Deck 4: Upper Limb
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Upper Limb
1
The third metacarpal of the hand articulates with the:
A) lunate.
B) scaphoid.
C) hamate.
D) capitate.
A) lunate.
B) scaphoid.
C) hamate.
D) capitate.
capitate.
2
How many phalanges are there in the thumb?
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Four
Two
3
How many phalanges are there in the hand?
A) 14
B) 27
C) 30
D) 32
A) 14
B) 27
C) 30
D) 32
14
4
Which of the following bones make up the wrist?
A) Five carpals
B) Five metacarpals
C) Eight carpals
D) Eight metacarpals
A) Five carpals
B) Five metacarpals
C) Eight carpals
D) Eight metacarpals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The first bone located on the proximal row and lateral side of the wrist is called the:
A) trapezoid.
B) trapezium.
C) lunate.
D) scaphoid.
A) trapezoid.
B) trapezium.
C) lunate.
D) scaphoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is the largest carpal bone?
A) Capitate
B) Hamate
C) Scaphoid
D) Triquetrum
A) Capitate
B) Hamate
C) Scaphoid
D) Triquetrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The capitulum of the humerus articulates with the:
A) radial head.
B) trochlea.
C) lateral epicondyle.
D) ulnar coronoid process.
A) radial head.
B) trochlea.
C) lateral epicondyle.
D) ulnar coronoid process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Soft tissue radiographs of the elbow in the lateral position are often ordered to demonstrate:
A) veins.
B) nerves.
C) fat pads.
D) fractures.
A) veins.
B) nerves.
C) fat pads.
D) fractures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For a lateral projection of the second through fifth digits, the central ray is directed:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 5 degrees cephalad.
D) 2 to 5 degrees cephalad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 5 degrees cephalad.
D) 2 to 5 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The most common oblique projection of the second through fifth digits is _____ with _____ rotation.
A) AP; medial
B) AP; lateral
C) PA; medial
D) PA; lateral
A) AP; medial
B) AP; lateral
C) PA; medial
D) PA; lateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For a PA projection of the second digit, the central ray is directed to the _____ joint.
A) distal interphalangeal
B) proximal interphalangeal
C) metacarpophalangeal
D) carpometacarpal
A) distal interphalangeal
B) proximal interphalangeal
C) metacarpophalangeal
D) carpometacarpal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The patient position most commonly used to perform a radiograph of a finger (digit) is:
A) AP.
B) PA.
C) sitting at the end of the table.
D) standing at the end of the table.
A) AP.
B) PA.
C) sitting at the end of the table.
D) standing at the end of the table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following passes through the carpal tunnel?
A) Radial vein
B) Radial nerve
C) Median vein
D) Median nerve
A) Radial vein
B) Radial nerve
C) Median vein
D) Median nerve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The hand consists of how many bones?
A) 8
B) 14
C) 27
D) 32
A) 8
B) 14
C) 27
D) 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The carpal bones articulate with the:
1)radius.
2)ulna.
3)phalanges.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)radius.
2)ulna.
3)phalanges.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The forearm consists of which of the following bones?
1)Ulna
2)Radius
3)Humerus
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Ulna
2)Radius
3)Humerus
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
At the lateral (thumb) side of the hand, the digit is called the _____ digit.
A) lateral
B) first
C) medial
D) fifth
A) lateral
B) first
C) medial
D) fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The arm is made up of which of the following bones?
1)Ulna
2)Radius
3)Humerus
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Ulna
2)Radius
3)Humerus
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The head of the radius articulates on the medial side with the:
A) coronoid process.
B) trochlear notch.
C) ulnar styloid process.
D) radial notch.
A) coronoid process.
B) trochlear notch.
C) ulnar styloid process.
D) radial notch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The palm of the hand is formed by:
A) five carpals.
B) five metacarpals.
C) eight carpals.
D) eight metacarpals.
A) five carpals.
B) five metacarpals.
C) eight carpals.
D) eight metacarpals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following projections clearly demonstrates the scaphoid?
1)PA in ulnar flexion
2)PA oblique in lateral rotation
3)PA axial (Stecher method)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)PA in ulnar flexion
2)PA oblique in lateral rotation
3)PA axial (Stecher method)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For a PA oblique projection of the first digit (thumb), the hand is placed in the _____ position.
A) supine
B) prone
C) medial rotation
D) lateral rotation
A) supine
B) prone
C) medial rotation
D) lateral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is the primary projection used to demonstrate anterior or posterior displacement of fractures of the hand or wrist?
