Deck 11: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/214
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Monopoly
1
Monopolies are characterized by all of the following,except one.Which is the exception?
A)a downward-sloping demand curve
B)potential for long-run profits
C)a perfectly elastic demand curve
D)barriers to entry
E)no close substitutes for the good produced
A)a downward-sloping demand curve
B)potential for long-run profits
C)a perfectly elastic demand curve
D)barriers to entry
E)no close substitutes for the good produced
a perfectly elastic demand curve
2
Although there are barriers to entry in a monopolized industry,there are usually many close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
False
3
A monopoly is a
A)large number of producers each with a small share of the total market output
B)single seller of a product that typically has no close substitutes
C)small group of producers with similar products
D)single buyer of an input into production
E)group of firms with incentives to cooperate
A)large number of producers each with a small share of the total market output
B)single seller of a product that typically has no close substitutes
C)small group of producers with similar products
D)single buyer of an input into production
E)group of firms with incentives to cooperate
single seller of a product that typically has no close substitutes
4
A market that involves only one seller of a good or service is known as
A)a monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)an oligopoly
E)perfect monopolistic competition
A)a monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)an oligopoly
E)perfect monopolistic competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Most firms are not monopolies in the real world because
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves
B)supply curves slope upward
C)price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms
D)monopolies are not efficient
E)there are substitutes for most goods
A)firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves
B)supply curves slope upward
C)price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms
D)monopolies are not efficient
E)there are substitutes for most goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A monopoly exists because of
A)barriers to entry
B)the large number of buyers and sellers
C)the absence of barriers to entry
D)collusion among the dominant firms
E)the absence of exclusive government franchises
A)barriers to entry
B)the large number of buyers and sellers
C)the absence of barriers to entry
D)collusion among the dominant firms
E)the absence of exclusive government franchises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A natural monopoly is created by
A)a patent
B)nature
C)substantial economies of scale
D)government regulation
E)control of scarce inputs
A)a patent
B)nature
C)substantial economies of scale
D)government regulation
E)control of scarce inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Economies of scale act as a barrier to entry because
A)one large firm can supply the market at a higher average cost than many small firms could
B)firms are not allowed by law to sell output below average cost
C)large firms can hire inputs at a higher price than smaller firms could
D)firms will not compete with a larger firm when there are differences in marginal cost
E)one large firm can produce the market output at a lower average cost than many small firms
A)one large firm can supply the market at a higher average cost than many small firms could
B)firms are not allowed by law to sell output below average cost
C)large firms can hire inputs at a higher price than smaller firms could
D)firms will not compete with a larger firm when there are differences in marginal cost
E)one large firm can produce the market output at a lower average cost than many small firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If average total cost per unit is minimized when a single producer supplies the entire market,this indicates
A)the presence of limit pricing
B)that the single producer is a perfect monopoly
C)the presence of substantial economies of scale
D)that the market has been narrowly defined
E)the existence of a single-price monopoly
A)the presence of limit pricing
B)that the single producer is a perfect monopoly
C)the presence of substantial economies of scale
D)that the market has been narrowly defined
E)the existence of a single-price monopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Copyrights and patents are examples of barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a potential barrier to entry?
A)a low market price
B)a high market price
C)a standardized product
D)economies of scale
E)diminishing marginal productivity
A)a low market price
B)a high market price
C)a standardized product
D)economies of scale
E)diminishing marginal productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A natural monopoly exists when
A)economies of scale are negligible
B)there are a few dominant firms that corner the market
C)one firm can produce the market output at lower average cost than two or more firms can
D)barriers to entry are low
E)only a few firms can minimize cost and maximize profit
A)economies of scale are negligible
B)there are a few dominant firms that corner the market
C)one firm can produce the market output at lower average cost than two or more firms can
D)barriers to entry are low
E)only a few firms can minimize cost and maximize profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following could be a barrier to entry?
