Deck 8: The Sun
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/95
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: The Sun
1
Both the gravitational and electromagnetic forces obey the inverse square law, and extend infinitely outward in their effects.
True
2
The solar corona is much cooler than the Sun's surface; hence we must wait for a total solar eclipse to glimpse it with the naked eye.
False
3
A sunbather on the clear day is receiving about 500 watts of solar power.
True
4
Solar activity cannot disrupt communications on Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The concept of hydrostatic equilibrium is critical to understanding how the Sun has remained stable long enough for live to evolve here.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The solar corona produces a lot more X-rays than it does visible light.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Sun's luminosity is greatest when there are few or no sunspots on the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The light we see from the Sun comes from which layer?
A) Troposphere
B) Chromosphere
C) Photosphere
D) Ionosphere
E) Corona
A) Troposphere
B) Chromosphere
C) Photosphere
D) Ionosphere
E) Corona

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the proton-proton cycle, you must first make deuterium, then helium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
At very large distances from the Sun, its corona turns into the solar wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
We know the Sun rotates differentially by observing sunspots; as with Jupiter the solar equator rotates the fastest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the proton-proton cycle, .007 of the mass ends up as energy, not helium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The proton-proton chain requires a temperature of 100 million K to get started.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Large sunspots are larger than our whole planet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Granulation is the most obvious proof of solar convective energy transport.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Sun is a fairly normal star.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The energy of the Sun starts as radiation, but is actually transported to its surface by convection, where it is radiated off into space at last.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The photosphere is about 100 times the diameter of the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Sunspots are only about 2,000 K cooler than the much brighter photosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Prominences hanging off the limb of the Sun are the same as filaments seen in front of the disk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The density of the Sun is most similar to which object?
A) Halley's Comet's nucleus
B) The Earth
C) Mercury
D) The Moon
E) Jupiter
A) Halley's Comet's nucleus
B) The Earth
C) Mercury
D) The Moon
E) Jupiter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When we glimpse the chromosphere at the start and end of totality, its color is
A) green (the famous flash).
B) yellow, like the photosphere below it.
C) red, due to ionized hydrogen at lower pressure.
D) blue, due to the ionization of nitrogen by the magnetic fields.
E) white from the moonlight.
A) green (the famous flash).
B) yellow, like the photosphere below it.
C) red, due to ionized hydrogen at lower pressure.
D) blue, due to the ionization of nitrogen by the magnetic fields.
E) white from the moonlight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The temperature of the layer of gas that produces the visible light of the Sun is
A) 3,500 K
B) 5,800 K
C) 12,300 K
D) 300,000 K
E) 15 million K
A) 3,500 K
B) 5,800 K
C) 12,300 K
D) 300,000 K
E) 15 million K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
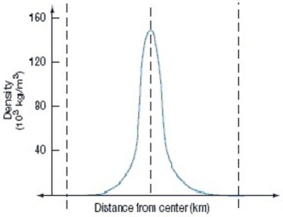
The above diagram indicates that
A) the Sun is most dense somewhere between its surface and its core.
B) the Sun is least dense somewhere between its surface and its core.
C) the Sun is more dense at its surface than at its core.
D) the Sun is more dense at its core than at its surface.
E) the Sun has about the same density throughout its interior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The vibrations of the Sun reveal information about
A) the temperature of the core of the Sun.
B) the structure of the atmosphere of the Sun.
C) the interior structure of the Sun.
D) the production of energy in the Sun.
E) the magnetic field of the Sun.
A) the temperature of the core of the Sun.
B) the structure of the atmosphere of the Sun.
C) the interior structure of the Sun.
D) the production of energy in the Sun.
E) the magnetic field of the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The outward pressure of hot gas in the Sun
A) is balanced by the inward gravitational pressure.
B) is increasing the Sun's diameter.
C) is cooling the photosphere.
D) is responsible for variations in the sunspot cycle.
E) weakens the magnetic field.
A) is balanced by the inward gravitational pressure.
B) is increasing the Sun's diameter.
C) is cooling the photosphere.
D) is responsible for variations in the sunspot cycle.
E) weakens the magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The pattern of rising hot gas cells all over the photosphere is called
A) filaments.
B) granulation.
C) sunspots.
D) convective projections.
E) prominences.
A) filaments.
B) granulation.
C) sunspots.
D) convective projections.
E) prominences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
From inside out, which is in the correct order for the structure of the Sun?
