Deck 28: The Life of a Flowering Plant
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: The Life of a Flowering Plant
1
Which of the following do guard cells act to regulate?
A) stomata
B) cuticle
C) epidermis
D) root hairs
A) stomata
B) cuticle
C) epidermis
D) root hairs
A
2
Which of the following is a stem modification for storage?
A) tuber
B) petiole
C) rhizome
D) runner
A) tuber
B) petiole
C) rhizome
D) runner
A
3
Most domesticated food crops come from which of the following plant groups?
A) cycads
B) gymnosperms
C) ferns
D) angiosperms
A) cycads
B) gymnosperms
C) ferns
D) angiosperms
D
4
Which of the following is a function of roots?
A) absorbs water
B) absorbs nutrients from the soil
C) stores food
D) all of the above
A) absorbs water
B) absorbs nutrients from the soil
C) stores food
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following cell types provide support in growing parts of a plant?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) water-conducting cells
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) water-conducting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the waxy coating secreted on leaves and most stems?
A) cuticle
B) lignin
C) endodermis
D) epidermis
A) cuticle
B) lignin
C) endodermis
D) epidermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are the tiny projections found on roots that increase the surface area?
A) root hairs
B) cotyledons
C) nodes
D) mesophyll
A) root hairs
B) cotyledons
C) nodes
D) mesophyll

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following describes the single layer of tightly packed cells that cover the entire root?
A) xylem
B) root hairs
C) epidermis
D) endodermis
A) xylem
B) root hairs
C) epidermis
D) endodermis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following best describes the condition in which the terminal bud of many plants produces hormones that inhibit growth of axillary buds?
A) foliage determination
B) cortical influence
C) apical dominance
D) axial dominance
A) foliage determination
B) cortical influence
C) apical dominance
D) axial dominance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
You trim two different houseplants.The first houseplant becomes bushier,but the pruning does not affect the growth of the second plant.A possible explanation is ______.
A) you removed the axillary bud on the first plant but not the second
B) the second plant forms tubers, but the first plant does not
C) the first plant has compound leaves and the second plant has simple leaves
D) you removed the terminal bud on the first plant but not the second
A) you removed the axillary bud on the first plant but not the second
B) the second plant forms tubers, but the first plant does not
C) the first plant has compound leaves and the second plant has simple leaves
D) you removed the terminal bud on the first plant but not the second

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the major component of plant cell walls?
A) chloroplasts
B) lignin
C) starch
D) cellulose
A) chloroplasts
B) lignin
C) starch
D) cellulose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following best characterizes the monocots?
A) embryo with one seed leaf, leaves with parallel veins, stems with vascular bundles scattered, and flower parts in threes
B) embryo with one seed leaf, leaves with parallel veins, stems with a ring of vascular tissue, and flower parts in fives
C) embryo with two seed leaves, leaf veins not parallel, stems with ring of vascular tissue, and flower parts in fives
D) embryo with two seed leaves, leaf veins not parallel, stems with vascular bundles scattered, and flower parts in threes
A) embryo with one seed leaf, leaves with parallel veins, stems with vascular bundles scattered, and flower parts in threes
B) embryo with one seed leaf, leaves with parallel veins, stems with a ring of vascular tissue, and flower parts in fives
C) embryo with two seed leaves, leaf veins not parallel, stems with ring of vascular tissue, and flower parts in fives
D) embryo with two seed leaves, leaf veins not parallel, stems with vascular bundles scattered, and flower parts in threes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following best characterizes the eudicots?
A) flower parts in threes
B) leaves with parallel veins
C) an embryo with two seed leaves
D) stems with scattered vascular bundles
A) flower parts in threes
B) leaves with parallel veins
C) an embryo with two seed leaves
D) stems with scattered vascular bundles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is the main site of photosynthesis in a typical leaf?
A) epidermis
B) endodermis
C) mesophyll
D) xylem
A) epidermis
B) endodermis
C) mesophyll
D) xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following describes the vascular system of a typical plant?
A) It is made up of xylem and phloem.
B) It provides support.
C) It transports nutrients throughout the plant.
D) It does all of the above.
A) It is made up of xylem and phloem.
B) It provides support.
C) It transports nutrients throughout the plant.
D) It does all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following products used by humans sometimes comes from plants?
A) fuel
B) clothing
C) food
D) all of the above
A) fuel
B) clothing
C) food
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following describes the sites of leaf attachment in a stem?
A) joints
B) nodes
C) internodes
D) cotyledons
A) joints
B) nodes
C) internodes
D) cotyledons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following constitute the shoot system of a plant?
A) leaves
B) stems
C) flowers
D) all of the above
A) leaves
B) stems
C) flowers
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is the selective barrier of a root that determines which substances pass between the cortex and vascular tissue?
A) epidermis
B) endodermis
C) cuticle
D) xylem
A) epidermis
B) endodermis
C) cuticle
D) xylem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following best describes the function of typical leaves?
A) anchoring
B) photosynthesis
C) shade
D) storage of the sugars produced
A) anchoring
B) photosynthesis
C) shade
D) storage of the sugars produced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The ______ enclose and protect the flower bud,while the ______ advertise the flower to insects and other pollinators.
A) anthers... petals
B) carpels... stigmata
C) sepals... stamens
D) sepals... petals
A) anthers... petals
B) carpels... stigmata
C) sepals... stamens
D) sepals... petals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following are the most abundant cell type found in most plants?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) food-conducting cells
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) food-conducting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In which structure do pollen grains develop?
A) stamen
B) sepal
C) filament
D) anther
A) stamen
B) sepal
C) filament
D) anther