A)diseconomies of scale
B)a large number of buyers and sellers
C)a standardized product
D)economies of scale
E)diseconomies of scope
A)diseconomies of scale
B)a large number of buyers and sellers
C)a standardized product
D)economies of scale
E)diseconomies of scope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose that a monopoly is earning economic profits in the short run.As a result,
A)no new firms will enter the industry because of barriers to entry
B)the monopolist will increase its price and lower its output
C)the market supply curve will shift to the right
D)profits will fall as new firms enter the market
E)the market demand curve will shift to the left
A)no new firms will enter the industry because of barriers to entry
B)the monopolist will increase its price and lower its output
C)the market supply curve will shift to the right
D)profits will fall as new firms enter the market
E)the market demand curve will shift to the left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A natural monopoly is producing an output level of 1,000 units per day.If the monopoly is broken up into 5 firms,then average total cost for each of the 5 firms
A)will exceed the monopolist's average total cost
B)will equal the monopolist's average total cost
C)will fall below the monopolist's average total cost
D)may equal or fall below the monopolist's average total cost
E)may equal or exceed the monopolist's average total cost
A)will exceed the monopolist's average total cost
B)will equal the monopolist's average total cost
C)will fall below the monopolist's average total cost
D)may equal or fall below the monopolist's average total cost
E)may equal or exceed the monopolist's average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The extent to which a firm is viewed by consumers as being a monopoly depends primarily on
A)how the government defines a monopoly
B)whether they believe there are close substitutes for the good it produces
C)the level of profits earned by the firm
D)the difference between price and marginal cost of the good it produces
E)the size of the firm
A)how the government defines a monopoly
B)whether they believe there are close substitutes for the good it produces
C)the level of profits earned by the firm
D)the difference between price and marginal cost of the good it produces
E)the size of the firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following goods would be most likely to be produced by a monopoly?
A)Lotso-Sugar brand cereal
B)Pepsi
C)margarine
D)electricity
E)Ford automobiles
A)Lotso-Sugar brand cereal
B)Pepsi
C)margarine
D)electricity
E)Ford automobiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A pure monopoly
A)is the only firm that produces all of the products its competitors produce
B)is the single seller of a unique product
C)is bigger than all its competitors combined
D)has only one customer
E)is always profitable in the short run
A)is the only firm that produces all of the products its competitors produce
B)is the single seller of a unique product
C)is bigger than all its competitors combined
D)has only one customer
E)is always profitable in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A monopoly is a
A)price taker
B)single buyer of an input into production
C)firm facing a perfectly elastic demand curve
D)group of firms controlling the price and output for an industry
E)price setter
A)price taker
B)single buyer of an input into production
C)firm facing a perfectly elastic demand curve
D)group of firms controlling the price and output for an industry
E)price setter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A natural monopoly is based on
A)diseconomies of scale
B)diseconomies of scope
C)external diseconomies
D)economic freedom
E)economies of scale
A)diseconomies of scale
B)diseconomies of scope
C)external diseconomies
D)economic freedom
E)economies of scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The U.S.Postal Service
A)has its monopoly status guaranteed by government franchise
B)enforces copyrights and patents in the United States.
C)owes its monopoly status to network externalities
D)is a monopoly because it controls a scarce resource
E)has a horizontal average total cost curve
A)has its monopoly status guaranteed by government franchise
B)enforces copyrights and patents in the United States.
C)owes its monopoly status to network externalities
D)is a monopoly because it controls a scarce resource
E)has a horizontal average total cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Patents grant
A)permanent monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions
B)permanent monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property
C)temporary monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions
D)temporary monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property
E)permanent monopoly status to natural monopolies
A)permanent monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions
B)permanent monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property
C)temporary monopoly status to creators of scientific inventions
D)temporary monopoly status to creators of any intellectual property
E)permanent monopoly status to natural monopolies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The fact that a single-price monopolist must lower its price to sell more output explains why price exceeds marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not considered a barrier to entry?
