Deck 7: The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/81
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes, Mechanisms, and Control
1
How do each of these compounds affect the function of ATCase?
A) ATP inhibits and CTP activates
B) ATP activates and CTP inhibits
C) Both ATP and CTP inhibit
D) Both ATP and CTP activate
E) none of these is true
A) ATP inhibits and CTP activates
B) ATP activates and CTP inhibits
C) Both ATP and CTP inhibit
D) Both ATP and CTP activate
E) none of these is true
B
2
Which of the following is a mechanism of regulating enzyme activity?
A) Feedback inhibition by product.
B) Addition or removal of phosphate groups from of the enzyme.
C) Presence of activators.
D) Activation of zymogens.
E) All of these regulate enzyme activity.
A) Feedback inhibition by product.
B) Addition or removal of phosphate groups from of the enzyme.
C) Presence of activators.
D) Activation of zymogens.
E) All of these regulate enzyme activity.
E
3
Which of the following best describes negative cooperativity?
A) Binding of one substrate molecule prevents the enzyme from working at all.
B) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of a second substrate.
C) Binding of one substrate molecule enhances the binding of a second substrate.
D) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of other effectors.
A) Binding of one substrate molecule prevents the enzyme from working at all.
B) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of a second substrate.
C) Binding of one substrate molecule enhances the binding of a second substrate.
D) Binding of one substrate molecule inhibits the binding of other effectors.
B
4
ATP is a negative allosteric effector for glycogen phosporylase. This is an example of
A) feedback inhibition.
B) positive cooperativity.
C) negative cooperativity.
D) competitive inhibition.
A) feedback inhibition.
B) positive cooperativity.
C) negative cooperativity.
D) competitive inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A velocity curve (V vs. [S]) for a typical allosteric enzyme will be
A) a rectangular hyperbola.
B) a sigmoid curve.
C) a straight line.
D) a parabola.
E) none of these
A) a rectangular hyperbola.
B) a sigmoid curve.
C) a straight line.
D) a parabola.
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Homotrophic effects for allosteric enzymes involve
A) the same molecule binding to different sites in the enzyme.
B) different molecules binding to the same site in an enzyme.
C) different molecules binding to different sites in the same enzyme.
D) All of these are homotrophic effects.
A) the same molecule binding to different sites in the enzyme.
B) different molecules binding to the same site in an enzyme.
C) different molecules binding to different sites in the same enzyme.
D) All of these are homotrophic effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
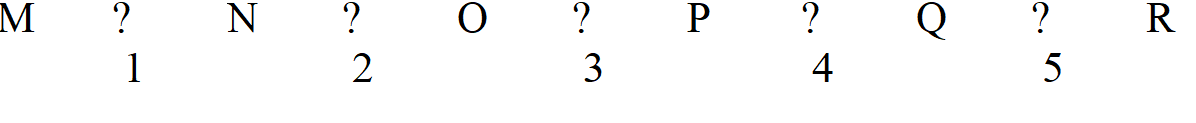
-Refer to Exhibit 7A. Which two enzymes would be the most likely ones to regulate if this pathway is dedicated to the formation of only one product?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 5
D) 2 and 4
E) 4 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Is the Michaelis-Menten equation useful when studying allosteric enzymes?
A) Yes
B) No
C) Only if the enzyme displays positive cooperativity.
D) Only if the enzyme displays negative cooperativity.
A) Yes
B) No
C) Only if the enzyme displays positive cooperativity.
D) Only if the enzyme displays negative cooperativity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Enzyme kinetics falls into two general categories, simple saturation and cooperative kinetics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How do each of these compounds affect the function of ATCase?
A) ATP is a K effector and CTP is a V effector.
B) ATP is a V effector and CTP is a K effector.
C) Both ATP and CTP are K effectors.
D) Both ATP and CTP are V effectors.
E) none of these
A) ATP is a K effector and CTP is a V effector.
B) ATP is a V effector and CTP is a K effector.
C) Both ATP and CTP are K effectors.
D) Both ATP and CTP are V effectors.
