Deck 1: Introduction- Biology Today
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction- Biology Today
1
How does taxonomy assist biologists?
A) by providing easily remembered scientific names for organisms
B) by categorizing diverse items into smaller and smaller numbers of groups
C) by reducing life to its smallest common denominator, the cell
D) all of the above
A) by providing easily remembered scientific names for organisms
B) by categorizing diverse items into smaller and smaller numbers of groups
C) by reducing life to its smallest common denominator, the cell
D) all of the above
B
2
Which of the following is not recycled but is lost from ecosystems?
A) nitrogen
B) energy
C) magnesium
D) carbon
A) nitrogen
B) energy
C) magnesium
D) carbon
B
3
The DNA of a eukaryotic cell is found within the ______.
A) archaea
B) nucleus
C) prokaryotic cell
D) insulin
A) archaea
B) nucleus
C) prokaryotic cell
D) insulin
B
4
Relative to prokaryotic cells,eukaryotic cells are usually ______.
A) larger and more complex
B) smaller and simpler
C) larger and equally complex
D) smaller and more complex
A) larger and more complex
B) smaller and simpler
C) larger and equally complex
D) smaller and more complex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The human genome consists of about ______ chemical letters.
A) 300,000
B) 1 million
C) 3 billion
D) 300 billion
A) 300,000
B) 1 million
C) 3 billion
D) 300 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is biology?
A) the scientific study of life
B) the scientific study of the environment
C) the scientific study of DNA
D) the scientific study of ecosystems
A) the scientific study of life
B) the scientific study of the environment
C) the scientific study of DNA
D) the scientific study of ecosystems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following structures can perform all the activities required for life?
A) DNA molecules
B) cells
C) organelles
D) nuclei
A) DNA molecules
B) cells
C) organelles
D) nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which domain(s)consist(s)of prokaryotic cells?
A) Bacteria only
B) Eukarya only
C) Archaea and Eukarya
D) Bacteria and Archaea
A) Bacteria only
B) Eukarya only
C) Archaea and Eukarya
D) Bacteria and Archaea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which kingdom of Eukarya consists primarily of unicellular organisms?
A) Plantae
B) Bacteria
C) Fungi
D) Protista
A) Plantae
B) Bacteria
C) Fungi
D) Protista

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is a gene?
A) a type of eukaryotic cell
B) an organelle that houses DNA
C) a type of prokaryotic cell
D) a unit of inheritance
A) a type of eukaryotic cell
B) an organelle that houses DNA
C) a type of prokaryotic cell
D) a unit of inheritance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not a property of life?
A) Populations of organisms rarely change over time.
B) Living things exhibit complex but ordered organization.
C) Organisms take in energy and use it to perform all of life's activities.
D) Organisms reproduce their own kind.
A) Populations of organisms rarely change over time.
B) Living things exhibit complex but ordered organization.
C) Organisms take in energy and use it to perform all of life's activities.
D) Organisms reproduce their own kind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a producer?
A) oak tree
B) earthworm
C) sun
D) cat
A) oak tree
B) earthworm
C) sun
D) cat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Humans are ______.
A) producers
B) producers and consumers
C) consumers
D) producers and decomposers
A) producers
B) producers and consumers
C) consumers
D) producers and decomposers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
More than half of all known species are ______.
A) plants
B) insects
C) bacteria
D) vertebrates
A) plants
B) insects
C) bacteria
D) vertebrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What are the two main processes that ecosystems depend upon?
A) speciation and evolution
B) nutrient recycling and energy flow
C) decomposition and nutrient recycling
D) sunlight and photosynthesis
A) speciation and evolution
B) nutrient recycling and energy flow
C) decomposition and nutrient recycling
D) sunlight and photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What name is given to the functional compartments of a cell?
A) genomes
B) nuclei
C) genes
D) organelles
A) genomes
B) nuclei
C) genes
D) organelles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Taxonomy is the ______.
A) study of cells
B) naming and classifying of species
C) study of organisms and their interaction with the environment
D) study of genes
A) study of cells
B) naming and classifying of species
C) study of organisms and their interaction with the environment
D) study of genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In what way(s)is the science of biology influencing and changing our culture?
