe
B) Universe, Milky Way, Sun, Earth, Solar System
C) Solar System, Earth, Sun, Universe, Milky Way
D) Universe, Milky Way, Solar System, Sun, Earth
E) Milky Way, Universe, Solar System, Sun, Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
At apogee, the Moon is at its farthest from Earth and thus appears smaller than normal. Because of this it can produce only annular solar eclipses, but not total solar eclipses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Constellations are close clusters of stars, all at about the same distance from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
No one knew that the Earth was round (spherical) until the 1500s, when explorers such as Magellan sailed around the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Full Moon rises around sunrise, and sets around sunset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As it orbits the Earth, the Moon appears to move eastward about its own diameter every hour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
From the South Pole, Polaris would appear directly overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following can be described as the totality of all space, time, matter, and energy?
A) The universe
B) Astronomy
C) The Milky Way
D) The Earth
E) The solar system
A) The universe
B) Astronomy
C) The Milky Way
D) The Earth
E) The solar system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
From full Moon to third quarter Moon takes about a week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
It was Aristotle who used the scientific method to show the Earth was a sphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a star rises about 9 PM tonight, and with the sidereal day being four minutes less than the solar one, then in a month it will rise about 7 PM.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Only at the equator are all the stars visible over the course of the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Where did most of the chemical elements that make up our bodies come from?
A) The Sun
B) Vanished Stars
C) The Big Bang
D) Other planets
A) The Sun
B) Vanished Stars
C) The Big Bang
D) Other planets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
There are 3,600 arc seconds in a degree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The distances to bodies in the solar system are a few light minutes to light hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Over the course of a night, Polaris moves less than any other visible star in the sky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
This diagram explains 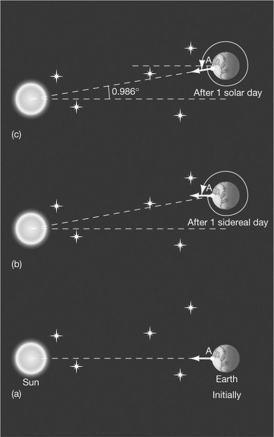
A) the difference between solar time and sidereal time.
B) precession.
C) the solar day's relation to the Moon.
D) the sidereal day's relation to the seasons.

A) the difference between solar time and sidereal time.
B) precession.
C) the solar day's relation to the Moon.
D) the sidereal day's relation to the seasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You note that a particular star is directly overhead. It will be directly overhead again in
A) 1 hour.
B) 12 hours.
C) 23 hours 56 minutes.
D) 24 hours.
E) 24 hours 4 minutes.
A) 1 hour.
B) 12 hours.
C) 23 hours 56 minutes.
D) 24 hours.
E) 24 hours 4 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What celestial line is a product of the Earth's orbit around the Sun?
A) Ecliptic
B) Prime Meridian
C) Equator
D) Galactic Plane
E) Analemma
A) Ecliptic
B) Prime Meridian
C) Equator
D) Galactic Plane
E) Analemma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
About how many stars are visible on a clear, dark night with the unaided eye alone?
A) A few dozen
B) A few hundred
C) A few thousand
D) Tens of thousands
E) Millions and millions
A) A few dozen
B) A few hundred
C) A few thousand
D) Tens of thousands
E) Millions and millions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Into how many constellations is the celestial sphere divided?
A) 12
B) 44
C) 57
D) 88
E) 110
A) 12
B) 44
C) 57
D) 88
E) 110

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The place the Sun stops its northward motion along the ecliptic is the
A) equator.
B) prime meridian.
C) summer solstice.
D) vernal equinox.
A) equator.
B) prime meridian.
C) summer solstice.
D) vernal equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Seasons on Earth are primarily caused by
A) the distance from the Earth to the Sun.
B) the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis.
C) the tilt of the Earth's magnetic axis.
D) the precession of the Earth's rotational axis.
E) the dates of the solstices and equinoxes.
A) the distance from the Earth to the Sun.
B) the tilt of the Earth's rotational axis.
C) the tilt of the Earth's magnetic axis.
D) the precession of the Earth's rotational axis.
E) the dates of the solstices and equinoxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
That Polaris will not always be the pole star is due to
A) the sidereal day being shorter than the solar day.
