Deck 26: Reproduction and Development
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 26: Reproduction and Development
1
Which one of the following STDs is not caused by a virus?
A) AIDS
B) chlamydia
C) genital warts
D) genital herpes
A) AIDS
B) chlamydia
C) genital warts
D) genital herpes
B
2
Where in a woman's reproductive tract does fertilization most often take place?
A) in the ovary
B) in the upper part of the oviduct
C) in the lower part of the oviduct
D) in the uterus
A) in the ovary
B) in the upper part of the oviduct
C) in the lower part of the oviduct
D) in the uterus
B
3
Which of the following is an aspect of asexual reproduction that is sometimes disadvantageous?
A) It allows animals that do not move around to produce offspring without finding mates.
B) It allows an animal to produce many offspring quickly.
C) It saves the time and energy of gamete production.
D) It produces genetically uniform populations.
A) It allows animals that do not move around to produce offspring without finding mates.
B) It allows an animal to produce many offspring quickly.
C) It saves the time and energy of gamete production.
D) It produces genetically uniform populations.
D
4
A sperm cell's acrosome ______.
A) contains the sperm's nucleus and is the part of the sperm that enters the egg during fertilization
B) fuses with the plasma membrane of the egg cell
C) contains enzymes that are released when the sperm encounters an egg and dissolves a hole in the jellylike matrix that surrounds the egg
D) contains the sperm's mitochondria
A) contains the sperm's nucleus and is the part of the sperm that enters the egg during fertilization
B) fuses with the plasma membrane of the egg cell
C) contains enzymes that are released when the sperm encounters an egg and dissolves a hole in the jellylike matrix that surrounds the egg
D) contains the sperm's mitochondria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which one of the following is the earliest event in the process of fertilization?
A) Sperm contact the jelly coat around the egg.
B) The sperm head plasma membrane fuses with the egg plasma membrane.
C) Enzymes from the acrosome are released.
D) The sperm nucleus enters the cytoplasm of the egg.
A) Sperm contact the jelly coat around the egg.
B) The sperm head plasma membrane fuses with the egg plasma membrane.
C) Enzymes from the acrosome are released.
D) The sperm nucleus enters the cytoplasm of the egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these events occurs first?
A) gastrulation
B) cleavage
C) implantation
D) formation of the placenta
A) gastrulation
B) cleavage
C) implantation
D) formation of the placenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What would happen if an embryo failed to secrete HCG?
A) The maternal elements of the placenta would fail to develop.
B) The fetal elements of the placenta would fail to develop.
C) Neural tube formation would not occur, and the embryo would not have a brain.
D) The embryo would be aborted.
A) The maternal elements of the placenta would fail to develop.
B) The fetal elements of the placenta would fail to develop.
C) Neural tube formation would not occur, and the embryo would not have a brain.
D) The embryo would be aborted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a human female reproductive system,the ______.
A) hymen partly covers the cervical opening
B) vagina secretes hormones that help maintain the uterine lining
C) labia minora are a pair of thick, fatty ridges that protect the entire genital region
D) outer features are collectively called the vulva
A) hymen partly covers the cervical opening
B) vagina secretes hormones that help maintain the uterine lining
C) labia minora are a pair of thick, fatty ridges that protect the entire genital region
D) outer features are collectively called the vulva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is associated with sexual reproduction?
A) fission
B) fragmentation
C) budding
D) none of the above
A) fission
B) fragmentation
C) budding
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Into which layer of the uterus does the embryo implant?
A) myometrium
B) perimetrium
C) epimetrium
D) endometrium
A) myometrium
B) perimetrium
C) epimetrium
D) endometrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Menstruation ______.
A) involves the breakdown of the endometrium
B) is stimulated by HCG
C) occurs after ovulation but prior to degeneration of the follicle
D) is triggered by an LH surge
A) involves the breakdown of the endometrium
B) is stimulated by HCG
C) occurs after ovulation but prior to degeneration of the follicle
D) is triggered by an LH surge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In human females,the ovarian cycle begins when the ______.
A) levels of estrogen reach their maximum
B) hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to increase its output of FSH and LH
C) level of progesterone drops precipitously
D) levels of FSH and LH drop precipitously
A) levels of estrogen reach their maximum
B) hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to increase its output of FSH and LH
C) level of progesterone drops precipitously
D) levels of FSH and LH drop precipitously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What moves the human egg through the oviduct?
A) the beating of the egg's cilia
B) rhythmic contractions of the oviduct
C) rhythmic contractions of the uterus
D) the beating of cilia in the oviduct
A) the beating of the egg's cilia
B) rhythmic contractions of the oviduct
C) rhythmic contractions of the uterus
D) the beating of cilia in the oviduct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Asexual reproduction
A) creates individuals with unique combinations of genes.
B) generates enormous genetic variation.
C) is an effective way for animals to expand their population quickly and exploit an available environment.
D) provides greater adaptability to changing environments.
A) creates individuals with unique combinations of genes.
B) generates enormous genetic variation.
C) is an effective way for animals to expand their population quickly and exploit an available environment.
D) provides greater adaptability to changing environments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following statements is true?
A) Natural family planning is one of the most reliable forms of birth control.
B) Morning-after pills are about 25% effective at preventing pregnancy.
C) Tubal ligation prevents ovulation.
D) A vasectomy involves removing a section of each vas deferens.
A) Natural family planning is one of the most reliable forms of birth control.
B) Morning-after pills are about 25% effective at preventing pregnancy.
C) Tubal ligation prevents ovulation.
D) A vasectomy involves removing a section of each vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following types of pathogens cause sexually transmitted diseases that are generally not curable?
A) bacteria
B) viruses
C) fungi
D) HIV but not other viruses
A) bacteria
B) viruses
C) fungi
D) HIV but not other viruses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which one of the following statements is true?
A) Meiosis in oogenesis produces four mature eggs from one primary oocyte.
B) Oogenesis begins during puberty.
C) Spermatogenesis begins before birth.
D) Oogenesis in humans is completed after stimulation by sperm.
A) Meiosis in oogenesis produces four mature eggs from one primary oocyte.
B) Oogenesis begins during puberty.
C) Spermatogenesis begins before birth.
D) Oogenesis in humans is completed after stimulation by sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Reproductive systems with external fertilization are most common in ______.
A) populations with many more males than females
B) animals that are widely dispersed
C) aquatic animals
D) populations with many more females than males
A) populations with many more males than females
B) animals that are widely dispersed
C) aquatic animals
D) populations with many more females than males