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The saturation curve for aspartyl transcarbamylase has a similar shape to the curve for:
A) Myoglobin
B) Hemoglobin
C) Chymotrypsin
D) Both hemoglobin and chymotrypsin.
E) All of these.
A) Myoglobin
B) Hemoglobin
C) Chymotrypsin
D) Both hemoglobin and chymotrypsin.
E) All of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
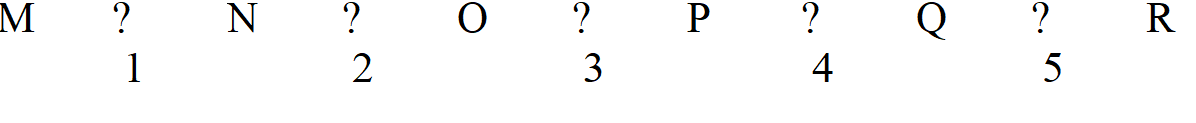
-Refer to Exhibit 7A. The final product, R, will most likely inhibit which reaction?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In a comparison of allosteric and non-allosteric enzymes
A) it is always possible to define a KM
B) it is always possible to define a Vmax
C) competitive inhibition is always a possibility
D) much of the terminology is completely unchanged
A) it is always possible to define a KM
B) it is always possible to define a Vmax
C) competitive inhibition is always a possibility
D) much of the terminology is completely unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is true?
A) Allosteric enzymes are rarely important in the regulation of metabolic pathways.
B) Michaelis-Menten kinetics describe the reactions of allosteric enzymes
C) Allosteric enzymes have a hyperbolic plot of reaction rate vs. substrate concentration
D) none of these is true
A) Allosteric enzymes are rarely important in the regulation of metabolic pathways.
B) Michaelis-Menten kinetics describe the reactions of allosteric enzymes
C) Allosteric enzymes have a hyperbolic plot of reaction rate vs. substrate concentration
D) none of these is true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The term K0.5 is analogous to the KM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In reactions catalyzed by allosteric enzymes
A) substrate, activators, and inhibitors all compete for the same binding site on the enzyme.
B) there is no distinction between catalytic and regulatory subunits.
C) the presence of an activator makes the plot of reaction rate against substrate concentration less cooperative.
D) the presence of an inhibitor makes the plot of reaction rate against substrate concentration less cooperative.
A) substrate, activators, and inhibitors all compete for the same binding site on the enzyme.
B) there is no distinction between catalytic and regulatory subunits.
C) the presence of an activator makes the plot of reaction rate against substrate concentration less cooperative.
D) the presence of an inhibitor makes the plot of reaction rate against substrate concentration less cooperative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is NOT required in order for an enzyme to display cooperative kinetics?
A) Multiple subunits.
B) A value for the Michaelis constant, KM.
C) Allosteric sites which affect the binding of substrate to the active site.
D) Ability to display a Vmax.
E) All of these are characteristic of cooperative enzymes.
A) Multiple subunits.
B) A value for the Michaelis constant, KM.
C) Allosteric sites which affect the binding of substrate to the active site.
D) Ability to display a Vmax.
E) All of these are characteristic of cooperative enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Where do allosteric inhibitors bind on an enzyme?
A) They always bind at a site different from the active site.
B) They always bind at the active site.
C) They can bind at either active site or another site.
D) They always bind directly to the substrate
E) none of these
A) They always bind at a site different from the active site.
B) They always bind at the active site.
C) They can bind at either active site or another site.
D) They always bind directly to the substrate
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
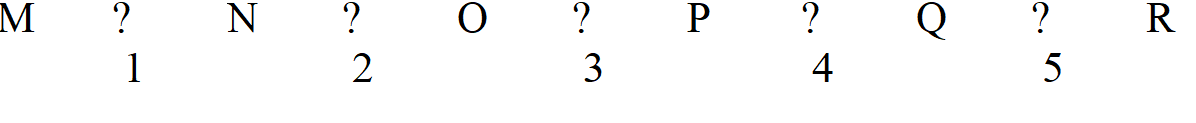
-Refer to Exhibit 7A. Which two enzymes would be the most likely ones to regulate if this pathway is freely reversible and can go both ways?
