Deck 6: Consumer Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/143
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Consumer Choice
1
The intercept of a budget line measures the
A)amount of a good that a consumer will purchase
B)maximum amount of a good that a consumer could purchase,given his consumption of some other good
C)maximum amount of a good that could be consumed at given prices and income
D)minimum amount of a good that could be consumed at given prices and income
E)minimum consumption of a good consistent with utility maximization
A)amount of a good that a consumer will purchase
B)maximum amount of a good that a consumer could purchase,given his consumption of some other good
C)maximum amount of a good that could be consumed at given prices and income
D)minimum amount of a good that could be consumed at given prices and income
E)minimum consumption of a good consistent with utility maximization
maximum amount of a good that could be consumed at given prices and income
2
If a consumer's budget line between meat and potatoes has a vertical axis intercept at 100 pounds of meat and a horizontal axis intercept at 100 pounds of potatoes
A)demand must be inelastic
B)the consumer's budget must equal $100
C)both meat and potatoes must be priced at $1 per pound
D)the price of a pound of meat must equal the price of a pound of potatoes
E)the opportunity cost of meat in terms of potatoes cannot be determined
A)demand must be inelastic
B)the consumer's budget must equal $100
C)both meat and potatoes must be priced at $1 per pound
D)the price of a pound of meat must equal the price of a pound of potatoes
E)the opportunity cost of meat in terms of potatoes cannot be determined
the price of a pound of meat must equal the price of a pound of potatoes
3
A family on a trip budgets $800 for restaurant meals and fast food.The price of a fast-food meal is $20 and the family can afford 16 restaurant meals if they don't buy any fast food.How many fast-food meals would the family gain if they gave up one restaurant meal?
A)1
B)0.4
C)2
D)2.5
E)5
A)1
B)0.4
C)2
D)2.5
E)5
2.5
4
If income doubles and the prices of all goods remain the same,the budget line will shift outward by 50 percent along each axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The ratio of the prices of two goods multiplied by -1 is equal to the slope of the budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The ratio of the price of the good on the horizontal axis divided by the price of the good on the vertical axis multiplied by -1
A)is the slope of the demand curve
B)measures the price elasticity of demand for a particular good
C)defines real income for the consumer
D)is the slope of the budget line
E)is the slope of the indifference curve
A)is the slope of the demand curve
B)measures the price elasticity of demand for a particular good
C)defines real income for the consumer
D)is the slope of the budget line
E)is the slope of the indifference curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If income decreases,there will be a parallel inward shift of the budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A family on a trip budgets $800 for restaurant meals and fast food.The family can buy 16 restaurant meals if they don't buy any fast food.What is the price of a fast-food meal for the family?
A)$5
B)$16
C)$20
D)$50
E)it is impossible to tell from the information given
A)$5
B)$16
C)$20
D)$50
E)it is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose that Trey spends all of his income on vacation trips and textbooks.If the price of a trip is $200 and the price of a textbook is $50,then the slope of his budget line (assuming vacation trips are measured on the vertical axis)would be
A)-4
B)4
C)0.25
D)-1.75
E)-0.25
A)-4
B)4
C)0.25
D)-1.75
E)-0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the price of bread were zero,a budget line between bread (on the vertical axis)and cheese (on the horizontal axis)would
A)not exist
B)be vertical
C)coincide with the vertical axis
D)be horizontal
E)coincide with the horizontal axis
A)not exist
B)be vertical
C)coincide with the vertical axis
D)be horizontal
E)coincide with the horizontal axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A family on a trip budgets $800 for sit-down restaurant meals and fast food.The family can buy 16 restaurant meals if they don't buy any fast food.What is the price of a restaurant meal for the family?
A)$5
B)$16
C)$20
D)$50
E)it is impossible to tell from the information given
A)$5
B)$16
C)$20
D)$50
E)it is impossible to tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 6-1
Income = $ 100
Price per Ticket = $20
Price per Compact Disk $ 10
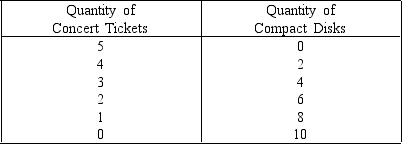
Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-1 shows his budget constraint when his income is $100.The price of a ticket is $20,while the price of a compact disk is $10.What is the opportunity cost of a compact disk?
A)1/2 ticket
B)$20
C)$10
D)1 ticket
E)2 tickets
Income = $ 100
Price per Ticket = $20
Price per Compact Disk $ 10

Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-1 shows his budget constraint when his income is $100.The price of a ticket is $20,while the price of a compact disk is $10.What is the opportunity cost of a compact disk?
A)1/2 ticket
B)$20
C)$10
D)1 ticket
E)2 tickets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The slope of the budget line
A)is always -1
B)represents the opportunity cost of consuming one more unit of the good measured on the horizontal axis
C)increases as more of one good is consumed
D)decreases as more of one good is consumed
E)is negative because of the law of demand
A)is always -1
B)represents the opportunity cost of consuming one more unit of the good measured on the horizontal axis
C)increases as more of one good is consumed
D)decreases as more of one good is consumed
E)is negative because of the law of demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A family on a trip budgets $800 for sit-down restaurant meals and fast food.If the price of a fast food meal for the family is $20,how many such meals can the family buy if they do not eat at restaurants?
A)8
B)15
C)20
D)40
E)160
A)8
B)15
C)20
D)40
E)160

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Figure 6-1
Income = $ 100
Price per Ticket = $20
Price per Compact Disk $ 10

Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-1 shows his budget constraint when his income is $100.The price of a ticket is $20,while the price of a compact disk is $10.If Joe currently buys 3 tickets and would like to purchase a fourth,his opportunity cost would be
A)1 compact disk
B)$20
C)$10
D)2 compact disks
E)4 compact disks
Income = $ 100
Price per Ticket = $20
Price per Compact Disk $ 10

Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-1 shows his budget constraint when his income is $100.The price of a ticket is $20,while the price of a compact disk is $10.If Joe currently buys 3 tickets and would like to purchase a fourth,his opportunity cost would be
A)1 compact disk
B)$20
C)$10
D)2 compact disks
E)4 compact disks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Budget constraints exist for consumers because
A)their utility from consuming goods eventually reaches a maximum level
B)even with unlimited incomes,they have to pay for each good they consume
C)they have to pay for goods and they have limited incomes
D)prices and income are inversely related
E)demand curves for goods generally slope downward
A)their utility from consuming goods eventually reaches a maximum level
B)even with unlimited incomes,they have to pay for each good they consume
C)they have to pay for goods and they have limited incomes
D)prices and income are inversely related
E)demand curves for goods generally slope downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A consumer's budget line shows
A)the utility that an individual would receive from consuming various combinations of two goods
B)the combinations of two goods that an individual is able to purchase,given prices and income
C)how income is influenced by prices of goods
D)how changes in income affect utility
E)the relationship between prices and income
A)the utility that an individual would receive from consuming various combinations of two goods
B)the combinations of two goods that an individual is able to purchase,given prices and income
C)how income is influenced by prices of goods
D)how changes in income affect utility
E)the relationship between prices and income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If income decreases,the budget constraint will shift in but the slope will remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If food is measured on the horizontal axis of a budget line diagram,and clothing is measured on the vertical axis,the slope of the budget line
A)may be positive if the price of clothing is high enough
B)may be positive if the price of food is high enough
C)may be positive if income is large enough
D)equals the maximum consumption of food divided by the maximum consumption of clothing times -1
E)equals the maximum consumption of clothing divided by the maximum consumption of food times -1
A)may be positive if the price of clothing is high enough
B)may be positive if the price of food is high enough
C)may be positive if income is large enough
D)equals the maximum consumption of food divided by the maximum consumption of clothing times -1
E)equals the maximum consumption of clothing divided by the maximum consumption of food times -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The budget line is useful for illustrating the notion of opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
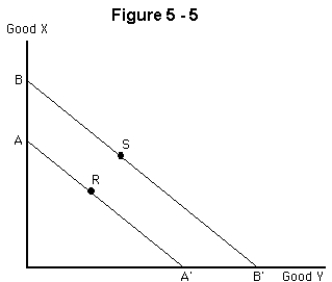
Suppose that a consumer used to be at point R on budget line AA' in Figure 6-5,and is now at point S on line BB'.Which of the following is true if the consumer enjoys both goods?
A)The utility level at point S is higher than at point R.
B)Good X is an inferior good.
C)The consumer's income fell.
D)The price of X rose.
E)The utility level at point S is lower than at point R.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 6-3
Income = $ 200
Price per Ticket = $40
Price per Compact Disk $ 20
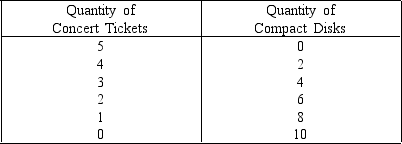
Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-3 shows his budget constraint when his income is $200.The price of a ticket is $40,while the price of a compact disk is $20.What would happen to Joe's budget line if his income increased to $300 and the prices of concert tickets and compact disks each increased by 50 percent?
A)There would be no change in the budget line.
B)His budget line would shift upward by 50 percent.
C)His budget line would shift downward by 50 percent.
D)He could purchase 50 percent more compact disks and the same number of tickets as before.
E)He could purchase 50 percent more tickets and the same number of compact disks as before.
Income = $ 200
Price per Ticket = $40
Price per Compact Disk $ 20