A)large economies of scale
B)control of inputs used in production
C)a homogeneous product
D)patents
E)copyrights
A)large economies of scale
B)control of inputs used in production
C)a homogeneous product
D)patents
E)copyrights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A natural monopoly occurs when
A)patents protect a firm from competition
B)copyrights protect a firm from competition
C)advertising costs exceed fixed costs
D)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
E)average costs decrease over the whole range of market output
A)patents protect a firm from competition
B)copyrights protect a firm from competition
C)advertising costs exceed fixed costs
D)marginal cost exceeds marginal revenue
E)average costs decrease over the whole range of market output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Intellectual property includes
A)all of the following
B)literary,artistic and musical works,and scientific inventions
C)computers,calculators,and word processors
D)desks,bookshelves,and notebooks
E)office space,computers,and telephones
A)all of the following
B)literary,artistic and musical works,and scientific inventions
C)computers,calculators,and word processors
D)desks,bookshelves,and notebooks
E)office space,computers,and telephones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Network externalities
A)explain why switching costs fall as the size of a network increases
B)are the service-industry equivalent of natural monopolies in goods-producing industries
C)are more important in the short run than in the long run
D)help explain why monopolies often do not last for very long
E)can explain the dominance of existing firms in some industries
A)explain why switching costs fall as the size of a network increases
B)are the service-industry equivalent of natural monopolies in goods-producing industries
C)are more important in the short run than in the long run
D)help explain why monopolies often do not last for very long
E)can explain the dominance of existing firms in some industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Patents and copyrights
A)are illegal in the United States
B)reduce barriers to entry in markets
C)protect small firms from large firms
D)lead to increased output and decreased prices
E)provide incentives for firms to engage in research and development
A)are illegal in the United States
B)reduce barriers to entry in markets
C)protect small firms from large firms
D)lead to increased output and decreased prices
E)provide incentives for firms to engage in research and development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An example of a barrier to entry is
A)patent law
B)government regulations
C)cost of advertising
D)economies of scale
E)all of the above
A)patent law
B)government regulations
C)cost of advertising
D)economies of scale
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A profit-maximizing,single-price monopoly must lower its price in order to sell more output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Patents allow manufacturers to block the entry of new firms into an industry through
A)infringement suits
B)economies of scale
C)limit pricing
D)price discrimination
E)a government franchise
A)infringement suits
B)economies of scale
C)limit pricing
D)price discrimination
E)a government franchise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A copyright
A)is required to sell printed material
B)grants exclusive rights over the protected material for at least seventy years
C)is granted only to best original works of art,literature,and music
D)grants the right to copy certain material such as printed material
E)grants communal rights over the protected material for at least seventy years
A)is required to sell printed material
B)grants exclusive rights over the protected material for at least seventy years
C)is granted only to best original works of art,literature,and music
D)grants the right to copy certain material such as printed material
E)grants communal rights over the protected material for at least seventy years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Patent laws establish property rights for new goods
A)for 10 years
B)for 20 years
C)for 5 years
D)until a better product comes along
E)until the firm goes out of business
A)for 10 years
B)for 20 years
C)for 5 years
D)until a better product comes along
E)until the firm goes out of business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Patents and copyrights are designed to
A)eliminate above-normal profit in the short run
B)move monopoly prices closer to prices that would occur under perfect competition
C)prevent the capitalization of monopoly profit
D)allow a period of above-normal profit to encourage innovation
E)limit a monopoly's rent-seeking activities
A)eliminate above-normal profit in the short run
B)move monopoly prices closer to prices that would occur under perfect competition
C)prevent the capitalization of monopoly profit
D)allow a period of above-normal profit to encourage innovation
E)limit a monopoly's rent-seeking activities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A patent
A)tends to discourage further innovation,since there are no other competitors to "push" the patentee
B)prevents anyone else from buying the same discovery or product for twenty years
C)grants exclusive rights over the protected firm for at least fifty years
D)is an infringement against an exclusive business right
E)prevents anyone else from selling the same discovery or product for twenty years
A)tends to discourage further innovation,since there are no other competitors to "push" the patentee
B)prevents anyone else from buying the same discovery or product for twenty years
C)grants exclusive rights over the protected firm for at least fifty years
D)is an infringement against an exclusive business right
E)prevents anyone else from selling the same discovery or product for twenty years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Marginal revenue,average revenue,and price are all equal for a monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For a monopolist,there is no difference between the market demand curve and the demand curve the monopolist uses when making output decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A network externality exists
A)in the television industry
B)outside the television industry
C)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its value to current and potential members
D)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its average total cost of production
E)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its total cost of production
