Deck 12: Monetary Policy in the Short Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Monetary Policy in the Short Run
1
What is a liquidity crisis?
Banks and financial institutions are prone to liquidity problems because they borrow in the short term and use the funds to make long-term investments.Therefore,if a large number of depositors want to withdraw funds,a bank may have trouble meeting demands and face a liquidity crisis.If many depositors try to withdraw their funds at the same time,the result is a bank run that may cause the bank to fail.
2
With its goal of price stability,the Bank of Canada attempts to
A) keep the inflation rate from falling below 5% and rising above 10%.
B) maintain an inflation rate of zero.
C) achieve a low, stable inflation rate.
D) counteract periods of inflation with periods of deflation.
A) keep the inflation rate from falling below 5% and rising above 10%.
B) maintain an inflation rate of zero.
C) achieve a low, stable inflation rate.
D) counteract periods of inflation with periods of deflation.
C
3
Although initially a ________ institution,the Bank of Canada is now a ________ corporation.
A) private; public
B) private; Crown
C) Crown; private
D) public; private
A) private; public
B) private; Crown
C) Crown; private
D) public; private
B
4
The Board of Directors of the Bank of Canada consists of
A) 12 outside directors, the governor, the senior deputy governor, and a deputy minister of finance.
B) the governor, a deputy minister, and several CEOs of large commercial banks.
C) 8 outside directors.
D) CEOs of the largest 5 commercial banks in Canada.
A) 12 outside directors, the governor, the senior deputy governor, and a deputy minister of finance.
B) the governor, a deputy minister, and several CEOs of large commercial banks.
C) 8 outside directors.
D) CEOs of the largest 5 commercial banks in Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
________ institutions are banks and other financial institutions whose failure would lead to large disruptions in the economy.
A) Systematically important
B) Commercial
C) Corporate
D) Federal
A) Systematically important
B) Commercial
C) Corporate
D) Federal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Through open market operations,the Bank of Canada
A) controls the demand for reserves, but not the supply of reserves, in the banking system.
B) controls the supply of reserves and the demand for reserves in the banking system.
C) controls the supply of reserves, but not the demand for reserves, in the banking system.
D) has influence over, but cannot directly control, the supply of reserves and the demand for reserves in the banking system.
A) controls the demand for reserves, but not the supply of reserves, in the banking system.
B) controls the supply of reserves and the demand for reserves in the banking system.
C) controls the supply of reserves, but not the demand for reserves, in the banking system.
D) has influence over, but cannot directly control, the supply of reserves and the demand for reserves in the banking system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Briefly explain the primary goal of the Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Governing Council consists of
A) the board of directors and CEOs of the largest 5 commercial banks in Canada.
B) the board of directors and the chairman of the prime minister's council of economic advisors.
C) the chairman of the prime minister's council of economic advisors and 4 of the 12 directors who serve on a rotating basis.
D) the governor, senior deputy governor, and the four deputy governors.
A) the board of directors and CEOs of the largest 5 commercial banks in Canada.
B) the board of directors and the chairman of the prime minister's council of economic advisors.
C) the chairman of the prime minister's council of economic advisors and 4 of the 12 directors who serve on a rotating basis.
D) the governor, senior deputy governor, and the four deputy governors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why does the Bank of Canada attempt to achieve a low,stable rate of inflation rather than an inflation rate of 0%?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In Canada,the preferred target for the inflation rate is
A) 2%.
B) 0%.
C) 1%.
D) 3%.
A) 2%.
B) 0%.
C) 1%.
D) 3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The rate that financial institutions use to lend and borrow from each other at the end of the day is called the
A) discount rate.
B) overnight rate.
C) interbank rate.
D) bank rate.
A) discount rate.
B) overnight rate.
C) interbank rate.
