Deck 7: Production and Cost
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Production and Cost
1
A firm's profit is
A)greater if it is a corporation rather than if it is a sole proprietorship
B)higher if it raises its price than if it does not
C)lower if it lowers its price than if it does not
D)never taxed by the government
E)its revenue minus its costs
A)greater if it is a corporation rather than if it is a sole proprietorship
B)higher if it raises its price than if it does not
C)lower if it lowers its price than if it does not
D)never taxed by the government
E)its revenue minus its costs
its revenue minus its costs
2
The law of diminishing marginal returns says that as more of a variable input is combined with a fixed input,total output will increase;however,the increases in the firm's output will become ever smaller.
True
3
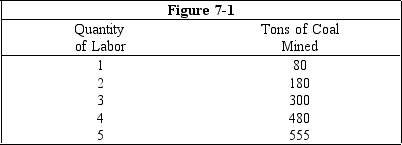
Figure 7-1 shows the amounts of coal that a mining company could produce per week by changing the number of workers while capital and technology remain constant.How many workers could the mine hire before the marginal product of labor begins to decline?
A)1 worker
B)2 workers
C)3 workers
D)4 workers
E)5 workers
4 workers
4
The "short run" may vary in length from industry to industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Fixed inputs are those whose
A)quantity changes as the level of output changes
B)costs are irreversible
C)quantity remains constant regardless of the level of output
D)quantity determines the level of profit
E)appearance was damaged while being transported,but has been fixed
A)quantity changes as the level of output changes
B)costs are irreversible
C)quantity remains constant regardless of the level of output
D)quantity determines the level of profit
E)appearance was damaged while being transported,but has been fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the long run,
A)at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
B)customer tastes and preferences are fixed
C)the firm may vary all inputs
D)sunk costs become variable costs
E)government intervention is inevitable
A)at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
B)customer tastes and preferences are fixed
C)the firm may vary all inputs
D)sunk costs become variable costs
E)government intervention is inevitable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Marginal product is the change in output divided by the change in the amount of an input used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed input in the short run for Joe's Garage?
A)the grease used to lubricate cars
B)the part-time labor employed to repair cars
C)the inventory of replacement parts
D)the electricity used to heat and light the garage
E)the garage used to repair cars
A)the grease used to lubricate cars
B)the part-time labor employed to repair cars
C)the inventory of replacement parts
D)the electricity used to heat and light the garage
E)the garage used to repair cars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a firm's planning horizon,the long run refers to
A)a period of one year or more
B)the term to which the current board of directors has been elected
C)the period during which all of the firm's inputs can be varied
D)the period during which at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
E)the period during which the level of available technology is fixed
A)a period of one year or more
B)the term to which the current board of directors has been elected
C)the period during which all of the firm's inputs can be varied
D)the period during which at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
E)the period during which the level of available technology is fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Variable inputs are those whose
A)quantity changes as the level of output changes
B)costs are irreversible
C)quantity remains constant regardless of the level of output
D)costs are considered sunk costs
E)price is continuously changing
A)quantity changes as the level of output changes
B)costs are irreversible
C)quantity remains constant regardless of the level of output
D)costs are considered sunk costs
E)price is continuously changing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider a firm that needs one day to hire more labor,one week to increase its purchases of raw materials,and three months to change the amount of its capital.This firm's long run is
A)three months
B)one week
C)one day
D)three months plus eight days
E)three months plus one week
A)three months
B)one week
C)one day
D)three months plus eight days
E)three months plus one week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
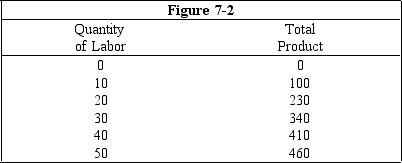
Figure 7-2 shows how much a firm could produce with various amounts of labor holding capital and technology constant.What is the marginal product of labor between 20 and 30 units of labor?
A)340 units
B)220 units
C)11 units
D)110 units
E)34 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