A)in the television industry
B)outside the television industry
C)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its value to current and potential members
D)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its average total cost of production
E)whenever an increase in the size of a network increases its total cost of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Patents stimulate innovation by
A)providing incentives to incur research and development costs
B)guaranteed profits for those who innovate
C)prosecuting anyone who purchases the good protected by the patent
D)providing tax breaks to investors
E)increasing the interest rate on borrowed funds
A)providing incentives to incur research and development costs
B)guaranteed profits for those who innovate
C)prosecuting anyone who purchases the good protected by the patent
D)providing tax breaks to investors
E)increasing the interest rate on borrowed funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When a monopoly is created through government franchise,
A)the firm is assured of above-normal profit
B)it is subject to government price regulation
C)the firm will discontinue any rent-seeking activity
D)price discrimination is forbidden
E)the government prevents both entry and exit in the long run
A)the firm is assured of above-normal profit
B)it is subject to government price regulation
C)the firm will discontinue any rent-seeking activity
D)price discrimination is forbidden
E)the government prevents both entry and exit in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
To maximize profit,a monopolist should produce the level of output at which
A)price equals marginal cost
B)price equals marginal revenue and marginal cost
C)price equals marginal revenue
D)marginal revenue equals marginal cost
E)price equals average total cost
A)price equals marginal cost
B)price equals marginal revenue and marginal cost
C)price equals marginal revenue
D)marginal revenue equals marginal cost
E)price equals average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The demand curve faced by a monopolist is
A)perfectly elastic
B)perfectly inelastic
C)undefined
D)the market demand curve
E)the sum of the demand curves for perfectly competitive firms in a similar industry
A)perfectly elastic
B)perfectly inelastic
C)undefined
D)the market demand curve
E)the sum of the demand curves for perfectly competitive firms in a similar industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The demand curve that a monopolist faces
A)is steeper than the market demand curve
B)is the same as its marginal revenue curve
C)is controlled by the government
D)does not exist
E)is the same as the market demand curve
A)is steeper than the market demand curve
B)is the same as its marginal revenue curve
C)is controlled by the government
D)does not exist
E)is the same as the market demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The monopoly's marginal revenue curve
A)is equivalent to its demand curve
B)lies below its demand curve
C)is perfectly elastic
D)is perfectly inelastic
E)has a positive slope
A)is equivalent to its demand curve
B)lies below its demand curve
C)is perfectly elastic
D)is perfectly inelastic
E)has a positive slope

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A non-discriminating monopolist's marginal revenue curve lies below its demand curve because
A)economists put it there by convention
B)in order to earn more profit,the monopolist must charge higher prices
C)a monopolist gouges its customers
D)in order to increase their profits,monopolists must produce in the inelastic range of the demand curve
E)in order to increase the number of units sold,the firm must lower the price on all units sold
A)economists put it there by convention
B)in order to earn more profit,the monopolist must charge higher prices
C)a monopolist gouges its customers
D)in order to increase their profits,monopolists must produce in the inelastic range of the demand curve
E)in order to increase the number of units sold,the firm must lower the price on all units sold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The monopoly that does not practice price discrimination
A)is a firm with a marginal revenue curve with a slope of zero
B)is a price taker
C)charges the same price for every unit of output it sells
D)operates in a market where all firms charge the same price
E)is always profitable in the short run
A)is a firm with a marginal revenue curve with a slope of zero
B)is a price taker
C)charges the same price for every unit of output it sells
D)operates in a market where all firms charge the same price
E)is always profitable in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If a non-discriminating monopolist decides to lower its price to sell one more unit of its product,then
A)total revenue rises by an amount equal to the price
B)some revenue is lost to the extent that units previously sold at a higher price now sell for a lower price;however,the additional unit sold brings in new revenue
C)marginal revenue increases when total revenue increases
D)the net effect on total revenue is typically zero since the price must fall
E)the net effect on total revenue is typically negative since the price must fall
A)total revenue rises by an amount equal to the price
B)some revenue is lost to the extent that units previously sold at a higher price now sell for a lower price;however,the additional unit sold brings in new revenue
C)marginal revenue increases when total revenue increases
D)the net effect on total revenue is typically zero since the price must fall
E)the net effect on total revenue is typically negative since the price must fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For a monopoly,
A)price and output are closely-linked choices
B)marginal revenue always exceeds marginal cost
C)price always exceeds average total cost in the short run
D)price is set independently from the output decision
E)price is always the highest that the market will bear
A)price and output are closely-linked choices
B)marginal revenue always exceeds marginal cost
C)price always exceeds average total cost in the short run
D)price is set independently from the output decision
E)price is always the highest that the market will bear

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

Figure 10-1 shows the demand schedule facing the only gas station in a small Midwestern town.The station does not price discriminate.Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The demand curve facing Friendly Stop has a constant price elasticity.
