Deck 12: Unemployment and Inflation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Unemployment and Inflation
1
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u - 0.05).When π = 0.06 and πe = 0.03,the unemployment rate is
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.
0)04.
2
In the extended classical model,an unanticipated increase in the money supply would cause output to ________ and the price level to ________ in the short run.
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; remain unchanged
C)remain unchanged; increase
D)decrease; decrease
A)increase; increase
B)decrease; remain unchanged
C)remain unchanged; increase
D)decrease; decrease
increase; increase
3
In the extended classical model,an anticipated decrease in the money supply would cause output to ________ and the price level to ________ in the short run.
A)increase; decrease
B)increase; remain unchanged
C)remain unchanged; increase
D)remain unchanged; decrease
A)increase; decrease
B)increase; remain unchanged
C)remain unchanged; increase
D)remain unchanged; decrease
remain unchanged; decrease
4
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u -  ).If π = 0.03 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then
).If π = 0.03 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then  =
=
A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.
 ).If π = 0.03 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then
).If π = 0.03 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then  =
=A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The short-run Phillips curve is the relation between inflation and unemployment that holds for a given natural rate of unemployment and a
A)given rate of inflation.
B)given expected rate of inflation.
C)given level of unemployment.
D)given expected level of unemployment.
A)given rate of inflation.
B)given expected rate of inflation.
C)given level of unemployment.
D)given expected level of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Milton Friedman and Edmund Phelps questioned
A)the use of expectations in the Phillips curve.
B)the stability of the relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C)the existence of a natural rate of unemployment.
D)the existence of a full-employment level of output.
A)the use of expectations in the Phillips curve.
B)the stability of the relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C)the existence of a natural rate of unemployment.
D)the existence of a full-employment level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u - 0.05).When π = 0.03 and πe = 0.06,the unemployment rate is
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Phillips curve is a negative empirical relationship between
A)bond prices and interest rates.
B)unemployment and output.
C)inflation and the real interest rate.
D)unemployment and inflation.
A)bond prices and interest rates.
B)unemployment and output.
C)inflation and the real interest rate.
D)unemployment and inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The negative relationship between unemployment and inflation is known as the
A)aggregate supply curve.
B)aggregate demand curve.
C)Phillips curve.
D)efficiency wage line.
A)aggregate supply curve.
B)aggregate demand curve.
C)Phillips curve.
D)efficiency wage line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u -  ).If π = 0.06 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.04,then
).If π = 0.06 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.04,then  =
=
A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.
 ).If π = 0.06 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.04,then
).If π = 0.06 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.04,then  =
=A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In the extended classical model,an unexpected decrease in aggregate demand would cause unanticipated inflation to be ________ and cyclical unemployment to be ________.
A)positive; negative
B)positive; positive
C)negative; negative
D)negative; positive
A)positive; negative
B)positive; positive
C)negative; negative
D)negative; positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The origin of the idea of a trade-off between inflation and unemployment was a 1958 article by
A)A)W. Phillips.
B)Edmund Phelps.
C)Milton Friedman.
D)Robert Gordon.
A)A)W. Phillips.
B)Edmund Phelps.
C)Milton Friedman.
D)Robert Gordon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Phillips curve appeared to fit the data well for the United States in the
A)1960s.
B)1970s.
C)1980s.
D)1990s.
A)1960s.
B)1970s.
C)1980s.
D)1990s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose most people had anticipated that inflation would be 3% in the coming year because the Fed would increase the money supply by 3%.Instead,the Fed increases the money supply by 5%.In the short run,this would cause actual output to be ________ full-employment output and prices to increase by ________ 3%.
A)above; more than
B)above; less than
C)below; more than
D)below; less than
A)above; more than
B)above; less than
C)below; more than
D)below; less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u - 0.06).When π = 0.06 and πe = 0.03,the unemployment rate is
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.
A)0)04.
B)0)05.
C)0)06.
D)0)07.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Based on the theory of the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,if the expected inflation rate is 2%,the short-run Phillips curve will
A)have a kink at an inflation rate of 2%.