Figure 7-1 shows the amounts of coal that a mining company could produce per week by changing the number of workers while capital and technology remain constant.Which worker has a marginal product of 120 tons of coal?
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the physical plant for a corporation is considered to be a fixed input,then
A)it is held constant in the long run
B)it can be changed in the long run
C)labor must be a variable input
D)technology must be changing
E)the firm will lose money in the short run,except under perfect competition
A)it is held constant in the long run
B)it can be changed in the long run
C)labor must be a variable input
D)technology must be changing
E)the firm will lose money in the short run,except under perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The short run for Barbara's Bakery is defined as
A)one year
B)one month
C)the period of time during which all inputs are variable
D)the period of time during which at least one input is fixed
E)the time needed for a transaction to occur
A)one year
B)one month
C)the period of time during which all inputs are variable
D)the period of time during which at least one input is fixed
E)the time needed for a transaction to occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the short run,
A)utilization of any input can be varied
B)production takes less than one year
C)all resources are limited in supply
D)utilization of some inputs is assumed constant
E)equilibrium cannot occur
A)utilization of any input can be varied
B)production takes less than one year
C)all resources are limited in supply
D)utilization of some inputs is assumed constant
E)equilibrium cannot occur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Total product begins to decline when diminishing marginal returns are first experienced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As a firm increases its output in the short run,
A)it also varies its technology
B)it increases all of its inputs
C)it increases its plant size
D)it increases only one of its inputs
E)at least one of its inputs is fixed
A)it also varies its technology
B)it increases all of its inputs
C)it increases its plant size
D)it increases only one of its inputs
E)at least one of its inputs is fixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the short run,
A)at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
B)customer tastes and preferences are fixed
C)the firm may vary all inputs
D)sunk costs are variable
E)government intervention is inevitable
A)at least one of the firm's inputs is fixed
B)customer tastes and preferences are fixed
C)the firm may vary all inputs
D)sunk costs are variable
E)government intervention is inevitable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Figure 7-1 shows the amounts of coal that a mining company could produce per week by changing the number of workers while capital and technology remain constant.The marginal product of employing the fourth worker is
A)120 tons of coal
B)480 tons of coal
C)319 tons of coal
D)180 tons of coal
E)106.33 tons of coal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The law of diminishing marginal returns says that as additional units of a variable input are added to
A)fixed amounts of other inputs,total output will eventually remain constant
B)varying amounts of other inputs,total output will eventually decline
C)fixed amounts of other inputs,the resulting increases in total output will eventually become smaller
D)varying amount of other inputs,the resulting increases in total output will eventually become smaller
E)a declining amount of output,technology will eventually deteriorate
A)fixed amounts of other inputs,total output will eventually remain constant
B)varying amounts of other inputs,total output will eventually decline
C)fixed amounts of other inputs,the resulting increases in total output will eventually become smaller
D)varying amount of other inputs,the resulting increases in total output will eventually become smaller
E)a declining amount of output,technology will eventually deteriorate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The law of diminishing marginal returns says that
A)total product will eventually remain constant as more of an input is added to production
B)total revenue decreases as output increases,holding technology fixed
C)marginal product eventually falls as more of an input is employed
D)the quantity demanded of a good decreases as its price rises
E)utility falls as more of a good is consumed
A)total product will eventually remain constant as more of an input is added to production
B)total revenue decreases as output increases,holding technology fixed
C)marginal product eventually falls as more of an input is employed
D)the quantity demanded of a good decreases as its price rises
E)utility falls as more of a good is consumed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The marginal product of labor is the
A)total output produced when one more worker is hired
B)change in average output produced when one more worker is hired
C)total output per worker when one more worker is hired
D)change in total output when one more worker is hired
E)maximum quantity of output when one more worker is hired
A)total output produced when one more worker is hired
B)change in average output produced when one more worker is hired
C)total output per worker when one more worker is hired
D)change in total output when one more worker is hired
E)maximum quantity of output when one more worker is hired

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns to labor,then
A)total output must be decreasing
B)total output rises more slowly as additional workers are added
C)the firm must decrease the amount of labor it hires
D)total output per worker must be rising
E)the firm must be operating in the long run
A)total output must be decreasing
B)total output rises more slowly as additional workers are added
C)the firm must decrease the amount of labor it hires
D)total output per worker must be rising
E)the firm must be operating in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

For the total product curve shown in Figure 7-3,the marginal product of hiring the fifth unit of labor is
A)200
B)50
C)20
D)1,000
E)1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When the marginal product of labor increases as the amount of labor employed increases,
A)the additional worker has made other workers more productive
B)the firm also must have increased the amount of capital
C)the firm is experiencing economies of scale
D)there has been an improvement in the available technology
E)the law of diminishing returns has been violated
A)the additional worker has made other workers more productive
B)the firm also must have increased the amount of capital
C)the firm is experiencing economies of scale
D)there has been an improvement in the available technology
E)the law of diminishing returns has been violated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

