Deck 8: Vertebral Column
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/175
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Vertebral Column
1
The first cervical vertebra is called the:
A) axis.
B) atlas.
C) dens.
D) vertebra prominens.
A) axis.
B) atlas.
C) dens.
D) vertebra prominens.
atlas.
2
Spinal nerves and blood vessels exit the spinal column through the:
A) vertebral arch.
B) vertebral notches.
C) vertebral foramen.
D) intervertebral foramina.
A) vertebral arch.
B) vertebral notches.
C) vertebral foramen.
D) intervertebral foramina.
intervertebral foramina.
3
An abnormal lateral curvature of the spine is termed:
A) scoliosis.
B) kyphosis.
C) lordosis.
D) scoliokyphosis.
A) scoliosis.
B) kyphosis.
C) lordosis.
D) scoliokyphosis.
scoliosis.
4
When viewed from the side, the vertebral column should present how many curves?
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five
A) Two
B) Three
C) Four
D) Five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The short, thick processes that project posteriorly on each side of a vertebral body are called the:
A) pedicles.
B) laminae.
C) transverse processes.
D) spinous processes.
A) pedicles.
B) laminae.
C) transverse processes.
D) spinous processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A typical vertebra is composed of which main parts?
1)Body
2)Lamina
3)Vertebral arch
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Body
2)Lamina
3)Vertebral arch
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The intervertebral foramina of the cervical spine open:
A) laterally.
B) 45 degrees anteriorly.
C) 70 degrees anteriorly.
D) 45 degrees anteriorly and 15 degrees inferiorly.
A) laterally.
B) 45 degrees anteriorly.
C) 70 degrees anteriorly.
D) 45 degrees anteriorly and 15 degrees inferiorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The articulations between the articular processes of the vertebral arches are called the _____ joints.
A) costovertebral
B) costotransverse
C) intervertebral
D) zygapophyseal
A) costovertebral
B) costotransverse
C) intervertebral
D) zygapophyseal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An abnormally increased concavity of the lumbar spine is termed:
A) lordosis.
B) kyphosis.
C) scoliosis.
D) scoliokyphosis.
A) lordosis.
B) kyphosis.
C) scoliosis.
D) scoliokyphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which vertebral process projects posteriorly from the junction of the laminae and pedicles?
A) Spinous process
B) Transverse process
C) Superior articular process
D) Inferior articular process
A) Spinous process
B) Transverse process
C) Superior articular process
D) Inferior articular process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following are functions of the vertebral column?
1)Supports the trunk
2)Protects the spinal cord
3)Supports the skull superiorly
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Supports the trunk
2)Protects the spinal cord
3)Supports the skull superiorly
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The vertebral column articulates with the hip bone at the:
A) sacroiliac joint.
B) pubic symphysis.
C) acetabulum.
D) lumbar-5, sacral-1 joint.
A) sacroiliac joint.
B) pubic symphysis.
C) acetabulum.
D) lumbar-5, sacral-1 joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The vertebra prominens is the name given to the _____ vertebra.
A) first cervical
B) second cervical
C) seventh cervical
D) first thoracic
A) first cervical
B) second cervical
C) seventh cervical
D) first thoracic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How many vertebrae make up the vertebral column?
A) 24
B) 27
C) 33
D) 54
A) 24
B) 27
C) 33
D) 54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An abnormal increase in the convexity of the thoracic spine is termed:
A) scoliosis.
B) spondylosis.
C) lordosis.
D) kyphosis.
A) scoliosis.
B) spondylosis.
C) lordosis.
D) kyphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many vertebrae are there in the sacrum?
A) Three
B) Four
C) Five
D) Three to five
A) Three
B) Four
C) Five
D) Three to five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The openings in the cervical vertebrae for the transmission of the vertebral artery and vein are called the:
A) transverse foramen.
B) vertebral foramina.
C) intervertebral foramina.
D) inferior vertebral notch.
A) transverse foramen.
B) vertebral foramina.
C) intervertebral foramina.
D) inferior vertebral notch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following vertebral areas have a kyphotic curve?
