Deck 15: Our City of Stars: the Milky Way
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Our City of Stars: the Milky Way
1
Which of the following astronomers first mapped the Milky Way as a disk?
A) Galileo
B) Newton
C) Shapley
D) Herschel
A) Galileo
B) Newton
C) Shapley
D) Herschel
Herschel
2
Which of the following provides evidence for past collisions between the Milky Way and its satellite galaxies?
A) the large number of satellite galaxies
B) the lack of young stars in the satellite galaxies
C) streams of stars in the halo
D) all of the above
A) the large number of satellite galaxies
B) the lack of young stars in the satellite galaxies
C) streams of stars in the halo
D) all of the above
streams of stars in the halo
3
In which part of the Milky Way are Population II stars most likely to be found?
A) bar
B) bulge
C) halo
D) disk
A) bar
B) bulge
C) halo
D) disk
halo
4
How does the density of stars (measured in stars per cubic parsec)in the Milky Way's bulge compare to that in the Sun's neighborhood?
A) The Sun's neighborhood is 10 times denser.
B) The bulge is 10 times denser.
C) The Sun's neighborhood is 104 times denser.
D) The bulge is 104 times denser.
A) The Sun's neighborhood is 10 times denser.
B) The bulge is 10 times denser.
C) The Sun's neighborhood is 104 times denser.
D) The bulge is 104 times denser.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which component of the Milky Way has the most stars?
A) disk
B) bar
C) bulge
D) halo
A) disk
B) bar
C) bulge
D) halo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What are the building blocks of cosmic structure?
A) sheets and filaments
B) galaxies
C) globular clusters
D) open clusters
A) sheets and filaments
B) galaxies
C) globular clusters
D) open clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following astronomers determined that the Sun was NOT at the center of the Milky Way?
A) Galileo
B) Shapley
C) Kapteyn
D) Herschel
A) Galileo
B) Shapley
C) Kapteyn
D) Herschel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
On average,which of the following stellar populations formed earliest in the Universe's history?
A) Population III
B) Population II
C) Population I
D) Populations are not related to age.
A) Population III
B) Population II
C) Population I
D) Populations are not related to age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A collection of gravitationally bound stars,numbering about 100 billion,is most likely a(n):
A) galaxy.
B) open cluster.
C) globular cluster.
D) supercluster.
A) galaxy.
B) open cluster.
C) globular cluster.
D) supercluster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many stars does an "average" galaxy like the Milky Way have?
A) 106
B) 109
C) 1011
D) 1013
A) 106
B) 109
C) 1011
D) 1013

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In which of the following ways are the bulge and halo of the Milky Way most similar?
A) gas content
B) the typical stellar metallicity
C) dust content
D) stellar velocities
A) gas content
B) the typical stellar metallicity
C) dust content
D) stellar velocities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How did Harlow Shapley avoid the bias of dust when measuring the size and shape of the Milky Way?
A) by observing in the infrared
B) by observing in the radio
C) with star counts
D) using globular clusters
A) by observing in the infrared
B) by observing in the radio
C) with star counts
D) using globular clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which component of the Milky Way is primarily composed of old stars?
A) disk
B) halo
C) bulge
D) bar
A) disk
B) halo
C) bulge
D) bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Where is the density of gas clouds largest within the disk of the Milky Way?
A) at large radii and inside spiral arms
B) at large radii and outside spiral arms
C) at small radii and inside spiral arms
D) at small radii and outside spiral arms
A) at large radii and inside spiral arms
B) at large radii and outside spiral arms
C) at small radii and inside spiral arms
D) at small radii and outside spiral arms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
How do stars in the disk of the Milky Way move?
A) on generally circular orbits in the same direction
B) on generally circular orbits, in either direction
C) on random orbits
D) on oscillatory orbits, in either direction
A) on generally circular orbits in the same direction
B) on generally circular orbits, in either direction
C) on random orbits
D) on oscillatory orbits, in either direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Where is the Sun located within the Milky Way?
A) at the center of the bulge
B) in the halo, about 1 kpc from the center
C) in the disk, about 1 kpc from the center
D) in the disk, about 8 kpc from the center
A) at the center of the bulge
B) in the halo, about 1 kpc from the center
C) in the disk, about 1 kpc from the center
D) in the disk, about 8 kpc from the center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the collection of galaxies near the Milky Way called?