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why are human testes located in an external sac rather than in the abdominal cavity?
A) to shorten the distance that semen must travel during ejaculation
B) so the testes can be kept at a constant temperature
C) so the testes can be kept cooler than the body's interior
D) so the testes can enlarge at sexual maturity
A) to shorten the distance that semen must travel during ejaculation
B) so the testes can be kept at a constant temperature
C) so the testes can be kept cooler than the body's interior
D) so the testes can enlarge at sexual maturity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Hermaphrodites ______.
A) possess both male and female reproductive systems
B) have the gonads of one sex but the external appearance of the other
C) usually fertilize themselves
D) have abnormal reproductive systems
A) possess both male and female reproductive systems
B) have the gonads of one sex but the external appearance of the other
C) usually fertilize themselves
D) have abnormal reproductive systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The animal in the accompanying figure illustrates ______. 
A) fission
B) regeneration
C) budding
D) none of the above

A) fission
B) regeneration
C) budding
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The liver,pancreas,and lining of the digestive tract come from ______.
A) ectoderm
B) endoderm
C) mesoderm
D) neural crest cells
A) ectoderm
B) endoderm
C) mesoderm
D) neural crest cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The human embryo's first blood cells arise in the ______.
A) developing liver
B) amnion
C) yolk sac
D) allantois
A) developing liver
B) amnion
C) yolk sac
D) allantois