B) precession shifting the celestial pole.
C) the Moon following the ecliptic, instead of the equator.
D) the Earth's revolution being slightly less than exactly 365.25 days.
E) the Solar winds blowing the Earth farther away from the Sun.
A) the sidereal day being shorter than the solar day.
B) precession shifting the celestial pole.
C) the Moon following the ecliptic, instead of the equator.
D) the Earth's revolution being slightly less than exactly 365.25 days.
E) the Solar winds blowing the Earth farther away from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A year is defined as
A) the time it takes for Earth to complete a rotation on its axis.
B) the time it takes for the Moon to complete an orbit of Earth.
C) the time it takes for the Moon to complete a phase cycle.
D) the time it takes for Earth to complete an orbit around the Sun.
E) the time it takes for the Sun to complete an orbit around Earth.
A) the time it takes for Earth to complete a rotation on its axis.
B) the time it takes for the Moon to complete an orbit of Earth.
C) the time it takes for the Moon to complete a phase cycle.
D) the time it takes for Earth to complete an orbit around the Sun.
E) the time it takes for the Sun to complete an orbit around Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
From a location in the United States of America, a star is observed to be rising due East. Where will this star be located 6 hours later?
A) Directly overhead
B) High in the Northern sky
C) High in the southern sky
D) Setting due West
E) The location of the star cannot be determined from the information given.
A) Directly overhead
B) High in the Northern sky
C) High in the southern sky
D) Setting due West
E) The location of the star cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which statement about the ecliptic is FALSE?
A) The Sun appears to move about a degree per day eastward long it.
B) It is tilted 23.5 degrees with respect to the equator.
C) The year is marked by the Sun's return to the same place along it.
D) The Moon can never leave it, but moves twelve times faster than the Sun.
E) The major planets stay close to it, but not always on it.
A) The Sun appears to move about a degree per day eastward long it.
B) It is tilted 23.5 degrees with respect to the equator.
C) The year is marked by the Sun's return to the same place along it.
D) The Moon can never leave it, but moves twelve times faster than the Sun.
E) The major planets stay close to it, but not always on it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Where would you be if the Sun sets for six continuous months, beginning about September 23rd?
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Equator
D) Antarctic Circle
E) South Pole
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Equator
D) Antarctic Circle
E) South Pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How many arc seconds are in a degree?
A) 60
B) 3600
C) 600
D) 86400
E) None; seconds measure time and degrees measure temperature.
A) 60
B) 3600
C) 600
D) 86400
E) None; seconds measure time and degrees measure temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What are constellations?
A) Groups of galaxies gravitationally bound and close together in the sky
B) Groups of stars making an apparent pattern in the celestial sphere
C) Groups of stars gravitationally bound and appearing close together in the sky
D) Ancient story boards, useless to modern astronomers
E) Apparent groupings of stars and planets visible on a given evening
A) Groups of galaxies gravitationally bound and close together in the sky
B) Groups of stars making an apparent pattern in the celestial sphere
C) Groups of stars gravitationally bound and appearing close together in the sky
D) Ancient story boards, useless to modern astronomers
E) Apparent groupings of stars and planets visible on a given evening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The angular size of an object depends on which two quantities?
A) The object's actual size and its mass
B) The object's distance from us and its brightness
C) The object's actual size and its distance from us
D) The object's brightness and its mass
A) The object's actual size and its mass
B) The object's distance from us and its brightness
C) The object's actual size and its distance from us
D) The object's brightness and its mass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How long is the precession cycle?
A) 1 day
B) 29.5 days
C) 365.24 days
D) 18 years, 11.3 days
E) 26,000 years
A) 1 day
B) 29.5 days
C) 365.24 days
D) 18 years, 11.3 days
E) 26,000 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Where on Earth would you be if Polaris were directly overhead?
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Tropic of Cancer
D) Equator
E) It lies overhead everywhere on Earth.
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Tropic of Cancer
D) Equator
E) It lies overhead everywhere on Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
While watching a star, you see it moves 15 degrees across the sky. How long have you been watching it?
A) 1 hour
B) 3 hours
C) 15 minutes
D) 15 seconds
E) 1 minute
A) 1 hour
B) 3 hours
C) 15 minutes
D) 15 seconds
E) 1 minute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Where on Earth can you observe all the stars in the sky over an entire year?