A) AP
B) PA
C) Lateral
D) AP oblique
A) AP
B) PA
C) Lateral
D) AP oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following should be in contact with the tabletop for a PA projection of the wrist?
1)Arm
2)Axilla
3)Forearm
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Arm
2)Axilla
3)Forearm
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The central-ray angle for a PA oblique projection of the wrist is _____ degrees.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 12
D) 0 to 5
A) 0
B) 5
C) 12
D) 0 to 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The central ray for a PA projection of the wrist is directed to the:
A) radiocarpal joint.
B) scaphoid.
C) midcarpal area.
D) third CMC joint.
A) radiocarpal joint.
B) scaphoid.
C) midcarpal area.
D) third CMC joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
For a lateral projection of the wrist, the elbow must be flexed _____ degrees.
A) 0
B) 25
C) 45
D) 90
A) 0
B) 25
C) 45
D) 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The PA oblique projection of the wrist in lateral rotation requires a wrist angulation of _____ degrees.
A) 25
B) 30
C) 40
D) 45
A) 25
B) 30
C) 40
D) 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following objects would be needed to perform a PA oblique projection of a finger?
1)2-inch block
2)Lead shield
3)45-degree foam wedge
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)2-inch block
2)Lead shield
3)45-degree foam wedge
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The central-ray angulation for the PA projection of the hand is _____ degrees.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For the AP projection of the thumb, Lewis suggests angling the central ray toward the wrist to demonstrate the first metacarpal free of the sesamoids and of the soft tissue of the palm. What is the suggested central-ray angle?
A) 10 degrees
B) 15 degrees
C) 5 to 10 degrees
D) 10 to 15 degrees
A) 10 degrees
B) 15 degrees
C) 5 to 10 degrees
D) 10 to 15 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following positions are used to demonstrate the hand in the lateral projection?
1)Ulnar surface down, hand extended
2)Radial surface down, hand extended
3)Ulnar surface down, finger in "fan lateral"
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Ulnar surface down, hand extended
2)Radial surface down, hand extended
3)Ulnar surface down, finger in "fan lateral"
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a lateral projection of the hand, the central ray is directed to the:
A) second digit MCP joint.
B) PIP joint.
C) distal PIP joint.
D) midmetacarpal area.
A) second digit MCP joint.
B) PIP joint.
C) distal PIP joint.
D) midmetacarpal area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following projections would be used to better demonstrate the carpal interspaces?
A) AP
B) PA
C) Lateral
D) PA oblique with lateral rotation
A) AP
B) PA
C) Lateral
D) PA oblique with lateral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following are well demonstrated on a PA oblique projection of the wrist?
1)Capitate
2)Trapezium
3)Scaphoid
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Capitate
2)Trapezium
3)Scaphoid
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following central-ray angles is used for the lateral projection of the wrist?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees
C) 7 degrees
D) 0 to 5 degrees
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees
C) 7 degrees
D) 0 to 5 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a PA projection of the hand, the central ray is directed to the _____ joint.
A) second MCP
B) third MCP
C) fourth MCP
D) third PIP
A) second MCP
B) third MCP
C) fourth MCP
D) third PIP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For exact positioning of the PA oblique wrist, and to ensure duplication in follow-up examinations, which of the following is required?
A) 30-degree foam wedge
B) 45-degree foam wedge
C) 2-inch block
D) 3-inch block
A) 30-degree foam wedge
B) 45-degree foam wedge
C) 2-inch block
D) 3-inch block

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How many degrees is the hand rotated for a PA oblique projection of the digit?
A) 25
B) 40
C) 45
D) 40 to 45
A) 25
B) 40
C) 45
D) 40 to 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Flexing the fingers for a PA projection of the wrist causes which of the following?
A) Placement of the carpal bones farther from the IR
B) Placement of the carpal bones closer to the IR
C) Less pain for the patient when the wrist is broken
D) Greater resolution of the carpal interspaces
A) Placement of the carpal bones farther from the IR
B) Placement of the carpal bones closer to the IR
C) Less pain for the patient when the wrist is broken
D) Greater resolution of the carpal interspaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following methods is used to demonstrate the carpal canal?
A) Stecher (PA axial)
B) Norgaard (AP oblique)
C) Lawrence (inferosuperior axial)
D) Gaynor-Hart (tangential)
A) Stecher (PA axial)
B) Norgaard (AP oblique)
C) Lawrence (inferosuperior axial)
D) Gaynor-Hart (tangential)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following tangential projections is used to demonstrate the carpal canal?