B)be the same as the long-run Phillips curve.
C)intersect the long-run Phillips curve at the natural unemployment rate, when the inflation rate is 2%.
D)be horizontal at an expected inflation rate of 2%.
A)have a kink at an inflation rate of 2%.
B)be the same as the long-run Phillips curve.
C)intersect the long-run Phillips curve at the natural unemployment rate, when the inflation rate is 2%.
D)be horizontal at an expected inflation rate of 2%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Phillips's research looked at British data on
A)unemployment and inflation.
B)unemployment and nominal wage growth.
C)inflation and nominal wage growth.
D)unemployment and output.
A)unemployment and inflation.
B)unemployment and nominal wage growth.
C)inflation and nominal wage growth.
D)unemployment and output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,π = πe - 3(u -  ).If π = 0.09 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then
).If π = 0.09 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then  =
=
A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.
 ).If π = 0.09 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then
).If π = 0.09 when πe = 0.06 and u = 0.06,then  =
=A)0)02.
B)0)03.
C)0)04.
D)0)05.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Friedman and Phelps suggested that there should not be a stable relationship between inflation and unemployment,but there should be a stable relationship between
A)anticipated inflation and frictional unemployment.
B)anticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.
C)unanticipated inflation and frictional unemployment.
D)unanticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.
A)anticipated inflation and frictional unemployment.
B)anticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.
C)unanticipated inflation and frictional unemployment.
D)unanticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Based on the expectations-augmented Phillips curve,if the natural rate of unemployment is 0.06,and if the actual inflation rate exceeds the expected inflation rate,then the unemployment rate is
A)less than 0.06.
B)0)06.
C)more than 0.06.
D)0)06 plus 0.5 times the difference between actual and expected inflation.
A)less than 0.06.
B)0)06.
C)more than 0.06.
D)0)06 plus 0.5 times the difference between actual and expected inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Friedman-Phelps analysis suggests that there is a long-term relationship between
A)inflation and unemployment.
B)cyclical inflation and structural unemployment.
C)unanticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.
D)anticipated inflation and structural unemployment.
A)inflation and unemployment.
B)cyclical inflation and structural unemployment.
C)unanticipated inflation and cyclical unemployment.
D)anticipated inflation and structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
State and briefly explain whether or not the empirical evidence generally supports the belief that there is a fixed trade-off between unemployment and inflation,such that monetary policymakers can achieve the combination they prefer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is given by
π = πe - 4(u - ).(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:
).(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:
A: π = .04,πe = .04
B: π = .08,πe = .08
C: π = .04,πe = .08
D: π = .08,πe = .04
Label points A,B,C,and D in your diagram.
The unemployment rate at point A equals .05.
(b)What are the values of the natural rate of unemployment and the unemployment rates at points B,C,and D?
π = πe - 4(u -
 ).(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:
).(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:A: π = .04,πe = .04
B: π = .08,πe = .08
C: π = .04,πe = .08
D: π = .08,πe = .04
Label points A,B,C,and D in your diagram.
The unemployment rate at point A equals .05.
(b)What are the values of the natural rate of unemployment and the unemployment rates at points B,C,and D?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A beneficial supply shock would cause
A)a movement up the short-run Phillips curve.
B)a movement down the short-run Phillips curve.
C)the short-run Phillips curve to shift upward and to the right.
D)the short-run Phillips curve to shift downward and to the left.
A)a movement up the short-run Phillips curve.
B)a movement down the short-run Phillips curve.
C)the short-run Phillips curve to shift upward and to the right.
D)the short-run Phillips curve to shift downward and to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the following misperceptions model of the economy.
AD: Y = 600 + 10(M/P)
SRAS: Y =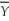 + P - Pe
+ P - Pe
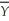
Okun's Law: (Y -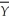 )/
)/ 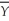 = -2(u -
= -2(u -  )
)
Let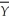 = 750,= 0.05,M = 600,and Pe = 40.