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 1 and 5
D) 2 and 4
E) 4 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
CTP is a known inhibitor of ATCase, the enzyme that catalyzes the first reaction in the pathway for the synthesis of this compound. This is an example of
A) irreversible inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) zymogenic inhibition
D) negative cooperativity
A) irreversible inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) zymogenic inhibition
D) negative cooperativity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What happens when a K-acting inhibitor is added to an allosteric enzyme system?
A) The apparent KM for the substrate increases.
B) The apparent KM for the substrate decreases.
C) The apparent Vmax for the substrate increases.
D) The apparent Vmax for the substrate decreases.
A) The apparent KM for the substrate increases.
B) The apparent KM for the substrate decreases.
C) The apparent Vmax for the substrate increases.
D) The apparent Vmax for the substrate decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The concerted and sequential models for the behavior of allosteric enzymes differ in
A) the conformational change in the enzyme in one model and not in the other.
B) the number of predicted binding sites on the enzyme.
C) the manner in which changes in quaternary structure take place.
D) the response of the enzyme to changes in temperature.
A) the conformational change in the enzyme in one model and not in the other.
B) the number of predicted binding sites on the enzyme.
C) the manner in which changes in quaternary structure take place.
D) the response of the enzyme to changes in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
According to the concerted model of allosteric behavior, an allosteric activator
A) favors the taut (tight) form of the enzyme.
B) favors the relaxed form of the enzyme.
C) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate is already bound.
D) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate has not already bound.
A) favors the taut (tight) form of the enzyme.
B) favors the relaxed form of the enzyme.
C) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate is already bound.
D) can only bind to the enzyme if the substrate has not already bound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the concerted model the most active enzyme form will be when
A) all subunits are in the R state.
B) all subunits are in the T state.
C) there is a 50:50 mix of R & T states.
D) none of these
A) all subunits are in the R state.
B) all subunits are in the T state.
C) there is a 50:50 mix of R & T states.
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The sequential model for allosteric enzymes was proposed by:
A) Koshland
B) Pauling
C) Pasteur
D) Monod, Wyman and Changeux
E) All of these
A) Koshland
B) Pauling
C) Pasteur
D) Monod, Wyman and Changeux
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is an advantage of an allosteric drug compared to an orthosteric one?
A) they can modulate their effect in a more subtle way
B) an allosteric drug may be more specific for a specific reaction than one that binds to the receptor itself
C) they may be safer as they have no effect at all unless the natural substrate is present
D) all of these are advantages
E) none of these is an advantage
A) they can modulate their effect in a more subtle way
B) an allosteric drug may be more specific for a specific reaction than one that binds to the receptor itself
C) they may be safer as they have no effect at all unless the natural substrate is present
D) all of these are advantages
E) none of these is an advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The main distinguishing feature of the concerted model for the behavior of allosteric enzymes is that
A) the conformation of all subunits changes simultaneously.
B) it applies only to dimeric enzymes.
C) it involves three possible conformations for all subunits.
D) the T and R conformations exist in roughly equal amounts.
A) the conformation of all subunits changes simultaneously.
B) it applies only to dimeric enzymes.
C) it involves three possible conformations for all subunits.
D) the T and R conformations exist in roughly equal amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The concerted model for allosteric behavior was proposed by:
A) Koshland
B) Pauling
C) Pasteur
D) Monod, Wyman and Changeux
E) All of these
A) Koshland
B) Pauling
C) Pasteur
D) Monod, Wyman and Changeux
E) All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the concerted model, which state binds the substrate more tightly?
A) the relaxed (R) state
B) the taut (T) state
C) Both states bind equally well.
A) the relaxed (R) state
B) the taut (T) state
C) Both states bind equally well.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The behavior of allosteric enzymes
A) does not play any role in feedback inhibition in metabolic pathways
B) is strongly dependent on the presence of metal ions
C) is related to their ability to hydrolyze themselves
D) depends on changes in their quaternary structure on binding of substrates or inhibitors
A) does not play any role in feedback inhibition in metabolic pathways
B) is strongly dependent on the presence of metal ions
C) is related to their ability to hydrolyze themselves
D) depends on changes in their quaternary structure on binding of substrates or inhibitors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The sequential model for allosteric behavior
A) cannot account for reactions that display negative cooperativity.