A) local halo
B) local Group
C) local cluster
D) nothing; the Milky Way is isolated
A) local halo
B) local Group
C) local cluster
D) nothing; the Milky Way is isolated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Astronomers detect an old star with a velocity perpendicular to the Sun's 1 kpc from Earth.Of which component is it most likely a part?
A) halo
B) disk
C) bulge
D) bar
A) halo
B) disk
C) bulge
D) bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following provides evidence that the Milky Way's halo is an old system?
A) the lack of gas clouds
B) the chemical composition of the halo stars
C) the HR diagrams of globular clusters
D) all of the above
A) the lack of gas clouds
B) the chemical composition of the halo stars
C) the HR diagrams of globular clusters
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which component of the Milky Way is the largest,in terms of physical size?
A) bar
B) bulge
C) halo
D) disk
A) bar
B) bulge
C) halo
D) disk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Within the Milky Way,which region has the highest density of stars?
A) the Galactic center
B) the bar
C) the spiral arms
D) none of the above
A) the Galactic center
B) the bar
C) the spiral arms
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following stars is most likely to have formed in a spiral arm?
A) massive stars
B) low-luminosity stars
C) M stars
D) all of the above
A) massive stars
B) low-luminosity stars
C) M stars
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The Magellanic Stream is evidence of:
A) a collision of the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
B) tidal stripping of the Magellanic Clouds by the Milky Way.
C) gravitational interactions with Andromeda.
D) continued gas accretion onto the Milky Way.
A) a collision of the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
B) tidal stripping of the Magellanic Clouds by the Milky Way.
C) gravitational interactions with Andromeda.
D) continued gas accretion onto the Milky Way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The bright radio source Sagittarius A* is a:
A) quasar.
B) gamma-ray burst.
C) massive black hole.
D) supernova remnant.
A) quasar.
B) gamma-ray burst.
C) massive black hole.
D) supernova remnant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to present observations,how does the Milky Way's black hole compare to those at the center of powerful active galactic nuclei?
A) The Milky Way's black hole is much more massive.
B) The Milky Way's black hole is not spinning.
C) The Milky Way's black hole is much less massive.
D) The Milky Way's black hole is spinning more rapidly.
A) The Milky Way's black hole is much more massive.
B) The Milky Way's black hole is not spinning.
C) The Milky Way's black hole is much less massive.
D) The Milky Way's black hole is spinning more rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How thick is the Milky Way's disk as a percentage of its radius?
A) 0.02 percent
B) 2 percent
C) 20 percent
D) It varies from 0.02 percent to 20 percent, depending on radius.
A) 0.02 percent
B) 2 percent
C) 20 percent
D) It varies from 0.02 percent to 20 percent, depending on radius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What wavelength range is used to map the motions of stars around Sagittarius A*?
A) radio
B) infrared
C) optical
D) X-ray
A) radio
B) infrared
C) optical
D) X-ray

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why do older stars tend to be at larger heights above the midplane of the Milky Way's disk?
A) The Milky Way was thicker in the past.
B) The halo's gravity has pulled them upward.
C) They were born with large velocities in their molecular clouds.
D) They have had many scattering encounters with other stars.
A) The Milky Way was thicker in the past.
B) The halo's gravity has pulled them upward.
C) They were born with large velocities in their molecular clouds.
D) They have had many scattering encounters with other stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which component contains most of the mass in the Milky Way?
A) stars in the disk
B) stars in the bulge and halo
C) dark matter
D) gas and dust
A) stars in the disk
B) stars in the bulge and halo
C) dark matter
D) gas and dust

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How did astronomers obtain the first direct evidence of spiral structure within the Milky Way?
A) associations of young stars
B) molecular emission lines
C) emission from neutral hydrogen
D) dust lanes
A) associations of young stars
B) molecular emission lines
C) emission from neutral hydrogen
D) dust lanes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the cause of spiral structure in galaxies?
A) the winding action of galactic rotation
B) a compression wave traveling through the galaxy
C) natural spreading of molecular clouds
D) gravitational forces from neighboring galaxies
A) the winding action of galactic rotation
B) a compression wave traveling through the galaxy
C) natural spreading of molecular clouds
D) gravitational forces from neighboring galaxies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The development of infrared astronomy enabled the discovery of:
A) dark matter.
B) the first extrasolar planets.
C) low-mass stars.
D) the Milky Way's bar.