D) bank rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The goal of the Bank of Canada is
A) a high foreign-exchange value of the dollar.
B) a high reserve ratio.
C) no inflation.
D) price stability.
A) a high foreign-exchange value of the dollar.
B) a high reserve ratio.
C) no inflation.
D) price stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Bank of Canada was created
A) to prevent bad loans by requiring banks to hold reserves.
B) to stimulate the economy in increasing bank reserves.
C) due to a recommendation by a royal commission that was created to analyze the lessons from the Great Depression.
D) to prevent inflation by decreasing the money supply.
A) to prevent bad loans by requiring banks to hold reserves.
B) to stimulate the economy in increasing bank reserves.
C) due to a recommendation by a royal commission that was created to analyze the lessons from the Great Depression.
D) to prevent inflation by decreasing the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The most important policy tool used by the Bank of Canada is
A) the target inflation rate.
B) the discount rate.
C) the required reserve rate.
D) the target for the overnight rate.
A) the target inflation rate.
B) the discount rate.
C) the required reserve rate.
D) the target for the overnight rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Bank of Canada conducts open market operations with the primary goal of
A) affecting the overnight rate.
B) affecting the discount rate.
C) stabilizing the foreign-exchange market.
D) adjusting reserve requirements.
A) affecting the overnight rate.
B) affecting the discount rate.
C) stabilizing the foreign-exchange market.
D) adjusting reserve requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
By controlling the ________,the Bank of Canada is able to influence ________.
A) overnight rate; market interest rates
B) interbank rate; market interest rates
C) exchange rate; overnight rate
D) exchange rate; market interest rates
A) overnight rate; market interest rates
B) interbank rate; market interest rates
C) exchange rate; overnight rate
D) exchange rate; market interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In a market economy,uncertain levels of inflation
A) make prices less useful as signals for resource allocation.
B) prompt firms to enter into fewer short-term contracts, and more long-term contracts, with suppliers.
C) balance out income redistribution in the long run.
D) are more beneficial to lenders than to borrowers, as lenders have a tendency to overestimate the expected inflation rate.
A) make prices less useful as signals for resource allocation.
B) prompt firms to enter into fewer short-term contracts, and more long-term contracts, with suppliers.
C) balance out income redistribution in the long run.
D) are more beneficial to lenders than to borrowers, as lenders have a tendency to overestimate the expected inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is not a reason that the central bank does not aim for zero inflation?
A) Measured inflation tends to be higher than actual inflation.
B) The inflation rate would be more likely to be negative.
C) This would limit the ability of the central bank to stimulate the economy
D) Positive inflation "greases the wheels" of the labour market.
A) Measured inflation tends to be higher than actual inflation.
B) The inflation rate would be more likely to be negative.
C) This would limit the ability of the central bank to stimulate the economy
D) Positive inflation "greases the wheels" of the labour market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When and why was the Bank of Canada created?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not one of the four tasks of the Bank of Canada?
A) Conduct monetary policy.
B) Regulate financial institutions.
C) Issue paper and coin currency.
D) Provide banking services for the federal government.
A) Conduct monetary policy.
B) Regulate financial institutions.
C) Issue paper and coin currency.
D) Provide banking services for the federal government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 12.1
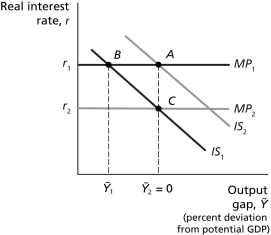
Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,the central bank response will
A) push the economy further down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate further.
B) push the economy back up the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate toward its full-employment level.
C) push the economy back down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate towards its full-employment level.
D) push the economy further up the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate further.