Joe spends all of his money on concert tickets and compact disks.Figure 6-3 shows his budget constraint when his income is $200.The price of a ticket is $40,while the price of a compact disk is $20.What would happen to Joe's budget line if his income increased to $300 and the prices of concert tickets and compact disks each increased by 50 percent?
A)There would be no change in the budget line.
B)His budget line would shift upward by 50 percent.
C)His budget line would shift downward by 50 percent.
D)He could purchase 50 percent more compact disks and the same number of tickets as before.
E)He could purchase 50 percent more tickets and the same number of compact disks as before.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
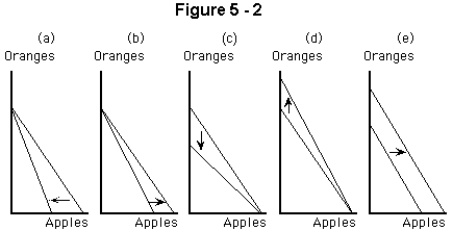
Which panel in Figure 6-2 shows the combined effects of an increase in the price of oranges and a decrease in the price of apples?
A)panel a
B)panel b
C)panel c
D)panel d
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Roger spends all of his money on racquetballs and food.What would happen to Roger's budget line if his income increased by 10 percent,holding prices constant?
A)It would shift inward.
B)It would rotate about the axis for food.
C)It would rotate about the axis for racquetballs.
D)Nothing would happen to the budget line,because the relative prices for food and racquetballs have not changed.
E)It would shift outward.
A)It would shift inward.
B)It would rotate about the axis for food.
C)It would rotate about the axis for racquetballs.
D)Nothing would happen to the budget line,because the relative prices for food and racquetballs have not changed.
E)It would shift outward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An increase in the price of the good measured on the vertical axis of a budget line diagram will
A)cause a parallel outward shift of the budget line
B)leave the budget line unchanged
C)cause a parallel inward shift of the budget line
D)make the budget line flatter
E)make the budget line steeper
A)cause a parallel outward shift of the budget line
B)leave the budget line unchanged
C)cause a parallel inward shift of the budget line
D)make the budget line flatter
E)make the budget line steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

Which panel in Figure 6-2 shows the effect of a decrease in the price of apples,other things constant?
A)panel a
B)panel b
C)panel c
D)panel d
E)panel e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
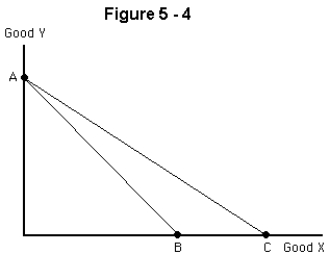
Suppose that a consumer's original budget line was AC in Figure 6-4,but it has now changed to line AB.Which of the following must have occurred?
A)The price of good X must have risen.
B)The price of good Y must have risen.
C)The price of good Y must have fallen.
D)The price of good X must have fallen.
E)The consumer's income must have risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An increase in the price of the good measured on the horizontal axis of a budget line diagram will
A)make the budget line flatter
B)make the budget line steeper
C)leave the budget line unchanged
D)cause a parallel inward shift of the budget line
E)cause a parallel outward shift of the budget line
A)make the budget line flatter
B)make the budget line steeper
C)leave the budget line unchanged
D)cause a parallel inward shift of the budget line
E)cause a parallel outward shift of the budget line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