B) postulates binding of substrates and inhibitors by the induced-fit model.
C) requires that the conformation of all subunits change simultaneously.
D) is mathematically simpler than the concerted model.
A) cannot account for reactions that display negative cooperativity.
B) postulates binding of substrates and inhibitors by the induced-fit model.
C) requires that the conformation of all subunits change simultaneously.
D) is mathematically simpler than the concerted model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Kinase reactions describe enzymes which
A) add phosphate groups to another molecule.
B) oxidize alcohols to aldehydes.
C) use NAD+/NADH in their reactions.
D) transfer groups from one part of a molecule to another.
E) add or remove double bonds in molecules.
A) add phosphate groups to another molecule.
B) oxidize alcohols to aldehydes.
C) use NAD+/NADH in their reactions.
D) transfer groups from one part of a molecule to another.
E) add or remove double bonds in molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The binding of aspartate to different subunits of ATCase is an example of
A) enzyme inhibition
B) a heterotropic effect
C) a homotropic effect
D) negative cooperativity
E) none of these
A) enzyme inhibition
B) a heterotropic effect
C) a homotropic effect
D) negative cooperativity
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is not a difference between the concerted model and the sequential model of allosteric enzymes?
A) The sequential model allows for different subunits to be in different conformations while the concerted model does not
B) Negative cooperativity can be explained by the sequential model but not by the concerted model
C) Positive cooperativity can be explained by the sequential model but not by the concerted model
D) The sequential model is explained better by considering the induced-fit model of substrate binding, whereas the concerted model focuses on perturbing the equilibrium between the T and R forms.
A) The sequential model allows for different subunits to be in different conformations while the concerted model does not
B) Negative cooperativity can be explained by the sequential model but not by the concerted model
C) Positive cooperativity can be explained by the sequential model but not by the concerted model
D) The sequential model is explained better by considering the induced-fit model of substrate binding, whereas the concerted model focuses on perturbing the equilibrium between the T and R forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following does not apply to the concerted model for subunit behavior:
A) Each subunit can exist in a relaxed (R) and taut (T) conformation.
B) All subunits will be in either the R or the T conformation at the same time.
C) Some subunits can be in the R state while others are in the T state.
D) The presence of inhibitors will lead to more of the enzyme being in the T form
E) the presence of activators will lead to more of the enzyme being in the R form
A) Each subunit can exist in a relaxed (R) and taut (T) conformation.
B) All subunits will be in either the R or the T conformation at the same time.
C) Some subunits can be in the R state while others are in the T state.
D) The presence of inhibitors will lead to more of the enzyme being in the T form
E) the presence of activators will lead to more of the enzyme being in the R form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the concerted model for allosteric enzymes, if the taut form of the enzyme cannot bind substrate then
A) KT < KR
B) L = R/T
C) c = 0
D) an inhibitor must be present
E) none of these
A) KT < KR
B) L = R/T
C) c = 0
D) an inhibitor must be present
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Allosteric enzymes must exhibit which of the following?
A) feedback inhibition
B) a phosphorylation site
C) general acid-base catalysis
D) a quaternary structure
E) none of these must be exhibited
A) feedback inhibition
B) a phosphorylation site
C) general acid-base catalysis
D) a quaternary structure
E) none of these must be exhibited

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Many metabolic pathways involve multistep reactions. Consider the following pathway. 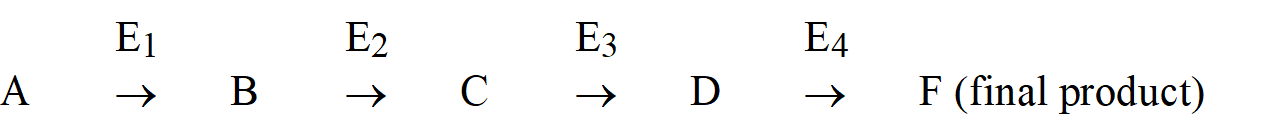
Which of the following would be an example of feedback inhibition?
