Deck 6: Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/43
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
1
Which of the following is the correct sequence of stages in cellular respiration?
A) glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport
B) citric acid cycle, glycolysis, electron transport
C) citric acid cycle, electron transport, glycolysis
D) electron transport, glycolysis, citric acid cycle
A) glycolysis, citric acid cycle, electron transport
B) citric acid cycle, glycolysis, electron transport
C) citric acid cycle, electron transport, glycolysis
D) electron transport, glycolysis, citric acid cycle
A
2
Plant cells ______.
A) do not need chloroplasts because their mitochondria meet their energy needs
B) have chloroplasts and mitochondria
C) use carbon dioxide but do not use oxygen
D) do not need mitochondria because their chloroplasts meet their energy needs
A) do not need chloroplasts because their mitochondria meet their energy needs
B) have chloroplasts and mitochondria
C) use carbon dioxide but do not use oxygen
D) do not need mitochondria because their chloroplasts meet their energy needs
B
3
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Oxygen is a product of cellular respiration; carbon dioxide is a product of photosynthesis.
B) Lactic acid is a product of aerobic respiration; ethyl alcohol is a product of fermentation.
C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons; reduction is the gain of electrons.
D) Glucose is a product of aerobic respiration; lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration.
A) Oxygen is a product of cellular respiration; carbon dioxide is a product of photosynthesis.
B) Lactic acid is a product of aerobic respiration; ethyl alcohol is a product of fermentation.
C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons; reduction is the gain of electrons.
D) Glucose is a product of aerobic respiration; lactic acid is a product of anaerobic respiration.
C
4
Respiration describes the exchange of gases between your blood and the outside air.Cellular respiration ______.
A) produces ATP
B) produces oxygen
C) produces glucose
D) uses carbon dioxide
A) produces ATP
B) produces oxygen
C) produces glucose
D) uses carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following are produced during cellular respiration?
A) ATP and water
B) carbon dioxide and ATP
C) carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
D) oxygen and glucose
A) ATP and water
B) carbon dioxide and ATP
C) carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
D) oxygen and glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Plants use photosynthesis to
A) store chemical energy, and they use cellular respiration to harvest energy.
B) store as well as harvest chemical energy.
C) harvest energy, and they use cellular respiration to store chemical energy.
D) obtain carbon dioxide.
A) store chemical energy, and they use cellular respiration to harvest energy.
B) store as well as harvest chemical energy.
C) harvest energy, and they use cellular respiration to store chemical energy.
D) obtain carbon dioxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Where in the cell does glycolysis occur?
A) cytoplasm
B) ER
C) within the fluid just inside the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane
A) cytoplasm
B) ER
C) within the fluid just inside the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) between the inner and outer mitochondrial membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Photosynthetic organisms are ______.
A) producers that make all of their organic matter from organic molecules that they take in
B) consumers that obtain organic molecules from other living organisms
C) producers that make all their own organic matter from inorganic molecules
D) decomposers that obtain nutrients from the soil
A) producers that make all of their organic matter from organic molecules that they take in
B) consumers that obtain organic molecules from other living organisms
C) producers that make all their own organic matter from inorganic molecules
D) decomposers that obtain nutrients from the soil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The final electron acceptor of aerobic respiration is ______.
A) ATP
B) oxygen
C) lactic acid
D) NAD+
A) ATP
B) oxygen
C) lactic acid
D) NAD+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What compound directly provides energy for cellular work?
A) C6H12O6
B) glucose
C) ATP
D) fat
A) C6H12O6
B) glucose
C) ATP
D) fat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Humans are both
A) heterotrophs and consumers.
B) heterotrophs and autotrophs.
C) producers and consumers.
D) autotrophs and producers.
A) heterotrophs and consumers.
B) heterotrophs and autotrophs.
C) producers and consumers.
D) autotrophs and producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An aerobic process requires ______.
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) carbohydrates
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) ATP
D) carbohydrates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A difference between marathon runners and sprinters is ______.