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,the central bank response will
A) push the economy further down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate further.
B) push the economy back up the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate toward its full-employment level.
C) push the economy back down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate towards its full-employment level.
D) push the economy further up the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate further.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A decrease in the policy rate ________ bank reserves and ________ the overnight rate.
A) increases; raises
B) increases; lowers
C) decreases; raises
D) decreases; lowers
A) increases; raises
B) increases; lowers
C) decreases; raises
D) decreases; lowers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 12.2
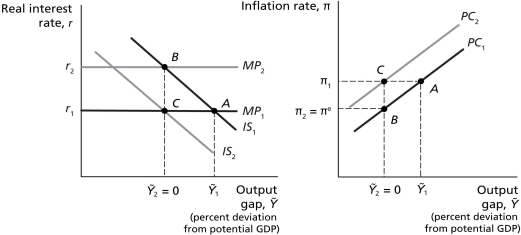
Refer to Figure 12.2.Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,this would be represented by a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
C) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Refer to Figure 12.2.Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,this would be represented by a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
C) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 12.2

Refer to Figure 12.2.Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,this would be represented by a movement on the Phillips curve from
A) point A to point B.
B) point C to point B.
C) point B to point A.
D) point A to point B to point C.

Refer to Figure 12.2.Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,this would be represented by a movement on the Phillips curve from
A) point A to point B.
B) point C to point B.
C) point B to point A.
D) point A to point B to point C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Targeting the overnight rate allows the Bank of Canada some ability to control bank reserves and thus the money supply.Explain how each of the following tools allows the central to fine-tune its control of bank reserves.
a. Conducting open market operations
b. Changing the bank rate
a. Conducting open market operations
b. Changing the bank rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 12.2

Refer to Figure 12.2 Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,the economy's new equilibrium would be at ________,with ________.
A) point B; lower inflation and a lower output gap
B) point C; unchanged inflation and a lower output gap
C) point A; higher inflation and a higher output gap
D) point C; higher inflation and an unchanged output gap

Refer to Figure 12.2 Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.If the Bank of Canada wants to achieve the goal of price stability,the economy's new equilibrium would be at ________,with ________.
A) point B; lower inflation and a lower output gap
B) point C; unchanged inflation and a lower output gap
C) point A; higher inflation and a higher output gap
D) point C; higher inflation and an unchanged output gap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assume that the term structure effect and the default-risk premium remain unchanged and that households and firms have adaptive expectations.At the beginning of 2013,a bank is offering car loans at a nominal interest rate of 7% and the expected rate of inflation is 2 %,and at the beginning of 2014,the bank decreases the nominal interest rate to 5%.The real interest rate at the beginning of 2014 is
A) 2%.
B) 3%.
C) 5%.
D) This cannot be determined without being given the expected inflation rate for 2014.
A) 2%.
B) 3%.
C) 5%.
D) This cannot be determined without being given the expected inflation rate for 2014.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 12.1

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,the central bank response will result in a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
C) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,the central bank response will result in a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
C) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When attempting to decrease the overnight rate,the Bank of Canada can
A) increase reserve requirements.
B) engage in an open market purchase.
C) increase the discount rate.
D) raise the interest rate paid on bank reserves.
A) increase reserve requirements.
B) engage in an open market purchase.
C) increase the discount rate.
D) raise the interest rate paid on bank reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In general,if the Bank of Canada increases its target for the overnight rate,
A) short-term nominal interest rates will increase and long-term nominal interest rates will not change.
B) short-term nominal interest rates will not change and long-term nominal interest rates increase.
C) short-term nominal interest rates will increase and long-term nominal interest rates will also increase.
D) short-term nominal interest rates will not change and long-term nominal interest rates will also not change.
A) short-term nominal interest rates will increase and long-term nominal interest rates will not change.
B) short-term nominal interest rates will not change and long-term nominal interest rates increase.
C) short-term nominal interest rates will increase and long-term nominal interest rates will also increase.
D) short-term nominal interest rates will not change and long-term nominal interest rates will also not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When the Bank of Canada makes an open market ________,the target short-term nominal interest rate will increase,which will ________ GDP.
A) purchase; increase
B) purchase; decrease
C) sale; increase
D) sale; decrease
A) purchase; increase
B) purchase; decrease
C) sale; increase
D) sale; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 12.1

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If an economic shock causes the IS curve to shift from IS₁ to IS₂,this will
A) push the economy down the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate.
B) push the economy up the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate.
C) push the economy down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate.
D) push the economy up the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate.

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If an economic shock causes the IS curve to shift from IS₁ to IS₂,this will
A) push the economy down the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate.
B) push the economy up the Phillips curve, raising the inflation rate.
C) push the economy down the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate.
D) push the economy up the Phillips curve, lowering the inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the Bank of Canada attempts to increase real GDP and employment by ________ its target for overnight rate,it is conducting ________ monetary policy.
A) raising; expansionary
B) raising; contractionary
C) lowering; expansionary
D) lowering; contractionary
A) raising; expansionary
B) raising; contractionary
C) lowering; expansionary
D) lowering; contractionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 12.1

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,this would best be represented by a movement from
A) point A to point B to point C.
B) point A to point C to point B.
C) point C to point B to point A.
D) point C to point A to point B.

