Deck 6: Lower Limb
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Lower Limb
1
The largest and strongest bone in the body is the:
A) tibia.
B) femur.
C) hip.
D) skull.
A) tibia.
B) femur.
C) hip.
D) skull.
tibia.
2
The second largest bone in the body is the:
A) hip.
B) tibia.
C) femur.
D) skull.
A) hip.
B) tibia.
C) femur.
D) skull.
tibia.
3
The fibula articulates with the tibia at the:
1)distal end.
2)proximal end.
3)posterior surface.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)distal end.
2)proximal end.
3)posterior surface.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
2 and 3
4
How many degrees are the lower leg and foot rotated for the AP oblique projection of the toes in medial rotation?
A) 10 to 15
B) 20 to 25
C) 40 to 60
D) 30 to 45
A) 10 to 15
B) 20 to 25
C) 40 to 60
D) 30 to 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
How many metatarsal bones are in the foot?
A) Four
B) Five
C) Six
D) Seven
A) Four
B) Five
C) Six
D) Seven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The inferior aspect of the foot is termed the _____ surface.
A) posterior
B) caudal
C) dorsal
D) plantar
A) posterior
B) caudal
C) dorsal
D) plantar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The largest and strongest tarsal bone is the:
A) calcaneus.
B) navicular.
C) medial cuneiform.
D) lateral cuneiform.
A) calcaneus.
B) navicular.
C) medial cuneiform.
D) lateral cuneiform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The second largest tarsal bone, and the one that occupies the highest position in the foot, is the:
A) talus.
B) navicular.
C) calcaneus.
D) medial cuneiform.
A) talus.
B) navicular.
C) calcaneus.
D) medial cuneiform.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The lower limb and its girdle comprise which of the following bones?
1)Foot and leg
2)Thigh
3)Hip
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Foot and leg
2)Thigh
3)Hip
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many phalanges are in the great toe?
A) None
B) One
C) Two
D) Three
A) None
B) One
C) Two
D) Three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How many tarsal bones are in the foot?
A) Four
B) Five
C) Six
D) Seven
A) Four
B) Five
C) Six
D) Seven

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How many degrees of angulation are required to open the IP joint spaces of the toes on an AP projection?
A) 0
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
A) 0
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The superior surface of the foot is termed the _____ surface.
A) dorsal
B) plantar
C) anterior
D) superior
A) dorsal
B) plantar
C) anterior
D) superior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The central-ray angulation for an AP oblique projection of the toes is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees posteriorly.
C) 10 degrees posteriorly.
D) 15 degrees posteriorly.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees posteriorly.
C) 10 degrees posteriorly.
D) 15 degrees posteriorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The name of the small round bones located on the plantar surface of the foot, typically beneath the first MTP joint, is the:
A) cuneiforms.
B) sesamoids.
C) tarsals.
D) epicondyles.
A) cuneiforms.
B) sesamoids.
C) tarsals.
D) epicondyles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many bones are in the foot?
A) 14
B) 26
C) 27
D) 29
A) 14
B) 26
C) 27
D) 29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
For an AP projection of the toes, the central ray is directed to the _____ MTP joint.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fourth
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fourth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How many phalanges are in the foot?
A) 5
B) 7
C) 14
D) 26
A) 5
B) 7
C) 14
D) 26

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How many bones make up the leg?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following forms the ankle mortise?
1)Lateral malleolus of the fibula
2)Medial malleolus of the tibia
3)Inferior surface of the tibia
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Lateral malleolus of the fibula
2)Medial malleolus of the tibia
3)Inferior surface of the tibia
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The most commonly performed oblique projection of the foot is the _____ oblique in _____.
A) AP; medial rotation
B) AP; lateral rotation
C) PA; medial rotation
D) PA; Grashey method
A) AP; medial rotation
B) AP; lateral rotation
C) PA; medial rotation
D) PA; Grashey method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For an AP projection of the ankle, the central ray must enter the:
A) talus.
B) subtalar joint.
C) talofibular joint.