= 750,= 0.05,M = 600,and Pe = 40.
(a)What is the price level?
(b)Suppose there is an unanticipated increase in the nominal money supply to 800.What is the short-run equilibrium level of output,the unemployment rate,and the price level?
(c)When price expectations adjust fully,what is the price level?
AD: Y = 600 + 10(M/P)
SRAS: Y =
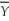 + P - Pe
+ P - Pe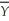
Okun's Law: (Y -
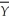 )/
)/ 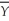 = -2(u -
= -2(u -  )
)Let
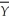 = 750,= 0.05,M = 600,and Pe = 40.
= 750,= 0.05,M = 600,and Pe = 40.(a)What is the price level?
(b)Suppose there is an unanticipated increase in the nominal money supply to 800.What is the short-run equilibrium level of output,the unemployment rate,and the price level?
(c)When price expectations adjust fully,what is the price level?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The short-run Phillips curve shifted during the 1970s primarily because of
A)the two large oil price shocks.
B)the changing demographics of the population.
C)tight monetary policy.
D)easy fiscal policy.
A)the two large oil price shocks.
B)the changing demographics of the population.
C)tight monetary policy.
D)easy fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An increase in the expected rate of inflation would
A)shift the short-run Phillips curve upward.
B)shift the short-run Phillips curve downward.
C)shift the long-run Phillips curve to the right.
D)shift the long-run Phillips curve to the left.
A)shift the short-run Phillips curve upward.
B)shift the short-run Phillips curve downward.
C)shift the long-run Phillips curve to the right.
D)shift the long-run Phillips curve to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is
π = πe - 2(u - 0.06).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and the short-run Phillips curve for an expected inflation rate of 0.04.If the Fed chooses to keep the actual inflation rate at 0.04,what will be the unemployment rate? Label the equilibrium point "A".What is the numerical value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)An aggregate demand shock (resulting from increased exports of goods)raises the inflation rate to 0.06 (the natural rate of unemployment and the expected inflation rate are not affected).Show what happens on your graph.Label the equilibrium point "B".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(c)In response to the aggregate demand shock,suppose the Fed allows the inflation rate of 0.06 to persist.Show what happens on your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "C".In the long run,what is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(d)From the situation in part (c),suppose a supply shock raises the natural rate of unemployment by .01 from its original value.If both the inflation rate and the expected inflation rate do not change,show what happens in your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "D".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
π = πe - 2(u - 0.06).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and the short-run Phillips curve for an expected inflation rate of 0.04.If the Fed chooses to keep the actual inflation rate at 0.04,what will be the unemployment rate? Label the equilibrium point "A".What is the numerical value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)An aggregate demand shock (resulting from increased exports of goods)raises the inflation rate to 0.06 (the natural rate of unemployment and the expected inflation rate are not affected).Show what happens on your graph.Label the equilibrium point "B".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(c)In response to the aggregate demand shock,suppose the Fed allows the inflation rate of 0.06 to persist.Show what happens on your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "C".In the long run,what is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(d)From the situation in part (c),suppose a supply shock raises the natural rate of unemployment by .01 from its original value.If both the inflation rate and the expected inflation rate do not change,show what happens in your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "D".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
You are given the following information about the economy.
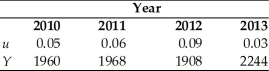
The natural rate of unemployment is 0.04,Okun's Law is that (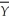 - Y)/
- Y)/ 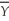 = 2(u -
= 2(u -  ),and the Phillips curve relationship is π = πe - 2 (u - 0.04).
),and the Phillips curve relationship is π = πe - 2 (u - 0.04).
(a)What was the full-employment level of output in each year?
(b)Calculate the growth rate of full-employment output each year.
(c)If expected inflation was 0.04 for all four years,what was the inflation rate each year?

The natural rate of unemployment is 0.04,Okun's Law is that (
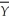 - Y)/
- Y)/ 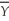 = 2(u -
= 2(u -  ),and the Phillips curve relationship is π = πe - 2 (u - 0.04).