A) the product of the final reaction, F, interacting with E1.
B) F interacting with an allosteric site in E4.
C) B interacting with an allosteric site in E1.
D) all of the intermediates or products in the reaction interacting with the active site in E1.
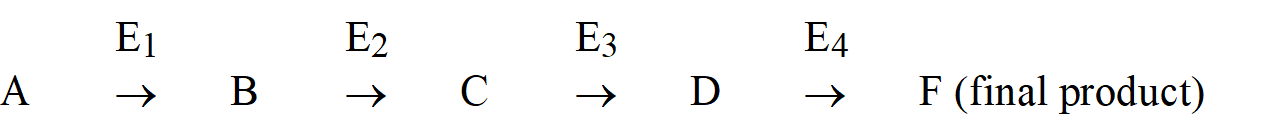
Which of the following would be an example of feedback inhibition?
A) the product of the final reaction, F, interacting with E1.
B) F interacting with an allosteric site in E4.
C) B interacting with an allosteric site in E1.
D) all of the intermediates or products in the reaction interacting with the active site in E1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In the concerted model for allosteric enzymes
A) the relative affinities of substrate for the T and R conformations plays an important role in the cooperativity of the reaction.
B) the equilibrium between the T and R conformations plays a minor role.
C) the enzymatic activity of the T conformation is considerably higher than that of the R form.
D) it is possible to describe the reactions of all allosteric enzymes accurately.
A) the relative affinities of substrate for the T and R conformations plays an important role in the cooperativity of the reaction.
B) the equilibrium between the T and R conformations plays a minor role.
C) the enzymatic activity of the T conformation is considerably higher than that of the R form.
D) it is possible to describe the reactions of all allosteric enzymes accurately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In the concerted model the binding of the first substrate molecule will achieve all except
A) facilitation of the binding of other substrate molecules.
B) facilitation of the conversion of other subunits to the active state.
C) facilitation of the binding of inhibitors to the enzyme.
D) All of these are facilitated by the binding of the first substrate molecule.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) facilitation of the binding of other substrate molecules.
B) facilitation of the conversion of other subunits to the active state.
C) facilitation of the binding of inhibitors to the enzyme.
D) All of these are facilitated by the binding of the first substrate molecule.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In zymogen activation
A) only digestive enzymes are involved.
B) a conformational change takes place with no alteration of primary structure.
C) an inactive protein is converted to an active one by bond cleavage.
D) there is aggregation of several enzyme molecules when the substrate binds.
A) only digestive enzymes are involved.
B) a conformational change takes place with no alteration of primary structure.
C) an inactive protein is converted to an active one by bond cleavage.
D) there is aggregation of several enzyme molecules when the substrate binds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Phosphorylation and allosteric control of enzymes.
A) are not involved in reactions of carbohydrates.
B) play an insignificant role in generating energy.
C) are important processes in prokaryotes, but not in eukaryotes.
D) can be combined to afford a high degree of control over enzymatic reactions.
E) none of these
A) are not involved in reactions of carbohydrates.
B) play an insignificant role in generating energy.
C) are important processes in prokaryotes, but not in eukaryotes.
D) can be combined to afford a high degree of control over enzymatic reactions.
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Kinases usually transfer phosphates from
A) ATP.
B) inorganic phosphate.
C) NADP+/NADPH.
D) amino acids.
A) ATP.
B) inorganic phosphate.
C) NADP+/NADPH.
D) amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following types of amino acids in an active site is least likely to be involved in enzyme catalysis?
A) Those with hydrophilic, neutral side-chains.
B) Those with negatively charged side-chains.
C) Those with positively charge side-chains.
D) Those with hydrocarbon side-chains.
A) Those with hydrophilic, neutral side-chains.
B) Those with negatively charged side-chains.
C) Those with positively charge side-chains.
D) Those with hydrocarbon side-chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is true about salicylate?