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which one of the following is a result of programmed cell death?
A) formation of fingers in humans
B) gastrulation
C) formation of the notochord
D) formation of the brain
A) formation of fingers in humans
B) gastrulation
C) formation of the notochord
D) formation of the brain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following processes dominates the third trimester of human development?
A) formation of internal organs
B) formation of external features such as arms and legs
C) growth
D) organ formation
A) formation of internal organs
B) formation of external features such as arms and legs
C) growth
D) organ formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The lifeline between the embryo and the placenta ______.
A) is derived from the yolk sac
B) is derived from the amnion
C) is called the chorion
D) is called the umbilical cord
A) is derived from the yolk sac
B) is derived from the amnion
C) is called the chorion
D) is called the umbilical cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is gestation?
A) conception
B) fertilization
C) development
D) pregnancy
A) conception
B) fertilization
C) development
D) pregnancy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The "grandmother hypothesis" suggests that a woman can increase her reproductive fitness by ______.
A) moving away from her children and grandchildren
B) focusing her energy on caring for her grandchildren, instead of on producing more children
C) focusing her energy on the production of as many children as possible before reaching menopause
D) helping her sisters produce more children
A) moving away from her children and grandchildren
B) focusing her energy on caring for her grandchildren, instead of on producing more children
C) focusing her energy on the production of as many children as possible before reaching menopause
D) helping her sisters produce more children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following correctly lists the three stages of labor,in the proper order?
A) dilation, expulsion, delivery of the placenta
B) dilation, crowning, expulsion
C) contractions, dilation, expulsion
D) contractions, dilation, crowning
A) dilation, expulsion, delivery of the placenta
B) dilation, crowning, expulsion
C) contractions, dilation, expulsion
D) contractions, dilation, crowning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Bill suffers from a low sperm count.After meeting with his physician,he tells his wife that there might be a simple solution.Bill's physician suggests that he might raise his sperm count by ______.
A) drinking more orange juice
B) wearing boxer shorts
C) having sex more often
D) riding a bicycle
A) drinking more orange juice
B) wearing boxer shorts
C) having sex more often
D) riding a bicycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At about what point in gestation can an ultrasound exam determine the sex of the fetus?
A) about 4 weeks after fertilization
B) at the end of the first trimester
C) about 20 weeks after fertilization
D) at the end of the second trimester
A) about 4 weeks after fertilization
B) at the end of the first trimester
C) about 20 weeks after fertilization
D) at the end of the second trimester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The figure shows male reproductive anatomy.In a human male reproductive system ______. 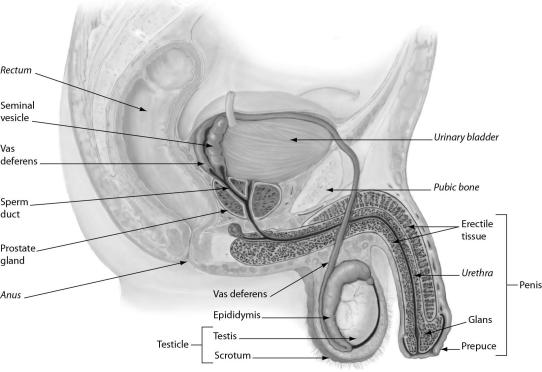
A) sperm mature in the urethra
B) the vas deferens conducts sperm between the testis and epididymis
C) the sperm travel through the urethra during ejaculation
D) sperm mature in the prostate gland

A) sperm mature in the urethra
B) the vas deferens conducts sperm between the testis and epididymis
C) the sperm travel through the urethra during ejaculation
D) sperm mature in the prostate gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
At about what point in gestation does the fetal heartbeat become audible by stethoscope and the fetus's movements easily felt by the mother?
A) 15 weeks
B) 20 weeks
C) 25 weeks
D) 30 weeks
A) 15 weeks
B) 20 weeks
C) 25 weeks
D) 30 weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When does the human embryo implant in the wall of the uterus?
A) within a few hours of fertilization
B) about a day after conception
C) about a week after conception
D) just after gastrulation
A) within a few hours of fertilization
B) about a day after conception
C) about a week after conception
D) just after gastrulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a chemical signal from a group of embryonic cells causes a different,nearby group of cells to embark on a particular developmental course (say,differentiating into a leg),the interaction between the two groups of cells is called ______.
A) induction
B) coordinated differentiation
C) programmed cell death
D) potentiation
A) induction
B) coordinated differentiation
C) programmed cell death
D) potentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Gastrulation ______.
A) changes a hollow embryo into a solid gastrula
B) changes the solid blastocyst into a hollow embryo that has three tissue layers
C) changes the hollow blastocyst into a hollow embryo that has three tissue layers
D) changes a gastrula into a blastocyst
A) changes a hollow embryo into a solid gastrula
B) changes the solid blastocyst into a hollow embryo that has three tissue layers
C) changes the hollow blastocyst into a hollow embryo that has three tissue layers
D) changes a gastrula into a blastocyst

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The yolk sac of humans ______.
A) stores nutrients to support the developing embryo
B) produces blood cells and gamete-forming cells
C) secretes HCG
D) absorbs nutrients from, and releases waste to, the mother's blood
A) stores nutrients to support the developing embryo
B) produces blood cells and gamete-forming cells
C) secretes HCG
D) absorbs nutrients from, and releases waste to, the mother's blood