For the total product curve shown in Figure 7-3,for which unit of labor is the marginal product 20 units of output?
A)first
B)second
C)third
D)fourth
E)fifth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If there are diminishing marginal returns to labor,
A)output diminishes as additional workers are added
B)the management team grows as more workers are hired
C)the rise in output becomes smaller and smaller with each successive worker hired
D)the management team shrinks as successive workers are added
E)macroeconomic business cycles are generated by microeconomic production functions
A)output diminishes as additional workers are added
B)the management team grows as more workers are hired
C)the rise in output becomes smaller and smaller with each successive worker hired
D)the management team shrinks as successive workers are added
E)macroeconomic business cycles are generated by microeconomic production functions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

For the total product curve shown in Figure 7-3,diminishing marginal returns to labor
A)do not occur over this range
B)begin with the third unit of labor
C)exist for every unit of labor
D)begin with the fourth unit of labor
E)begin with the first unit of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
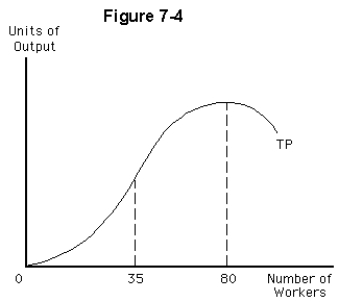
In Figure 7-4,marginal product of labor is increasing for levels of employment
A)between 0 and 35 workers
B)equal to 35 workers
C)between 35 and 80 workers
D)greater than 80 workers
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Last month,Sally spent $3,000 in repairing her old car.Now her car requires an additional $2,000 in repairs.She could get a comparable car for $2,500.She should
A)repair her car because the money she has already spent repairing the car ($3,000)exceeds the price of the new car ($2,500)
B)buy a new car because sunk costs should be ignored in decision making
C)buy a new car because the price of the new car ($2,500)is less than the total amount she would spend on her current car ($5,000)
D)repair her car since the cost of repairing it is lower than the cost of buying another car
E)repair the car or buy a comparable one because the opportunity costs are the same
A)repair her car because the money she has already spent repairing the car ($3,000)exceeds the price of the new car ($2,500)
B)buy a new car because sunk costs should be ignored in decision making
C)buy a new car because the price of the new car ($2,500)is less than the total amount she would spend on her current car ($5,000)
D)repair her car since the cost of repairing it is lower than the cost of buying another car
E)repair the car or buy a comparable one because the opportunity costs are the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The marginal product of labor is the
A)additional output produced when one more worker is hired
B)amount of output associated with labor inputs
C)maximum amount of output produced by a given set of inputs
D)maximum profit "produced" by selling a firm's output
E)additional cost associated with an additional unit of labor
A)additional output produced when one more worker is hired
B)amount of output associated with labor inputs
C)maximum amount of output produced by a given set of inputs
D)maximum profit "produced" by selling a firm's output
E)additional cost associated with an additional unit of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

In Figure 7-4,marginal product of labor is negative for levels of employment
A)between 0 and 80 workers
B)equal to 35 workers
C)between 35 and 80 workers
D)greater than 80 workers
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

In Figure 7-4,marginal product of labor is diminishing for levels of employment
A)between 0 and 35 workers
B)equal to 35 workers
C)between 35 and 80 workers
D)greater than 80 workers
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Sunk costs should be ignored in decision making because they
A)increase the cost of the transaction
B)lead to an increase in the opportunity cost of any decision
C)have already been paid
D)often exceed marginal and average costs
E)are usually negligible when compared with the explicit costs of decisions
A)increase the cost of the transaction
B)lead to an increase in the opportunity cost of any decision
C)have already been paid
D)often exceed marginal and average costs
E)are usually negligible when compared with the explicit costs of decisions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the marginal product of labor is positive and increasing,then the total product of labor curve is
A)constant
B)upward sloping and becoming steeper
C)downward sloping and becoming flatter
D)lies above the total cost curve
E)lies below the total cost curve
A)constant
B)upward sloping and becoming steeper
C)downward sloping and becoming flatter
D)lies above the total cost curve
E)lies below the total cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