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following describes the delivery of pollen to the stigma?
A) fertilization
B) double fertilization
C) germination
D) pollination
A) fertilization
B) double fertilization
C) germination
D) pollination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following form chains with overlapping ends and are dead when mature?
A) collenchyma cells
B) sclerenchyma cells
C) water-conducting cells
D) food-conducting cells
A) collenchyma cells
B) sclerenchyma cells
C) water-conducting cells
D) food-conducting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
While on a hike,you notice that several burrs have become attached to your socks.You quickly pull them off.Burrs are produced by certain plants and frequently catch on animal fur (or people's clothing).After thinking about it,you decide that the burr is a type of _____ that is an adaptation for _____.
A) leaf...protecting plants from herbivores
B) fruit...seed dispersal
C) cambium...seed protection
D) pollen grain...successful pollination
A) leaf...protecting plants from herbivores
B) fruit...seed dispersal
C) cambium...seed protection
D) pollen grain...successful pollination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A plant grows taller through ______,which involves cell division in the ______.
A) primary growth... vascular cambium
B) secondary growth... vascular cambium
C) primary growth... apical meristem
D) secondary growth... cork cambium
A) primary growth... vascular cambium
B) secondary growth... vascular cambium
C) primary growth... apical meristem
D) secondary growth... cork cambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following have thick secondary cell walls strengthened with ligin,and support plants like steel beams in a building?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) water-conducting cells
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) sclerenchyma cells
D) water-conducting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following plant types complete their life cycle in two years?
A) annuals
B) semiannuals
C) biennials
D) perennials
A) annuals
B) semiannuals
C) biennials
D) perennials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What typically has to happen before a fruit develops?
A) flowering
B) pollination
C) double fertilization
D) all of the above
A) flowering
B) pollination
C) double fertilization
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Flowering plants reproduce through ______.
A) asexual reproduction only
B) sexual reproduction only
C) asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction
D) budding
A) asexual reproduction only
B) sexual reproduction only
C) asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction
D) budding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A plant's diploid form is called the ______; the haploid form is called the ______.
A) sporophyte... pollen
B) sporophyte... gametophyte
C) gametophyte... sporophyte
D) gametophyte... fruit
A) sporophyte... pollen
B) sporophyte... gametophyte
C) gametophyte... sporophyte
D) gametophyte... fruit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a function of parenchyma cells?
A) food storage
B) support
C) nutrient transport
D) all of the above
A) food storage
B) support
C) nutrient transport
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is responsible for the increase in girth (width)of trees?
A) primary growth
B) secondary growth
C) growth in apical meristems
D) an increase in the width of vessel elements
A) primary growth
B) secondary growth
C) growth in apical meristems
D) an increase in the width of vessel elements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is a multicellular mass that nourishes the embryo until it becomes a self-supporting seedling?
A) the endosperm
B) a seed coat
C) a fruit
D) a cotyledon
A) the endosperm
B) a seed coat
C) a fruit
D) a cotyledon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following contains the developing egg and cells that support it?