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Tropic of Cancer
D) Equator
E) Everyone on Earth can see the whole sky.
A) North Pole
B) Arctic Circle
C) Tropic of Cancer
D) Equator
E) Everyone on Earth can see the whole sky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The places where the Sun crosses the equator are called the
A) annalemmas.
B) prime meridians.
C) zeniths.
D) equinoxes.
E) solstices.
A) annalemmas.
B) prime meridians.
C) zeniths.
D) equinoxes.
E) solstices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An effective theory must
A) have been proven.
B) must have been around for centuries or longer.
C) be continuously tested.
D) include mathematical formulae.
A) have been proven.
B) must have been around for centuries or longer.
C) be continuously tested.
D) include mathematical formulae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What conditions are necessary for an annular solar eclipse?
A) New Moon on equator at perigee
B) Full Moon on ecliptic at perihelion
C) New Moon on ecliptic at perigee
D) New Moon on equator at apogee
E) New Moon on ecliptic at apogee
A) New Moon on equator at perigee
B) Full Moon on ecliptic at perihelion
C) New Moon on ecliptic at perigee
D) New Moon on equator at apogee
E) New Moon on ecliptic at apogee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Some type of solar eclipse will happen about
A) every month at new Moon.
B) every week at full Moon.
C) every month at full Moon.
D) about every six months at new Moon.
E) every year at new Moon.
A) every month at new Moon.
B) every week at full Moon.
C) every month at full Moon.
D) about every six months at new Moon.
E) every year at new Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Modern scientific theories are NOT
A) testable.
B) continuously tested.
C) simple.
D) perfect.
E) elegant.
A) testable.
B) continuously tested.
C) simple.
D) perfect.
E) elegant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If new Moon fell on March 2nd, what is the Moon's phase on March 14th?
A) Waxing crescent
B) First quarter
C) Waxing gibbous
D) Full
E) Waning crescent
A) Waxing crescent
B) First quarter
C) Waxing gibbous
D) Full
E) Waning crescent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What conditions are necessary for a partial solar eclipse?
A) New Moon on ecliptic, with us in the penumbral shadow
B) Full Moon on equator, with us in the umbral shadow
C) New Moon at perigee
D) Full Moon at apogee
E) First or third quarter Moon crossing the ecliptic
A) New Moon on ecliptic, with us in the penumbral shadow
B) Full Moon on equator, with us in the umbral shadow
C) New Moon at perigee
D) Full Moon at apogee
E) First or third quarter Moon crossing the ecliptic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement about the first quarter Moon is FALSE?
A) It rises about noon.
B) From the Earth, it appears 25% sunlit.
C) It is the half Moon of the evening sky.
D) It is highest in the sky at sunset.
E) It occurs about a week after new Moon.
A) It rises about noon.
B) From the Earth, it appears 25% sunlit.
C) It is the half Moon of the evening sky.
D) It is highest in the sky at sunset.
E) It occurs about a week after new Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If you are in the Moon's umbral shadow, then you will witness
A) nighttime.
B) a total solar eclipse.
C) a total lunar eclipse.
D) a partial solar eclipse.
E) some kind of lunar eclipse.
A) nighttime.
B) a total solar eclipse.
C) a total lunar eclipse.
D) a partial solar eclipse.
E) some kind of lunar eclipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Milky Way galaxy contains about ________ stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What conditions are necessary for a total solar eclipse?
A) New Moon on ecliptic near perigee
B) Full Moon on ecliptic near aphelion
C) New Moon on equator at perigee
D) Full Moon on equator at perigee
E) New Moon on ecliptic near aphelion
A) New Moon on ecliptic near perigee
B) Full Moon on ecliptic near aphelion
C) New Moon on equator at perigee
D) Full Moon on equator at perigee
E) New Moon on ecliptic near aphelion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A solar eclipse can only happen during a
A) new Moon.
B) solstice.
C) first quarter Moon.
D) full Moon.
E) perihelion passage of the Sun.
A) new Moon.
B) solstice.
C) first quarter Moon.
D) full Moon.
E) perihelion passage of the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The distances to other stars are best measured in ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A lunar eclipse can only happen during a
A) new Moon.
B) equinox.
C) full Moon.