A) Core, convective zone, radiative zone
B) Photosphere, radiative zone, corona
C) Radiative zone, convective zone, chromosphere
D) Core, chromosphere, photosphere
E) Convective zone, radiative zone, granulation
A) Core, convective zone, radiative zone
B) Photosphere, radiative zone, corona
C) Radiative zone, convective zone, chromosphere
D) Core, chromosphere, photosphere
E) Convective zone, radiative zone, granulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What two energy transport mechanisms, in order from outside the core to the surface, is found in the Sun?
A) Convection, conduction
B) Fadiative diffusion, convection
C) Conduction, radiative diffusion
D) Fadiative diffusion, conduction
E) Conduction, convection
A) Convection, conduction
B) Fadiative diffusion, convection
C) Conduction, radiative diffusion
D) Fadiative diffusion, conduction
E) Conduction, convection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The area in the Sun's atmosphere located above the chromosphere (1,500 - 10,000 km) where the temperature rises dramatically is called the
A) photosphere.
B) corona.
C) solar wind.
D) transition zone.
E) convection zone.
A) photosphere.
B) corona.
C) solar wind.
D) transition zone.
E) convection zone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Studies by the Global Oscillations Network Group, along with satellite observations, indicate
A) that the standard solar model requires substantial modification.
B) that all stars show the same kind of vibrations that our Sun does.
C) that there is an unknown energy transport mechanism in the Sun.
D) that there is less convection in the Sun than predicted by the standard solar model.
E) that the standard solar model accurately models the observed solar vibrations.
A) that the standard solar model requires substantial modification.
B) that all stars show the same kind of vibrations that our Sun does.
C) that there is an unknown energy transport mechanism in the Sun.
D) that there is less convection in the Sun than predicted by the standard solar model.
E) that the standard solar model accurately models the observed solar vibrations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the size of a typical granule or convection cell seen in the photosphere?
A) 10,000 km
B) 1,000 km
C) 100 km
D) 10 km
E) 1 km
A) 10,000 km
B) 1,000 km
C) 100 km
D) 10 km
E) 1 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When the chromosphere can be seen during a solar eclipse, it appears
A) invisible.
B) violet.
C) blue.
D) yellow.
E) red.
A) invisible.
B) violet.
C) blue.
D) yellow.
E) red.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
By what mechanism does solar energy reach the Sun's photosphere from the layer just underneath it?
A) Differentiation
B) Ionization
C) Radiation
D) Convection
E) Conduction
A) Differentiation
B) Ionization
C) Radiation
D) Convection
E) Conduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The luminosity of the Sun is a measure of
A) the energy received by the Sun on Earth's surface.
B) the energy received by the Sun at the location of Earth.
C) the energy received by the Sun at any location in the solar system.
D) the energy emitted by the Sun at the photosphere.
E) the total energy emitted by the Sun in all directions.
A) the energy received by the Sun on Earth's surface.
B) the energy received by the Sun at the location of Earth.
C) the energy received by the Sun at any location in the solar system.
D) the energy emitted by the Sun at the photosphere.
E) the total energy emitted by the Sun in all directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Why couldn't you stand on the Sun's surface?
A) The Sun has no surface at all...the photosphere is an illusion.
B) You could stand on the surface.
C) The Sun doesn't have a solid surface.
D) The Sun's surface is too highly magnetized for anything to survive there.
E) You could stand on it, if a sufficiently protective spacesuit could be designed.
A) The Sun has no surface at all...the photosphere is an illusion.
B) You could stand on the surface.
C) The Sun doesn't have a solid surface.
D) The Sun's surface is too highly magnetized for anything to survive there.
E) You could stand on it, if a sufficiently protective spacesuit could be designed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Hydrostatic equilibrium in our Sun is the balance between
A) convection and radiation.
B) convection and gravitation.
C) pressure and radiation.
D) radiation and gravitation.
E) gravitation and pressure.
A) convection and radiation.
B) convection and gravitation.
C) pressure and radiation.
D) radiation and gravitation.
E) gravitation and pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
From where does most of the solar wind flow?
A) Granules
B) Sunspots
C) Flares
D) Prominences
E) Coronal holes
A) Granules
B) Sunspots
C) Flares
D) Prominences
E) Coronal holes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is it about the Sun's corona that astronomers don't understand?
A) No one knows why that part of the Sun's atmosphere does not drift away into space.