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,and the central bank responds to the results of the demand shock with an appropriate monetary policy,this would best be represented by a movement from
A) point A to point B to point C.
B) point A to point C to point B.
C) point C to point B to point A.
D) point C to point A to point B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 12.1

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,the shock will cause a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
C) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Refer to Figure 12.1.Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.If the economy then experiences a negative demand shock,the shock will cause a
A) shift from IS₁ to IS₂.
B) shift from MP₁ to MP₂.
C) shift from IS₂ to IS₁.
D) shift from MP₂ to MP₁.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
To increase the money supply,the Bank of Canada could
A) engage in an open market purchase.
B) increase reserve requirements.
C) decrease income tax rates.
D) raise the discount rate.
A) engage in an open market purchase.
B) increase reserve requirements.
C) decrease income tax rates.
D) raise the discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When the Bank of Canada makes an open market purchase,the money supply will ________,which will cause long-term real interest rates to ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When a bank receives a $50 million discount loan from the Bank of Canada,the bank's reserves
A) remain the same.
B) increase by less than $50 million.
C) increase by $50 million.
D) increase by more than $50 million.
A) remain the same.
B) increase by less than $50 million.
C) increase by $50 million.
D) increase by more than $50 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the Bank of Canada makes an open market purchase,long-term real interest rates will ________,which will ________ GDP.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To decrease bank reserves,the Bank of Canada can
A) engage in an open market sale.
B) reduce reserve requirements.
C) lower the discount rate.
D) set a lower interest rate for term deposits.
A) engage in an open market sale.
B) reduce reserve requirements.
C) lower the discount rate.
D) set a lower interest rate for term deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume it takes the Bank of Canada four months to understand that a demand shock has occurred in the economy,and another one month to adjust policy to the shock.The initial four-month time period refers to the ________,and the following one-month time period refers to the ________.
A) impact lag; implementation lag
B) recognition lag; implementation lag
C) implementation lag; policy lag
D) policy lag; impact lag
A) impact lag; implementation lag
B) recognition lag; implementation lag
C) implementation lag; policy lag
D) policy lag; impact lag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose oil prices suddenly begin to rise and the Bank of Canada announces that the increase in oil prices is not expected to generate excessive inflation.If the Bank of Canada is incorrect in its assumption that rising oil prices will not generate excessive inflation and the inflation rate increases before the Bank of Canada takes corrective action,then other things equal,this would result in ________ and ________.
A) the IS curve shifting to the right; a movement up the Phillips curve
B) the IS curve shifting to the left; a movement down the Phillips curve
C) the MP curve shifting up; a movement up the Phillips curve
D) the MP curve shifting down; a movement down the Phillips curve
A) the IS curve shifting to the right; a movement up the Phillips curve
B) the IS curve shifting to the left; a movement down the Phillips curve
C) the MP curve shifting up; a movement up the Phillips curve
D) the MP curve shifting down; a movement down the Phillips curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose the economy is initially above potential GDP,and the actual inflation rate is greater than the expected inflation rate.Use the IS-MP model and the Phillips curve to explain what happens if the Bank of Canada adjusts the interest rate to achieve the goal of price stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the Bank of Canada decides to increase interest rates to fight off potential inflation,and their policy action keeps the inflation rate stable,then other things equal,this would result in
A) the IS curve shifting to the right.
B) the IS curve shifting to the left.
C) the MP curve shifting up.
D) the MP curve shifting down.
A) the IS curve shifting to the right.
B) the IS curve shifting to the left.
C) the MP curve shifting up.
D) the MP curve shifting down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose the economy is initially at full employment,with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the expected inflation rate equal to the actual inflation rate.Use the IS-MP model and the Phillips curve to explain what happens if the economy experiences a negative demand shock,and the Bank of Canada responds to the shock by changing its target for the overnight rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the Bank of Canada is facing ________,the bank lending channel provides one explanation for why monetary policy may still be effective even when short-term nominal interest rates equal 0%.
A) an upward-shifting Phillips curve
B) stagflation
C) the zero bound constraint
D) an economy where real GDP has surpassed potential GDP
A) an upward-shifting Phillips curve
B) stagflation
C) the zero bound constraint
D) an economy where real GDP has surpassed potential GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Figure 12.4
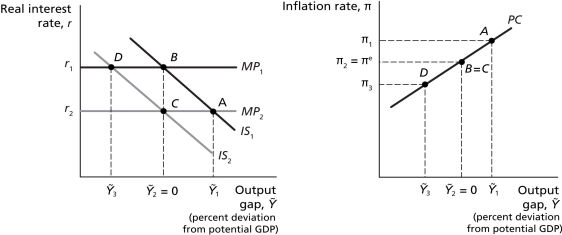
Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.Since the housing bubble burst and the economy returned to its initial,pre-bubble level before the corrective policy changed output,the economy actually moved from ________ after the bubble burst.
A) point A to point B
B) point B to point D
C) point A to point C
D) point C to point B