D) perigee.
E) aphelion.
A) new Moon.
B) equinox.
C) full Moon.
D) perigee.
E) aphelion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The Last Quarter phase of the Moon
A) rises at sunrise.
B) sets at sunrise.
C) crosses the meridian at sunrise.
D) rises at sunset.
E) sets at sunset.
A) rises at sunrise.
B) sets at sunrise.
C) crosses the meridian at sunrise.
D) rises at sunset.
E) sets at sunset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The constellations of the zodiac fall along
A) the ecliptic.
B) the celestial equator.
C) lines of longitude.
D) lines of latitude.
A) the ecliptic.
B) the celestial equator.
C) lines of longitude.
D) lines of latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the Sun rises it is located in the constellation Gemini. When the Sun sets later that same day it will be
A) in the constellation Aries.
B) in the constellation Taurus.
C) in the constellation Gemini.
D) in the constellation Cancer.
E) in the constellation Leo.
A) in the constellation Aries.
B) in the constellation Taurus.
C) in the constellation Gemini.
D) in the constellation Cancer.
E) in the constellation Leo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the Moon rose tonight at 6 PM, then tomorrow it will rise about
A) the same time.
B) 7 PM.
C) 5 PM.
D) dawn.
E) midnight.
A) the same time.
B) 7 PM.
C) 5 PM.
D) dawn.
E) midnight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Aristotle's hypothesis was that
A) lunar eclipses were created by our shadow.
B) only a spherical Earth would always cast a circular shadow on the Moon.
C) lunar eclipses would have to happen every full Moon.
D) the Sun lay at the center of the planet orbits.
E) the Moon orbited the Earth.
A) lunar eclipses were created by our shadow.
B) only a spherical Earth would always cast a circular shadow on the Moon.
C) lunar eclipses would have to happen every full Moon.
D) the Sun lay at the center of the planet orbits.
E) the Moon orbited the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why is there a two-day difference in the sidereal and synodic months?
A) The Moon speeds up at perigee, and slows down at apogee.
B) The sidereal day is four minutes shorter than the solar day, and it adds up.
C) The Earth is closer to the Sun during the sidereal month.
D) The Earth is also revolving around the Sun, so the Moon must "catch up."
E) The Moslem lunar year is only 354 days long, on average.
A) The Moon speeds up at perigee, and slows down at apogee.
B) The sidereal day is four minutes shorter than the solar day, and it adds up.
C) The Earth is closer to the Sun during the sidereal month.
D) The Earth is also revolving around the Sun, so the Moon must "catch up."
E) The Moslem lunar year is only 354 days long, on average.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Where would you be if the Sun passes directly overhead on December 21st?
A) Equator
B) Tropic of Cancer
C) Tropic of Capricorn
D) Antarctic Circle
E) South Pole
A) Equator
B) Tropic of Cancer
C) Tropic of Capricorn
D) Antarctic Circle
E) South Pole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The ________ of the Earth causes the Sun and Moon to rise in the east and set in the west.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If a theory is testable, its underlying ________ and its ________ can be exposed to experimental verification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The ________ is the totality of all space, time, matter, and energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The four extra minutes in the solar day are due to our ________ around the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Why are some solar eclipses total, and others annular?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How far above or below the ecliptic can the Sun move?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The celestial sphere appears to move fastest above the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If the bright star Sirius transits my local meridian tonight at 6:43 PM, when will it transit tomorrow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A solar eclipse can only happen during a ________ Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Early astronomers picture the Earth as stationary, with the ________ spinning, moving the stars along with it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the Moon rises exactly at sunset, what will its phase be? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which is longer, the sidereal or solar day? By how much?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The two days when the Sun rises due east and sets due west are the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A solar eclipse can only happen during a ________ Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If intending to teach his students the constellations by season, why would an astronomy instructor be advised to always assign the stars in the current western sky at the beginning of each term?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The first quarter Moon rises about noon today; what will its phase be, and when will it rise tomorrow?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Sun's lowest position in the sky occurs at the ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A ________ is a framework of ideas and assumption used to explain some set of observations and make predictions about the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the name of the point on the celestial sphere that all stars seem to circle around, when viewing the sky from North America?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How far above and below the celestial equator can the Sun move?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 88 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