Figure 7-2 shows how much a firm could produce with various amounts of labor holding capital and technology constant.What is the average product of labor when 20 units of labor are employed?
A)230 units
B)11.5 units
C)130 units
D)6.5 units
E)110 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
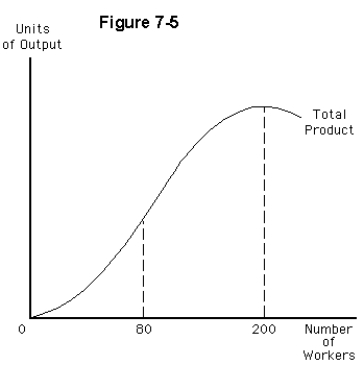
Consider the total product curve depicted in Figure 7-5.The firm experiences the greatest marginal returns to labor
A)when employing more than 200 workers
B)when employing between 80 and 200 workers
C)when employing 80 workers
D)when employing between zero and 80 workers
E)at all levels of employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The change in total output when one additional unit of labor is hired is known as the
A)capacity utilization rate
B)average product of labor
C)marginal product of labor
D)total product of labor
E)marginal output of labor
A)capacity utilization rate
B)average product of labor
C)marginal product of labor
D)total product of labor
E)marginal output of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

In Figure 7-4,marginal product of labor is positive for levels of employment
A)between 0 and 80 workers
B)equal to 35 workers
C)between 35 and 80 workers
D)greater than 80 workers
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A firm's total cost of production is
A)the owners' opportunity cost
B)labor costs plus the cost of materials
C)the payments for its inputs
D)depreciation plus payments for inputs
E)taxes plus depreciation plus payments for inputs
A)the owners' opportunity cost
B)labor costs plus the cost of materials
C)the payments for its inputs
D)depreciation plus payments for inputs
E)taxes plus depreciation plus payments for inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Samantha has been working for a law firm and earning an annual salary of $90,000.She decides to open her own practice.Her annual expenses will include $15,000 for office rent,$3,000 for equipment rental,$1,000 for supplies,$1,200 for utilities,and a $35,000 salary for a secretary/bookkeeper.Samantha will cover her start-up expenses by cashing in a $20,000 certificate of deposit on which she was earning annual interest of $1,000.Assuming that there are no additional expenses,Samantha's annual explicit costs will equal
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an implicit cost?
A)salaries paid to owners who work for their own firm
B)interest on money borrowed to finance equipment purchases
C)cash payments for raw materials
D)wages paid to hourly employees
E)foregone interest on money taken from bank accounts to buy equipment
A)salaries paid to owners who work for their own firm
B)interest on money borrowed to finance equipment purchases
C)cash payments for raw materials
D)wages paid to hourly employees
E)foregone interest on money taken from bank accounts to buy equipment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Average fixed cost is
A)the sum of variable and fixed costs
B)total cost minus variable cost
C)variable cost plus marginal cost
D)total fixed cost per unit of output
E)constant as output changes
A)the sum of variable and fixed costs
B)total cost minus variable cost
C)variable cost plus marginal cost
D)total fixed cost per unit of output
E)constant as output changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Variable costs are
A)the same as sunk costs
B)irrelevant to decision making,because they are sunk
C)the costs of inputs that vary with the level of production
D)the costs of inputs that do not vary with the level of production
E)the additional total cost associated with producing an additional unit of output
A)the same as sunk costs
B)irrelevant to decision making,because they are sunk
C)the costs of inputs that vary with the level of production
D)the costs of inputs that do not vary with the level of production
E)the additional total cost associated with producing an additional unit of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following,necessarily,equals zero when the firm's short-run output level is zero?
A)sunk costs
B)fixed costs
C)implicit costs
D)variable costs
E)opportunity costs
A)sunk costs
B)fixed costs
C)implicit costs
D)variable costs
E)opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is an implicit cost?
A)salaries paid to owners who work for their own firm
B)interest on money borrowed to finance equipment purchases
C)cash payments for raw materials
D)wages paid to hourly employees
E)foregone rent on office space owned and used by the firm
A)salaries paid to owners who work for their own firm
B)interest on money borrowed to finance equipment purchases
C)cash payments for raw materials
D)wages paid to hourly employees
E)foregone rent on office space owned and used by the firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Samantha has been working for a law firm and earning an annual salary of $90,000.She decides to open her own practice.Her annual expenses will include $15,000 for office rent,$3,000 for equipment rental,$1,000 for supplies,$1,200 for utilities,and a $35,000 salary for a secretary/bookkeeper.Samantha will cover her start-up expenses by cashing in a $20,000 certificate of deposit on which she was earning annual interest of $1,000.Assuming that there are no additional expenses,Samantha's total annual cost of production will equal
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The spreading of fixed costs over more output explains why the long-run average cost falls as output rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A firm's total cost of production is the
A)employees' opportunity cost
B)owners' opportunity cost
C)owners' opportunity cost minus the employees' opportunity cost
D)owners' opportunity cost plus the employees' opportunity cost
E)employees' opportunity cost minus the owners' opportunity cost
A)employees' opportunity cost
B)owners' opportunity cost
C)owners' opportunity cost minus the employees' opportunity cost
D)owners' opportunity cost plus the employees' opportunity cost
E)employees' opportunity cost minus the owners' opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is irrelevant when deciding whether to undertake an action?
A)opportunity costs
B)implicit costs
C)sunk costs
D)implicit costs and explicit costs
E)fixed costs and implicit costs
A)opportunity costs
B)implicit costs
C)sunk costs
D)implicit costs and explicit costs
E)fixed costs and implicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A corporation has been steadily losing money on one of its product lines.The factory used to produce that brand cost $20 million to build.The firm now is considering an offer to buy that factory for $15 million.Which of the following statements about the decision to sell or not is correct?
A)The firm should turn down the purchase offer because the factory cost more than $15 million to build.
B)The $20 million spent on the factory is a sunk cost that should not affect the decision.
C)The $20 million spent on the factory is an implicit cost that should be included in the decision.
D)The firm should sell the factory only if it can reduce its costs elsewhere by $5 million.
E)The firm's opportunity cost would be $35 million if it decides to sell the factory.
A)The firm should turn down the purchase offer because the factory cost more than $15 million to build.
B)The $20 million spent on the factory is a sunk cost that should not affect the decision.
C)The $20 million spent on the factory is an implicit cost that should be included in the decision.
D)The firm should sell the factory only if it can reduce its costs elsewhere by $5 million.
E)The firm's opportunity cost would be $35 million if it decides to sell the factory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Total fixed costs decrease as output expands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A firm's implicit costs are
A)its maintenance costs
B)its paid-out costs of production
C)its main source of executive costs
D)irrelevant to the determination of economic profit
E)opportunity costs of production that do not involve money outlays
A)its maintenance costs
B)its paid-out costs of production
C)its main source of executive costs
D)irrelevant to the determination of economic profit
E)opportunity costs of production that do not involve money outlays

