Deck 11: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/192
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly
1
An important difference between a perfectly competitive market and a monopolistically competitive market is that,in the latter,
A)there are more sellers of the good
B)there are only a few large sellers
C)there are no barriers to entry or exit
D)there is only one seller of the good
E)the product is not standardized
A)there are more sellers of the good
B)there are only a few large sellers
C)there are no barriers to entry or exit
D)there is only one seller of the good
E)the product is not standardized
the product is not standardized
2
Firms in a monopolistically competitive market follow the same MR = MC profit maximization rule used by firms in other market structures.
True
3
Each of the following,except one,is a characteristic of a monopolistically competitive market.Which is the exception?
A)differentiated products
B)no significant barriers to entry
C)many buyers
D)a standardized product
E)many sellers
A)differentiated products
B)no significant barriers to entry
C)many buyers
D)a standardized product
E)many sellers
a standardized product
4
In the short run,a monopolistic competitor can
A)not earn an economic profit because of competition
B)use limit pricing to reduce competition
C)maximize profits by charging the highest price the market will bear
D)earn an economic profit
E)maximize profit by selecting the minimum efficient scale
A)not earn an economic profit because of competition
B)use limit pricing to reduce competition
C)maximize profits by charging the highest price the market will bear
D)earn an economic profit
E)maximize profit by selecting the minimum efficient scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A firm in a monopolistically competitive market is similar to a monopolist in the sense that it
A)must overcome significant barriers to entry
B)faces a downward-sloping demand curve
C)produces a large share of the market output
D)is dependent on the actions of other firms
E)produces the same product as its competitors do
A)must overcome significant barriers to entry
B)faces a downward-sloping demand curve
C)produces a large share of the market output
D)is dependent on the actions of other firms
E)produces the same product as its competitors do

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A major difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition is the degree of product differentiation.Pure competition has none and differentiation always exists in monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Monopolistically competitive firms are similar to perfectly competitive firms in the sense that both face horizontal demand curves for their product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The model of monopolistic competition assumes that
A)there are only a few sellers
B)there are significant barriers to exit
C)each firm charges the same price for its output
D)the buyers are price setters
E)firms are strategically independent
A)there are only a few sellers
B)there are significant barriers to exit
C)each firm charges the same price for its output
D)the buyers are price setters
E)firms are strategically independent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Firms in a monopolistically competitive market will produce where the difference between TR and TC are maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All of the following,except one,are characteristics of monopolistic competition.Which is the exception?
A)There is a large number of sellers.
B)Each seller faces a horizontal demand curve for its product.
C)There are no significant barriers to entry or exit.
D)Sellers produce differentiated products.
E)There is a large number of buyers.
A)There is a large number of sellers.
B)Each seller faces a horizontal demand curve for its product.
C)There are no significant barriers to entry or exit.
D)Sellers produce differentiated products.
E)There is a large number of buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm
A)is the same as the market demand curve
B)is less elastic than the one faced by firms in perfect competition
C)is perfectly elastic
D)is perfectly inelastic
E)has a constant slope
A)is the same as the market demand curve
B)is less elastic than the one faced by firms in perfect competition
C)is perfectly elastic
D)is perfectly inelastic
E)has a constant slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry maximize profits by
A)equating total revenue and total cost
B)treating price as given and maximizing output
C)minimizing costs
D)producing the level of output at which MR = MC
E)producing the level of output at which TR = TC
A)equating total revenue and total cost
B)treating price as given and maximizing output
C)minimizing costs
D)producing the level of output at which MR = MC
E)producing the level of output at which TR = TC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a market has more than one seller,but fewer sellers than under perfect competition,it is referred to as
A)a monopoly
B)competitive
C)imperfect competition
D)an efficient market
E)optimal
A)a monopoly
B)competitive
C)imperfect competition
D)an efficient market
E)optimal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Of the following markets,which is most likely to be monopolistically competitive?
A)automobiles
B)corn
C)overnight package delivery
D)air travel between a small city and a larger one
E)fast food
A)automobiles
B)corn
C)overnight package delivery
D)air travel between a small city and a larger one
E)fast food