1)Thoracic
2)Lumbar
3)Sacrum and coccyx
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Thoracic
2)Lumbar
3)Sacrum and coccyx
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The condition in which an intervertebral disk "slips" and protrudes into the vertebral canal is called:
A) vertebrogenesis.
B) spondylolysis.
C) spondylolisthesis.
D) herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP).
A) vertebrogenesis.
B) spondylolysis.
C) spondylolisthesis.
D) herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following vertebral areas have a lordotic curve?
1)Cervical
2)Thoracic
3)Lumbar
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Cervical
2)Thoracic
3)Lumbar
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Where is the center of the IR positioned for the AP projection of the dens, Fuchs method?
A) Acanthion
B) Mental point
C) External acoustic meatus
D) Tip of the mastoid process
A) Acanthion
B) Mental point
C) External acoustic meatus
D) Tip of the mastoid process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How many thoracic vertebrae have a small concave facet on the transverse process, for articulation with the tubercle of a rib?
A) 7
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12
A) 7
B) 8
C) 10
D) 12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The intervertebral foramina of the thoracic spine are clearly demonstrated on which projection?
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) PA oblique
D) AP oblique
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) PA oblique
D) AP oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For which projection is the patient instructed to softly phonate "ah" during the exposure?
A) Lateral cervical vertebrae
B) AP "open mouth" atlas and axis
C) AP dens, Fuchs method
D) AP axial cervical spine
A) Lateral cervical vertebrae
B) AP "open mouth" atlas and axis
C) AP dens, Fuchs method
D) AP axial cervical spine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The zygapophyseal joints of the lumbar spine form an angle of how many degrees from the posterior midsagittal plane?
A) 45
B) 15 to 20
C) 30 to 50
D) 70 to 75
A) 45
B) 15 to 20
C) 30 to 50
D) 70 to 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following methods is used to demonstrate the dens within the foramen magnum?
A) Grandy
B) Fuchs
C) Twining
D) Pawlow
A) Grandy
B) Fuchs
C) Twining
D) Pawlow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The angle of the articulation between the sacrum and the ilia (the sacroiliac joints) is _____ degrees.
A) 10 to 15
B) 15 to 20
C) 25 to 30
D) 45 to 50
A) 10 to 15
B) 15 to 20
C) 25 to 30
D) 45 to 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How much is the body rotated from the lateral position to demonstrate the zygapophyseal joints of the thoracic region?
A) 30 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 15 to 20 degrees
D) 70 to 75 degrees
A) 30 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 15 to 20 degrees
D) 70 to 75 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following lines must be perpendicular to the IR for the AP "open mouth" atlas and axis?
A) Glabellomeatal line
B) Orbitomeatal line
C) Acanthiomeatal line
D) A line drawn from the lower edge of the upper incisors to the tip of the mastoid process
A) Glabellomeatal line
B) Orbitomeatal line
C) Acanthiomeatal line
D) A line drawn from the lower edge of the upper incisors to the tip of the mastoid process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Where should the center of the IR be positioned for the "open mouth" AP projection of the atlas and axis?
A) To the "Adam's apple"
B) First cervical vertebra
C) Second cervical vertebra
D) Fourth cervical vertebra
A) To the "Adam's apple"
B) First cervical vertebra
C) Second cervical vertebra
D) Fourth cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
On each side of the sacral base is a large winglike mass called the:
A) ala.
B) base.
C) promontory.
D) superior articular process.
A) ala.
B) base.
C) promontory.
D) superior articular process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The zygapophyseal joints of the thoracic spine form an angle of how many degrees with the midsagittal plane?
A) 45
B) 90
C) 15 to 20
D) 70 to 75
A) 45
B) 90
C) 15 to 20
D) 70 to 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The zygapophyseal joints of the cervical spine are clearly demonstrated on which projection?
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP oblique
D) PA oblique
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP oblique
D) PA oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The respiration phase for the "open mouth" AP projection of the atlas and axis is:
A) inspiration.
B) expiration.
C) suspended respiration.
D) softly phonate "ah" during the exposure.