B) During total solar eclipses, the corona sometimes disappears from view.
C) The corona seems to absorb 2/3 of the neutrinos that pass through it.
D) The corona is much hotter than layers of the Sun that are closer to the solar interior.
E) The Sun's corona extends to the outer reaches of the solar system.
A) No one knows why that part of the Sun's atmosphere does not drift away into space.
B) During total solar eclipses, the corona sometimes disappears from view.
C) The corona seems to absorb 2/3 of the neutrinos that pass through it.
D) The corona is much hotter than layers of the Sun that are closer to the solar interior.
E) The Sun's corona extends to the outer reaches of the solar system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
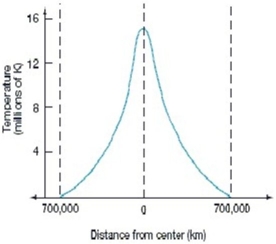
The above diagram indicates that
A) the Sun is hottest somewhere between its surface and its core.
B) the Sun is coolest somewhere between its surface and its core.
C) the Sun is hotter at its surface than at its core.
D) the Sun is hotter at its core than at its surface.
E) the Sun has about the same temperature throughout its interior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The most striking example of solar variability was the
A) Dust Bowl drought of the 1930s.
B) Maunder Minimum from 1645-1715.
C) Sporer Minimum that doomed the Anasazi.
D) fall of Rome.
E) Joseph's seven lean years in the Old Testament.
A) Dust Bowl drought of the 1930s.
B) Maunder Minimum from 1645-1715.
C) Sporer Minimum that doomed the Anasazi.
D) fall of Rome.
E) Joseph's seven lean years in the Old Testament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The numbers of sunspots and their activity peak about every
A) 36 days.
B) six months.
C) year.
D) eleven years.
E) 76 years.
A) 36 days.
B) six months.
C) year.
D) eleven years.
E) 76 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
During a period of high solar activity, the corona
A) disappears.
B) is more irregular.
C) cools almost to the temperature of the photosphere.
D) becomes smooth and even.
E) shrinks to half its normal size.
A) disappears.
B) is more irregular.
C) cools almost to the temperature of the photosphere.
D) becomes smooth and even.
E) shrinks to half its normal size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sunspots are dark splotches on the Sun. Which statement is TRUE?
A) They are hotter than the surrounding areas of the Sun.
B) They are extremely cold objects, as cold as Pluto.
C) They are extremely hot, but cooler than the surrounding areas of the Sun.
D) They are solid bodies floating on the surface of the Sun.
E) They are associated with areas of very low magnetic fields.
A) They are hotter than the surrounding areas of the Sun.
B) They are extremely cold objects, as cold as Pluto.
C) They are extremely hot, but cooler than the surrounding areas of the Sun.
D) They are solid bodies floating on the surface of the Sun.
E) They are associated with areas of very low magnetic fields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Loops of glowing hydrogen seen hanging over the solar limb during totality are
A) solar rainbows.
B) haloes.
C) prominences.
D) filaments.
E) flares.
A) solar rainbows.
B) haloes.
C) prominences.
D) filaments.
E) flares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Suppose a large flare is detected optically. How long until radio interference arrives?
A) Simultaneously
B) 8.5 minutes later
C) About 12 hours
D) About four days
E) No relation between the two
A) Simultaneously
B) 8.5 minutes later
C) About 12 hours
D) About four days
E) No relation between the two

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The percentage (by number of atoms) of the Sun that is hydrogen is about
A) 91%.
B) 71%.
C) 27%.
D) 9%.
E) less than 1%.
A) 91%.
B) 71%.
C) 27%.
D) 9%.
E) less than 1%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What natural barrier tries to prevent two protons from combining?
A) Dark energy
B) Antigravity
C) Electromagnetic repulsion
D) The weak nuclear force
E) The strong nuclear force
A) Dark energy
B) Antigravity
C) Electromagnetic repulsion
D) The weak nuclear force
E) The strong nuclear force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The critical temperature the core must reach for a star to shine by fusion is
A) 5,800 K.
B) 11,000 K.
C) 127,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.
A) 5,800 K.
B) 11,000 K.
C) 127,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The primary source of the Sun's energy is
A) oxidation of carbon in the core.
B) gravitational collapse of the helium coreward.
C) dark energy.
D) the strong force fusing hydrogen into helium.
E) the weak force creating energy from uranium decay.
A) oxidation of carbon in the core.