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Mesoderm gives rise to the ______.
A) heart
B) kidneys
C) muscles
D) all of the above
A) heart
B) kidneys
C) muscles
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following substances stimulates contractions in uterine smooth muscle during labor?
A) progesterone
B) estrogen
C) oxytocin
D) prolactin
A) progesterone
B) estrogen
C) oxytocin
D) prolactin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following results from cleavage?
A) formation of the nervous system
B) formation of the notochord
C) more cells
D) segmentation
A) formation of the nervous system
B) formation of the notochord
C) more cells
D) segmentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The figure shows oogenesis.What is the function of the polar bodies that are produced during oogenesis? They are a mechanism that allows for ______. 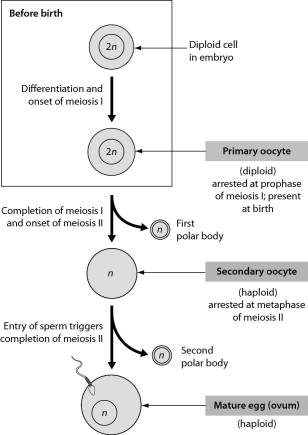
A) the shedding of excess cytoplasm during the production of a haploid ovum
B) the shedding of excess genetic material during the production of a haploid ovum
C) the shedding of excess mitochondria during the production of a haploid ovum
D) streamlining of the ovum so as to facilitate the penetration of an ovum by a sperm

A) the shedding of excess cytoplasm during the production of a haploid ovum
B) the shedding of excess genetic material during the production of a haploid ovum
C) the shedding of excess mitochondria during the production of a haploid ovum
D) streamlining of the ovum so as to facilitate the penetration of an ovum by a sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Please read the following paragraph and then answer the following question(s).
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
Which of the following birth control methods provides the most effective protection against pregnancy and sexually transmitted disease for sexually active people?
A) the pill
B) latex condoms
C) a diaphragm
D) the rhythm method
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
Which of the following birth control methods provides the most effective protection against pregnancy and sexually transmitted disease for sexually active people?
A) the pill
B) latex condoms
C) a diaphragm
D) the rhythm method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Examine the embryo in the following figure.The hands and feet of this embryo appear paddle-like,with no distinct toes or fingers.What process is needed to define each of the toes and fingers? 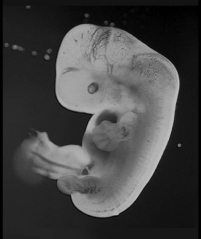
A) programmed cell death
B) neurulation
C) gastrulation
D) induction

A) programmed cell death
B) neurulation
C) gastrulation
D) induction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The figure shows a human embryo 31 days after conception.Which of the following structures is part of the placenta? 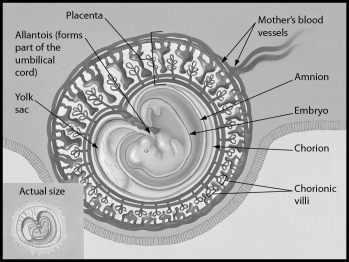
A) embryo
B) chorion
C) amnion
D) yolk sac

A) embryo
B) chorion
C) amnion
D) yolk sac

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Please read the following paragraph and then answer the following question(s).
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
A vasectomy ______.
A) prevents the production of sperm in the testes
B) prevents the production of semen
C) prevents the movement of sperm into the urethra
D) is an effective method to prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted disease
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
A vasectomy ______.
A) prevents the production of sperm in the testes
B) prevents the production of semen
C) prevents the movement of sperm into the urethra
D) is an effective method to prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Please read the following paragraph and then answer the following question(s).
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
A diaphragm functions as a birth control device by ______.
A) preventing ovulation
B) preventing implantation of an embryo
C) stimulating the production of sperm-killing antibodies
D) preventing the movement of sperm into the uterus
Birth control methods act at many points in the reproductive cycle. Some options, such as birth control pills, are highly effective at preventing pregnancy. However, only a few commonly available methods are effective at preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted disease. The Center for Disease Control estimates that each year about 10 million new STD infections strike people ages 15 to 24.
A diaphragm functions as a birth control device by ______.
A) preventing ovulation
B) preventing implantation of an embryo
C) stimulating the production of sperm-killing antibodies
D) preventing the movement of sperm into the uterus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