),and the Phillips curve relationship is π = πe - 2 (u - 0.04).(a)What was the full-employment level of output in each year?
(b)Calculate the growth rate of full-employment output each year.
(c)If expected inflation was 0.04 for all four years,what was the inflation rate each year?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Historically,Brazil has suffered higher and more variable rates of inflation than Venezuela.You would expect the short-run aggregate supply curve of Brazil to be ________ than that of Venezuela,and the short-run Phillips curve of Brazil to be ________ than that of Venezuela.
A)flatter; flatter
B)flatter; steeper
C)steeper; flatter
D)steeper; steeper
A)flatter; flatter
B)flatter; steeper
C)steeper; flatter
D)steeper; steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Friedman-Phelps analysis shows that a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment holds
A)even when expected inflation changes.
B)even when the natural rate of unemployment changes.
C)even if both the expected inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment change.
D)as long as the expected inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment are approximately constant.
A)even when expected inflation changes.
B)even when the natural rate of unemployment changes.
C)even if both the expected inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment change.
D)as long as the expected inflation rate and the natural rate of unemployment are approximately constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the expected rate of inflation rose at the same time the natural rate of unemployment rose,the short-run Phillips curve
A)would shift down.
B)would shift up.
C)would not move.
D)might shift up or down or not move, depending on which effect was larger.
A)would shift down.
B)would shift up.
C)would not move.
D)might shift up or down or not move, depending on which effect was larger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose Okun's law holds and a one percentage point increase in the unemployment rate reduces real output by 2% of full-employment output.The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is given by
π = πe - 2.5 (u - 0.04).
Suppose π = 0.08 and πe = 0.03.
(a)What is the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)What is the actual rate of unemployment?
(c)How much is actual GDP compared with full-employment GDP?
π = πe - 2.5 (u - 0.04).
Suppose π = 0.08 and πe = 0.03.
(a)What is the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)What is the actual rate of unemployment?
(c)How much is actual GDP compared with full-employment GDP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Examining data on cyclical unemployment plotted against unanticipated inflation shows
A)a positive relationship.
B)a negative relationship.
C)no significant relationship.
D)a relationship only during the 1960s.
A)a positive relationship.
B)a negative relationship.
C)no significant relationship.
D)a relationship only during the 1960s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An analysis of the American economy since 1960 shows that there is a stable relationship between inflation and unemployment
A)only in the short run.
B)only in the long run.
C)in neither the short run nor the long run.
D)in both the short run and the long run.
A)only in the short run.
B)only in the long run.
C)in neither the short run nor the long run.
D)in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Classicals argue that an adverse supply shock would
A)raise neither the natural rate of unemployment nor the actual rate of unemployment.
B)raise the actual rate of unemployment, but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C)raise the natural rate of unemployment, but not the actual rate of unemployment.
D)raise both the natural rate of unemployment and the actual rate of unemployment.
A)raise neither the natural rate of unemployment nor the actual rate of unemployment.
B)raise the actual rate of unemployment, but not the natural rate of unemployment.
C)raise the natural rate of unemployment, but not the actual rate of unemployment.
D)raise both the natural rate of unemployment and the actual rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is
π = πe - 3(u - 0.05).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and the short-run Phillips curve for an expected inflation rate of 0.03.If the Fed chooses to keep the actual inflation rate at 0.03,what will be the unemployment rate? Label the equilibrium point "A".What is the numerical value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)An aggregate demand shock (resulting from increased exports of goods)raises the inflation rate to 0.06 (the natural rate of unemployment and the expected inflation rate are not affected).Show what happens on your graph.Label the equilibrium point "B".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(c)In response to the aggregate demand shock,suppose the Fed allows the inflation rate of 0.06 to persist.Show what happens on your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "C".In the long run,what is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(d)From the situation in part (c),suppose a supply shock (an oil price increase)raises the natural rate of unemployment by .01 from its original value.If the expected inflation rate does not change,show what happens in your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "D".