A) inspiration.
B) expiration.
C) suspended respiration.
D) softly phonate "ah" during the exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following describes the anatomy of interest for the Fuchs method?
A) AP, dens
B) AP, atlas and axis
C) AP, cervicothoracic region
D) Lateral, cervicothoracic region
A) AP, dens
B) AP, atlas and axis
C) AP, cervicothoracic region
D) Lateral, cervicothoracic region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Where is the central ray directed for an "open mouth" AP projection of the atlas and axis?
A) Perpendicular through the open mouth
B) Perpendicular to the acanthion
C) Parallel to the acanthiomeatal line
D) Parallel to the orbitomeatal line
A) Perpendicular through the open mouth
B) Perpendicular to the acanthion
C) Parallel to the acanthiomeatal line
D) Parallel to the orbitomeatal line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The intervertebral foramina of the thoracic spine form an angle of how many degrees with the midsagittal plane?
A) 45
B) 90
C) 15 to 20
D) 70 to 75
A) 45
B) 90
C) 15 to 20
D) 70 to 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The intervertebral foramina of the superior four lumbar vertebrae are situated how many degrees from the midsagittal plane?
A) 90
B) 15 to 20
C) 30 to 50
D) 70 to 75
A) 90
B) 15 to 20
C) 30 to 50
D) 70 to 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The condition of the lumbar spine in which there is anterior displacement of one vertebra over another is termed:
A) scoliosis.
B) spondylolysis.
C) spondylolisthesis.
D) scoliokyphosis.
A) scoliosis.
B) spondylolysis.
C) spondylolisthesis.
D) scoliokyphosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the central-ray angulation for the AP projection of the dens, Fuchs method?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 15 degrees cephalad
D) 20 degrees cephalad
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 15 degrees cephalad
D) 20 degrees cephalad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The phase of respiration for a hyperflexion or hyperextension lateral cervical spine is:
A) shallow breathing.
B) suspended respiration.
C) full expiration.
D) full inspiration.
A) shallow breathing.
B) suspended respiration.
C) full expiration.
D) full inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Where is the central ray directed for the AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Where is the IR centered for a lateral cervical spine (Grandy method)?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the recommended SID for the AP axial oblique projection of the cervical spine?
A) 40 inches
B) 48 inches
C) 54 inches
D) 60 to 72 inches
A) 40 inches
B) 48 inches
C) 54 inches
D) 60 to 72 inches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is placed perpendicular to the tabletop for the AP axial cervical vertebrae?
A) Glabellomeatal line
B) Orbitomeatal line
C) Acanthiomeatal line
D) The occlusal plane
A) Glabellomeatal line
B) Orbitomeatal line
C) Acanthiomeatal line
D) The occlusal plane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the recommended SID for the lateral cervical spine (Grandy method)?
A) 40 inches
B) 48 inches
C) 40 to 55 inches
D) 60 to 72 inches
A) 40 inches
B) 48 inches
C) 40 to 55 inches
D) 60 to 72 inches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The central-ray angle for an AP axial of cervical vertebrae is:
A) 10 degrees cephalad.
B) 20 degrees cephalad.
C) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad.
D) variable, depending on the body habitus.
A) 10 degrees cephalad.
B) 20 degrees cephalad.
C) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad.
D) variable, depending on the body habitus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is the central-ray angle for the AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) 15 degrees cephalad
B) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
C) 15 to 20 degrees caudad
D) Perpendicular
A) 15 degrees cephalad
B) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
C) 15 to 20 degrees caudad
D) Perpendicular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The intervertebral foramina of the cervical spine are demonstrated on which of the following projections?
1)AP axial
2)AP axial oblique
3)PA axial oblique
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)AP axial
2)AP axial oblique
3)PA axial oblique
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How are small weights applied to the arms for the lateral projection of the cervical spine (Grandy method)?
A) Affixed to the elbows
B) Affixed to the wrists
C) Held in the hands
D) Held by the fingers
A) Affixed to the elbows
B) Affixed to the wrists
C) Held in the hands
D) Held by the fingers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which projection of the cervical spine will demonstrate the lower five zygapophyseal joints of the cervical spine?