Suppose that a consumer used to be at point S on budget line BB' in Figure 6-5,and is now at point R on line AA'.Which of the following is true?
A)The price of X rose.
B)The price of X fell.
C)The consumer's income fell.
D)The utility level at point R is higher than at point S.
E)The substitution effect is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If income and the prices of both goods all double,the budget line will
A)become flatter
B)become steeper
C)remain unchanged
D)experience a parallel outward shift
E)experience a parallel inward shift
A)become flatter
B)become steeper
C)remain unchanged
D)experience a parallel outward shift
E)experience a parallel inward shift

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If food is measured on the horizontal axis of a budget line diagram,and clothing is measured on the vertical axis,an increase in
A)the price of food will decrease the slope (e.g. ,-9 instead of -6)of the budget line
B)the price of food will increase the slope of the budget line
C)income will decrease the slope of the budget line
D)income will increase the slope of the budget line
E)the price of clothing will decrease the slope of the budget line
A)the price of food will decrease the slope (e.g. ,-9 instead of -6)of the budget line
B)the price of food will increase the slope of the budget line
C)income will decrease the slope of the budget line
D)income will increase the slope of the budget line
E)the price of clothing will decrease the slope of the budget line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following could change a consumer's budget line?
A)a change in utility
B)an increase in the availability of substitute goods
C)additional responsibilities taken on by the consumer
D)a change in the price of one or more goods
E)a reduction in the level of technical inefficiency in the market
A)a change in utility
B)an increase in the availability of substitute goods
C)additional responsibilities taken on by the consumer
D)a change in the price of one or more goods
E)a reduction in the level of technical inefficiency in the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Imagine a budget line depicting a consumer's possible allocation of a given income between fruit and vegetables.If the consumer's income increases at the same time the price of vegetables rises,the budget line's intercept with the
A)fruit axis will be unaffected
B)fruit axis will move toward the origin
C)vegetable axis will be unaffected
D)fruit axis will move toward the origin.
E)vegetable axis might remain unchanged,move toward the origin,or move away from the origin
A)fruit axis will be unaffected
B)fruit axis will move toward the origin
C)vegetable axis will be unaffected
D)fruit axis will move toward the origin.
E)vegetable axis might remain unchanged,move toward the origin,or move away from the origin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the price of good X (measured on the horizontal axis of a budget line diagram)increases at the same time that the price of good Y (measured on the vertical axis)decreases,the budget line
A)will become flatter
B)will become steeper
C)could become either steeper or flatter,depending on the sizes of the price changes
D)will rotate about its original point of intersection with the horizontal axis
E)will shift outward,but not in a parallel fashion
A)will become flatter
B)will become steeper
C)could become either steeper or flatter,depending on the sizes of the price changes
D)will rotate about its original point of intersection with the horizontal axis
E)will shift outward,but not in a parallel fashion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If food is measured on the horizontal axis of budget line diagram,and clothing is measured on the vertical axis,an increase in
A)the price of clothing will make the budget line steeper
B)income will make the budget line steeper
C)income will make the budget line flatter
D)the price of food will make the budget line steeper
E)the price of food will make the budget line flatter
A)the price of clothing will make the budget line steeper
B)income will make the budget line steeper
C)income will make the budget line flatter
D)the price of food will make the budget line steeper
E)the price of food will make the budget line flatter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Economists usually assume that all consumers have the same tastes and preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Suppose that a consumer's original budget line was AB in Figure 6-4,but it has now changed to line AC.Which of the following must have occurred?
A)The price of good X must have risen.
B)The price of good Y must have risen.
C)The price of good Y must have fallen.
D)The price of good X must have fallen.
E)The consumer's income must have risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