1)Axial
2)Inferosuperior
3)Superoinferior
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Axial
2)Inferosuperior
3)Superoinferior
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The PA projection of the wrist in ulnar deviation clearly demonstrates the:
A) trapezium.
B) trapezoid.
C) hamate.
D) scaphoid.
A) trapezium.
B) trapezoid.
C) hamate.
D) scaphoid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The IR must be elevated how many degrees for the PA axial projection of the wrist (Stecher method)?
A) 5 degrees
B) 10 degrees
C) 15 degrees
D) 20 degrees
A) 5 degrees
B) 10 degrees
C) 15 degrees
D) 20 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The lateral projection of the forearm should clearly demonstrate which of the following?
1)Elbow joint
2)Radius and ulna
3)Proximal row of carpal bones
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Elbow joint
2)Radius and ulna
3)Proximal row of carpal bones
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For the AP projection of the elbow, the hand is:
A) pronated.
B) supinated.
C) placed in the lateral position.
D) placed in the 45-degree oblique position.
A) pronated.
B) supinated.
C) placed in the lateral position.
D) placed in the 45-degree oblique position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following joints should be clearly demonstrated on the AP projection of the forearm?
1)Wrist
2)Elbow
3)Proximal humerus
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Wrist
2)Elbow
3)Proximal humerus
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For the lateral projection of the forearm, the elbow should be flexed _____ degrees.
A) 45
B) 80
C) 90
D) 120
A) 45
B) 80
C) 90
D) 120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the AP projection of the elbow, the humeral epicondyles are:
A) perpendicular to the IR.
B) parallel to the IR.
C) superimposed over each other.
D) not clearly seen.
A) perpendicular to the IR.
B) parallel to the IR.
C) superimposed over each other.
D) not clearly seen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The PA axial projection of the wrist (Stecher method) clearly demonstrates the:
A) lunate.
B) capitate.
C) scaphoid.
D) distal row of carpal bones.
A) lunate.
B) capitate.
C) scaphoid.
D) distal row of carpal bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For the lateral projection of the elbow, the elbow joint should be flexed _____ degrees.
A) 25
B) 45
C) 75
D) 90
A) 25
B) 45
C) 75
D) 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For the PA projection of the wrist in ulnar deviation, the central ray is directed to the:
A) pisiform.
B) scaphoid.
C) radiocarpal joint.
D) midcarpal area.
A) pisiform.
B) scaphoid.
C) radiocarpal joint.
D) midcarpal area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The central-ray angulation for the tangential projection (inferosuperior) of demonstrating the carpal canal is _____ degrees.
A) 25
B) 30
C) 25 to 30
D) 35 to 45
A) 25
B) 30
C) 25 to 30
D) 35 to 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the IR and wrist are placed flat on the table for the PA axial projection of the wrist (Stecher method), the central ray must be angled _____ degrees.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 15 to 20
A) 5
B) 10
C) 20
D) 15 to 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following projections corrects foreshortening of the scaphoid?
A) PA
B) PA oblique in lateral rotation
C) PA in radial deviation
D) PA in ulnar deviation
A) PA
B) PA oblique in lateral rotation
C) PA in radial deviation
D) PA in ulnar deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For the PA projection of the wrist in ulnar deviation, the central ray is angled _____ degrees.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following should be on the same plane for a lateral projection of the elbow?
1)Wrist joint
2)Elbow joint
3)Shoulder joint
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Wrist joint
2)Elbow joint
3)Shoulder joint
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The central-ray angulation for the PA axial projection of the wrist (Stecher method) is _____ degrees.
A) 0
B) 5
C) 8
D) 10
A) 0
B) 5
C) 8
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the AP projection of the forearm, the hand is:
A) supinated.
B) pronated.
C) placed in the lateral position.
D) placed in a 45-degree oblique position.
A) supinated.
B) pronated.
C) placed in the lateral position.
D) placed in a 45-degree oblique position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
How many degrees is the central ray angled for the AP forearm?
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7
A) 0
B) 5
C) 7
D) 5 to 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following projections of the elbow will demonstrate the radial head and neck free of superimposition?
A) AP oblique projection, lateral rotation
B) AP oblique projection, medial rotation
C) AP projection, partial flexion
D) AP projection, acute flexion
A) AP oblique projection, lateral rotation
B) AP oblique projection, medial rotation
C) AP projection, partial flexion
D) AP projection, acute flexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following projections of the elbow will demonstrate the olecranon process within the olecranon fossa?