D) ankle joint, midway between the malleoli.
A) talus.
B) subtalar joint.
C) talofibular joint.
D) ankle joint, midway between the malleoli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not clearly demonstrated on an AP projection of the ankle?
A) Tibiotalar
B) Lateral malleoli
C) Ankle mortise
D) Tibiofibular overlapping
A) Tibiotalar
B) Lateral malleoli
C) Ankle mortise
D) Tibiofibular overlapping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The central-ray angulation for the AP ankle projection is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 10 degrees caudad.
D) 15 to 20 degrees caudad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 10 degrees caudad.
D) 15 to 20 degrees caudad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How is the patient placed for a lateral projection of the great toe and second toe?
A) Supine, with the affected leg turned out
B) Supine, with the affected leg turned in
C) Lateral, on the affected side
D) Recumbent, on the unaffected side
A) Supine, with the affected leg turned out
B) Supine, with the affected leg turned in
C) Lateral, on the affected side
D) Recumbent, on the unaffected side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The central ray is directed to which of the following for an AP or AP axial projection of the foot?
A) Head of the second metatarsal
B) Head of the third metatarsal
C) Base of the third metatarsal
D) Base of the fourth metatarsal
A) Head of the second metatarsal
B) Head of the third metatarsal
C) Base of the third metatarsal
D) Base of the fourth metatarsal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which lateral projection of the foot is the most commonly performed?
A) Lateromedial (lateral recumbent position)
B) Mediolateral (lateral recumbent position)
C) Lateromedial (standing weight-bearing)
D) Mediolateral (standing weight-bearing)
A) Lateromedial (lateral recumbent position)
B) Mediolateral (lateral recumbent position)
C) Lateromedial (standing weight-bearing)
D) Mediolateral (standing weight-bearing)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The central-ray angulation for a lateral projection of the calcaneus is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 10 degrees cephalad.
D) 5 to 10 degrees cephalad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 10 degrees cephalad.
D) 5 to 10 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the patient position for a lateral projection of the third, fourth, or fifth toes?
A) Supine, with the leg and foot laterally rotated
B) 45 degrees oblique, with the leg and foot laterally rotated
C) Lateral recumbent, on the affected side
D) Lateral recumbent, on the unaffected side
A) Supine, with the leg and foot laterally rotated
B) 45 degrees oblique, with the leg and foot laterally rotated
C) Lateral recumbent, on the affected side
D) Lateral recumbent, on the unaffected side

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the essential lateral projection of the calcaneus?
A) Lateral (lateromedial)
B) Lateral (mediolateral)
C) Lateromedial oblique
D) Lateromedial oblique, weight-bearing
A) Lateral (lateromedial)
B) Lateral (mediolateral)
C) Lateromedial oblique
D) Lateromedial oblique, weight-bearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
To better demonstrate the TMT joint spaces of the foot, a posterior angulation of how many degrees is required?
A) 0
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
A) 0
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the central-ray angulation for the axial (plantodorsal) projection of the calcaneus?
A) 25 degrees
B) 30 degrees
C) 35 degrees
D) 40 degrees
A) 25 degrees
B) 30 degrees
C) 35 degrees
D) 40 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
For a lateral projection of the foot, the central ray is directed to the:
A) head of the third metatarsal.
B) base of the third metatarsal.
C) tibiotalar joint.
D) navicular.
A) head of the third metatarsal.
B) base of the third metatarsal.
C) tibiotalar joint.
D) navicular.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following will clearly demonstrate the cuboid?
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP oblique in lateral rotation
D) AP oblique in medial rotation
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP oblique in lateral rotation
D) AP oblique in medial rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The essential projections of the calcaneus are:
1)axial (plantodorsal).
2)axial (dorsoplantar).
3)lateral (mediolateral).
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)axial (plantodorsal).
2)axial (dorsoplantar).
3)lateral (mediolateral).
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For an axial projection of the calcaneus, the ankle should be dorsiflexed so the plantar surface of the foot is:
A) parallel with the central ray.