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For the monopolistically competitive firm,
A)competition is blocked by barriers to entry
B)limit pricing can forestall competition indefinitely
C)marginal revenue is less than the product's price
D)price discrimination is a key tool
E)marginal revenue is equal to the product's price
A)competition is blocked by barriers to entry
B)limit pricing can forestall competition indefinitely
C)marginal revenue is less than the product's price
D)price discrimination is a key tool
E)marginal revenue is equal to the product's price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When there are many buyers and sellers,no significant barriers to entry,and a differentiated product,the market structure is called
A)an oligopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)a monopoly
E)unbalanced monopoly
A)an oligopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)a monopoly
E)unbalanced monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All of the following,except one,are sources of product differentiation.Which is the exception?
A)product quality
B)location
C)price
D)consumer tastes
E)buyers' perceptions
A)product quality
B)location
C)price
D)consumer tastes
E)buyers' perceptions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor is
A)a horizontal line at the market price
B)upward sloping
C)perfectly elastic
D)perfectly inelastic
E)downward sloping
A)a horizontal line at the market price
B)upward sloping
C)perfectly elastic
D)perfectly inelastic
E)downward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monopolistic competition exists when there is one large firm in an otherwise perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a monopolistically competitive firm raises its price,
A)quantity demanded falls to zero
B)quantity demanded declines,but not to zero
C)the market supply curve shifts outward
D)the market supply curve shifts inward
E)quantity demanded remains constant
A)quantity demanded falls to zero
B)quantity demanded declines,but not to zero
C)the market supply curve shifts outward
D)the market supply curve shifts inward
E)quantity demanded remains constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
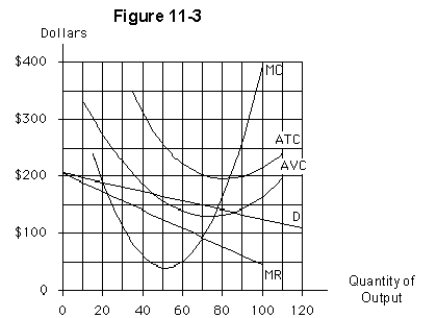
The profit-maximizing price for the firm in Figure 11-3 is
A)$165
B)$150
C)less than $150,but more than $100
D)irrelevant because the firm should shut down immediately
E)less than $100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the short run,a monopolistically competitive firm
A)must earn zero economic profit
B)may earn positive or negative economic profits
C)will produce output up at the point where TR = TC
D)will be protected from competition by barriers to entry
E)will equate price and marginal cost
A)must earn zero economic profit
B)may earn positive or negative economic profits
C)will produce output up at the point where TR = TC
D)will be protected from competition by barriers to entry
E)will equate price and marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

The best outcome the firm illustrated in Figure 11-3 can achieve is a(n)
A)economic loss equal to its fixed cost
B)economic loss of $3,500
C)economic loss of slightly more than $7,000
D)economic loss of approximately $4,000
E)profit per unit of output approximately equal to $40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
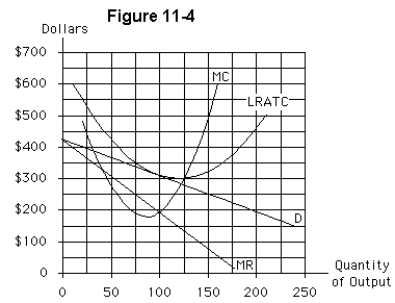
The monopolistically competitive firm shown in Figure 11-4
A)achieves a break-even outcome as its best alternative
B)earns an economic profit in the long run
C)suffers an economic loss in the long run
D)shuts down since it suffers an economic loss
E)produces at the minimum point of its LRATC curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
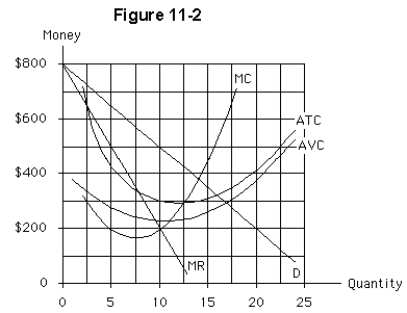
Figure 11-2 illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm.In order to maximize profit,or minimize loss,the firm will
A)close down
B)produce approximately 10 units of output and charge approximately $500
C)produce approximately 7.5 units of output and charge nearly $600
D)produce approximately 12.5 units of output and charge approximately $425
E)produce 5 units of output and charge $650