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.Since the housing bubble burst and the economy returned to its initial,pre-bubble level before the corrective policy changed output,the economy actually moved from ________ after the bubble burst.
A) point A to point B
B) point B to point D
C) point A to point C
D) point C to point B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure 12.4

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.The implementation of corrective policy by the central bank is designed to move the economy from
A) point A to point B.
B) point B to point D.
C) point D to point C.
D) point C to point A.

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.The implementation of corrective policy by the central bank is designed to move the economy from
A) point A to point B.
B) point B to point D.
C) point D to point C.
D) point C to point A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Quantitative easing is a central bank policy that attempts to stimulate the economy by possibly
A) selling Treasury securities.
B) making discount loans to nonfinancial corporations.
C) slowly reducing the required reserve ratio.
D) buying long-term securities.
A) selling Treasury securities.
B) making discount loans to nonfinancial corporations.
C) slowly reducing the required reserve ratio.
D) buying long-term securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 12.4

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.The increase in consumer wealth resulting from the housing bubble is best represented by a movement from
A) point A to point B.
B) point B to point D.
C) point D to point C.
D) point C to point A.

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.The increase in consumer wealth resulting from the housing bubble is best represented by a movement from
A) point A to point B.
B) point B to point D.
C) point D to point C.
D) point C to point A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 12.4

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.Since the housing bubble burst and the economy returned to its initial,pre-bubble level before the corrective policy changed output,the impact of the change in policy is best represented as a movement from
A) point A to point B.
B) point C to point D.
C) point B to point D.
D) point C to point B.

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.Since the housing bubble burst and the economy returned to its initial,pre-bubble level before the corrective policy changed output,the impact of the change in policy is best represented as a movement from
A) point A to point B.
B) point C to point D.
C) point B to point D.
D) point C to point B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
By engaging in quantitative easing,the Bank of Canada is attempting to reduce the ________,causing the MP curve to ________.
A) term premium and the real interest rate; shift down
B) unemployment rate and the inflation rate; shift down
C) short-term nominal and real interest rates; shift up
D) federal funds rate; shift up
A) term premium and the real interest rate; shift down
B) unemployment rate and the inflation rate; shift down
C) short-term nominal and real interest rates; shift up
D) federal funds rate; shift up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 12.3
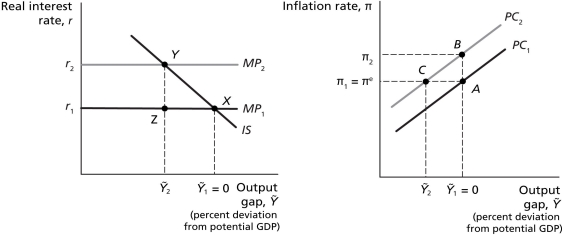
Refer to Figure 12.3 Suppose that after a negative supply shock,the economy is at point X in the IS-MP model and at point B on the Phillips curve.If the Bank of Canada has a goal of high employment and therefore does not adjust interest rates,the economy would ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ on the Phillips curve.
A) remain at point X; move to point C
B) remain at point X; remain at point B
C) move to point Z; move to point A
D) move to point Z; move to point C