π = πe - 3(u - 0.05).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and the short-run Phillips curve for an expected inflation rate of 0.03.If the Fed chooses to keep the actual inflation rate at 0.03,what will be the unemployment rate? Label the equilibrium point "A".What is the numerical value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(b)An aggregate demand shock (resulting from increased exports of goods)raises the inflation rate to 0.06 (the natural rate of unemployment and the expected inflation rate are not affected).Show what happens on your graph.Label the equilibrium point "B".What is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(c)In response to the aggregate demand shock,suppose the Fed allows the inflation rate of 0.06 to persist.Show what happens on your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "C".In the long run,what is the numerical value of the unemployment rate?
(d)From the situation in part (c),suppose a supply shock (an oil price increase)raises the natural rate of unemployment by .01 from its original value.If the expected inflation rate does not change,show what happens in your graph,labeling the equilibrium point "D".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is given by
π = πe - 3(u - 0.06).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and three short-run Phillips curves.
(b)What is the value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(c)If actual inflation is 0.02 and expected inflation is 0.05,what is the unemployment rate?
(d)If actual inflation is 0.08 and expected inflation is 0.05,what is the unemployment rate?
π = πe - 3(u - 0.06).
(a)Graph the long-run Phillips curve and three short-run Phillips curves.
(b)What is the value of the natural rate of unemployment?
(c)If actual inflation is 0.02 and expected inflation is 0.05,what is the unemployment rate?
(d)If actual inflation is 0.08 and expected inflation is 0.05,what is the unemployment rate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the expected inflation rate is unchanged,a fall in the natural rate of unemployment would
A)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
B)not shift the short-run Phillips curve.
C)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
D)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the left and shift the long-run Phillips curve to the right.
A)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
B)not shift the short-run Phillips curve.
C)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
D)shift the short-run Phillips curve to the left and shift the long-run Phillips curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is given by
π = πe - 2(u - ).
).
(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:
A: π = .03,πe = .03
B: π = .06,πe = .06
C: π = .03,πe = .06
D: π = .06,πe = .03
Label points A,B,C,and D in your diagram.
The unemployment rate at point A equals .05.
(b)What are the values of the natural rate of unemployment and the unemployment rates at points B,C,and D?
π = πe - 2(u -
 ).
).(a)Draw a diagram showing a long-run Phillips curve and two short-run Phillips curves that contain the following points:
A: π = .03,πe = .03
B: π = .06,πe = .06
C: π = .03,πe = .06
D: π = .06,πe = .03
Label points A,B,C,and D in your diagram.
The unemployment rate at point A equals .05.
(b)What are the values of the natural rate of unemployment and the unemployment rates at points B,C,and D?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The natural rate of unemployment in the United States generally ________ from 1960 to 1980 and ________ from 1980 to 2000.
A)fell; rose
B)fell; fell
C)rose; fell
D)rose; rose
A)fell; rose
B)fell; fell
C)rose; fell
D)rose; rose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Can macroeconomic policy be used systematically to create unanticipated inflation?
A)Yes, according to Keynesian economists.
B)Yes, according to classical economists.
C)No, according to Keynesian economists.
D)Yes, according to classical economists, if Ricardian equivalence holds.
A)Yes, according to Keynesian economists.
B)Yes, according to classical economists.
C)No, according to Keynesian economists.
D)Yes, according to classical economists, if Ricardian equivalence holds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The long-run Phillips curve is
A)vertical.
B)horizontal.
C)upward sloping.
D)downward sloping.
A)vertical.
B)horizontal.
C)upward sloping.
D)downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Some economists argue that Okun's Law overstates the cost of cyclical unemployment because
A)the cost of retraining workers must be offset against the loss in output that occurs when workers are unemployed.
B)if efficiency wages prevail, and workers are paid their real wage, already employed workers will reduce their effort, reducing output.
C)it ignores the fact that leisure increases during a recession.
D)it ignores the loss of government revenue and additional government expenditures that occur when unemployment rises.
A)the cost of retraining workers must be offset against the loss in output that occurs when workers are unemployed.