B) gravitational collapse of the helium coreward.
C) dark energy.
D) the strong force fusing hydrogen into helium.
E) the weak force creating energy from uranium decay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
How long does the sunspot cycle last, on average?
A) Between 25 and 35 days
B) 365.25 days
C) About seven years
D) About 11 years
E) About 76 years
A) Between 25 and 35 days
B) 365.25 days
C) About seven years
D) About 11 years
E) About 76 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of these are NOT associated with the active Sun?
A) Sunspots
B) Prominences
C) Granulation
D) Flares
E) Aurora
A) Sunspots
B) Prominences
C) Granulation
D) Flares
E) Aurora

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
As the Sun rotates, an individual sunspot can be tracked across its face. From eastern to western limb, this takes about
A) 12 hours.
B) a week.
C) two weeks.
D) a month.
E) 5.5 years.
A) 12 hours.
B) a week.
C) two weeks.
D) a month.
E) 5.5 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
While observing the Sun, you note a large number of sunspots. What can you conclude?
A) The Sun is less luminous than usual.
B) This is a period of low solar activity.
C) Earth's climate will be unusually cold.
D) The Sun's rotation is slower than average.
E) There are likely to be an above average number of flares and prominences.
A) The Sun is less luminous than usual.
B) This is a period of low solar activity.
C) Earth's climate will be unusually cold.
D) The Sun's rotation is slower than average.
E) There are likely to be an above average number of flares and prominences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the proton-proton cycle, the positron is
A) massless.
B) a spin conservation particle.
C) an anti-electron.
D) the chief means energy reaches the photosphere.
E) intermediate between the proton and neutron in mass.
A) massless.
B) a spin conservation particle.
C) an anti-electron.
D) the chief means energy reaches the photosphere.
E) intermediate between the proton and neutron in mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In the proton-proton cycle, the helium atom and neutrino have less mass than the original hydrogen. What happens to the "lost" mass?
A) It is recycled back into hydrogen.
B) It is ejected into space.
C) It is converted to energy.
D) It is transformed into electrons.
E) Conservation of mass dictates no mass can be lost.
A) It is recycled back into hydrogen.
B) It is ejected into space.
C) It is converted to energy.
D) It is transformed into electrons.
E) Conservation of mass dictates no mass can be lost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
On the Sun, what takes approximately 22 years to happen?
A) The Sun takes that time to rotate on its axis.
B) The complete sunspot cycle, including magnetic field reversals.
C) Solar vibrations begin every 22 years.
D) Solar activities goes from its maximum to minimum.
E) The corona reaches its maximum temperature and ejects gas every 22 years.
A) The Sun takes that time to rotate on its axis.
B) The complete sunspot cycle, including magnetic field reversals.
C) Solar vibrations begin every 22 years.
D) Solar activities goes from its maximum to minimum.
E) The corona reaches its maximum temperature and ejects gas every 22 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How would sunspots appear if you could magically remove them from the Sun?
A) They would appear blue-white, like Sirius but brighter.
B) Because sunspots are dark spots, they would be invisible against the blackness of space.
C) They would shine bright orange in color, like Arcturus.
D) They would not appear any differently than on the surface of the Sun.
E) They would shine only with reflected sunlight, appearing similar to Venus.
A) They would appear blue-white, like Sirius but brighter.
B) Because sunspots are dark spots, they would be invisible against the blackness of space.
C) They would shine bright orange in color, like Arcturus.
D) They would not appear any differently than on the surface of the Sun.
E) They would shine only with reflected sunlight, appearing similar to Venus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Visible sunspots lie in the
A) chromosphere.
B) transition zone.
C) corona.
D) radiative zone.
E) granulation in the photosphere.
A) chromosphere.
B) transition zone.
C) corona.
D) radiative zone.
E) granulation in the photosphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Sunspots
A) are always found close to the Sun's poles.
B) come in pairs, representing the north and south magnetic fields.
C) were most numerous during the Maunder Minimum.
D) travel over the surface of the Sun from pole to pole.
E) are relatively constant in number every year.
A) are always found close to the Sun's poles.
B) come in pairs, representing the north and south magnetic fields.
C) were most numerous during the Maunder Minimum.
D) travel over the surface of the Sun from pole to pole.