Which panel in Figure 6-2 shows the effect of an increase in the price of oranges,other things constant?
A)panel a
B)panel b
C)panel c
D)panel d
E)panel e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the price of good X (measured on the horizontal axis of a budget line diagram)increases at the same time that the price of good Y (measured on the vertical axis)increases,the budget line
A)will necessarily become steeper
B)will necessarily become flatter
C)will remain unchanged
D)will shift outward in a parallel fashion
E)could become either steeper or flatter,depending on the sizes of the price changes
A)will necessarily become steeper
B)will necessarily become flatter
C)will remain unchanged
D)will shift outward in a parallel fashion
E)could become either steeper or flatter,depending on the sizes of the price changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

Which panel in Figure 6-2 shows the effect of an increase in income,other things constant?
A)panel a
B)panel b
C)panel c
D)panel d
E)panel e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consuming goods until the ratio of marginal utilities of the goods is equal to the ratio of their prices is consistent with maximizing total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
As Reba consumes four slices of pizza,her total utility rises from 0 to 18,to 24,to 28,and to 30,respectively.What is her marginal utility of the first slice of pizza?
A)18
B)24
C)2
D)7
E)8
A)18
B)24
C)2
D)7
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Marginal utility is the extra utility a consumer derives from consuming an extra unit of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If Bill asks for a second helping of pancakes,then his
A)second helping must be free
B)marginal utility of the second helping must be negative
C)price per helping is too low
D)marginal utility of the second helping must be positive
E)marginal utility of the second helping must be less than the marginal utility of the first helping
A)second helping must be free
B)marginal utility of the second helping must be negative
C)price per helping is too low
D)marginal utility of the second helping must be positive
E)marginal utility of the second helping must be less than the marginal utility of the first helping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The change in total utility arising from a one-unit increase in consumption of a good is referred to as
A)average utility
B)the principle of diminishing marginal utility
C)real income
D)marginal utility
E)price
A)average utility
B)the principle of diminishing marginal utility
C)real income
D)marginal utility
E)price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consuming to the point where the marginal utility of each good is equal to the price of that good is consistent with utility maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Marginal utility
A)increases as more of a good is consumed
B)increases as the total utility of consuming a good increases
C)is the same as the utility of consuming a good
D)is the same as the utility of consuming an additional unit of a good
E)is the same for all units of a good,but varies from one consumer to another
A)increases as more of a good is consumed
B)increases as the total utility of consuming a good increases
C)is the same as the utility of consuming a good
D)is the same as the utility of consuming an additional unit of a good
E)is the same for all units of a good,but varies from one consumer to another

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
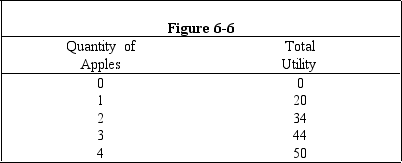
Figure 6-6 shows the total utility that Jerry would receive from consuming several different quantities of apples per week.What can be said about Jerry's utility schedule for apples?
A)It conforms to the law of supply.
B)Marginal utility rises as consumption rises.
C)Average utility rises as consumption rises.
D)It conforms to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
E)The marginal and total utility lines cross at four apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that total utility falls as consumption rises above a certain level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

Figure 6-6 shows the total utility that Jerry would receive from consuming different numbers of apples per week.What is Jerry's marginal utility from consuming the second apple after he already consumed the first one?
A)0
B)17
C)20
D)14
E)34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If marginal utility from consuming an extra unit of a good is positive,then the consumer's total utility must increase as more of the good is consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If diminishing marginal utility holds,and a person consumes less of a good,then all else being equal
A)the price of the good will rise
B)total utility will rise
C)marginal utility will rise
D)expenditure on the good will increase
E)marginal utility will decline
A)the price of the good will rise
B)total utility will rise
C)marginal utility will rise
D)expenditure on the good will increase
E)marginal utility will decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