A) endosperm
B) ovule
C) anther
D) stigma
A) endosperm
B) ovule
C) anther
D) stigma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The formation of a zygote and a cell with a triploid nucleus is unique to flowering plants. What is this process called?
A) fertilization
B) double fertilization
C) germination
D) pollination
A) fertilization
B) double fertilization
C) germination
D) pollination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is the part of a flower that contains the female reproductive structures?
A) carpel
B) stamen
C) sepal
D) stigma
A) carpel
B) stamen
C) sepal
D) stigma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The main parts of a flower are modified versions of which of the following?
A) stems
B) rhizomes
C) internodes
D) leaves
A) stems
B) rhizomes
C) internodes
D) leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following form tubes and are alive when mature?
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) water-conducting cells
D) food-conducting cells
A) parenchyma cells
B) collenchyma cells
C) water-conducting cells
D) food-conducting cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
In late 2006, bee workers in the United States started to notice a disturbing phenomenon: the sudden disappearance of honeybees from commercial hives. This mysterious condition was called "colony collapse disorder," and it has caused a drastic reduction in commercial honeybee populations all over the country. It is estimated that one-third of our food supply relies on bees and is in danger. Crops that rely most heavily on honeybees include apples, almonds, blueberries, and pumpkins. If colony collapse disorder cannot be cured or treated effectively, farmers may have to turn to other insects, perhaps other bee species or even moths.
Without honeybees,which process in the life cycle of plants such as apples,almonds,blueberries,and pumpkins is most affected?
A) seed dispersal
B) secondary growth
C) pollination
D) seed germination
In late 2006, bee workers in the United States started to notice a disturbing phenomenon: the sudden disappearance of honeybees from commercial hives. This mysterious condition was called "colony collapse disorder," and it has caused a drastic reduction in commercial honeybee populations all over the country. It is estimated that one-third of our food supply relies on bees and is in danger. Crops that rely most heavily on honeybees include apples, almonds, blueberries, and pumpkins. If colony collapse disorder cannot be cured or treated effectively, farmers may have to turn to other insects, perhaps other bee species or even moths.
Without honeybees,which process in the life cycle of plants such as apples,almonds,blueberries,and pumpkins is most affected?
A) seed dispersal
B) secondary growth
C) pollination
D) seed germination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is an example of flowering plant/animal interdependence?
A) Most angiosperms depend on insects, birds, or mammals for pollination.
B) Most angiosperms depend on insects, birds, or mammals for seed dispersal.
C) Most land animals depend on angiosperms for food.
D) All of the above are examples of such interdependencies.
A) Most angiosperms depend on insects, birds, or mammals for pollination.
B) Most angiosperms depend on insects, birds, or mammals for seed dispersal.
C) Most land animals depend on angiosperms for food.
D) All of the above are examples of such interdependencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is the usual trigger for seed germination?
A) water
B) warm temperatures
C) oxygen
D) sunlight
A) water
B) warm temperatures
C) oxygen
D) sunlight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the likely effect of pruning a plant? 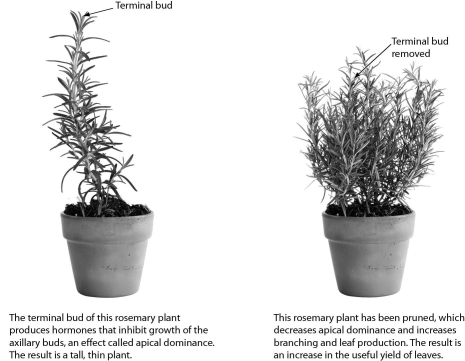
A) the plant will grow taller
B) the plant will grow bushier
C) the plant will produce flowers
D) the plant will grow more roots