B)If the station increases sales from 100 to 110 gallons,marginal revenue will equal $1.40.
C)If the station increases sales from 100 to 110 gallons,marginal revenue will equal $14.00.
D)Demand is price elastic throughout the demand schedule.
E)The owner of the station would be unwilling to charge either $1.00 or $0.90 per gallon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a non-discriminating monopolist is maximizing profit,its marginal revenue
A)must be positive
B)must be negative
C)must equal zero
D)may be either positive or negative
E)must be upward sloping
A)must be positive
B)must be negative
C)must equal zero
D)may be either positive or negative
E)must be upward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Marginal revenue is
A)the change in total revenue obtained by selling an additional unit of output
B)average revenue per unit of output
C)the change in total revenue per unit of cost
D)total revenue divided by average revenue
E)average revenue divided by marginal cost
A)the change in total revenue obtained by selling an additional unit of output
B)average revenue per unit of output
C)the change in total revenue per unit of cost
D)total revenue divided by average revenue
E)average revenue divided by marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The change in total revenue obtained by selling an additional unit of output is
A)average revenue
B)business revenue
C)marginal revenue
D)overhead revenue
E)profit margin
A)average revenue
B)business revenue
C)marginal revenue
D)overhead revenue
E)profit margin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Absent an ability to price discriminate,if a monopoly wants to sell more output,it must
A)raise its price
B)lower its price
C)increase barriers to entry
D)obtain government permission
E)negate its patent protection
A)raise its price
B)lower its price
C)increase barriers to entry
D)obtain government permission
E)negate its patent protection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When a non-discriminating monopolist is maximizing profit,then
A)its price equals its marginal cost
B)its price equals its marginal revenue
C)it is producing all units for which marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
D)its supply curve intersects the market demand curve
E)its marginal cost curve intersects the market demand curve
A)its price equals its marginal cost
B)its price equals its marginal revenue
C)it is producing all units for which marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
D)its supply curve intersects the market demand curve
E)its marginal cost curve intersects the market demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose that a non-discriminating monopolist lowers its price from $75 to $70 in order to sell more output.Marginal revenue will
A)equal $75
B)equal $70
C)be between $75 and $70
D)be less than $70
E)be greater than $75
A)equal $75
B)equal $70
C)be between $75 and $70
D)be less than $70
E)be greater than $75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A monopoly
A)can ignore the law of demand
B)faces a demand curve for its output that is nowhere price inelastic
C)establishes the market price when it decides how much to charge
D)can sell additional units of output without lowering its price
E)is also a perfect price discriminator
A)can ignore the law of demand
B)faces a demand curve for its output that is nowhere price inelastic
C)establishes the market price when it decides how much to charge
D)can sell additional units of output without lowering its price
E)is also a perfect price discriminator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following limits the price a monopolist charges?