A) AP, acute flexion
B) AP, partial flexion
C) AP oblique, medial rotation
D) AP oblique, lateral rotation
A) AP, acute flexion
B) AP, partial flexion
C) AP oblique, medial rotation
D) AP oblique, lateral rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following positions of the hand will place the epicondyles parallel with the plane of the IR?
A) Lateral
B) Prone
C) Supine
D) 45 degrees oblique
A) Lateral
B) Prone
C) Supine
D) 45 degrees oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the central-ray angulation for the AP elbow when the forearm is partially flexed?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees
C) 10 degrees
D) 5 to 10 degrees
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees
C) 10 degrees
D) 5 to 10 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
How many degrees should the elbow be angled for an AP oblique projection in lateral rotation?
A) 30 degrees
B) 40 degrees
C) 45 degrees
D) 50 degrees
A) 30 degrees
B) 40 degrees
C) 45 degrees
D) 50 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Where is the central ray directed for an AP projection of the humerus?
A) Elbow joint
B) Shoulder joint
C) Body of the humerus
D) Midpoint of the humerus
A) Elbow joint
B) Shoulder joint
C) Body of the humerus
D) Midpoint of the humerus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The position recommended to increase patient comfort when performing an AP projection of the humerus is:
A) prone.
B) recumbent.
C) supine.
D) upright.
A) prone.
B) recumbent.
C) supine.
D) upright.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is shown in profile on a lateral projection of the elbow?
A) Radial neck
B) Radial head
C) Olecranon process
D) Humeral epicondyles
A) Radial neck
B) Radial head
C) Olecranon process
D) Humeral epicondyles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following breathing techniques should be used for an AP projection of the humerus?
A) Suspended respiration
B) Full inspiration
C) Full expiration
D) Shallow breathing
A) Suspended respiration
B) Full inspiration
C) Full expiration
D) Shallow breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How many degrees should the elbow be angled for an AP oblique projection in medial rotation?
A) 35 degrees
B) 40 degrees
C) 45 degrees
D) 55 degrees
A) 35 degrees
B) 40 degrees
C) 45 degrees
D) 55 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How far above the humeral head should the upper margin of the IR be placed for a lateral projection of the humerus?
A)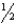 inch
inch
B) 1 inch
C) 1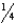 inch
inch
D) 1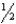 inch
inch
A)
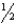 inch
inchB) 1 inch
C) 1
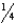 inch
inchD) 1
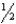 inch
inch
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following objects would be necessary to perform an x-ray examination of the humerus?
1)Sandbag
2)30-degree angle sponge
3)Lead shield
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Sandbag
2)30-degree angle sponge
3)Lead shield
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is demonstrated free of superimposition on an AP oblique projection of the elbow in lateral rotation?
A) Capitulum
B) Trochlea
C) Radial head and neck
D) Olecranon process
A) Capitulum
B) Trochlea
C) Radial head and neck
D) Olecranon process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following must be clearly demonstrated on an AP projection of the humerus?
1)Elbow joint
2)Glenoid cavity
3)Shoulder joint
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Elbow joint
2)Glenoid cavity
3)Shoulder joint
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a patient is unable to extend the forearm for an AP projection of the elbow, how many projections are necessary to avoid distortion of the joint?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is shown in profile on an AP projection of the humerus?
A) Capitulum
B) Glenoid cavity
C) Greater tubercle
D) Lesser tubercle
A) Capitulum
B) Glenoid cavity
C) Greater tubercle
D) Lesser tubercle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Rotating the arm medially for a lateral projection of the humerus will place the epicondyles _____ with the plane of the IR.
A) at a 30-degree angle
B) at a 45-degree angle
C) parallel
D) perpendicular
A) at a 30-degree angle
B) at a 45-degree angle
C) parallel
D) perpendicular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In what position should the hand be placed for the AP projection of the humerus?
A) Supine
B) Prone
C) Lateral
D) 30 degrees oblique, medial rotation
A) Supine
B) Prone
C) Lateral
D) 30 degrees oblique, medial rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How far above the humeral head should the upper margin of the IR be placed for an AP humerus?
A)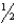 inch
inch
B) 1 inch
C) 1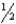 inches
inches
D) 2 inches
A)
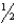 inch
inchB) 1 inch
C) 1
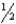 inches
inchesD) 2 inches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following would be projected free of superimposition for an AP oblique projection of the elbow with medial rotation?
A) Lateral epicondyle
B) Coronoid process
C) Olecranon process
D) Olecranon fossa
A) Lateral epicondyle
B) Coronoid process
C) Olecranon process
D) Olecranon fossa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