A) by helping us understand the relevance of evolution to human health
B) by revealing how mutations in genes can lead to disease
C) by providing new tools for forensic investigations
D) all of the above
A) by helping us understand the relevance of evolution to human health
B) by revealing how mutations in genes can lead to disease
C) by providing new tools for forensic investigations
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What are eukaryotic genes composed of?
A) RNA
B) organelles
C) RNA and DNA
D) DNA
A) RNA
B) organelles
C) RNA and DNA
D) DNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Humans are composed of ______ cells.
A) bacterial
B) eukaryotic
C) plant
D) prokaryotic
A) bacterial
B) eukaryotic
C) plant
D) prokaryotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these would be a valid hypothesis?
A) Human history is determined by a series of supernatural events.
B) Humans should help in the conservation of other animal species.
C) Humans are controlled by forces beyond our understanding.
D) Humans and bacteria share a common genetic code.
A) Human history is determined by a series of supernatural events.
B) Humans should help in the conservation of other animal species.
C) Humans are controlled by forces beyond our understanding.
D) Humans and bacteria share a common genetic code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of these statements is correct?
A) Scientific ideas are subjected to repeated testing.
B) Science can be used to prove or disprove the idea that deities or spirits cause earthquakes and other natural disasters.
C) Science does not require observations that other people can confirm.
D) Only discovery science can lead to important conclusions about nature.
A) Scientific ideas are subjected to repeated testing.
B) Science can be used to prove or disprove the idea that deities or spirits cause earthquakes and other natural disasters.
C) Science does not require observations that other people can confirm.
D) Only discovery science can lead to important conclusions about nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Science is ______.
A) the inquiry-based effort to describe and explain nature
B) the search for truth
C) an organized set of principles for how to ethically and morally behave
D) all of the above
A) the inquiry-based effort to describe and explain nature
B) the search for truth
C) an organized set of principles for how to ethically and morally behave
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
You try to start your car,but it does not start.Which of these is a prediction?
A) My car's battery is dead.
B) If I recharge the battery, then my car will start.
C) My car is too old to function properly.
D) What is wrong with my car?
A) My car's battery is dead.
B) If I recharge the battery, then my car will start.
C) My car is too old to function properly.
D) What is wrong with my car?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Over a span of two decades,scientists measured changes in the beak size of a population of Galápagos ground finches.This ______.
A) provided evidence of natural selection in action
B) is an example of artificial selection
C) is an example of overproduction
D) led Darwin to his theory of evolution through natural selection
A) provided evidence of natural selection in action
B) is an example of artificial selection
C) is an example of overproduction
D) led Darwin to his theory of evolution through natural selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You try to start your car,but it does not start.Which of these is a hypothesis?
A) My car's battery is dead.
B) If I recharge the battery, then my car will start.
C) My car is too old to function properly.
D) What is wrong with my car?
A) My car's battery is dead.
B) If I recharge the battery, then my car will start.
C) My car is too old to function properly.
D) What is wrong with my car?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of these is most closely associated with Darwin?
A) energy flow
B) ecosystem structure
C) the three domains of life
D) natural selection
A) energy flow
B) ecosystem structure
C) the three domains of life
D) natural selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How do hypotheses differ from theories?
A) Theories are more comprehensive than hypotheses.
B) Theories must be testable; hypotheses do not need to be testable.
C) Hypotheses are educated guesses, and theories are tentative explanations.
D) Hypotheses are derived from experimentation, whereas theories are derived from observation.
A) Theories are more comprehensive than hypotheses.
B) Theories must be testable; hypotheses do not need to be testable.
C) Hypotheses are educated guesses, and theories are tentative explanations.
D) Hypotheses are derived from experimentation, whereas theories are derived from observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A newly discovered multicellular organism obtains food by digesting dead organisms.Such an organism is most likely a member of the kingdom ______.
A) Plantae
B) Fungi
C) Protista
D) Animalia
A) Plantae
B) Fungi
C) Protista
D) Animalia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A hypothesis is a(n)______.
A) tentative answer to a question
B) guess
C) observation
D) theory
A) tentative answer to a question
B) guess
C) observation
D) theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Members of the kingdom Plantae differ from members of the other kingdoms of Eukarya in that most members of the kingdom Plantae ______.