A)patents
B)copyrights
C)competition from other firms
D)market demand
E)market supply
A)patents
B)copyrights
C)competition from other firms
D)market demand
E)market supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The supply curve of a single-price monopolist
A)coincides with its marginal cost curve above its average total cost curve
B)coincides with its marginal cost curve above its average variable cost curve
C)is established by the government
D)slopes downward due to substantial economies of scale
E)does not exist
A)coincides with its marginal cost curve above its average total cost curve
B)coincides with its marginal cost curve above its average variable cost curve
C)is established by the government
D)slopes downward due to substantial economies of scale
E)does not exist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the single-price monopoly,marginal revenue is
A)more important than marginal cost
B)always more than marginal cost
C)always less than average cost
D)always less than the price of output
E)more significant than total revenue
A)more important than marginal cost
B)always more than marginal cost
C)always less than average cost
D)always less than the price of output
E)more significant than total revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A monopolist that does not price discriminate will set the output level where
A)P = MC
B)P = MR
C)TR = TC
D)MR = MC
E)P = ATC
A)P = MC
B)P = MR
C)TR = TC
D)MR = MC
E)P = ATC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
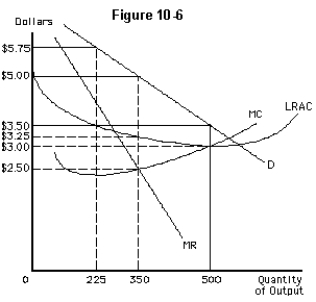
The profit-maximizing monopoly in Figure 10-6 does not price discriminate.It will produce
A)0 units
B)225 units
C)350 units
D)500 units
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A monopolist's supply curve
A)is the upward-sloping portion of its marginal cost curve
B)is the portion of its marginal cost curve above AVC
C)is parallel to its long run ATC curve
D)does not exist because quantity supplied depends on the market demand curve
E)is derived from the average variable cost curve
A)is the upward-sloping portion of its marginal cost curve
B)is the portion of its marginal cost curve above AVC
C)is parallel to its long run ATC curve
D)does not exist because quantity supplied depends on the market demand curve
E)is derived from the average variable cost curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
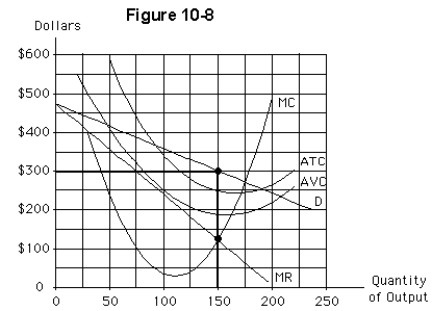
The non-price-discriminating firm depicted in Figure 10-8 will produce
A)approximately 100 units of output
B)approximately 150 units of output
C)approximately 175 units of output
D)more than 200 units of output
E)nothing since it should close

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
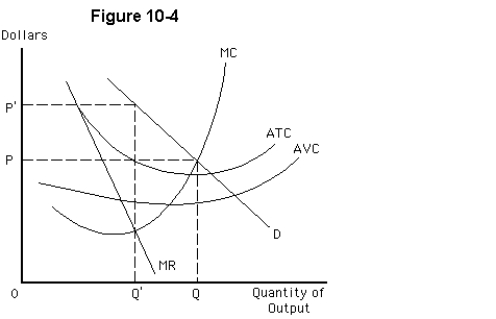
Figure 10-4 depicts a monopoly that does not price discriminate.What are the equilibrium price and output?
A)there is no equilibrium under monopoly
B)P' and Q'
C)P and Q
D)P' and Q
E)P and Q'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following statements about a non-discriminating monopoly firm is correct?
A)It charges a price greater than its marginal cost.
B)Its high prices generate inflation.
C)It charges a price that maximizes its total revenues.
D)As a price setter,it can ignore market demand.
E)It has no incentive to produce each output level at the lowest possible cost.
A)It charges a price greater than its marginal cost.
B)Its high prices generate inflation.
C)It charges a price that maximizes its total revenues.
D)As a price setter,it can ignore market demand.
E)It has no incentive to produce each output level at the lowest possible cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A monopolist will
A)never produce at an output level where marginal cost is positive
B)always produce at an output level where marginal revenue is positive
C)seek network externalities whenever switching costs are high
D)always produce where marginal revenue exceeds price
E)never produce where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost
A)never produce at an output level where marginal cost is positive
B)always produce at an output level where marginal revenue is positive
C)seek network externalities whenever switching costs are high
D)always produce where marginal revenue exceeds price
E)never produce where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Unlike perfectly competitive firms,monopolists can control
A)how much of the good to produce
B)what inputs to use in production
C)its plant size
D)the price charged per unit of output
E)the quality of inputs used in production
A)how much of the good to produce
B)what inputs to use in production
C)its plant size
D)the price charged per unit of output
E)the quality of inputs used in production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

The firm illustrated in Figure 10-8 will charge a single price of
A)approximately $125
B)approximately $250
C)approximately $275
D)approximately $300
E)more than $325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
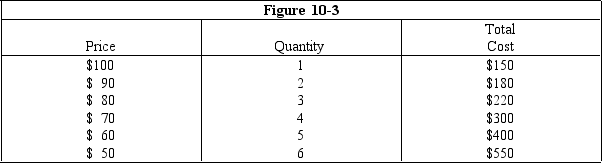
How much profit will the profit-maximizing level of output for the non-discriminating monopolist in Figure 10-3 yield?