Refer to Figure 12.3 Suppose that after a negative supply shock,the economy is at point X in the IS-MP model and at point B on the Phillips curve.If the Bank of Canada has a goal of high employment and therefore does not adjust interest rates,the economy would ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ on the Phillips curve.
A) remain at point X; move to point C
B) remain at point X; remain at point B
C) move to point Z; move to point A
D) move to point Z; move to point C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 12.4

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.As a result of the monetary policy taking effect after the housing bubble had already burst,real GDP will be ________ potential GDP and the rate of inflation will be ________ the rate of inflation when the economy was initially in equilibrium.
A) greater than; greater than
B) greater than; less than
C) less than; less than
D) less than; equal to

Scenario: The above figures represent the economy of Mondolvia, where points A, B, C, and D in the first figure reflect the corresponding points in the second figure. The economy of Mondolvia is initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In April 2012, Mondolvia reached the peak of a rapid housing bubble that dramatically increased consumer wealth. The central bank of Mondolvia recognized this housing bubble peak existed in June, 2012 and implemented corrective policy in August 2012. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 12 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the housing bubble burst in December 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-bubble equilibrium level.
Refer to Figure 12.4.As a result of the monetary policy taking effect after the housing bubble had already burst,real GDP will be ________ potential GDP and the rate of inflation will be ________ the rate of inflation when the economy was initially in equilibrium.
A) greater than; greater than
B) greater than; less than
C) less than; less than
D) less than; equal to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
By rescuing large,troubled institutions,as happened during the Great Recession with institutions like AIG and General Motors,policymakers attempted to achieve financial and economic stability in the short run,but their actions may encourage even riskier behaviour on the part of these large institutions in the future if these institutions believe that they,too,will be bailed out if they get in trouble.This risk faced by policymakers is known as
A) asymmetric information.
B) quantitative easing.
C) too-big-to-fail policy.
D) moral hazard.
A) asymmetric information.
B) quantitative easing.
C) too-big-to-fail policy.
D) moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Assume that the Bank of Canada knows a demand shock has occurred in the economy.It takes the Bank of Canada two months to adjust policy to the shock,and it takes the economy 14 months for the policy change to affect the economy.The two-month time period refers to the ________,and the following 14-month time period refers to the ________.
A) policy lag; implementation lag
B) recognition lag; implementation lag
C) implementation lag; impact lag
D) policy lag; recognition lag
A) policy lag; implementation lag
B) recognition lag; implementation lag
C) implementation lag; impact lag
D) policy lag; recognition lag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain the dilemma that supply shocks pose when the Bank of Canada chooses to use monetary policy to achieve its goals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 12.3

Refer to Figure 12.3 Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the Bank of Canada does not target interest rates,allowing the real interest rate to change like it did during the Great Depression.This would be reflected as a movement from ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ the Phillips curve.
A) point Y to point X; a movement up
B) point X to point Y; a movement down
C) point Z to point Y; a movement up
D) point Y to point Z; a movement down

Refer to Figure 12.3 Suppose the economy is initially at full employment with real GDP equal to potential GDP,and the Bank of Canada does not target interest rates,allowing the real interest rate to change like it did during the Great Depression.This would be reflected as a movement from ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ the Phillips curve.
A) point Y to point X; a movement up
B) point X to point Y; a movement down
C) point Z to point Y; a movement up
D) point Y to point Z; a movement down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Some economists and policymakers criticized the Fed (the central bank in the United States)for taking too much time understanding and identifying the problems in financial markets which led to the financial crisis of 2007-2009.This criticism best describes the ________ as a limitation of monetary policy.
A) implementation lag
B) recognition lag
C) impact lag
D) asymmetry lag
A) implementation lag
B) recognition lag
C) impact lag
D) asymmetry lag

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 12.3

Refer to Figure 12.3.Suppose that after a negative supply shock,the economy is at point X in the IS-MP model and at point B on the Phillips curve.If the Bank of Canada has a goal of price stability,the economy would ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ on the Phillips curve.
A) move to point Y; move to point C
B) remain at X; move to point A
C) move to point Y; remain at point B
D) move to point Z; move to point A