B) perpendicular to the central ray.
C) 70 degrees from the plane of the IR.
D) 90 degrees from the plane of the IR.
A) parallel with the central ray.
B) perpendicular to the central ray.
C) 70 degrees from the plane of the IR.
D) 90 degrees from the plane of the IR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For an AP oblique projection of the foot in either medial or lateral rotation, the plantar surface of the foot should form an angle of _____ degrees.
A) 15
B) 30
C) 45
D) 60
A) 15
B) 30
C) 45
D) 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which projections of the foot will best demonstrate the structural status of the longitudinal arch?
A) AP axial
B) AP oblique medial rotation
C) Lateral (lateromedial)
D) Lateral (lateromedial) weight-bearing
A) AP axial
B) AP oblique medial rotation
C) Lateral (lateromedial)
D) Lateral (lateromedial) weight-bearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The central ray for an AP oblique projection of the foot is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees posteriorly.
C) 10 degrees posteriorly.
D) 15 degrees posteriorly.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees posteriorly.
C) 10 degrees posteriorly.
D) 15 degrees posteriorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To prevent lateral rotation, how should the foot be positioned for a lateral projection of the ankle?
A) In dorsiflexion
B) In plantar flexion
C) On a 10-degree angle wedge
D) On a 15-degree angle wedge
A) In dorsiflexion
B) In plantar flexion
C) On a 10-degree angle wedge
D) On a 15-degree angle wedge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To demonstrate the ankle mortise, the leg and foot should be rotated medially how many degrees?
A) 10
B) 25
C) 45
D) 15 to 20
A) 10
B) 25
C) 45
D) 15 to 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Where is the IR centered for an AP projection of the knee?
A)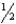 inch above the patellar apex
inch above the patellar apex
B) 1 inch above the patellar apex
C)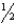 inch below the patellar apex
inch below the patellar apex
D) 1 inch below the patellar apex
A)
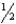 inch above the patellar apex
inch above the patellar apexB) 1 inch above the patellar apex
C)
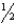 inch below the patellar apex
inch below the patellar apexD) 1 inch below the patellar apex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Often, the leg is too long to fit on one IR for radiographs. Which joint or joints should be included on the IR when the site of a lesion is known?
A) The ankle joint
B) The knee joint
C) Both joints on two IRs
D) The joint closest to the lesion
A) The ankle joint
B) The knee joint
C) Both joints on two IRs
D) The joint closest to the lesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The central-ray angle for a lateral projection of the ankle is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 7 degrees cephalad.
D) 10 degrees caudad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 7 degrees cephalad.
D) 10 degrees caudad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Where will the fibula be located on a properly positioned lateral radiograph of the ankle?
A) Directly over the tibia
B) Behind the tibia
C) Over the anterior half of the tibia
D) Over the posterior half of the tibia
A) Directly over the tibia
B) Behind the tibia
C) Over the anterior half of the tibia
D) Over the posterior half of the tibia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the position of the femoral condyles when the leg is properly positioned for an AP projection?
A) Perpendicular to the IR
B) Parallel to the IR
C) At a 15- to 20-degree oblique position (laterally)
D) At a 15- to 20-degree oblique position (medially)
A) Perpendicular to the IR
B) Parallel to the IR
C) At a 15- to 20-degree oblique position (laterally)
D) At a 15- to 20-degree oblique position (medially)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How far should the IR or collimated field extend beyond the ankle or knee joint for an AP projection of the leg?
A)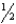 to 1 inch
to 1 inch
B) 1 to 2 inches
C) 1 to 1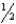 inches
inches
D) 2 to 2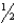 inches
inches
A)
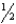 to 1 inch
to 1 inchB) 1 to 2 inches
C) 1 to 1
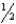 inches
inchesD) 2 to 2
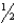 inches
inches
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which specific projections of the ankle are performed to diagnose a tear of the medial or lateral ligament?