A) dark matter.
B) the first extrasolar planets.
C) low-mass stars.
D) the Milky Way's bar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Two stars have identical masses,but star A is part of Population I and star B is part of Population II.
How do these stars compare,if they are both on the main sequence?
A) Star A is redder than star B.
B) Star A is hotter than star B.
C) Star A has weaker absorption lines than star B.
D) The stars are nearly identical.
How do these stars compare,if they are both on the main sequence?
A) Star A is redder than star B.
B) Star A is hotter than star B.
C) Star A has weaker absorption lines than star B.
D) The stars are nearly identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Within the Milky Way,which of the following astronomical objects are preferentially found inside spiral arms?
A) molecular clouds
B) massive stars
C) atomic gas
D) all of the above
A) molecular clouds
B) massive stars
C) atomic gas
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following helps prove that spiral structure is not a result of the winding action of galactic rotation?
A) the appearance of molecular clouds inside spiral arms
B) the 21-cm line
C) the orbital period of the Sun around the Milky Way
D) the presence of a bulge
A) the appearance of molecular clouds inside spiral arms
B) the 21-cm line
C) the orbital period of the Sun around the Milky Way
D) the presence of a bulge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is most likely to cause Sagittarius A* to increase its luminosity suddenly?
A) the infall of a nearby gas cloud
B) a change in its spin
C) the formation of a new spiral arm in the Milky Way
D) gravitational interactions with globular clusters
A) the infall of a nearby gas cloud
B) a change in its spin
C) the formation of a new spiral arm in the Milky Way
D) gravitational interactions with globular clusters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How does the stellar population within a few parsecs of the galactic center differ from the rest of the bulge?
A) It is made up of more massive stars.
B) It is made up of redder stars.
C) It is made up of lower metallicity stars.
D) It is made up of stars with slower orbital velocities.
A) It is made up of more massive stars.
B) It is made up of redder stars.
C) It is made up of lower metallicity stars.
D) It is made up of stars with slower orbital velocities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is present near the center of the Milky Way?
A) a supermassive black hole
B) an absence of luminous stars
C) an active galactic nucleus
D) a bright ultraviolet source on the night sky
A) a supermassive black hole
B) an absence of luminous stars
C) an active galactic nucleus
D) a bright ultraviolet source on the night sky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The appearance of O and B stars in spiral arms suggests that:
A) star formation occurs inside the spiral arms.
B) the spiral arms' gravity pulls in nearby stars.
C) all stars are confined to spiral arms.
D) most stars end their lives in spiral arms.
A) star formation occurs inside the spiral arms.
B) the spiral arms' gravity pulls in nearby stars.
C) all stars are confined to spiral arms.
D) most stars end their lives in spiral arms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following provides evidence for a black hole at the center of our galaxy?
A) optical flashes from the galactic center
B) high-energy gamma-ray emission from the galactic center
C) strong magnetic fields near the galactic center
D) tidal effects on stars surrounding the galactic center
A) optical flashes from the galactic center
B) high-energy gamma-ray emission from the galactic center
C) strong magnetic fields near the galactic center
D) tidal effects on stars surrounding the galactic center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The figure below shows a pair of rotation curves.Which of the following statements correctly matches the curve to astronomical systems? Consider only the shape of the curve in answering this question. 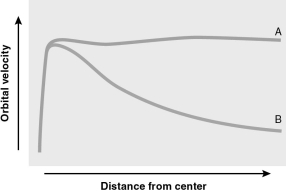
A) Curve A describes both the Milky Way and the Solar System.
B) Curve B describes both the Milky Way and the Solar System.
C) Curve A describes the Milky Way, while curve B describes the Solar System.
D) Curve B describes the Milky Way, while curve A describes the Solar System.

A) Curve A describes both the Milky Way and the Solar System.
B) Curve B describes both the Milky Way and the Solar System.
C) Curve A describes the Milky Way, while curve B describes the Solar System.
D) Curve B describes the Milky Way, while curve A describes the Solar System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 1906,Jacobus Kapteyn measured the size of the Milky Way.Why were his estimates inaccurate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following components of the Milky Way formed first?
A) stars in the disk
B) globular clusters
C) the bulge
D) the bar
A) stars in the disk
B) globular clusters
C) the bulge
D) the bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Why is the metallicity of Population I stars greater than that of Population II stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What are the three major components of the Milky Way galaxy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
How did William and Caroline Herschel measure the size and shape of the Milky Way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How did astronomers rule out the MACHO dark matter hypothesis?