E) are relatively constant in number every year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In contrast to the photosphere's continuum, the spectrum of the chromosphere is dominated by ________ lines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What do sunspots tell us about the Sun's rotation rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Energy produced in the solar core is transferred by ________ until it reaches a point about 500,000 km from the center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Neutrinos travel from the Sun's core to the Earth in
A) millions of years.
B) thousands of years.
C) a few days.
D) a few hours.
E) a few minutes.
A) millions of years.
B) thousands of years.
C) a few days.
D) a few hours.
E) a few minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How is energy transfer from the solar interior to surface similar to a process in Earth's atmosphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The solar magnetic field is strongest in those regions called ________, which are poles and usually thus occur in pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the main constituents of the solar wind?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The critical temperature the core must reach for a star to shine by fusion is
A) 5,800 K.
B) 11,000 K.
C) 127,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.
A) 5,800 K.
B) 11,000 K.
C) 127,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
There appears to be a correlation between the 22-year solar cycle and
A) droughts in North America.
B) asteroid impacts on Earth.
C) change of which political party has the majority in the U.S. Congress.
D) the length of Mercury's day.
E) the length of Saturn's year.
A) droughts in North America.
B) asteroid impacts on Earth.
C) change of which political party has the majority in the U.S. Congress.
D) the length of Mercury's day.
E) the length of Saturn's year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Initially, fewer neutrinos were detected than predicted by theoretical models because
A) neutrinos changed form to undetected types of neutrinos.
B) the wrong liquid was being used in neutrino detectors.
C) particle physicists did not understand the proton-proton chain.
D) the proton-proton chain does not actually produce neutrinos.
E) neutrinos take many years to pass out of the sun from its core.
A) neutrinos changed form to undetected types of neutrinos.
B) the wrong liquid was being used in neutrino detectors.
C) particle physicists did not understand the proton-proton chain.
D) the proton-proton chain does not actually produce neutrinos.
E) neutrinos take many years to pass out of the sun from its core.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In spite of its high temperature, we observe the solar corona best during ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The ________-year solar cycle is characterized by a variation in the number of sunspots and a reversal of the polarity of the Sun as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which is the net result of the proton-proton chain?
A) 4 protons = 1 helium 4 + a positron + a neutrino + gamma rays
B) 2 protons = deuterium + a positron + an antineutrino + X-rays
C) 4 protons = 2 heliums 2 + 2 positrons + ultraviolet radiation
D) 4 protons = 1 helium 4 + 2 neutrinos + gamma rays
E) 6 protons = 2 heliums + 3 positrons + 3 neutrinos + gamma rays
A) 4 protons = 1 helium 4 + a positron + a neutrino + gamma rays
B) 2 protons = deuterium + a positron + an antineutrino + X-rays
C) 4 protons = 2 heliums 2 + 2 positrons + ultraviolet radiation
D) 4 protons = 1 helium 4 + 2 neutrinos + gamma rays
E) 6 protons = 2 heliums + 3 positrons + 3 neutrinos + gamma rays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The observable ________ is a thin layer of the Sun in which the solar material becomes suddenly much more opaque as we look deeper into the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The chromosphere is red because it is hot enough to ________ hydrogen atoms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The critical temperature to initiate the proton-proton cycle in the cores of stars is
A) 3,000 K.
B) 5,800 K.
C) 2,300,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.
A) 3,000 K.
B) 5,800 K.
C) 2,300,000 K.
D) 10 million K.
E) 100 million K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The speed of light is 3.00 × 10⁸ m/s. If 2.00 kg of mass is converted to energy, how much energy will be produced?
A) 1.80 × 10¹⁷ J
B) 6.00 × 10⁸ J
C) 1.50 × 10⁸ J
D) 6.00 × 10⁴ J
E) 9.00 × 10¹⁶ J
A) 1.80 × 10¹⁷ J
B) 6.00 × 10⁸ J
C) 1.50 × 10⁸ J
D) 6.00 × 10⁴ J
E) 9.00 × 10¹⁶ J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Iron is observed in the Sun's ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is NOT a property of neutrinos?
A) Can change forms in the eight minutes from the Sun's core to us
B) Almost massless
C) Can travel very close to the speed of light
D) Neutral in charge
E) Cannot interact at all with normal matter
A) Can change forms in the eight minutes from the Sun's core to us
B) Almost massless
C) Can travel very close to the speed of light
D) Neutral in charge
E) Cannot interact at all with normal matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the last peak in sunspot numbers occurred in 2013, then the next solar max is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 95 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