1)AP, eversion stress
2)AP, inversion stress
3)AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)AP, eversion stress
2)AP, inversion stress
3)AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the central-ray angle for an AP projection of the leg?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 7 degrees caudad
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 7 degrees caudad
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The medial and lateral oblique projections of the ankle require the leg and foot to be rotated how many degrees?
A) 15
B) 20
C) 45
D) 15 to 20
A) 15
B) 20
C) 45
D) 15 to 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following should be clearly demonstrated on a lateral projection of the leg?
1)Knee joint
2)Ankle joint
3)Entire femoral condyles
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Knee joint
2)Ankle joint
3)Entire femoral condyles
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which projection will clearly demonstrate the joint spaces between the talus and both malleoli?
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree internal rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree internal rotation
D) AP oblique, 45-degree external rotation
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree internal rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree internal rotation
D) AP oblique, 45-degree external rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following objects should be available in the radiography room for performing radiographs of the lower limb?
1)Angle sponges
2)Sandbags
3)Pull straps
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Angle sponges
2)Sandbags
3)Pull straps
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For a lateral projection of the ankle, the central ray must enter the:
A) navicular.
B) tibiofibular joint.
C) medial malleolus.
D) lateral malleolus.
A) navicular.
B) tibiofibular joint.
C) medial malleolus.
D) lateral malleolus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the malleoli of the ankle are positioned parallel with the IR, the ankle is in position for which projection?
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 45-degree lateral rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree medial rotation
D) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation for the ankle mortise
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 45-degree lateral rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree medial rotation
D) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation for the ankle mortise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following are the essential oblique projections of the ankle?
1)AP oblique, 45-degree medial rotation
2)AP oblique, 45-degree lateral rotation
3)AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation for the ankle mortise
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)AP oblique, 45-degree medial rotation
2)AP oblique, 45-degree lateral rotation
3)AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree medial rotation for the ankle mortise
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following must be rotated for all oblique projections of the ankle?
1)Pelvis
2)Leg
3)Foot
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Pelvis
2)Leg
3)Foot
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which ankle projection will clearly demonstrate the ankle mortise in profile?
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree internal rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree internal rotation
D) AP oblique, 45-degree external rotation
A) AP
B) AP oblique, 15- to 20-degree internal rotation
C) AP oblique, 45-degree internal rotation
D) AP oblique, 45-degree external rotation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The central-ray angulation for an AP oblique projection of the ankle is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 7 degrees caudad.
D) 15 degrees caudad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 7 degrees caudad.
D) 15 degrees caudad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which projections of the ankle are performed on a patient following an inversion or eversion injury?
A) AP and lateral
B) AP and both obliques
C) AP stress studies
D) AP, lateral, and both obliques
A) AP and lateral
B) AP and both obliques
C) AP stress studies
D) AP, lateral, and both obliques

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The central-ray angle for AP oblique projections of the knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 7 degrees cephalad.
D) variable, depending on the ASIS-to-tabletop distance.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees caudad.
C) 7 degrees cephalad.
D) variable, depending on the ASIS-to-tabletop distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement is between 19 and 24 cm, the central-ray angulation for an AP knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees cephalad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How much should the leg be flexed for a lateral projection of the knee?
A) 10 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 10 to 20 degrees
D) 20 to 30 degrees
A) 10 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 10 to 20 degrees
D) 20 to 30 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
For an AP oblique projection of the knee, the limb is rotated _____ degrees.
A) 25
B) 30
C) 45
D) 30 to 40
A) 25
B) 30
C) 45
D) 30 to 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Where is the central ray directed for an AP projection of the knee?
A)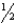 inch above the patellar base
inch above the patellar base
B)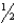 inch above the patellar apex
inch above the patellar apex
C)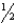 inch below the patellar base
inch below the patellar base
D)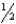 inch below the patellar apex
inch below the patellar apex
A)
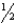 inch above the patellar base
inch above the patellar baseB)
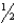 inch above the patellar apex
inch above the patellar apexC)
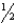 inch below the patellar base
inch below the patellar baseD)
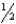 inch below the patellar apex
inch below the patellar apex
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Valgus and varus deformities of the knee can be evaluated with which of the following projections?