A) rotation curves
B) gamma-ray bursts
C) underground dark matter detectors
D) microlensing
A) rotation curves
B) gamma-ray bursts
C) underground dark matter detectors
D) microlensing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How do physicists search for evidence of WIMPs?
A) through their gravitational effects
B) through collisions with other matter
C) through gamma rays produced during collisions
D) all of the above
A) through their gravitational effects
B) through collisions with other matter
C) through gamma rays produced during collisions
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the four fundamental forces of nature could dark matter experience?
A) gravity and the weak nuclear force
B) gravity, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force
C) gravity and the strong nuclear force
D) gravity only
A) gravity and the weak nuclear force
B) gravity, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force
C) gravity and the strong nuclear force
D) gravity only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Baade's window is one of the few regions of the sky where astronomers can study the galactic bulge in the optical band.What makes it special in this way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following provides the best evidence that the Milky Way's halo formed before its disk?
A) the prevalence of Population II stars in the halo
B) the lack of gas and dust in the disk
C) spiral structure in the disk
D) all of the above
A) the prevalence of Population II stars in the halo
B) the lack of gas and dust in the disk
C) spiral structure in the disk
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What happened to most of the stars of small galaxies that collided with the Milky Way?
A) They collided with stars in the Milky Way, destroying themselves.
B) They were incorporated into the Milky Way's disk.
C) They were incorporated into the black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
D) They were incorporated into the Milky Way's stellar halo.
A) They collided with stars in the Milky Way, destroying themselves.
B) They were incorporated into the Milky Way's disk.
C) They were incorporated into the black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
D) They were incorporated into the Milky Way's stellar halo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The figure below shows a sketch of the Milky Way.Label the three components marked A,B,and C.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the shape of the Milky Way's central component?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An observer far from any city lights might see the feature shown in the figure below at night.What generates the diffuse light seen here?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The figure below shows the rotation curve of a galaxy.How does the mass enclosed within a given distance from the galaxy's center vary? 
A) The mass is concentrated near the center.
B) The enclosed mass increases linearly with distance.
C) The enclosed mass increases with the square of distance.
D) The enclosed mass increases like the square root of distance.

A) The mass is concentrated near the center.
B) The enclosed mass increases linearly with distance.
C) The enclosed mass increases with the square of distance.
D) The enclosed mass increases like the square root of distance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In the gas cloud that would eventually become the Milky Way,how might an observer identify the gas that would eventually make up our galaxy's bulge?
A) material outside the central plane of the cloud
B) material with a small orbital velocity
C) material in the central plane of the cloud
D) material with a large orbital velocity
A) material outside the central plane of the cloud
B) material with a small orbital velocity
C) material in the central plane of the cloud
D) material with a large orbital velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How do the orbits of globular clusters differ from those of stars in the Milky Way's disk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How does the fraction of heavy elements inside gas clouds vary with location in the Milky Way's disk?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Why does the Milky Way's dark matter have a roughly spherical distribution?
A) Dark matter does not collide with other particles.
B) There is more dark matter than normal matter in the Milky Way.
C) Dark matter particles do not orbit the Milky Way's center.
D) The disk is younger than the dark matter halo.
A) Dark matter does not collide with other particles.
B) There is more dark matter than normal matter in the Milky Way.
C) Dark matter particles do not orbit the Milky Way's center.
D) The disk is younger than the dark matter halo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The figure below shows a spiral arm inside a galaxy.Relative to the spiral arm,in which direction (if any)are the gas and stars inside the galaxy moving?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Two stars orbit the center of the Milky Way with semimajor axes of 200 and 800 AU.If the first star has a period of 44 years,what is the period of the other star?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Why are O and B stars preferentially found within spiral arms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why might it be surprising that the black hole at the center of the Milky Way is not luminous?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During the formation of the Milky Way,why did the gas collapse to a disk while the stars remained in a spherical distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What does the distribution of gas and dust in the Milky Way tell us about the relative ages of the disk and stellar halo?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Where is most of the Milky Way's dark matter? How do astronomers know?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
What is a WIMP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the "conundrum of old age" to an astronomer?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What force provided the initial impetus for a primordial gas cloud to form the Milky Way?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