Which of the following most clearly illustrates the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A)The total satisfaction from consuming a good falls as more of the good is consumed.
B)Marginal utility falls as total utility falls.
C)The quantity of a good demanded falls as its price rises.
D)The additional satisfaction from consuming a good falls as more of the good is consumed.
E)There is a direct relationship between the price of a good and its total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The law of diminishing marginal utility
A)is valid only after basic necessities (such as food and shelter)have been obtained
B)says that marginal utility decreases as more of a good is consumed
C)implies that spending on a good will decrease as more of that good is consumed
D)says that marginal utility decreases as income increases
E)implies that spending on a good decreases as income increases
A)is valid only after basic necessities (such as food and shelter)have been obtained
B)says that marginal utility decreases as more of a good is consumed
C)implies that spending on a good will decrease as more of that good is consumed
D)says that marginal utility decreases as income increases
E)implies that spending on a good decreases as income increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A rational consumer who prefers one apple to two oranges,and two oranges to one orange,
A)must prefer two oranges to one apple
B)must prefer one apple to one orange
C)must prefer two oranges to two apples
D)must be indifferent between two oranges and two apples
E)might prefer one orange to one apple
A)must prefer two oranges to one apple
B)must prefer one apple to one orange
C)must prefer two oranges to two apples
D)must be indifferent between two oranges and two apples
E)might prefer one orange to one apple

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
According to the assumption of consumer rationality,a consumer who prefers one head of broccoli to one head of cauliflower,one head of cauliflower to one package of brussel sprouts,and one
A)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of cabbage to a head of cauliflower
B)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of broccoli to any other vegetable
C)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a package of brussel sprouts to a head of cauliflower
D)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of cauliflower to a head of cabbage
E)head of cabbage to one package of brussel sprouts,must prefer the package of brussel sprouts to a head of broccoli
A)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of cabbage to a head of cauliflower
B)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of broccoli to any other vegetable
C)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a package of brussel sprouts to a head of cauliflower
D)package of brussel sprouts to one head of cabbage,must prefer a head of cauliflower to a head of cabbage
E)head of cabbage to one package of brussel sprouts,must prefer the package of brussel sprouts to a head of broccoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

Figure 6-6 shows the total utility that Jerry receives from consuming different numbers of apples per week.What is his marginal utility from the fourth apple ?
A)20
B)6
C)34
D)14
E)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The feature of preferences that "more is better"
A)is a logical consequence of transitivity
B)is shared by most people,most of the time.
C)implies that 5 apples will always be preferred to 4 oranges
D)implies that 5 apples will always be preferred to 5 oranges
E)means that,when dining,people always try to eat as much as they possibly can
A)is a logical consequence of transitivity
B)is shared by most people,most of the time.
C)implies that 5 apples will always be preferred to 4 oranges
D)implies that 5 apples will always be preferred to 5 oranges
E)means that,when dining,people always try to eat as much as they possibly can