A) the plant will grow taller
B) the plant will grow bushier
C) the plant will produce flowers
D) the plant will grow more roots

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
In late 2006, bee workers in the United States started to notice a disturbing phenomenon: the sudden disappearance of honeybees from commercial hives. This mysterious condition was called "colony collapse disorder," and it has caused a drastic reduction in commercial honeybee populations all over the country. It is estimated that one-third of our food supply relies on bees and is in danger. Crops that rely most heavily on honeybees include apples, almonds, blueberries, and pumpkins. If colony collapse disorder cannot be cured or treated effectively, farmers may have to turn to other insects, perhaps other bee species or even moths.
Which plant structure is adapted for attracting beneficial insects such as honeybees?
A) axillary bud
B) terminal bud
C) flower
D) petiole
In late 2006, bee workers in the United States started to notice a disturbing phenomenon: the sudden disappearance of honeybees from commercial hives. This mysterious condition was called "colony collapse disorder," and it has caused a drastic reduction in commercial honeybee populations all over the country. It is estimated that one-third of our food supply relies on bees and is in danger. Crops that rely most heavily on honeybees include apples, almonds, blueberries, and pumpkins. If colony collapse disorder cannot be cured or treated effectively, farmers may have to turn to other insects, perhaps other bee species or even moths.
Which plant structure is adapted for attracting beneficial insects such as honeybees?
A) axillary bud
B) terminal bud
C) flower
D) petiole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The figure below illustrates ______. 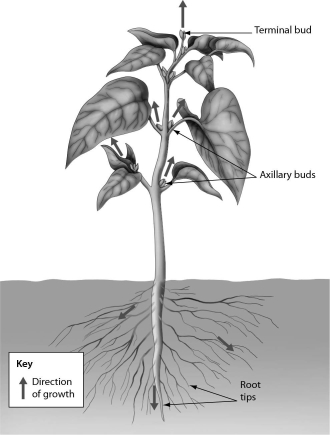
A) lateral dominance
B) secondary growth
C) determinate growth
D) primary growth

A) lateral dominance
B) secondary growth
C) determinate growth
D) primary growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Examine the figure below.What process has to occur to produce a haploid embryo sac? 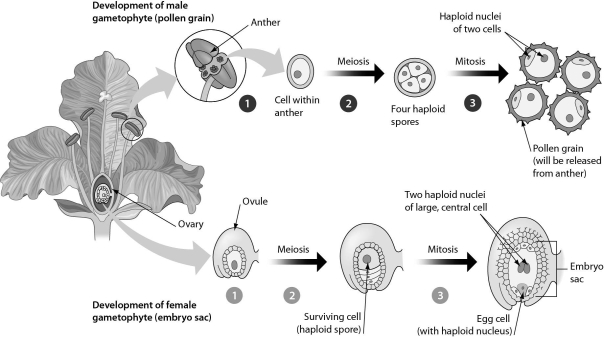
A) meiosis
B) meiosis followed by mitosis
C) mitosis followed by meiosis
D) mitosis

A) meiosis
B) meiosis followed by mitosis
C) mitosis followed by meiosis
D) mitosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Examine the figure below.Secondary growth involves cell division in the ______. 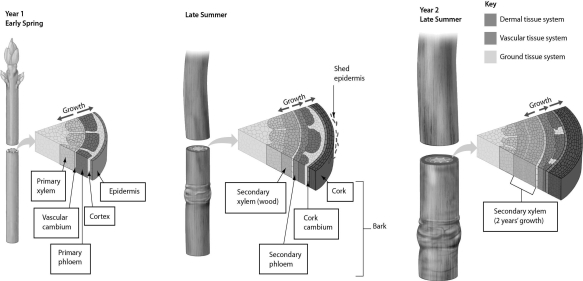
A) primary xylem, primary phloem, and cork cambium
B) vascular cambium and apical meristem
C) vascular cambium and cork cambium
D) secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and cork cambium

A) primary xylem, primary phloem, and cork cambium
B) vascular cambium and apical meristem
C) vascular cambium and cork cambium
D) secondary xylem, secondary phloem, and cork cambium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