A) marathon runners have more slow-twitch fibers in their leg muscles
B) marathon runners have more fast-twitch muscle fibers in their leg muscles
C) sprinters have a high proportion of muscle fibers that require oxygen to make ATP
D) sprinters perform better in activities that require slow, steady muscle activity
A) marathon runners have more slow-twitch fibers in their leg muscles
B) marathon runners have more fast-twitch muscle fibers in their leg muscles
C) sprinters have a high proportion of muscle fibers that require oxygen to make ATP
D) sprinters perform better in activities that require slow, steady muscle activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The waste products of cellular respiration include ______.
A) water only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) water and carbon dioxide
D) water and glucose
A) water only
B) carbon dioxide only
C) water and carbon dioxide
D) water and glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
During cellular respiration,electrons move through a series of electron acceptor molecules.Which of the following is a true statement about this process?
A) The electrons gain energy as they move from one electron acceptor to another.
B) Oxygen is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
C) The electrons release large amounts of energy each time they are transferred from one electron acceptor to another.
D) Glucose is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
A) The electrons gain energy as they move from one electron acceptor to another.
B) Oxygen is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.
C) The electrons release large amounts of energy each time they are transferred from one electron acceptor to another.
D) Glucose is eventually reduced by the electrons to form water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these equations describes aerobic cellular respiration?
A) glucose → lactic acid + energy
B) energy + carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen + water
C) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
D) none of the above
A) glucose → lactic acid + energy
B) energy + carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen + water
C) glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The first electron acceptor of cellular respiration is ______.
A) CO2
B) O2
C) NAD+
D) H2O
A) CO2
B) O2
C) NAD+
D) H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A horse eating some hay is an example of ______.
A) an autotroph eating a producer
B) an autotroph eating a consumer
C) a consumer eating a producer
D) a consumer eating a heterotroph
A) an autotroph eating a producer
B) an autotroph eating a consumer
C) a consumer eating a producer
D) a consumer eating a heterotroph

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
During redox reactions,______.
A) the loss of electrons from one substance is called reduction
B) a substance that gains electrons is said to be oxidized
C) electrons are lost from one substance and added to another substance
D) protons from one molecule replace the electrons lost from another molecule
A) the loss of electrons from one substance is called reduction
B) a substance that gains electrons is said to be oxidized
C) electrons are lost from one substance and added to another substance
D) protons from one molecule replace the electrons lost from another molecule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ultimate source of the energy in food is ______.
A) the sun
B) producers
C) ATP
D) consumers
A) the sun
B) producers
C) ATP
D) consumers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Some friends are trying to make wine in their basement.They've added yeast to a sweet grape juice mixture and have allowed the yeast to grow.After several days they find that sugar levels in the grape juice have dropped,but there's no alcohol in the mixture.The most likely explanation is that ______.
A) the mixture needs more sugar; yeast need a lot of energy before they can begin to produce alcohol
B) the mixture needs less oxygen; yeast only produce alcohol in the absence of oxygen
C) the mixture needs more oxygen; yeast need oxygen to break down sugar to produce alcohol
D) the mixture needs less sugar; high sugar concentrations stimulate cellular respiration, and alcohol is not a by-product of cellular respiration
A) the mixture needs more sugar; yeast need a lot of energy before they can begin to produce alcohol
B) the mixture needs less oxygen; yeast only produce alcohol in the absence of oxygen
C) the mixture needs more oxygen; yeast need oxygen to break down sugar to produce alcohol
D) the mixture needs less sugar; high sugar concentrations stimulate cellular respiration, and alcohol is not a by-product of cellular respiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Aerobic cellular respiration generates about ______ ATP from one glucose.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 38
D) The number generated depends on whether the end product of aerobic respiration is lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.
A) 2
B) 6
C) 38
D) The number generated depends on whether the end product of aerobic respiration is lactic acid or ethyl alcohol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to
A) produce more ATP than is possible through aerobic respiration.
B) produce ATP using the electron transport chain.
C) regenerate NADH.
D) produce ATP without O2.
A) produce more ATP than is possible through aerobic respiration.
B) produce ATP using the electron transport chain.
C) regenerate NADH.
D) produce ATP without O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following metabolic pathways is common to both aerobic and anaerobic processes of sugar breakdown?
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid
D) glycolysis
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic acid
D) glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What must pyruvic acid be converted to before it can enter the citric acid cycle?