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Total cost is
A)fixed cost plus variable cost
B)irrelevant to decision making
C)marginal cost plus fixed cost
D)total product minus total input
E)the additional cost associated with producing an additional unit
A)fixed cost plus variable cost
B)irrelevant to decision making
C)marginal cost plus fixed cost
D)total product minus total input
E)the additional cost associated with producing an additional unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Samantha has been working for a law firm and earning an annual salary of $90,000.She decides to open her own practice.Her annual expenses will include $15,000 for office rent,$3,000 for equipment rental,$1,000 for supplies,$1,200 for utilities,and a $35,000 salary for a secretary/bookkeeper.Samantha will cover her start-up expenses by cashing in a $20,000 certificate of deposit on which she was earning annual interest of $1,000.Assuming that there are no additional expenses,Samantha's annual implicit costs will equal
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200
A)$55,200
B)$221,400
C)$91,000
D)$146,200
E)$145,200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A sunk cost is one that
A)changes as the level of output changes in the short run
B)was paid in the past and will not change regardless of later decisions
C)should determine the rational course of action in the future
D)has the most impact on profit-maximizing decisions
E)influences rational decision makers
A)changes as the level of output changes in the short run
B)was paid in the past and will not change regardless of later decisions
C)should determine the rational course of action in the future
D)has the most impact on profit-maximizing decisions
E)influences rational decision makers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Bob gives up his factory job in order to open a bait-and-tackle shop.The earnings from his factory job represent
A)the hourly wage paid by the shop
B)the marginal cost of running the shop
C)the average cost of running the shop
D)a fixed cost that can vary in the long run
E)an implicit cost of opening the shop
A)the hourly wage paid by the shop
B)the marginal cost of running the shop
C)the average cost of running the shop
D)a fixed cost that can vary in the long run
E)an implicit cost of opening the shop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A firm's explicit costs are
A)the opportunity costs of the owners
B)its depreciation costs
C)the money paid for use of inputs
D)the foregone rents on owner occupied office space
E)irrelevant to the determination of economic profit
A)the opportunity costs of the owners
B)its depreciation costs
C)the money paid for use of inputs
D)the foregone rents on owner occupied office space
E)irrelevant to the determination of economic profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Average variable cost is
A)total cost minus fixed cost
B)total variable cost divided by the quantity of output
C)total cost plus marginal cost
D)total cost per unit of output
E)output divided by the quantity of inputs used
A)total cost minus fixed cost
B)total variable cost divided by the quantity of output
C)total cost plus marginal cost
D)total cost per unit of output
E)output divided by the quantity of inputs used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the short run,costs that arise from resources that cannot vary in quantity are known as ____________,whereas costs from inputs that can vary in quantity are known as ____________.
A)fixed costs;variable costs
B)explicit costs;implicit costs
C)opportunity costs;variable costs
D)fixed costs;opportunity costs
E)variable costs;fixed costs
A)fixed costs;variable costs
B)explicit costs;implicit costs
C)opportunity costs;variable costs
D)fixed costs;opportunity costs
E)variable costs;fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The change in cost resulting from producing one additional unit of output is
A)average total cost
B)total variable cost
C)average variable cost
D)marginal cost
E)total cost
A)average total cost
B)total variable cost
C)average variable cost
D)marginal cost
E)total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
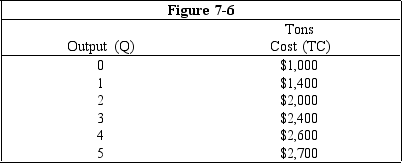
Figure 7-6 shows the total cost for six different levels of output for a particular firm.What is the average total cost (ATC)of producing four units of output?
A)$2,600
B)$200
C)$650
D)$50
E)$10,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following always decreases as output increases?
A)ATC
B)MC
C)AFC
D)TC
E)TVC
A)ATC
B)MC
C)AFC
D)TC
E)TVC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Average total cost is
A)the change in cost as output decreases
B)the change in cost as output increases
C)TC / quantity of output
D)MC - TC
E)AVC - AFC
A)the change in cost as output decreases
B)the change in cost as output increases
C)TC / quantity of output
D)MC - TC
E)AVC - AFC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