B)if efficiency wages prevail, and workers are paid their real wage, already employed workers will reduce their effort, reducing output.
C)it ignores the fact that leisure increases during a recession.
D)it ignores the loss of government revenue and additional government expenditures that occur when unemployment rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why did the government use expansionary monetary policies in the late 1970s,and what was the principal negative macroeconomic effect of these policies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The idea that new policies change the economic rules and affect economic behavior,so that no one can safely assume that historical relationships between variables will hold when policies change,is known as
A)Okun's Law.
B)Say's Law.
C)the equation of exchange.
D)the Lucas critique.
A)Okun's Law.
B)Say's Law.
C)the equation of exchange.
D)the Lucas critique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the Lucas critique,and why was it so important to macroeconomists in the 1970s?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Both classicals and Keynesians agree that policymakers
A)can exploit the Phillips curve in the short run.
B)cannot exploit the Phillips curve in the short run.
C)can keep the unemployment rate permanently below the natural rate by permanently running a high rate of inflation.
D)cannot keep the unemployment rate permanently below the natural rate by permanently running a high rate of inflation.
A)can exploit the Phillips curve in the short run.
B)cannot exploit the Phillips curve in the short run.
C)can keep the unemployment rate permanently below the natural rate by permanently running a high rate of inflation.
D)cannot keep the unemployment rate permanently below the natural rate by permanently running a high rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The argument that when policy changes,people's behavior changes so that historical relationships between macroeconomic variables will no longer hold is known as
A)the Phillips curve.
B)the policy irrelevance hypothesis.
C)hysteresis.
D)the Lucas critique.
A)the Phillips curve.
B)the policy irrelevance hypothesis.
C)hysteresis.
D)the Lucas critique.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Lucas critique is an objection to the assumption that
A)inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
B)there is a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C)historical relationships between macroeconomic variables will continue to hold after new policies are in place.
D)people form expectations rationally.
A)inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
B)there is a negative relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C)historical relationships between macroeconomic variables will continue to hold after new policies are in place.
D)people form expectations rationally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Starting on a Phillips curve with expected inflation equal to 5% and unemployment at its natural rate,show what happens to unemployment if the Fed tries to reduce inflation,but has no credibility.As time passes and people realize that the inflation rate is now lower,what happens to the short-run Phillips curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
One reason for the fall in the natural rate of unemployment from 1980 to 2000 is
A)changes in the demographic composition of the work force.
B)the decline in inflation.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.
A)changes in the demographic composition of the work force.
B)the decline in inflation.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to Okun's law,if full-employment output is $5000 billion,then each percentage point of unemployment sustained for one year reduces output by
A)$50 billion.
B)$100 billion.
C)$150 billion.
D)$200 billion.
A)$50 billion.
B)$100 billion.
C)$150 billion.
D)$200 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following forms of unemployment probably imposes the greatest personal costs?
A)frictional unemployment.
B)structural unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)voluntary unemployment.
A)frictional unemployment.
B)structural unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)voluntary unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Keynesian macroeconomists argue that the short-run Phillips curve ________ represent a usable trade-off for policymakers because ________.
A)does; prices are sticky
B)does; prices are not sticky
C)does not; prices are not sticky
D)does not; prices are sticky
A)does; prices are sticky
B)does; prices are not sticky
C)does not; prices are not sticky
D)does not; prices are sticky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Classical macroeconomists argue that the short-run Phillips curve ________ represent a usable trade-off for policymakers because ________.
A)does; people have rational expectations
B)does; people do not have rational expectations
C)does not; people do not have rational expectations
D)does not; people have rational expectations
A)does; people have rational expectations
B)does; people do not have rational expectations
C)does not; people do not have rational expectations
D)does not; people have rational expectations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
When the economy goes into a recession,there's an increase in
A)frictional unemployment.
B)structural unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)voluntary unemployment.
A)frictional unemployment.
B)structural unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)voluntary unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Can macroeconomic policy be used systematically to create unanticipated inflation?