A) it is a natural compound from the bark of a tree
B) it is structurally similar to aspirin
C) it stimulates the protein kinase, AMPK
D) it has therapeutic effects in lowering the risk of heart disease
E) all of these
A) it is a natural compound from the bark of a tree
B) it is structurally similar to aspirin
C) it stimulates the protein kinase, AMPK
D) it has therapeutic effects in lowering the risk of heart disease
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The initial bond formation in the covalent intermediate in the reaction catalyzed by chymotrypsin is between
A) serine and the carbonyl carbon in the peptide backbone
B) serine and the nitrogen in the peptide backbone
C) histidine and the carbonyl carbon in the peptide backbone
D) histidine and the nitrogen in the peptide backbone
A) serine and the carbonyl carbon in the peptide backbone
B) serine and the nitrogen in the peptide backbone
C) histidine and the carbonyl carbon in the peptide backbone
D) histidine and the nitrogen in the peptide backbone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which groups of amino acids are most likely to be found in the active site of an enzyme?
A) leucine, lysine, alanine.
B) cysteine, isoleucine, phenylalanine.
C) tyrosine, threonine, leucine.
D) serine, histidine, aspartate.
A) leucine, lysine, alanine.
B) cysteine, isoleucine, phenylalanine.
C) tyrosine, threonine, leucine.
D) serine, histidine, aspartate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Generally speaking, enzymes involved in pathways which generate ATP will be activated by addition of phosphate groups to the enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following enzymes is not a serine protease?
A) trypsin
B) chymotrypsin
C) thrombin
D) aspartyl transcarbamylase (ATCase)
A) trypsin
B) chymotrypsin
C) thrombin
D) aspartyl transcarbamylase (ATCase)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An important step in elucidating the behavior of an enzyme is
A) obtaining a crystalline sample of the enzyme.
B) insuring that metal ions are always excluded from the enzyme sample.
C) determining the active site residues.
D) none of these
A) obtaining a crystalline sample of the enzyme.
B) insuring that metal ions are always excluded from the enzyme sample.
C) determining the active site residues.
D) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is true about caspases?
A) they are a class of proteases
B) they are involved in apoptosis
C) they are initially produced as inactive procaspases
D) once activated, they attach specific targets leading to cell death
E) all of these
A) they are a class of proteases
B) they are involved in apoptosis
C) they are initially produced as inactive procaspases
D) once activated, they attach specific targets leading to cell death
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The active site of chymotrypsin contains all of the following, except:
A) Histidine residue.
B) A magnesium ion.
C) Hydrophobic pocket to bind the substrate.
D) Serine residue.
E) All of these are in the active site of chymotrypsin.
A) Histidine residue.
B) A magnesium ion.
C) Hydrophobic pocket to bind the substrate.
D) Serine residue.
E) All of these are in the active site of chymotrypsin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The pH profile of an enzyme can help identify specific amino acids in the active site because:
A) all enzymes have a pH optimum
B) only the active site amino acids can detect changes in pH
C) acidic and basic amino acids are often involved in the active site and pH changes can change their ability to catalyze a reaction
D) the pH optimum is always the pI of the most critical amino acid in the active site
A) all enzymes have a pH optimum
B) only the active site amino acids can detect changes in pH
C) acidic and basic amino acids are often involved in the active site and pH changes can change their ability to catalyze a reaction
D) the pH optimum is always the pI of the most critical amino acid in the active site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The amino acids in the active site can be involved in all of these processes, except:
A) Binding of the substrate.
B) Becoming part of the product of the reaction.
C) The actual chemical mechanism for the reaction.
D) Binding of some necessary cofactor for the reaction.
E) All of these can be functions of the amino acids in the active site
A) Binding of the substrate.
B) Becoming part of the product of the reaction.
C) The actual chemical mechanism for the reaction.
D) Binding of some necessary cofactor for the reaction.
E) All of these can be functions of the amino acids in the active site

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Phosphorylation of enzymes
A) has no effect on their catalytic activity.
B) does not require ATP.
C) usually takes place on serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues.
D) always increases the activity of the enzyme
A) has no effect on their catalytic activity.
B) does not require ATP.
C) usually takes place on serine, threonine, and tyrosine residues.
D) always increases the activity of the enzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Labeling the amino acid residues in the active site of an enzyme requires
A) a reagent structurally similar to the substrate.