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

The maximum total economic profit,or minimum economic loss,for the monopolistically competitive firm in Figure 11-2 is
A)zero
B)a profit of $575.00
C)a profit of $1,562.50
D)a profit of $2,000.00
E)a loss of $375.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

The total fixed cost in Figure 11-2 is
A)increasing as more is produced
B)decreasing as more is produced
C)larger than variable costs
D)less than $1,000
E)more than $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
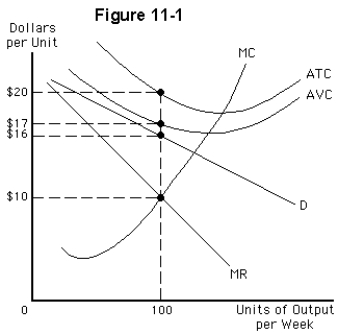
Consider the monopolistically competitive firm whose demand curve and cost structure are illustrated in Figure 11-1.Which of the following statements is correct in the short run?
A)The firm will produce 100 units and suffer a loss of $400 per week.
B)The firm will produce 100 units and suffer a loss of $300 per week.
C)The firm will produce 100 units and suffer a loss of $1,000 per week.
D)The firm will produce 100 units and suffer a loss of $100 per week.
E)The firm will produce zero units and suffer a loss of $300 per week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

At the profit-maximizing,or loss-minimizing,level of output in Figure 11-3,the firm's total cost is approximately
A)$14,000
B)$12,750
C)$9,100
D)$16,185
E)$8,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the firms in a monopolistically competitive market are earning short-run economic profits,then
A)each existing firm will increase output in the long run as its marginal revenue curve shifts rightward
B)each firm will experience an increase in the demand for its output in the long run
C)each firm's profit will drop to normal in the long run as its demand curve shifts leftward due to entry of new firms
D)barriers to entry will enable them to earn economic profits in the long run
E)decreased demand for a key input will reduce that input's price in the long run and lower each firm's average total cost curve
A)each existing firm will increase output in the long run as its marginal revenue curve shifts rightward
B)each firm will experience an increase in the demand for its output in the long run
C)each firm's profit will drop to normal in the long run as its demand curve shifts leftward due to entry of new firms
D)barriers to entry will enable them to earn economic profits in the long run
E)decreased demand for a key input will reduce that input's price in the long run and lower each firm's average total cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

Given the environment illustrated in Figure 11-3,the best outcome the firm can achieve in the short run is
A)both c and e
B)an economic profit
C)to shut down to minimize short-run loss
D)a break-even outcome
E)an economic loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

The profit-maximizing,or loss-minimizing,output for the firm in Figure 11-3 is
A)zero units
B)50 units
C)70 units
D)75 units
E)83 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In monopolistic competition,nonprice competition
A)allows firms to earn above-normal profit in the long run
B)initially causes a leftward shift in the demand curve for each firm's output
C)causes each firm to move upward along a given average total cost curve
D)might lead to economic profit in the short run
E)causes each firm to move toward the right along the given demand curve for its output
A)allows firms to earn above-normal profit in the long run
B)initially causes a leftward shift in the demand curve for each firm's output
C)causes each firm to move upward along a given average total cost curve
D)might lead to economic profit in the short run
E)causes each firm to move toward the right along the given demand curve for its output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