Figure 7-7 shows a firm's total variable cost for different daily output levels.In addition,the firm has total fixed cost of $50 per day.If output increases from 20 to 30 units,average total cost rises from
A)$17.50 to $19.17,and marginal cost is $225.00
B)$400 to $625,and marginal cost is $225.00
C)$15.00 to $22.50,and marginal cost is $22.50
D)$20.00 to $20.83,and marginal cost is $22.50
E)$20.00 to $20.83,and marginal cost is $225.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following formulas is not correct?
A)ATC = AVC + (TFC/Q)
B)TVC = TC/Q
C)TC = TFC + TVC
D)AFC = TFC/Q
E)TVC = AVC × Q
A)ATC = AVC + (TFC/Q)
B)TVC = TC/Q
C)TC = TFC + TVC
D)AFC = TFC/Q
E)TVC = AVC × Q

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
To produce a firm's current output level,total cost is $600,and the total variable cost is $450.Therefore,the firm has
A)a marginal cost of $150
B)sunk costs of $150
C)a marginal cost of $1,450
D)total fixed cost of $1,450
E)total fixed cost of $150
A)a marginal cost of $150
B)sunk costs of $150
C)a marginal cost of $1,450
D)total fixed cost of $1,450
E)total fixed cost of $150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If a firm increases its output level in the short run,then
A)variable cost rises but fixed cost remains unchanged
B)both variable cost and fixed cost rise
C)variable cost rises,but fixed cost fall
D)both variable cost and fixed cost fall
E)variable cost remains unchanged,but fixed cost rises
A)variable cost rises but fixed cost remains unchanged
B)both variable cost and fixed cost rise
C)variable cost rises,but fixed cost fall
D)both variable cost and fixed cost fall
E)variable cost remains unchanged,but fixed cost rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A firm's cost of variable inputs per unit of output is known as
A)average total cost
B)average fixed cost
C)marginal cost
D)total variable cost
E)average variable cost
A)average total cost
B)average fixed cost
C)marginal cost
D)total variable cost
E)average variable cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