B) a highly polar reagent.
C) a reagent that contains an aromatic group.
D) a reagent that contains a halogen atom.
A) a reagent structurally similar to the substrate.
B) a highly polar reagent.
C) a reagent that contains an aromatic group.
D) a reagent that contains a halogen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Inhibitors which bind covalently to specific amino acids are useful in determining which amino acids are in the active site of an enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The critical serine residue in the active site of chymotrypsin functions as
A) a nucleophile.
B) an electrophile.
C) a base.
D) a methyl donor.
E) none of these
A) a nucleophile.
B) an electrophile.
C) a base.
D) a methyl donor.
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Zymogens are
A) inactive precursors of enzymes which can be activated by the irreversible cleavage of covalent bonds.
B) inactive forms of enzymes which require phosphorylation by a kinase to become active.
C) allosteric enzymes that are always in the R state.
D) allosteric enzymes that are always in the T state.
A) inactive precursors of enzymes which can be activated by the irreversible cleavage of covalent bonds.
B) inactive forms of enzymes which require phosphorylation by a kinase to become active.
C) allosteric enzymes that are always in the R state.
D) allosteric enzymes that are always in the T state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is true?
A) Phosphorylation always increases enzyme activity
B) Kinases often use AMP as a co-substrate in their phosphorylation reactions
C) Some enzymes are activated by phosphorylation while others are inhibited
D) ADP is the most common substrate for a kinase reaction
A) Phosphorylation always increases enzyme activity
B) Kinases often use AMP as a co-substrate in their phosphorylation reactions
C) Some enzymes are activated by phosphorylation while others are inhibited
D) ADP is the most common substrate for a kinase reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following can function as coenzymes?
A) lead ion, biotin, and lipoic acid.
B) copper ion, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, diisopropylphophofluoridate.
C) zinc ion, pyridoxal phosphate, and nicotinamide adenine nucleotides.
D) lead ion, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, diisopropylphophofluoridate.
A) lead ion, biotin, and lipoic acid.
B) copper ion, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, diisopropylphophofluoridate.
C) zinc ion, pyridoxal phosphate, and nicotinamide adenine nucleotides.
D) lead ion, p-hydroxymercuribenzoate, diisopropylphophofluoridate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Pyridoxal phosphate is required for transfer of
A) one-carbon groups
B) amino groups
C) acyl groups
D) aldehyde groups
A) one-carbon groups
B) amino groups
C) acyl groups
D) aldehyde groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The vitamin pantothenic acid is involved in this type of reaction:
A) Carboxylation reactions
B) Decarboxylation reactions
C) Redox reactions
D) Acyl transfer reactions
E) Transamination reactions
A) Carboxylation reactions
B) Decarboxylation reactions
C) Redox reactions
D) Acyl transfer reactions
E) Transamination reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A transition-state analog is likely to bind to an enzyme
A) more tightly than the substrate.
B) less tightly than the substrate.
C) about as tightly as the substrate.
D) at a site other than the catalytic site.
A) more tightly than the substrate.
B) less tightly than the substrate.
C) about as tightly as the substrate.
D) at a site other than the catalytic site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Metal ions play an important role in reaction mechanisms because
A) they block the active site of enzymes so that inhibitors cannot bind.
B) they can act as Lewis acids.
C) water is excluded from the active site when metal ions are bound.
D) they prevent protein aggregation.
A) they block the active site of enzymes so that inhibitors cannot bind.
B) they can act as Lewis acids.
C) water is excluded from the active site when metal ions are bound.
D) they prevent protein aggregation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is unlikely to occur in binding of a substrate to an enzyme?
A) stereospecific interactions.
B) hydrogen bonding.
C) adsorption to surfaces of metallic catalysts.
D) interactions with metal-ions.
A) stereospecific interactions.
B) hydrogen bonding.
C) adsorption to surfaces of metallic catalysts.