A) are decomposers
B) are unicellular
C) are consumers
D) produce their own food
A) are decomposers
B) are unicellular
C) are consumers
D) produce their own food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Discovery science is primarily based on ______.
A) hypothesis testing
B) deduction
C) experimentation
D) observation
A) hypothesis testing
B) deduction
C) experimentation
D) observation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following are the proper components of the scientific method?
A) experiment, conclusion, application
B) question, observation, experiment, analysis, prediction
C) observation, question, hypothesis, prediction, experiment, results, conclusion
D) observation, question, opinion, conclusion, hypothesis
A) experiment, conclusion, application
B) question, observation, experiment, analysis, prediction
C) observation, question, hypothesis, prediction, experiment, results, conclusion
D) observation, question, opinion, conclusion, hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What accounts for the different breeds of domesticated dogs?
A) overproduction
B) natural selection
C) competition
D) artificial selection
A) overproduction
B) natural selection
C) competition
D) artificial selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the difference between discovery science and hypothesis-driven science?
A) Discovery science "discovers" new knowledge, whereas hypothesis-driven science does not.
B) Discovery science is based on deductive reasoning, whereas hypothesis-driven science is based on inductive reasoning.
C) Discovery science is mostly about describing nature, whereas hypothesis-driven science tries to explain nature.
D) Discovery science involves predictions about outcomes, whereas hypothesis-driven science involves tentative answers to specific questions.
A) Discovery science "discovers" new knowledge, whereas hypothesis-driven science does not.
B) Discovery science is based on deductive reasoning, whereas hypothesis-driven science is based on inductive reasoning.
C) Discovery science is mostly about describing nature, whereas hypothesis-driven science tries to explain nature.
D) Discovery science involves predictions about outcomes, whereas hypothesis-driven science involves tentative answers to specific questions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Unequal reproductive success ______.
A) can lead to a population being less well adapted to its environment
B) increases variation
C) does not affect the frequency of expression of traits in succeeding generations of a population
D) can lead to natural selection
A) can lead to a population being less well adapted to its environment
B) increases variation
C) does not affect the frequency of expression of traits in succeeding generations of a population
D) can lead to natural selection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a scientific experiment,the control group ______.
A) serves as a basis of comparison with the experimental group
B) is subjected to the factor whose effect is being tested
C) allows for the simultaneous testing of multiple variables
D) is required for the validity of discovery science
A) serves as a basis of comparison with the experimental group
B) is subjected to the factor whose effect is being tested
C) allows for the simultaneous testing of multiple variables
D) is required for the validity of discovery science

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The branch of biology that explains both the diversity and the unity of life is ______.
A) evolution
B) microbiology
C) taxonomy
D) genetics
A) evolution
B) microbiology
C) taxonomy
D) genetics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of these is required for natural selection to occur?
A) inheritance
B) unequal reproductive success
C) individual variation
D) all of the above
A) inheritance
B) unequal reproductive success
C) individual variation
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What does adaptation mean in a biological context?
A) the way an individual's body adjusts to its environment
B) the accumulation of favorable variations in a population over time
C) the ability of organisms to alter their appearance under changing environmental conditions
D) all of the above
A) the way an individual's body adjusts to its environment
B) the accumulation of favorable variations in a population over time
C) the ability of organisms to alter their appearance under changing environmental conditions
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Identify the experimental group of this case study.
A) brightly colored female lizards
B) brightly colored male lizards
C) dull-colored female lizards
D) dull-colored male lizards
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Identify the experimental group of this case study.
A) brightly colored female lizards
B) brightly colored male lizards
C) dull-colored female lizards
D) dull-colored male lizards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the process of evolution by natural selection illustrated in the accompanying figure,which of the following is the mechanism or agent of natural selection? 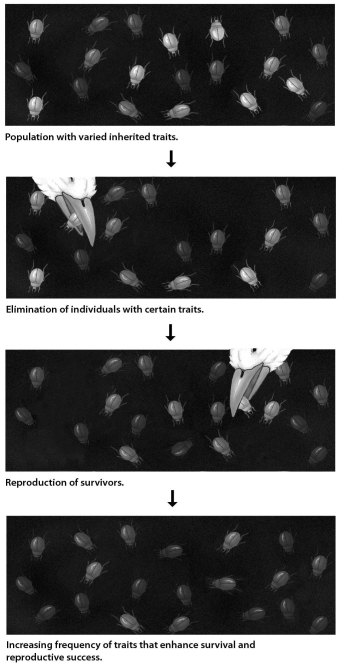
A) artificial selection
B) selective breeding
C) selective predation
D) selective beetles

A) artificial selection
B) selective breeding
C) selective predation
D) selective beetles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Which of the following is the hypothesis of this case study?