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
As Reba consumes four slices of pizza,her total utility rises from 0 to 18,to 24,to 28,and to 30,respectively.What is her marginal utility of the fourth slice of pizza?
A)28
B)24
C)2
D)7
E)8
A)28
B)24
C)2
D)7
E)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Economists usually assume
A)that Americans' preferences are systematically different from Europeans
B)that there are some features common to the preferences of a wide variety of people
C)that everyone has the same preferences
D)that everyone has the same preferences that they (the economists)do
E)that individuals prefer to purchases goods rather than services
A)that Americans' preferences are systematically different from Europeans
B)that there are some features common to the preferences of a wide variety of people
C)that everyone has the same preferences
D)that everyone has the same preferences that they (the economists)do
E)that individuals prefer to purchases goods rather than services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Beginning at the vertical axis intercept,as a consumer moves down the budget line,she will find that
A)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good decreases
B)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good increases
C)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good increases
D)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods increase
E)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods remain constant along that particular budget line
A)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good decreases
B)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good increases
C)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good increases
D)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods increase
E)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods remain constant along that particular budget line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If all consumers satisfy economists' assumptions regarding utility,then
A)they will each choose a consumption bundle that is inside the budget line
B)everyone will choose the same consumption bundle
C)everyone will have the same budget line
D)all consumers will react in the same way to a price change
E)each person will choose a consumption bundle on his or her budget line
A)they will each choose a consumption bundle that is inside the budget line
B)everyone will choose the same consumption bundle
C)everyone will have the same budget line
D)all consumers will react in the same way to a price change
E)each person will choose a consumption bundle on his or her budget line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A utility-maximizing consumer will choose a collection of goods
A)represented by a point below her budget line
B)represented by a point above her budget line
C)for which the marginal utility from each good is the same
D)for which the marginal utility divided by the price is the same or each good
E)for which the total utility from each good is the same
A)represented by a point below her budget line
B)represented by a point above her budget line
C)for which the marginal utility from each good is the same
D)for which the marginal utility divided by the price is the same or each good
E)for which the total utility from each good is the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that the price of a pizza is $10 and that the price of a blouse is $30.At her present level of consumption,Magda's ratio of marginal utility of pizza to marginal utility of blouses is 1/4.To maximize total utility,she should
A)buy more pizzas and fewer blouses
B)buy fewer pizzas and more blouses
C)continue to buy the same quantities of pizza and blouses
D)spend more time consuming pizza
E)spend more time buying blouses
A)buy more pizzas and fewer blouses
B)buy fewer pizzas and more blouses
C)continue to buy the same quantities of pizza and blouses
D)spend more time consuming pizza
E)spend more time buying blouses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Beginning at the horizontal axis intercept,as a consumer moves upward along the budget line,he will find that
A)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good increases
B)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good increases
C)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good decreases
D)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods increase
E)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods remain constant along that particular budget line
A)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the vertical axis good increases
B)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good increases
C)the marginal utility per dollar spent on the horizontal axis good decreases
D)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods increase
E)the marginal utilities per dollar spent on both goods remain constant along that particular budget line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A utility-maximizing consumer will
A)consume at a point on her budget line
B)consume each good until its marginal utility is zero
C)adjust her consumption pattern so that the marginal utilities of all goods are equal
D)consume more of a good only if its price rises
E)stop consuming any good whose price rises
A)consume at a point on her budget line
B)consume each good until its marginal utility is zero
C)adjust her consumption pattern so that the marginal utilities of all goods are equal
D)consume more of a good only if its price rises
E)stop consuming any good whose price rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The combination of two goods at which total utility is maximized must lie somewhere on the consumer's budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Ignoring all other goods,if Yong's marginal utility per pound of bread is 10 utils and per pound of cheese is 30 utils,his
A)total utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is triple the price per pound of bread
B)total utility could be increased by buying more bread and less cheese
C)total utility could be increased by buying more cheese and less bread
D)total utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is one-third the price per pound of bread
E)marginal utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is one-third the price per pound of bread
A)total utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is triple the price per pound of bread
B)total utility could be increased by buying more bread and less cheese
C)total utility could be increased by buying more cheese and less bread
D)total utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is one-third the price per pound of bread
E)marginal utility would be maximized if the price per pound of cheese is one-third the price per pound of bread

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If MUₓ/Pₓ is less than MUᵧ/Pᵧ,then the consumer should consume more of X and less of Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If bread costs $1 per pound and meat costs $4 per pound,a consumer whose marginal utility of meat equals 80 utils per pound is maximizing utility only if the marginal utility per pound of bread equals
A)4 utils
B)5 utils
C)10 utils
D)20 utils
E)80 utils
A)4 utils
B)5 utils
C)10 utils
D)20 utils
E)80 utils