Refer to Figure 12.3.Suppose that after a negative supply shock,the economy is at point X in the IS-MP model and at point B on the Phillips curve.If the Bank of Canada has a goal of price stability,the economy would ________ in the IS-MP model and ________ on the Phillips curve.
A) move to point Y; move to point C
B) remain at X; move to point A
C) move to point Y; remain at point B
D) move to point Z; move to point A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In Canada,
A) exchange rate stability is sacrificed to pursue the goals of monetary policy independence and free capital flows.
B) monetary policy independence is sacrificed to pursue the goals of exchange rate stability and free capital flows.
C) free capital flows are sacrificed to pursue the goals of exchange rate stability and monetary policy independence.
D) the goals of exchange rate stability, monetary policy independence, and free capital flows are all able to be pursued at the same time.
A) exchange rate stability is sacrificed to pursue the goals of monetary policy independence and free capital flows.
B) monetary policy independence is sacrificed to pursue the goals of exchange rate stability and free capital flows.
C) free capital flows are sacrificed to pursue the goals of exchange rate stability and monetary policy independence.
D) the goals of exchange rate stability, monetary policy independence, and free capital flows are all able to be pursued at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 12.6
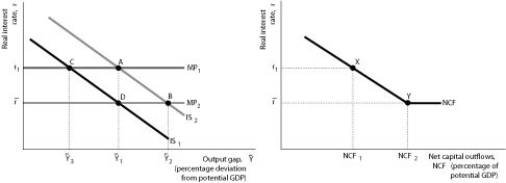
Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.6.Under a fixed exchange rate system,the central bank cannot increase the output gap with expansionary policy and still maintain the fixed exchange rate if the economy is at
A) point A.
B) point B.
C) point C.
D) point X.

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.6.Under a fixed exchange rate system,the central bank cannot increase the output gap with expansionary policy and still maintain the fixed exchange rate if the economy is at
A) point A.
B) point B.
C) point C.
D) point X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If exchange rates are floating,a contractionary monetary policy in Canada will cause the dollar to ________ relative to other currencies and cause net capital outflows to ________.
A) appreciate; increase
B) appreciate; decrease
C) depreciate; increase
D) depreciate; decrease
A) appreciate; increase
B) appreciate; decrease
C) depreciate; increase
D) depreciate; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If exchange rates are floating,the Bank of Canada increasing its target inflation rate will cause the dollar to ________ relative to other currencies and cause net capital outflows to ________.
A) appreciate; increase
B) appreciate; decrease
C) depreciate; increase
D) depreciate; decrease
A) appreciate; increase
B) appreciate; decrease
C) depreciate; increase
D) depreciate; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 12.6

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.6.Under a fixed exchange rate system,if the central bank can increase the output gap with expansionary policy and still maintain the fixed exchange rate,this would best be represented by a movement from ________ in Panel (a)and a movement from ________ in Panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.6.Under a fixed exchange rate system,if the central bank can increase the output gap with expansionary policy and still maintain the fixed exchange rate,this would best be represented by a movement from ________ in Panel (a)and a movement from ________ in Panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the goals pursued by policymakers in an open economy is desirable because it reduces the uncertainty of conducting economic activity across borders?
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are policy lags? Explain the three policy lags faced by the Bank of Canada when implementing monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
With a contractionary monetary policy,as the output gap increases,the response of the central bank will tend to cause net capital outflows to ________ and cause the nominal exchange rate to ________.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Under a fixed exchange rate system,if the real interest rate is at its lower bound and the central bank implements expansionary policy,real GDP will ________ and the output gap will ________.
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) not change; not change
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) not change; not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the goals pursued by policymakers in an open economy is desirable because it can help reduce the volatility of economic activity?
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What are the main arguments for and against central bank independence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the policy trilemma hypothesis,of the three goals generally pursued by policymakers in an open economy,
A) only one of the goals is possible to achieve at any one time.
B) it is possible for a country to achieve two of the goals at the same time, but not all three.
C) it is possible for a country to achieve all three goals at the same time in the short run, but not in the long run.
D) it is only possible for a country to achieve all three goals at the same time in the long run.
A) only one of the goals is possible to achieve at any one time.
B) it is possible for a country to achieve two of the goals at the same time, but not all three.
C) it is possible for a country to achieve all three goals at the same time in the short run, but not in the long run.
D) it is only possible for a country to achieve all three goals at the same time in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 12.5
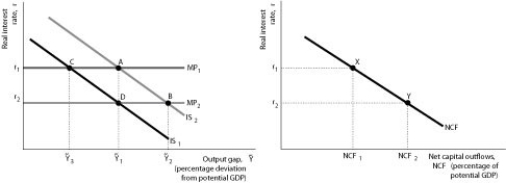
Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.5.If exchange rates are floating,an expansionary monetary policy would best be represented by a movement from ________ in panel (a)and a corresponding movement from ________ in panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.5.If exchange rates are floating,an expansionary monetary policy would best be represented by a movement from ________ in panel (a)and a corresponding movement from ________ in panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A study conducted by Alberto Alesina and Lawrence Summers concluded that countries with highly independent central banks had ________ than countries whose central banks had little independence.
A) higher average inflation rates
B) lower average inflation rates
C) higher average unemployment rates
D) lower average unemployment rates
A) higher average inflation rates
B) lower average inflation rates
C) higher average unemployment rates
D) lower average unemployment rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 12.5