At the profit-maximizing,or loss-minimizing,output level,the firm in Figure 11-2 has total cost approximately equal to
A)$2,000
B)$3,000
C)$3,600
D)$800
E)$1,625

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

The monopolistic competitor in Figure 11-4 will maximize its economic profits,or minimize its losses,by
A)producing 100 units of output and charging $200
B)producing 100 units of output and charging slightly more than $300
C)producing 125 units of output and charging $300
D)shutting down,since it has greater losses at any level of production than at zero
E)producing approximately 180 units of output and charging approximately $225

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
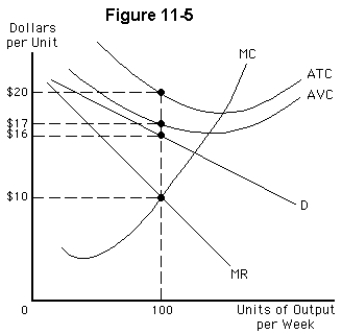
Consider the typical monopolistically competitive firm whose demand curve and cost structure is illustrated in Figure 11-5.Which of the following statements is correct in the long run?
A)Some firms will exit this market,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift rightward.
B)Some firms will exit this market,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift leftward.
C)Firms will enter this market,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift rightward.
D)Firms will enter this market,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift leftward.
E)Firms will enter this market,but the demand curves facing the remaining firms will not change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Assume the firm in Figure 11-2 is currently producing 13 units of output and charging $380 each.The firm
A)will increase its profit if it raises its price and reduces its production level
B)will increase its profit if it lowers its price and expands its production level
C)cannot increase economic profit by changing its price and output since it is already maximizing its profit
D)will increase its profit if it raises its price and expands its production level
E)will increase its profit by lowering its price and reducing its production level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

The firm in Figure 11-2 is monopolistically competitive.The diagram illustrates a
A)shut-down case
B)long-run economic loss
C)short-run economic loss
D)long-run economic profit
E)short-run economic profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

At the profit-maximizing,or loss-minimizing,level of output for the firm in Figure 11-3,total revenue is approximately
A)$10,500
B)$11,000
C)$5,600
D)$8,250
E)zero because the firm should shut down immediately

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

Consider the monopolistically competitive firm whose demand curve and cost structure are illustrated in Figure 11-1.In the short run the firm's fixed costs are
A)$100
B)$200
C)$300
D)$400
E)$500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the long run,monopolistically competitive firms earn zero economic profits because
A)each firm produces a small share of total market output
B)each firm produces a standardized product
C)firms do not equate marginal cost and marginal revenue in the long run
D)there is only one seller in the market
E)entry of new firms eliminate profits
A)each firm produces a small share of total market output
B)each firm produces a standardized product
C)firms do not equate marginal cost and marginal revenue in the long run
D)there is only one seller in the market
E)entry of new firms eliminate profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Any action,other than lowering its price,that a firm undertakes to increase the demand for its output is called
A)limit pricing
B)price enhancement
C)illicit competition
D)nonprice competition
E)price intensive competition
A)limit pricing
B)price enhancement
C)illicit competition
D)nonprice competition
E)price intensive competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Since the demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping,
A)the firm is a price-taker in the short run
B)in the long run there will be excess capacity
C)the output decisions of one firm will influence profits of all other firms
D)the product in the market is viewed by consumers as being standardized
E)the ATC curve is U-shaped
A)the firm is a price-taker in the short run
B)in the long run there will be excess capacity
C)the output decisions of one firm will influence profits of all other firms
D)the product in the market is viewed by consumers as being standardized
E)the ATC curve is U-shaped