A) acetyl CoA
B) lactic acid
C) ethyl alcohol
D) citric acid
A) acetyl CoA
B) lactic acid
C) ethyl alcohol
D) citric acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Large amounts of oxygen gas first appeared in Earth's atmosphere about ______ years ago.
A) 500,000
B) 10 million
C) 2.7 billion
D) 3.5 billion
A) 500,000
B) 10 million
C) 2.7 billion
D) 3.5 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A product of glycolysis is ______.
A) lactic acid
B) ethyl alcohol
C) O2
D) pyruvic acid
A) lactic acid
B) ethyl alcohol
C) O2
D) pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Examine the following figure.Which of these stages occur(s)in the cytoplasm? 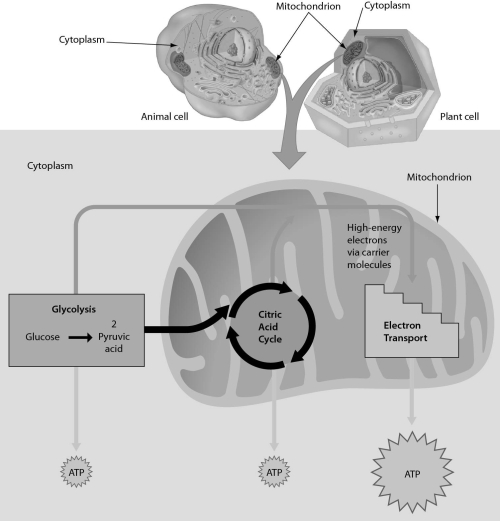
A) glycolysis
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis and citric acid cycle
D) citric acid cycle and electron transport

A) glycolysis
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis and citric acid cycle
D) citric acid cycle and electron transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In cellular respiration,most ATP is produced directly as a result of ______.
A) the movement of hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B) the citric acid cycle
C) fermentation
D) the electron transport chain
A) the movement of hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B) the citric acid cycle
C) fermentation
D) the electron transport chain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Examine the following figure.Which of the following reactants primarily come(s)from the air? 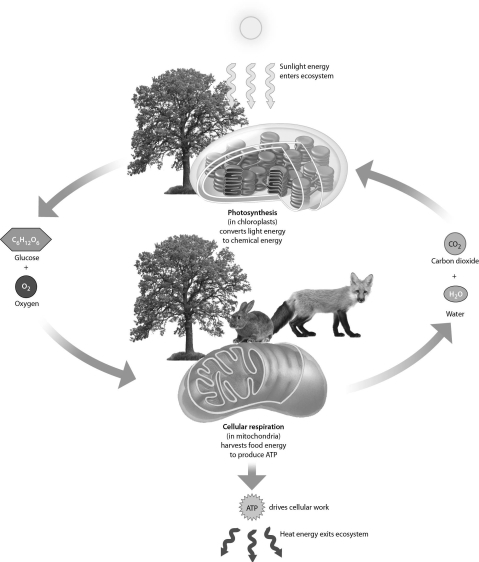
A) water
B) glucose
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen and carbon dioxide

A) water
B) glucose
C) carbon dioxide
D) oxygen and carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What waste product do yeast produce under anaerobic conditions?
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvic acid
C) lactic acid
D) creatine
A) ethyl alcohol
B) pyruvic acid
C) lactic acid
D) creatine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Electron transport takes place in the ______.
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplasts
C) cytoplasm
D) ribosomes
A) mitochondria
B) chloroplasts
C) cytoplasm
D) ribosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The figure below shows 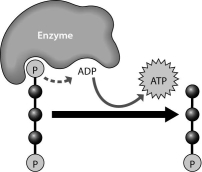
A) the synthesis of ADP
B) the breakdown of ATP to perform cellular work
C) the removal of a phosphate group from ADP
D) the synthesis of ATP through the addition of a phosphate group

A) the synthesis of ADP
B) the breakdown of ATP to perform cellular work
C) the removal of a phosphate group from ADP
D) the synthesis of ATP through the addition of a phosphate group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The second stage of aerobic respiration is ______.
A) ATP production
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis
A) ATP production
B) the citric acid cycle
C) lactic acid fermentation
D) glycolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is a result of glycolysis?