A) Male collared lizards exhibit color variation.
B) Dull males are less likely to be eaten by predators.
C) A function of male coloration is to attract females.
D) Males prefer brightly colored females.
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Which of the following is the hypothesis of this case study?
A) Male collared lizards exhibit color variation.
B) Dull males are less likely to be eaten by predators.
C) A function of male coloration is to attract females.
D) Males prefer brightly colored females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
"Male collared lizards show considerable color variation." This is a(n)______.
A) hypothesis
B) conclusion
C) observation
D) result
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
"Male collared lizards show considerable color variation." This is a(n)______.
A) hypothesis
B) conclusion
C) observation
D) result

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Using the branching tree of life for bears depicted in the accompanying figure,choose from among the following bear species the one that is most distantly related to the sun bear. 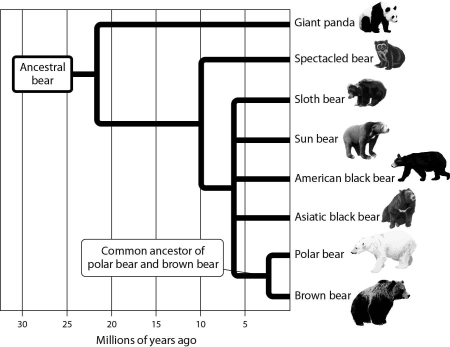
A) brown bear
B) sloth bear
C) spectacled bear
D) giant panda

A) brown bear
B) sloth bear
C) spectacled bear
D) giant panda

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Is it reasonable to conclude (i.e.,is it supported by the data)that female collared lizards prefer more brightly colored male lizards over dull-colored males?
A) Yes, this conclusion is supported by the data.
B) No, this conclusion is not supported by the data.
C) The data do not clearly indicate a preference one way or the other.
D) None of the above choices are correct.
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Is it reasonable to conclude (i.e.,is it supported by the data)that female collared lizards prefer more brightly colored male lizards over dull-colored males?
A) Yes, this conclusion is supported by the data.
B) No, this conclusion is not supported by the data.
C) The data do not clearly indicate a preference one way or the other.
D) None of the above choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Antibiotic resistance evolves in bacteria because ______.
A) the presence of antibiotics favors bacteria that already have genes for resistance
B) farmers do not use enough antibiotics in animal feed
C) the antibiotics create resistance genes in bacteria
D) none of the above
A) the presence of antibiotics favors bacteria that already have genes for resistance
B) farmers do not use enough antibiotics in animal feed
C) the antibiotics create resistance genes in bacteria
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Please use the following information to answer the following question(s).
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Dull-colored males were part of the ______.
A) observation group
B) control group
C) experimental group
D) predicted group
The collared lizard is a species found in the Desert Southwest. Male collared lizards show considerable color variation, ranging from brightly colored to a very dull pattern. Your goal is to determine the function, if any, of male color patterns in collared lizards, using the scientific method. Your tentative explanation is that male color plays a role in attracting females for mating purposes. You predict that females will preferentially choose brightly colored males over dull-colored ones. To test this prediction, you observed the interactions of female collared lizards with their male counterparts. You selected males that were the same age and size, and that differed only in their coloration pattern. You placed equal numbers of the two types of male lizards, bright and dull, in aquariums, along with one female lizard per aquarium. Out of 350 aquariums observed, the female chose to mate with the brightly colored male 277 times, and the dull-colored male 70 times. In 3 instances, the females did not mate with either type.
Create a bar graph of your data, plotting the type of male (dull or brightly colored) on the x-axis. On the y-axis, plot the frequency with which each type of male was chosen by females. Using this graph, answer the following question(s).
Dull-colored males were part of the ______.
A) observation group
B) control group
C) experimental group
D) predicted group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