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
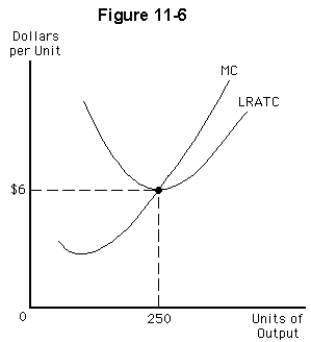
Given the marginal cost and average total cost curves in Figure 11-6,a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium will produce
A)250 units and charge a price of $6
B)less than 250 units and charge a price below $6
C)more than 250 units and charge a price below $6
D)more than 250 units and charge a price above $6
E)less than 250 units and charge a price above $6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the long run,equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm resembles equilibrium for a monopoly in the sense that
A)both types of firms are able to earn economic profits
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
C)price equals marginal cost
D)price exceeds marginal cost
E)average revenue exceeds price
A)both types of firms are able to earn economic profits
B)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
C)price equals marginal cost
D)price exceeds marginal cost
E)average revenue exceeds price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the long run,entry ensures that the typical monopolistically competitive firm will
A)produce at minimum efficient scale
B)earn an economic profit
C)earn a normal profit
D)price its output at marginal cost
E)standardize its product
A)produce at minimum efficient scale
B)earn an economic profit
C)earn a normal profit
D)price its output at marginal cost
E)standardize its product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following best describes the idea of excess capacity in monopolistic competition?
A)Firms produce more output than is socially desirable.
B)The output produced by a typical firm is less than what would occur at the minimum point on its ATC curve.
C)Due to product differentiation,firms choose output levels at which P > ATC.
D)Firms keep some surplus output on hand in case there is a shift in demand for their product.
E)The collective output of all firms in the market typically exceeds the quantity demanded.
A)Firms produce more output than is socially desirable.
B)The output produced by a typical firm is less than what would occur at the minimum point on its ATC curve.
C)Due to product differentiation,firms choose output levels at which P > ATC.
D)Firms keep some surplus output on hand in case there is a shift in demand for their product.
E)The collective output of all firms in the market typically exceeds the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
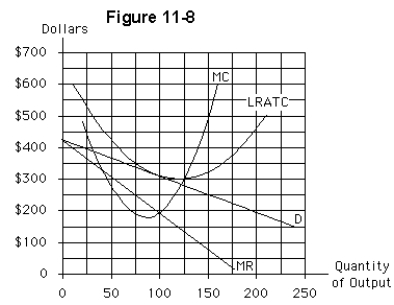
If the monopolistically competitive firm in Figure 11-8 is typical of its competitors,the industry will likely experience
A)increasing returns to scale
B)entry of new firms
C)exit of existing firms
D)no change in the long run
E)exit of all firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
At the long-run equilibrium output level,a monopolistically competitive firm's average total cost curve
A)lies below the demand curve
B)is tangent to (just touches but does not cross)the demand curve
C)crosses the demand curve from below
D)crosses the demand curve from above
E)is at its minimum point
A)lies below the demand curve
B)is tangent to (just touches but does not cross)the demand curve
C)crosses the demand curve from below
D)crosses the demand curve from above
E)is at its minimum point