A) production of CO2
B) conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid
C) a net loss of two ATPs per glucose molecule
D) conversion of NADH to NAD+
A) production of CO2
B) conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid
C) a net loss of two ATPs per glucose molecule
D) conversion of NADH to NAD+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Anaerobic respiration produces a maximum of ______ ATP per glucose.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 10
D) 38
A) 2
B) 4
C) 10
D) 38

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In aerobic respiration,how many molecules of acetic acid are produced from six molecules of glucose?
A) 1
B) 38
C) 6
D) 12
A) 1
B) 38
C) 6
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
ATP synthase plays a role in ______.
A) pulling electrons down the electron transport chain
B) glycolysis
C) pumping hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) generating ATP
A) pulling electrons down the electron transport chain
B) glycolysis
C) pumping hydrogen ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D) generating ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A child is born with a rare disease in which mitochondria are missing from certain skeletal muscle cells.Physicians find that the muscle cells function.Not surprisingly,they also find that ______.
A) the muscles contain large amounts of lactic acid following even mild physical exercise
B) the muscles contain large amounts of carbon dioxide following even mild physical exercise
C) the muscles require extremely high levels of oxygen to function
D) the muscle cells cannot split glucose to pyruvic acid
A) the muscles contain large amounts of lactic acid following even mild physical exercise
B) the muscles contain large amounts of carbon dioxide following even mild physical exercise
C) the muscles require extremely high levels of oxygen to function
D) the muscle cells cannot split glucose to pyruvic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which part of cellular respiration produces the most NADH?
A) electron transport chain
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis
D) Calvin cycle
A) electron transport chain
B) citric acid cycle
C) glycolysis
D) Calvin cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
Breathing faster when we exercise is necessary to expel ______.
A) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support aerobic metabolism
B) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support aerobic metabolism
C) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support anaerobic metabolism
D) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support anaerobic metabolism
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
Breathing faster when we exercise is necessary to expel ______.
A) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support aerobic metabolism
B) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support aerobic metabolism
C) carbon dioxide and bring in more oxygen to support anaerobic metabolism
D) oxygen and bring in more carbon dioxide to support anaerobic metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Read the following scenario to answer the following question(s).
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
When oxygen delivery becomes insufficient to support a runner's aerobic metabolism,cells switch to an emergency mode in which ______.
A) ATP is generated less efficiently by harvesting the heat energy in a cell
B) ATP is inefficiently produced and lactic acid is generated as a by-product
C) lactic acid is broken down to produce smaller amounts of ATP
D) carbon dioxide is joined with water to generate much smaller amounts of ATP
An abundant and continual supply of ATP is necessary for all living cells. Active muscle cells require an extraordinary amount of ATP to permit strenuous exercise for prolonged periods. Toxins, reduced blood flow, and a compromised respiratory system can interfere with the transport of oxygen to active cells. A runner in a marathon faces multiple obstacles to continue to produce sufficient ATP to remain competitive.
When oxygen delivery becomes insufficient to support a runner's aerobic metabolism,cells switch to an emergency mode in which ______.
A) ATP is generated less efficiently by harvesting the heat energy in a cell
B) ATP is inefficiently produced and lactic acid is generated as a by-product
C) lactic acid is broken down to produce smaller amounts of ATP
D) carbon dioxide is joined with water to generate much smaller amounts of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The figure below shows that ______. 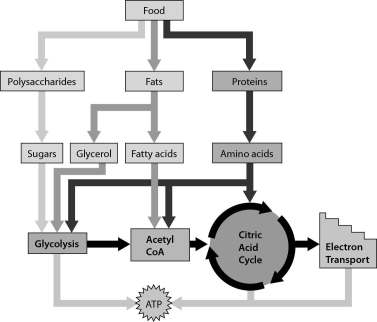
A) amino acids can move directly into the electron transport chain
B) our cells can use sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids to produce ATP
C) our cells can produce ATP only from glucose
D) our cells can produce ATP from sugars and glycerol, but not fatty acids

A) amino acids can move directly into the electron transport chain
B) our cells can use sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids to produce ATP
C) our cells can produce ATP only from glucose
D) our cells can produce ATP from sugars and glycerol, but not fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 43 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