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.5.If exchange rates are floating,the Bank of Canada decreasing its target inflation rate would best be represented by a movement from ________ in panel (a)and a corresponding movement from ________ in panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Panel (a) Panel (b)
-Refer to Figure 12.5.If exchange rates are floating,the Bank of Canada decreasing its target inflation rate would best be represented by a movement from ________ in panel (a)and a corresponding movement from ________ in panel (b).
A) point A to point B; point X to point Y
B) point C to point A; point X to point Y
C) point D to point C; point Y to point X
D) point B to point D; point Y to point X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the goals pursued by policymakers in an open economy is desirable because it can reduce the severity of business cycles?
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency
A) exchange-rate stability
B) monetary policy independence
C) free capital flows
D) appreciation of the domestic currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Bank of Canada
A) has complete independence from the Canadian government.
B) is influenced by the federal government which appoints a governor, but has flexibility in meeting the goals of monetary policy.
C) is a government agency run by the Ministry of Finance.
D) is run by elected officials but is only subject to oversight by the Canadian prime minister.
A) has complete independence from the Canadian government.
B) is influenced by the federal government which appoints a governor, but has flexibility in meeting the goals of monetary policy.
C) is a government agency run by the Ministry of Finance.
D) is run by elected officials but is only subject to oversight by the Canadian prime minister.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The governor of the Bank of Canada is appointed every ________ years,while the maximum period between federal elections is ________ years.
A) seven; five
B) two; four
C) four: five
D) five; four
A) seven; five
B) two; four
C) four: five
D) five; four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Scenario 12.1
The economy of Ludmilla was initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In October 2011, the stock market in Ludmilla crashed, decreasing consumer wealth. The central bank of Ludmilla recognized the crash that same month and implemented corrective policy one month later. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 18 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the stock market made a miraculous recovery in June 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-crash equilibrium level.
Refer to Scenario 12.1.Use the IS-MP model and the Phillips curve to explain the above changes in the economy of Ludmilla.Be sure to identify each of the changes to the economy on your graphs.
The economy of Ludmilla was initially at equilibrium with real GDP equal to potential GDP. In October 2011, the stock market in Ludmilla crashed, decreasing consumer wealth. The central bank of Ludmilla recognized the crash that same month and implemented corrective policy one month later. The corrective policy actually changed output in the economy 18 months after it was implemented. In the meantime, the stock market made a miraculous recovery in June 2012, returning the economy back to its initial, pre-crash equilibrium level.
Refer to Scenario 12.1.Use the IS-MP model and the Phillips curve to explain the above changes in the economy of Ludmilla.Be sure to identify each of the changes to the economy on your graphs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Under a fixed exchange rate system,a currency devaluation will ________ the nominal exchange rate and will ________ net exports.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