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Excess capacity arises when firms cannot sell all of their output at the current market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the long run,a monopolistic competitor will
A)always produce at minimum efficient scale
B)produce too little output to achieve minimum cost per unit
C)use limit pricing to forestall competition
D)earn economic profits
E)standardize its product
A)always produce at minimum efficient scale
B)produce too little output to achieve minimum cost per unit
C)use limit pricing to forestall competition
D)earn economic profits
E)standardize its product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Camille's Chicken operates in a monopolistically competitive market.If Camille implements a new free delivery service for customers,
A)this is an example of advertising
B)this is a form of nonprice competition
C)total revenue will increase
D)total cost will decrease
E)her firm will be acting as if it were perfectly competitive market
A)this is an example of advertising
B)this is a form of nonprice competition
C)total revenue will increase
D)total cost will decrease
E)her firm will be acting as if it were perfectly competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the long run,a monopolistically competitive firm will produce too little output to minimize average cost.Therefore,it will have
A)positive economic profit
B)negative economic profit
C)excess profit
D)X-inefficiency
E)excess capacity
A)positive economic profit
B)negative economic profit
C)excess profit
D)X-inefficiency
E)excess capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An oligopoly is a market
A)dominated by a single seller
B)dominated by a single buyer
C)dominated by a small number of strategically interdependent firms
D)with many buyers and sellers,no barriers to entry and differentiated products
E)with many buyers and sellers,no barriers to entry and a standardized product
A)dominated by a single seller
B)dominated by a single buyer
C)dominated by a small number of strategically interdependent firms
D)with many buyers and sellers,no barriers to entry and differentiated products
E)with many buyers and sellers,no barriers to entry and a standardized product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
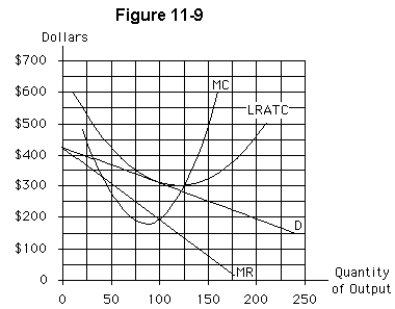
Which of the following is not true of the firm in Figure 11-9?
A)It has excess capacity.
B)It produces at the minimum efficient scale of production.
C)It cannot earn an economic profit.
D)It is operating in the long run.
E)It has no fixed costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is an example of nonprice competition?
A)giving coupons for 10 percent discounts to potential customers
B)having a Memorial Day Sale
C)lowering the price on several selected brands
D)offering a product in three colors-blue,green,and red-in addition to the standard black
E)increasing the price on all products
A)giving coupons for 10 percent discounts to potential customers
B)having a Memorial Day Sale
C)lowering the price on several selected brands
D)offering a product in three colors-blue,green,and red-in addition to the standard black
E)increasing the price on all products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A market in which a small number of strategically interdependent firms produce the dominant share of output is called
A)perfect competition
B)a monopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)regulated
E)an oligopoly
A)perfect competition
B)a monopoly
C)monopolistic competition
D)regulated
E)an oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
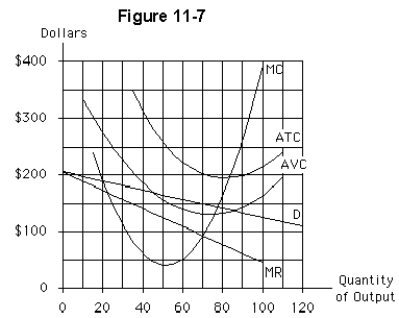
If the firm represented in Figure 11-7 is typical of other firms in the industry,then,as the long run approaches,
A)some firms will exit,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift to the left
B)some firms will exit,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift to the right
C)some firms will enter,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift to the left
D)some firms will enter,and the demand curves facing the remaining firms will shift to the right
E)the industry will eventually disappear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In monopolistic competition,product differentiation causes
A)the firms to earn economic profits in the long run
B)a horizontal demand curve for each firm's output
C)the firms to operate with excess capacity
D)significant barriers to entry
E)high concentration ratios
A)the firms to earn economic profits in the long run
B)a horizontal demand curve for each firm's output
C)the firms to operate with excess capacity
D)significant barriers to entry
E)high concentration ratios