1)Lateral
2)Lateral in hyperflexion
3)Lateral in hyperextension
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Lateral
2)Lateral in hyperflexion
3)Lateral in hyperextension
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Where is the IR centered for a hyperflexion or hyperextension lateral projection of the cervical spine?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which intervertebral foramina are demonstrated on an AP axial oblique projection of the cervical spine?
A) Those farthest from the IR
B) Those closest to the IR
C) Both sides equally demonstrated
D) The inferior six closest to the IR
A) Those farthest from the IR
B) Those closest to the IR
C) Both sides equally demonstrated
D) The inferior six closest to the IR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Where is the central ray centered for a hyperflexion or hyperextension lateral cervical spine?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Where is the IR centered for an AP axial cervical spine?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How much is the body rotated for an AP axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) 45 degrees
B) 60 degrees
C) 70 degrees
D) 40 to 60 degrees
A) 45 degrees
B) 60 degrees
C) 70 degrees
D) 40 to 60 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How much is the body rotated for a PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) 30 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 50 degrees
D) 60 degrees
A) 30 degrees
B) 45 degrees
C) 50 degrees
D) 60 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The Grandy method is a(n):
A) lateral projection of the cervical vertebrae.
B) lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region.
C) AP/PA thoracolumbar spine.
D) lateral thoracolumbar spine.
A) lateral projection of the cervical vertebrae.
B) lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region.
C) AP/PA thoracolumbar spine.
D) lateral thoracolumbar spine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Where is the central ray directed for a lateral cervical spine?
A) Third cervical vertebra
B) Fourth cervical vertebra
C) Fifth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Third cervical vertebra
B) Fourth cervical vertebra
C) Fifth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The respiration phase for a lateral cervical spine is:
A) full expiration.
B) full inspiration.
C) suspended respiration.
D) softly phonate "ah" during the exposure.
A) full expiration.
B) full inspiration.
C) suspended respiration.
D) softly phonate "ah" during the exposure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Where is the central ray directed for the lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region (swimmer's technique)?
A) C4
B) C5
C) C6-C7 interspace
D) C7-T1 interspace
A) C4
B) C5
C) C6-C7 interspace
D) C7-T1 interspace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following should be performed to place the back in contact with the table for an AP thoracic spine?
1)Flex the hips.
2)Flex the knees.
3)Flex the cervical spine.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
1)Flex the hips.
2)Flex the knees.
3)Flex the cervical spine.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The respiration phase for an AP or PA axial oblique projection of the cervical spine is:
A) shallow breathing.
B) suspended respiration.
C) full inspiration.
D) full expiration.
A) shallow breathing.
B) suspended respiration.
C) full inspiration.
D) full expiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How is the neck positioned for the AP axial projection of the vertebral arch (pillars)?
A) With the occlusal plane perpendicular to the image receptor
B) With the occlusal plane parallel to the image receptor
C) In hyperextension
D) In hyperflexion
A) With the occlusal plane perpendicular to the image receptor
B) With the occlusal plane parallel to the image receptor
C) In hyperextension
D) In hyperflexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the central-ray angulation for the lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region (swimmer's technique) when the shoulder can be depressed?
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 10 degrees caudad
D) 15 degrees caudad
A) 0 degrees
B) 5 degrees caudad
C) 10 degrees caudad
D) 15 degrees caudad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The swimmer's technique demonstrates the cervicothoracic region in which projection?
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP axial
D) AP axial oblique
A) AP
B) Lateral
C) AP axial
D) AP axial oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which intervertebral foramina are demonstrated on the PA axial oblique projection of the cervical spine?
A) Those closest to the IR
B) Those farthest from the IR
C) Both sides are equally demonstrated
D) The inferior side farthest from the IR
A) Those closest to the IR
B) Those farthest from the IR
C) Both sides are equally demonstrated
D) The inferior side farthest from the IR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Where does the central ray exit for the AP axial oblique projection to demonstrate the cervical spine pillars and laminae?