A)No, according to Keynesian economists.
B)Yes, according to classical economists.
C)No, according to classical economists.
D)Yes, according to Keynesian economists, if Ricardian equivalence holds.
A)No, according to Keynesian economists.
B)Yes, according to classical economists.
C)No, according to classical economists.
D)Yes, according to Keynesian economists, if Ricardian equivalence holds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
One reason for the rise in the natural rate of unemployment from 1960 to 1980 is
A)changes in the demographic composition of the work force.
B)the decline in inflation.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.
A)changes in the demographic composition of the work force.
B)the decline in inflation.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The fact that the long-run Phillips curve is vertical implies that
A)monetary policy can't affect unemployment.
B)money is neutral in the long run.
C)there is a natural rate of inflation.
D)money can't affect inflation in the long run.
A)monetary policy can't affect unemployment.
B)money is neutral in the long run.
C)there is a natural rate of inflation.
D)money can't affect inflation in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One cost of a perfectly anticipated inflation is that it
A)transfers wealth from lenders to borrowers.
B)transfers wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)increases menu costs.
D)damages the role of prices as signals in the economy.
A)transfers wealth from lenders to borrowers.
B)transfers wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)increases menu costs.
D)damages the role of prices as signals in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Unanticipated deflation can create unemployment if
A)nominal wages are sticky, causing real wages to rise over time.
B)nominal wages are flexible, causing people's real incomes to decline.
C)banks refuse to make loans at low nominal interest rates.
D)nominal interest rates remain positive.
A)nominal wages are sticky, causing real wages to rise over time.
B)nominal wages are flexible, causing people's real incomes to decline.
C)banks refuse to make loans at low nominal interest rates.
D)nominal interest rates remain positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In years when teenagers become a greater percentage of the labor force,
A)the natural rate of unemployment falls.
B)the natural rate of unemployment rises.
C)the inflation rate rises.
D)the inflation rate falls.
A)the natural rate of unemployment falls.
B)the natural rate of unemployment rises.
C)the inflation rate rises.
D)the inflation rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Many central banks around the world target an inflation rate of about ________,because of upward bias in measured inflation and to reduce the risk of deflation.
A)-2%.
B)0%.
C)2%.
D)5%.
A)-2%.
B)0%.
C)2%.
D)5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Because the natural rate of unemployment is not known precisely,policymakers who use it as a guide for policy must be
A)less aggressive with policy changes than they would be if they knew the value of the natural rate.
B)more aggressive with policy changes than they would be if they knew the value of the natural rate.
C)ready to change policy more quickly.
D)aware of other data.
A)less aggressive with policy changes than they would be if they knew the value of the natural rate.
B)more aggressive with policy changes than they would be if they knew the value of the natural rate.
C)ready to change policy more quickly.
D)aware of other data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Hyperinflation occurs when
A)the inflation rate rises.
B)the inflation rate declines.
C)the inflation rate is extremely high.
D)the inflation rate is extremely low.
A)the inflation rate rises.
B)the inflation rate declines.
C)the inflation rate is extremely high.
D)the inflation rate is extremely low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
One cost of an unanticipated inflation is that it
A)transfers wealth from lenders to borrowers.
B)transfers wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)decreases menu costs.
D)increases the purchasing power of money.
A)transfers wealth from lenders to borrowers.
B)transfers wealth from borrowers to lenders.
C)decreases menu costs.
D)increases the purchasing power of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If nominal interest rates have a lower bound of zero and deflation occurs at 3% (i.e.,the inflation rate equals -3%,then the lowest real interest rate possible is
A)-3%.
B)0%.
C)3%.
D)6%.
A)-3%.
B)0%.
C)3%.
D)6%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The costs in time and effort incurred by people and firms who are trying to minimize their holdings of cash because of inflation are called
A)menu costs.
B)shoe leather costs.
C)transactions costs.
D)imperfect competition costs.
A)menu costs.
B)shoe leather costs.
C)transactions costs.