Figure 7-6 shows the total cost for six different levels of output for a particular firm.Total fixed cost (TFC)if five units of output are produced is
A)$1,700
B)$540
C)$1,000
D)$100
E)$2,700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The vertical distance between a firm's total cost curve and its total variable cost curve
A)is zero
B)is negative when the firm incurs fixed costs in the short run
C)represents total fixed costs
D)represents marginal costs
E)represents average fixed costs
A)is zero
B)is negative when the firm incurs fixed costs in the short run
C)represents total fixed costs
D)represents marginal costs
E)represents average fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

Figure 7-6 shows the total cost for six different levels of output for a particular firm.What is the marginal cost (MC)of the last unit of output listed in the table (i.e. ,the fifth unit of output)?
A)$2,700
B)$540
C)$100
D)$90
E)$500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
At a firm's current output level of 200 units per week,it has 10 employees at a weekly wage of $500 each.Raw materials,which are ordered and delivered daily,cost $1,000 per week.The weekly cost of the firm's capital is $1,250.Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Total variable cost is $5,000;total fixed cost is $2,250;total cost is $7,250.
B)Total variable cost is $6,000;total fixed cost is $1,250;total cost is $7,250.
C)Total variable cost is $1,250;total fixed cost is $6,000;total cost is $7,250.
D)Total variable cost is $2,250;total fixed cost is $500;total cost is $2,750.
E)Total variable cost is $1,500;total fixed cost is $1,250;total cost is $2,750.
A)Total variable cost is $5,000;total fixed cost is $2,250;total cost is $7,250.
B)Total variable cost is $6,000;total fixed cost is $1,250;total cost is $7,250.
C)Total variable cost is $1,250;total fixed cost is $6,000;total cost is $7,250.
D)Total variable cost is $2,250;total fixed cost is $500;total cost is $2,750.
E)Total variable cost is $1,500;total fixed cost is $1,250;total cost is $2,750.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is the best example of a variable cost?
A)property taxes
B)lease payments for equipment rental
C)rent on office space
D)wages for hourly workers
E)interest on outstanding loans
A)property taxes
B)lease payments for equipment rental
C)rent on office space
D)wages for hourly workers
E)interest on outstanding loans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

Figure 7-7 shows a firm's total variable cost for different daily output levels.In addition,the firm has total fixed cost of $50 per day.At an output level of 20 units,average variable cost is
A)$75.00,and average fixed cost is $2.50
B)$17.50,and average fixed cost is $50.00
C)$150.00,and average fixed cost is $2.50
D)$7.50,and average fixed cost is $50.00
E)$17.50,and average fixed cost is $2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
As a firm increases its output in the short run,average fixed cost
A)rises steadily
B)falls and then rises
C)falls steadily
D)rises and then falls
E)remains unchanged
A)rises steadily
B)falls and then rises
C)falls steadily
D)rises and then falls
E)remains unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Marginal cost is
A)the increase in total cost from producing one more unit of output
B)total variable cost per unit of output
C)fixed cost per marginal unit
D)average total cost divided by the quantity of inputs used
E)total cost per unit of output
A)the increase in total cost from producing one more unit of output
B)total variable cost per unit of output
C)fixed cost per marginal unit
D)average total cost divided by the quantity of inputs used
E)total cost per unit of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If Babette's Bicycle shop can rebuild three bicycles for $200 and four bicycles for $240,then the average variable cost of four bicycles
A)equals $40
B)cannot be determined without more information
C)equals $60
D)equals $240
E)equals $10
A)equals $40
B)cannot be determined without more information
C)equals $60
D)equals $240
E)equals $10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Average variable cost is
A)the change in cost as output decreases
B)the change in cost as output increases
C)TC / quantity of output
D)TVC / quantity of output
E)AFC + AVC
A)the change in cost as output decreases
B)the change in cost as output increases
C)TC / quantity of output
D)TVC / quantity of output
E)AFC + AVC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