D) interactions with metal-ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is true about cocaine addiction
A) it is easy to treat by using a drug that blocks a neurotransmitter receptor
B) it is based on release of the neurotransmitter GABA
C) it can be treated with catalytic antibodies
D) catalytic antibodies against coacaine are designed to mimic the cocaine molecule itself
E) none of these
A) it is easy to treat by using a drug that blocks a neurotransmitter receptor
B) it is based on release of the neurotransmitter GABA
C) it can be treated with catalytic antibodies
D) catalytic antibodies against coacaine are designed to mimic the cocaine molecule itself
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
B vitamins are often stored in the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Important mechanisms of enzymatic catalysis include
A) nucleophilic reactions
B) general acid-base catalysis
C) Lewis acid-base catalysis
D) all of these
A) nucleophilic reactions
B) general acid-base catalysis
C) Lewis acid-base catalysis
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Cofactors are
A) non-protein in chemical nature.
B) always small proteins.
C) modified amino acids.
D) never required for enzymatic activity.
A) non-protein in chemical nature.
B) always small proteins.
C) modified amino acids.
D) never required for enzymatic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The serine in the active site of chymotrypsin functions as
A) a Lewis acid.
B) a metal ion.
C) an electrophile.
D) a nucleophile.
A) a Lewis acid.
B) a metal ion.
C) an electrophile.
D) a nucleophile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements about coenzymes is true?
A) They are commonly derived from vitamins.
B) They bind to the active site region on specific types of enzymes.
C) They can be metal ions, such as Zn(II).
D) NAD+, FAD and biotin are all examples of coenzymes.
E) All of these statements are true.
A) They are commonly derived from vitamins.
B) They bind to the active site region on specific types of enzymes.
C) They can be metal ions, such as Zn(II).
D) NAD+, FAD and biotin are all examples of coenzymes.
E) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Redox reactions often use this cofactor:
A) Riboflavin
B) Lipoic acid
C) Pyridoxal
D) Thiamine
E) Biotin
A) Riboflavin
B) Lipoic acid
C) Pyridoxal
D) Thiamine
E) Biotin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is
A) an enzyme inhibitor used in smoking cessation programs.
B) an inhibitor of ATP production.
C) a coenzyme in reactions that transfer acyl groups.
D) a coenzyme in oxidation-reduction reactions.
A) an enzyme inhibitor used in smoking cessation programs.
B) an inhibitor of ATP production.
C) a coenzyme in reactions that transfer acyl groups.
D) a coenzyme in oxidation-reduction reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The vitamin biotin is involved in this type of reaction:
A) Carboxylation reactions
B) Decarboxylation reactions
C) Redox reactions
D) Acyl transfer reactions
E) Transamination reactions
A) Carboxylation reactions
B) Decarboxylation reactions
C) Redox reactions
D) Acyl transfer reactions
E) Transamination reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is not true about B vitamins?
A) They are usually fully active in the form we eat them
B) They are usually water soluble
C) Niacin and riboflavin are examples
D) They are important in many metabolic reactions
A) They are usually fully active in the form we eat them
B) They are usually water soluble
C) Niacin and riboflavin are examples
D) They are important in many metabolic reactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Enzymes that catalyze similar functions will invariably have
A) similar overall structures.
B) serine in their active sites.
C) histidine in their active sites.
D) active sites that can catalyze the reactions in question.
A) similar overall structures.
B) serine in their active sites.
C) histidine in their active sites.
D) active sites that can catalyze the reactions in question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Abzymes
A) invariably bind to pyridoxal phosphate.
B) are antibodies with catalytic activity.
C) differ markedly from transition states in enzymatic reactions.
D) have proline as part of their structure.
A) invariably bind to pyridoxal phosphate.
B) are antibodies with catalytic activity.
C) differ markedly from transition states in enzymatic reactions.
D) have proline as part of their structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How are cofactors bound to their enzymes?
A) always covalently
B) always non-covalently
C) either covalently or non-covalently
D) via linking with a metal ion
E) none of these
A) always covalently
B) always non-covalently
C) either covalently or non-covalently
D) via linking with a metal ion
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following amino acid side chains would best serve as a general acid, assuming the protein functions at a pH of 7?
A) alanine
B) aspartic acid
C) lysine
D) asparagine
A) alanine
B) aspartic acid
C) lysine
D) asparagine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 81 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