A)$10
B)$20
C)$30
D)$40
E)$50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A monopolist will
A)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is positive
B)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is constant
C)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is negative
D)never produce at an output level where marginal cost is positive
E)ignore marginal revenue as long as average revenue is positive
A)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is positive
B)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is constant
C)never produce at an output level where marginal revenue is negative
D)never produce at an output level where marginal cost is positive
E)ignore marginal revenue as long as average revenue is positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

The profit-maximizing monopoly in Figure 10-6 will charge a single price of
A)$2.50
B)$3.50
C)$5.00
D)$5.75
E)$3.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Where is the monopoly supply curve located?
A)above the marginal revenue curve
B)below the marginal revenue curve
C)to the right of the marginal cost curve
D)coincident with the marginal cost curve
E)there is no monopoly supply curve
A)above the marginal revenue curve
B)below the marginal revenue curve
C)to the right of the marginal cost curve
D)coincident with the marginal cost curve
E)there is no monopoly supply curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
As a price setter,a monopoly
A)can establish any price it wants for each output level
B)can sell any output level it wants for each price
C)is constrained by the market demand curve
D)can use its pricing policy to shift the market demand curve
E)faces an upward-sloping demand curve for its output
A)can establish any price it wants for each output level
B)can sell any output level it wants for each price
C)is constrained by the market demand curve
D)can use its pricing policy to shift the market demand curve
E)faces an upward-sloping demand curve for its output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Monopolies charge
A)the highest possible price
B)a price determined by cost
C)the price consistent with the output level where total revenue equals total cost
D)the price associated with the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
E)the price at which total revenue equals average total cost
A)the highest possible price
B)a price determined by cost
C)the price consistent with the output level where total revenue equals total cost
D)the price associated with the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
E)the price at which total revenue equals average total cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
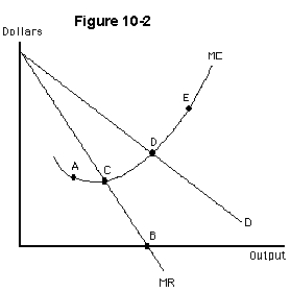
For the monopolist in Figure 10-2 producing at point D,which of the following statements is true?
A)profit will be greater than producing at point C
B)profit will be the same as producing at point C
C)profit will be less than producing at C
D)profit will be maximized
E)cannot compare profit level at C and D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
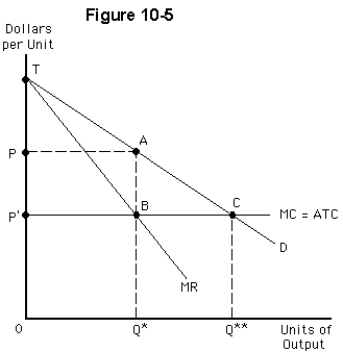
Figure 10-5 shows the cost and demand curves facing a monopolist whose marginal cost is constant.The firm has no fixed costs.If it does not discriminate,it will produce
A)Q** units and charge price P'
B)Q* units and charge price P
C)between Q* and Q** units while charging a price between P and P'
D)between 0 and Q* units while charging price P
E)Q* units and charge price P'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

What is the profit-maximizing level of output for the non-discriminating monopolist in Figure 10-3?
A)1 unit
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

For the monopolist in Figure 10-2,which point corresponds to the profit-maximizing level of output?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Figure 10-5 shows the cost and demand curves facing a monopolist whose marginal cost is constant.The firm has no fixed costs.If it does not discriminate what will it's profit be?
A)area PP'BA
B)area OPAQ*
C)area PP'CA
D)area APC
E)area OP"BQ*

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
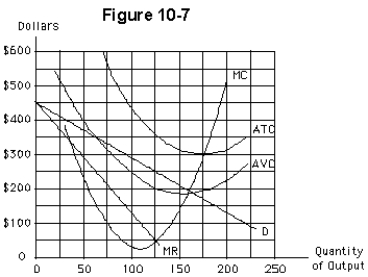
The firm in Figure 10-7 does not practice price discrimination.Its price and output will be
A)$300 and 175
B)$50 and 125
C)$250 and 125
D)$180 and 160
E)none of these since the firm should immediately shut down in the short run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 214 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