A) C4
B) C5
C) C7
D) T2
A) C4
B) C5
C) C7
D) T2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Where is the IR centered for the lateral projection of the cervicothoracic region (swimmer's technique)?
A) C5
B) C6
C) C6-C7 interspace
D) C7-T1 interspace
A) C5
B) C6
C) C6-C7 interspace
D) C7-T1 interspace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the central-ray angle for the PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) 45 degrees cephalad
B) 45 degrees caudad
C) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
D) 15 to 20 degrees caudad
A) 45 degrees cephalad
B) 45 degrees caudad
C) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
D) 15 to 20 degrees caudad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following methods uses a chewing motion of the mandible to demonstrate the cervical spine in an AP projection?
A) Ottonello
B) Grandy
C) Twining
D) Fuchs
A) Ottonello
B) Grandy
C) Twining
D) Fuchs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Where should the superior edge of the IR/collimated field be placed for an AP projection of the thoracic vertebrae?
A) 1 inch above the shoulders
B) 1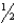 to 2 inches above the shoulders
to 2 inches above the shoulders
C) 1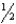 to 2 inches below the shoulders
to 2 inches below the shoulders
D) At the level of the shoulders
A) 1 inch above the shoulders
B) 1
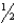 to 2 inches above the shoulders
to 2 inches above the shouldersC) 1
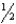 to 2 inches below the shoulders
to 2 inches below the shouldersD) At the level of the shoulders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What is the central-ray angulation for an AP axial oblique projection of the cervical spine on a trauma patient?
A) 15 to 20 degrees caudad
B) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
C) 30 to 40 degrees caudad
D) 30 to 40 degrees cephalad
A) 15 to 20 degrees caudad
B) 15 to 20 degrees cephalad
C) 30 to 40 degrees caudad
D) 30 to 40 degrees cephalad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which projection is recommended to demonstrate the cervical vertebral arches or pillars when the patient cannot hyperextend the neck?
A) AP axial
B) PA axial
C) AP axial oblique with right and left head rotation
D) Lateral projection, dorsal decubitus position
A) AP axial
B) PA axial
C) AP axial oblique with right and left head rotation
D) Lateral projection, dorsal decubitus position

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For the cervicothoracic region lateral projection (swimmer's technique), the recommended position of the humeral head closest to the IR is move
A) anteriorly.
B) posteriorly.
C) medially.
D) laterally.
A) anteriorly.
B) posteriorly.
C) medially.
D) laterally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Where is the central ray directed for a PA axial oblique projection of the cervical intervertebral foramina?
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra
A) Second cervical vertebra
B) Third cervical vertebra
C) Fourth cervical vertebra
D) Seventh cervical vertebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When the shoulder is immobile and cannot be depressed sufficiently for the cervicothoracic region lateral projection (swimmer's technique), the central ray is angled:
A) 10 to 20 degrees cephalad.
B) 10 to 20 degrees caudad.
C) 3 to 5 degrees caudad.
D) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad.
A) 10 to 20 degrees cephalad.
B) 10 to 20 degrees caudad.
C) 3 to 5 degrees caudad.
D) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The swimmer's technique lateral projection is performed to demonstrate the:
A) cervical vertebrae.
B) thoracic vertebrae.
C) atlas and axis.
D) cervicothoracic vertebrae.
A) cervical vertebrae.
B) thoracic vertebrae.
C) atlas and axis.
D) cervicothoracic vertebrae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following will demonstrate the cervicothoracic region in the lateral projection?
A) Ottonello method
B) Swimmer's technique
C) Ferguson method
D) Fuchs method
A) Ottonello method
B) Swimmer's technique
C) Ferguson method
D) Fuchs method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the central-ray angle for an AP thoracic spine?
A) 3 to 5 degrees caudad
B) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad
C) 5 to 7 degrees caudad
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad
A) 3 to 5 degrees caudad
B) 3 to 5 degrees cephalad
C) 5 to 7 degrees caudad
D) 5 to 7 degrees cephalad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 175 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