D)imperfect competition costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If you were president of the United States,what would you do to reduce the natural rate of unemployment? Propose at least three different methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A COLA is
A)a center of labor activity.
B)a cost of living adjustment.
C)a contract on long-term assets.
D)a crisis of labor analysis.
A)a center of labor activity.
B)a cost of living adjustment.
C)a contract on long-term assets.
D)a crisis of labor analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
With fixed interest rates,unanticipated deflation hurts ________ because ________.
A)lenders; they get paid back in less valuable dollars
B)lenders; they get paid back in more valuable dollars
C)borrowers; they repay the loan in more valuable dollars
D)borrowers; they repay the loan in less valuable dollars
A)lenders; they get paid back in less valuable dollars
B)lenders; they get paid back in more valuable dollars
C)borrowers; they repay the loan in more valuable dollars
D)borrowers; they repay the loan in less valuable dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A difficulty faced by policymakers who wish to use the unemployment rate as a guide to whether the economy is weak or strong is that
A)the natural rate of unemployment is hard to measure.
B)the natural rate of unemployment almost never changes.
C)policymakers must use data on output to tell whether the unemployment rate is too high or too low.
D)the impact of policy on the economy is subject to long and variable lags.
A)the natural rate of unemployment is hard to measure.
B)the natural rate of unemployment almost never changes.
C)policymakers must use data on output to tell whether the unemployment rate is too high or too low.
D)the impact of policy on the economy is subject to long and variable lags.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When actual inflation is less than expected inflation
A)the natural rate of unemployment falls, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
B)cyclical unemployment falls, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
C)there are transfers from borrowers to lenders.
D)there are transfers from lenders to borrowers.
A)the natural rate of unemployment falls, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
B)cyclical unemployment falls, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
C)there are transfers from borrowers to lenders.
D)there are transfers from lenders to borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When actual inflation is greater than expected inflation
A)the natural rate of unemployment rises, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
B)cyclical unemployment rises, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
C)there are transfers from borrowers to lenders.
D)there are transfers from lenders to borrowers.
A)the natural rate of unemployment rises, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
B)cyclical unemployment rises, according to Phillips-curve analysis.
C)there are transfers from borrowers to lenders.
D)there are transfers from lenders to borrowers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe the major costs of inflation,being sure to distinguish between anticipated and unanticipated inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The bulk of the decline in the natural rate of unemployment from 1980 to 2000 is because of
A)a decline in the inflation rate.
B)a decline in the share of young workers in the labor force.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.
A)a decline in the inflation rate.
B)a decline in the share of young workers in the labor force.
C)increased competition from foreign workers.
D)the depreciation of the dollar relative to foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the relation between the unemployment rate and the proportion of unemployed workers who have been unemployed for 15 weeks or longer?
A)Both rise in recessions.
B)Both rise in expansions.
C)The unemployment rises in recessions but the proportion of unemployed workers who have been unemployed for 15 weeks or longer declines in recessions.
D)The unemployment falls in recessions but the proportion of unemployed workers who have been unemployed for 15 weeks or longer rises in recessions.
A)Both rise in recessions.
B)Both rise in expansions.
C)The unemployment rises in recessions but the proportion of unemployed workers who have been unemployed for 15 weeks or longer declines in recessions.
D)The unemployment falls in recessions but the proportion of unemployed workers who have been unemployed for 15 weeks or longer rises in recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Describe the principal costs of unemployment.Are there any benefits to unemployment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Shoe leather costs are
A)the costs in time and effort incurred by people and firms who are trying to minimize their holdings of cash because of inflation.
B)the costs of changing prices, such as printing and mailing catalogues.
C)the costs of the redistribution of wealth between lenders and borrowers.
D)the costs associated with the confusion of prices as signals.
A)the costs in time and effort incurred by people and firms who are trying to minimize their holdings of cash because of inflation.
B)the costs of changing prices, such as printing and mailing catalogues.
C)the costs of the redistribution of wealth between lenders and borrowers.
D)the costs associated with the confusion of prices as signals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