A) AP
B) AP oblique
C) PA, bilateral weight-bearing
D) AP, bilateral weight-bearing
A) AP
B) AP oblique
C) PA, bilateral weight-bearing
D) AP, bilateral weight-bearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following will ensure that the knee is in proper position for a lateral projection?
1)Epicondyles perpendicular to the IR
2)Patella perpendicular to the IR
3)Leg flexed 20 to 30 degrees
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Epicondyles perpendicular to the IR
2)Patella perpendicular to the IR
3)Leg flexed 20 to 30 degrees
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How is the central ray directed for the PA axial projection (Holmblad method) of the intercondylar fossa?
A) Perpendicular to the lower leg
B) Perpendicular to the femur
C) 40 to 50 degrees to lower leg
D) 40 to 50 degrees to the femur
A) Perpendicular to the lower leg
B) Perpendicular to the femur
C) 40 to 50 degrees to lower leg
D) 40 to 50 degrees to the femur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The central-ray angle for an AP, bilateral weight-bearing knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 to 7 degrees caudad.
D) dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 to 7 degrees caudad.
D) dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How much is the knee joint flexed for the PA axial projection (Holmblad method) of the intercondylar fossa?
A) 20 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 50 degrees
D) 70 degrees
A) 20 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 50 degrees
D) 70 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following projections of the knee best demonstrates the narrowing of a joint space?
A) AP
B) AP oblique
C) Lateral
D) AP of both knees with weight-bearing
A) AP
B) AP oblique
C) Lateral
D) AP of both knees with weight-bearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement is less than 19 cm, the central-ray angulation for an AP knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees caudad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees caudad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When the knee is properly positioned for an AP projection, the patella will lie:
A) directly in the center of the limb.
B) slightly to the medial side.
C) slightly to the lateral side.
D) parallel with the tabletop.
A) directly in the center of the limb.
B) slightly to the medial side.
C) slightly to the lateral side.
D) parallel with the tabletop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
To place the patella parallel with the plane of the IR for a PA projection, the heel must be rotated:
A) 5 to 10 degrees laterally.
B) 5 to 10 degrees medially.
C) 10 to 15 degrees laterally.
D) 10 to 15 degrees medially.
A) 5 to 10 degrees laterally.
B) 5 to 10 degrees medially.
C) 10 to 15 degrees laterally.
D) 10 to 15 degrees medially.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following methods are used to demonstrate the intercondylar fossa?
1)Holmblad (PA axial)
2)Camp-Coventry (PA axial)
3)Settegast (tangential)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Holmblad (PA axial)
2)Camp-Coventry (PA axial)
3)Settegast (tangential)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
When the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement is greater than 24 cm, the central-ray angulation for an AP knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees cephalad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 5 degrees cephalad.
C) 5 degrees caudad.
D) 7 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following positions can be used to demonstrate the intercondylar fossa using the Holmblad method?
1)Standing (horizontal central ray)
2)Kneeling on the table (vertical central ray)
3)Standing with knee on stool (vertical central ray)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Standing (horizontal central ray)
2)Kneeling on the table (vertical central ray)
3)Standing with knee on stool (vertical central ray)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In which position is the patient placed for a PA projection of the patella?
A) Supine
B) Prone
C) Lateral
D) Upright
A) Supine
B) Prone
C) Lateral
D) Upright

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following is clearly demonstrated on an AP oblique projection of the knee in medial rotation?
A) Distal fibula
B) Tibiotalar articulation
C) Patellofemoral joint space
D) Tibiofibular articulation
A) Distal fibula
B) Tibiotalar articulation
C) Patellofemoral joint space
D) Tibiofibular articulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The central-ray angulation for a lateral projection of the knee is:
A) 0 degrees.
B) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad.
C) dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement.
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad.
A) 0 degrees.
B) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad.
C) dependent upon the ASIS-to-tabletop measurement.
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