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Cecilia's Cafe is a monopolistic competitor.If Cecilia's is currently producing at the output level at which her average total cost is minimized and the cafe is earning an economic profit,then,in the long run,output will
A)decline and average total cost will increase
B)decline and average total cost will decrease
C)remain unchanged as Cecilia's strives to minimize costs
D)increase and average total cost will be greater
E)increase and average total cost will be smaller
A)decline and average total cost will increase
B)decline and average total cost will decrease
C)remain unchanged as Cecilia's strives to minimize costs
D)increase and average total cost will be greater
E)increase and average total cost will be smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Oligopolies feature
A)the absence of barriers to entry
B)extensive competition
C)the goal of profit maximization
D)strategic interaction of firms
E)product differentiation
A)the absence of barriers to entry
B)extensive competition
C)the goal of profit maximization
D)strategic interaction of firms
E)product differentiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
All of the following are examples of barriers to entry,except one.Which is the exception?
A)significant economies of scale
B)reputation of established firms
C)special deals with distributors
D)excessive prices
E)patents
A)significant economies of scale
B)reputation of established firms
C)special deals with distributors
D)excessive prices
E)patents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The output level at which a firm's long-run average total cost is minimized is known as its
A)profit-maximizing output level
B)long-run marginal cost
C)minimum efficient scale
D)revenue maximization level
E)equilibrium cost structure
A)profit-maximizing output level
B)long-run marginal cost
C)minimum efficient scale
D)revenue maximization level
E)equilibrium cost structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
By keeping new firms from entering the market,oligopolies are more likely to have
A)long-run economic profit
B)low prices
C)great efficiency
D)decreasing marginal costs
E)economies of scale
A)long-run economic profit
B)low prices
C)great efficiency
D)decreasing marginal costs
E)economies of scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In order for a market to be classified as an oligopoly,
A)there must be fewer than 10 firms
B)the four largest firms must have 90 percent of the market
C)there must be fewer than 5 firms
D)the firms must be strategically interacting
E)the firms must be strategically independent
A)there must be fewer than 10 firms
B)the four largest firms must have 90 percent of the market
C)there must be fewer than 5 firms
D)the firms must be strategically interacting
E)the firms must be strategically independent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The airline and long-distance telephone service industries are examples of
A)monopolistic competition
B)monopolies
C)oligopolies
D)perfect competition
E)oligopolistic competition
A)monopolistic competition
B)monopolies
C)oligopolies
D)perfect competition
E)oligopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The key characteristic of oligopoly is
A)that firms are price takers
B)strategic interaction among firms
C)strategic independence among firms
D)that firms deal with few resource suppliers
E)a low minimum efficient scale of production
A)that firms are price takers
B)strategic interaction among firms
C)strategic independence among firms
D)that firms deal with few resource suppliers
E)a low minimum efficient scale of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Natural oligopolies occur when
A)the government establishes a market with a few large producers
B)the market output could be produced at a higher cost by several large firms rather than many small firms
C)there are no barriers to entry
D)the total market output could be produced at a lower cost by several large firms rather than many small firms
E)one large firm can produce the total market output at a lower cost than several smaller firms could
A)the government establishes a market with a few large producers
B)the market output could be produced at a higher cost by several large firms rather than many small firms
C)there are no barriers to entry
D)the total market output could be produced at a lower cost by several large firms rather than many small firms
E)one large firm can produce the total market output at a lower cost than several smaller firms could