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Lin is maximizing total utility while consuming food and clothing.Her marginal utilities of food and clothing are 50 utils and 25 utils,respectively.If clothing is priced at $10 per unit,the price of a unit of food
A)must be rising
B)must be falling
C)must equal $10 as well
D)must equal $20
E)cannot be determined without additional information.
A)must be rising
B)must be falling
C)must equal $10 as well
D)must equal $20
E)cannot be determined without additional information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose that the price of a pizza is $10 and that the price of a blouse is $30.At her present level of consumption,Magda's ratio of marginal utility of pizza to marginal utility of blouses is 1/2.To maximize total utility,she should
A)buy more pizzas and fewer blouses
B)buy fewer pizzas and more blouses
C)continue to buy the same quantities of pizza and blouses
D)spend more time consuming pizza
E)spend more time buying blouses
A)buy more pizzas and fewer blouses
B)buy fewer pizzas and more blouses
C)continue to buy the same quantities of pizza and blouses
D)spend more time consuming pizza
E)spend more time buying blouses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
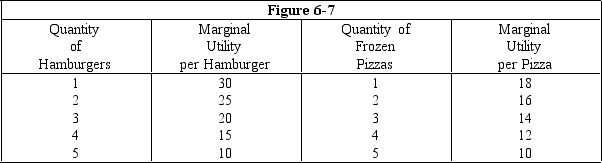
Figure 6-7 shows the marginal utilities Kate receives from buying hamburgers and frozen pizzas,assuming she buys only these two goods.Each hamburger sells for $5 and each pizza sells for $4.What is her marginal utility per dollar spent on the fourth hamburger?
A)15
B)4
C)3
D)20
E)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If Sally maximizes her total utility by allocating time between two different activities,she will select the combination at which the marginal utility per hour spent is the same in both activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suzy spends all of her income on potato chips and textbooks.To maximize her total utility,she should
A)allocate her income so that the marginal utilities of potato chips and textbooks are equal
B)allocate her income so that the marginal utilities per dollar spent on potato chips and textbooks are equal
C)change her eating habits
D)choose a consumption point that is inside her budget constraint
E)allocate her income so that the total utilities of potato chips and textbooks are equal
A)allocate her income so that the marginal utilities of potato chips and textbooks are equal
B)allocate her income so that the marginal utilities per dollar spent on potato chips and textbooks are equal
C)change her eating habits
D)choose a consumption point that is inside her budget constraint
E)allocate her income so that the total utilities of potato chips and textbooks are equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The marginal utility per dollar spent on a good represents the
A)satisfaction received for each dollar spent on the last unit consumed
B)total satisfaction received from consuming a certain number of units of that good
C)dollar value of average utility
D)change in price due to a one-unit increase in total utility
E)price paid for the last unit of utility
A)satisfaction received for each dollar spent on the last unit consumed
B)total satisfaction received from consuming a certain number of units of that good
C)dollar value of average utility
D)change in price due to a one-unit increase in total utility
E)price paid for the last unit of utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Among all the combinations of goods attainable by a consumer facing a budget constraint,the one that maximizes total utility is the one that
A)maximizes marginal utility per dollar spent on each good
B)maximizes marginal utility per pound,or other physical quantity,of each good
C)equates the marginal utilities per dollar spent on each good
D)equates the marginal utilities per pound,or other physical quantity,of each good
E)drives the marginal utility of each good to zero
A)maximizes marginal utility per dollar spent on each good
B)maximizes marginal utility per pound,or other physical quantity,of each good
C)equates the marginal utilities per dollar spent on each good
D)equates the marginal utilities per pound,or other physical quantity,of each good
E)drives the marginal utility of each good to zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Stanley receives the following marginal utilities from the first four car washes that he buys each year,respectively: 20,15,10,and 5.If each car wash sells for $10,then the marginal utility per dollar spent on the third car wash is
A)10
B)4.5
C)1
D)45
E)5
A)10
B)4.5
C)1
D)45
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Jeffrey spends all of his income on warm-up suits and running shoes,and the price of a warm-up suit is four times the price per pair of shoes.Then,in order to maximize total utility,Jeffrey should
A)buy four times as many warm-up suits as pairs of running shoes
B)buy four times as many pairs of running shoes as warm-up suits
C)divide his income equally between warm-up suits and running shoes
D)buy both items until the marginal utility of a warm-up suit is four times the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes
E)buy both items until the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes is four times the marginal utility of a warm-up suit
A)buy four times as many warm-up suits as pairs of running shoes
B)buy four times as many pairs of running shoes as warm-up suits
C)divide his income equally between warm-up suits and running shoes
D)buy both items until the marginal utility of a warm-up suit is four times the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes
E)buy both items until the marginal utility of a pair of running shoes is four times the marginal utility of a warm-up suit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For dessert,Mac has the choice between cheesecake and apple pie.The cheesecake has a marginal utility of 50 and a price of $5,and the apple pie has a marginal utility of 30 and a price of $3.Therefore,Mac should buy
A)the cheesecake since the marginal utility is greater
B)the apple pie because its price is lower
C)two servings of apple pie and no cheesecake
D)four servings of cheesecake
E)either the apple pie or the cheesecake,it makes no difference
A)the cheesecake since the marginal utility is greater
B)the apple pie because its price is lower
C)two servings of apple pie and no cheesecake
D)four servings of cheesecake
E)either the apple pie or the cheesecake,it makes no difference

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 143 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