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A firm's minimum efficient scale occurs where the long-run average total cost curve reaches its minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Oligopoly
A)is a market structure of many small firms
B)is the only seller of a good or service
C)is a market structure of a few consumers of a product
D)is a market structure of a few interdependent firms
E)is a more efficient market structure than perfect competition
A)is a market structure of many small firms
B)is the only seller of a good or service
C)is a market structure of a few consumers of a product
D)is a market structure of a few interdependent firms
E)is a more efficient market structure than perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A natural oligopoly occurs when
A)few firms can afford to compete in the industry
B)the minimum efficient scale is a large fraction of the market
C)there are a large number of buyers and sellers of a standardized product
D)minimum efficient scale is greater than total market demand at the price equal to minimum long run average total cost
E)competitive pricing drives firms from the market
A)few firms can afford to compete in the industry
B)the minimum efficient scale is a large fraction of the market
C)there are a large number of buyers and sellers of a standardized product
D)minimum efficient scale is greater than total market demand at the price equal to minimum long run average total cost
E)competitive pricing drives firms from the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is a distinguishing characteristic of oligopolies?
A)a standardized product
B)the goal of profit maximization
C)the interdependence among firms
D)downward-sloping demand curves faced by firms
E)a downward-sloping market demand curve
A)a standardized product
B)the goal of profit maximization
C)the interdependence among firms
D)downward-sloping demand curves faced by firms
E)a downward-sloping market demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If consumers are loyal to the products of an existing firm,this loyalty may
A)reduce the incentives for the firm to invest
B)result in more responsive management and better quality products
C)reduce the demand for imported goods
D)serve as a barrier to new entry into the market
E)force the firm to produce at higher costs
A)reduce the incentives for the firm to invest
B)result in more responsive management and better quality products
C)reduce the demand for imported goods
D)serve as a barrier to new entry into the market
E)force the firm to produce at higher costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
One strategic barrier that may keep new firms out of a market is
A)producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
B)a low minimum efficient scale
C)bounded markup pricing
D)efficiency wages,which may make it impossible for new entrants to compete profitably
E)excess capacity,which may serve as a signal to new entrants to stay away
A)producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue
B)a low minimum efficient scale
C)bounded markup pricing
D)efficiency wages,which may make it impossible for new entrants to compete profitably
E)excess capacity,which may serve as a signal to new entrants to stay away

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following must be true in an oligopoly?
A)The firms produce a differentiated product.
B)There is one dominant firm in the market.
C)The firms are strategically interacting.
D)The market is international in scope.
E)There are no significant barriers to entry.
A)The firms produce a differentiated product.
B)There is one dominant firm in the market.
C)The firms are strategically interacting.
D)The market is international in scope.
E)There are no significant barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
One explanation for why oligopolies exist is that
A)it is easier to regulate a smaller number of firms
B)minimum efficient scale is small relative to the market,allowing a large number of firms to achieve minimum long-run average total cost
C)minimum efficient scale is large relative to the market,allowing only a few firms to achieve minimum long-run average total cost
D)minimum efficient scale may be greater than the market quantity demanded at the price equal to minimum long-run average total cost
E)competitive pricing drives firms from the market
A)it is easier to regulate a smaller number of firms
B)minimum efficient scale is small relative to the market,allowing a large number of firms to achieve minimum long-run average total cost
C)minimum efficient scale is large relative to the market,allowing only a few firms to achieve minimum long-run average total cost
D)minimum efficient scale may be greater than the market quantity demanded at the price equal to minimum long-run average total cost
E)competitive pricing drives firms from the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a market is dominated by a few large,interdependent firms,it is said to be a(n)
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)integrated monopoly
D)monopolistically competitive market
E)perfectly competitive market
A)oligopoly
B)monopoly
C)integrated monopoly
D)monopolistically competitive market
E)perfectly competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A market with more than one seller and significant barriers to entry is called
A)perfect competition
B)monopolistic competition
C)an oligopoly
D)collusive
E)regulated
A)perfect competition
B)monopolistic competition
C)an oligopoly
D)collusive
E)regulated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In which market structure do firms consider the actions of their rivals when setting prices and output?
A)monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)perfect competition
D)both monopoly and perfect competition
E)monopolistic competition
A)monopoly
B)oligopoly
C)perfect competition
D)both monopoly and perfect competition
E)monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If the sellers in a market are aware of their strategic interdependence,then
A)each firm bases its pricing and output decisions on the monopoly model
B)each firm,when making pricing or output decisions,must consider the reactions of its competitors
C)the firms have little incentive to collude in their pricing and output decisions
D)the firms undertake little advertising because they cannot recoup the cost through higher prices
E)no firm is able to earn above-normal profit in the long run
A)each firm bases its pricing and output decisions on the monopoly model
B)each firm,when making pricing or output decisions,must consider the reactions of its competitors
C)the firms have little incentive to collude in their pricing and output decisions
D)the firms undertake little advertising because they cannot recoup the cost through higher prices
E)no firm is able to earn above-normal profit in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 192 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



