Deck 11: Measuring the Stars: the Main Sequence and Its Meaning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/70
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Measuring the Stars: the Main Sequence and Its Meaning
1
Which of the following combinations of measurements CANNOT be used to determine a star's radius?
A) brightness and peak wavelength
B) angular size and distance
C) brightness, distance, and temperature
D) luminosity and peak wavelength
A) brightness and peak wavelength
B) angular size and distance
C) brightness, distance, and temperature
D) luminosity and peak wavelength
brightness and peak wavelength
2
What property of a star's spectral lines allows astronomers to measure stellar masses?
A) depth
B) width
C) wavelength
D) spacing
A) depth
B) width
C) wavelength
D) spacing
width
3
Why are stars considered to be thermodynamic systems?
A) Stars are hot.
B) Stars are always in motion.
C) Stars are giant collections of atoms.
D) Stars are powered by combustion.
A) Stars are hot.
B) Stars are always in motion.
C) Stars are giant collections of atoms.
D) Stars are powered by combustion.
Stars are giant collections of atoms.
4
What property of a star can best be used to determine its temperature?
A) luminosity
B) color
C) brightness
D) velocity
A) luminosity
B) color
C) brightness
D) velocity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Star A's spectrum is most intense at 500 nm,while star B's spectrum is most intense at 750 nm.If star A has a temperature of 5,800 K,what is the temperature of star B?
A) 13,000 K
B) 8,700 K
C) 4,500 K
D) 3,850 K
A) 13,000 K
B) 8,700 K
C) 4,500 K
D) 3,850 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How would astronomers measure the velocity of the star shown in the figure below? 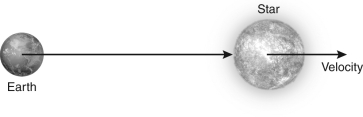
A) through its spectrum
B) through a transit
C) through its angular velocity across the sky
D) through its brightening or dimming with time

A) through its spectrum
B) through a transit
C) through its angular velocity across the sky
D) through its brightening or dimming with time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If star A has an apparent magnitude of 8 while star B has an apparent magnitude of 13,then star A is ________ than star B.
A) 100 times fainter
B) 5 times fainter
C) 5 times brighter
D) 100 times brighter
A) 100 times fainter
B) 5 times fainter
C) 5 times brighter
D) 100 times brighter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What properties of Cepheid variable stars are most often measured to determine their distance?
A) luminosity and brightness
B) period and brightness
C) luminosity and temperature
D) period and temperature
A) luminosity and brightness
B) period and brightness
C) luminosity and temperature
D) period and temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How have astronomers learned about the life cycles of stars?
A) through laboratory experiments
B) by studying the Big Bang
C) by studying the complete life cycles of individual stars
D) by measuring the properties of many stars at a single instant
A) through laboratory experiments
B) by studying the Big Bang
C) by studying the complete life cycles of individual stars
D) by measuring the properties of many stars at a single instant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What was Henrietta Leavitt's most important contribution to astronomy?
A) the spectral typing of stars
B) the relationship of stellar spectral type to temperature
C) the period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variables
D) the discovery of interstellar reddening
A) the spectral typing of stars
B) the relationship of stellar spectral type to temperature
C) the period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variables
D) the discovery of interstellar reddening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two stars orbit each other on circular orbits.The star with the larger orbital radius has a:
A) larger orbital period.
B) smaller mass.
C) smaller orbital speed.
D) smaller orbital period.
A) larger orbital period.
B) smaller mass.
C) smaller orbital speed.
D) smaller orbital period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A star has a parallax of 0.05 arcseconds.How far away from Earth is the star?
A) 20 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 0.5 parsecs
D) 0.05 parsecs
A) 20 parsecs
B) 5 parsecs
C) 0.5 parsecs
D) 0.05 parsecs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What property of a star's spectral lines allows astronomers to measure stellar masses?
A) redshift
B) width
C) variability
D) depth
A) redshift
B) width
C) variability
D) depth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Star A has an apparent magnitude of 7,while star B has an apparent magnitude of 12.If star A is four times more luminous than star B,how do the distances of the two stars compare?
A) Star A is 25 times farther than star B.
B) Star A is 5 times farther than star B.
C) Star A is 25 times closer than star B.
D) Star A is 5 times closer than star B.
A) Star A is 25 times farther than star B.
B) Star A is 5 times farther than star B.
C) Star A is 25 times closer than star B.
D) Star A is 5 times closer than star B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What quantities must be measured in order to calculate the luminosity of a star?
A) brightness and radius
B) radius and distance
C) temperature and distance
D) brightness and distance
A) brightness and radius
B) radius and distance
C) temperature and distance
D) brightness and distance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following must be measured in order to determine a star's proper motion?
A) angular position at multiple times
B) mass
C) redshift or blueshift
D) radius
A) angular position at multiple times
B) mass
C) redshift or blueshift
D) radius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Stars A and B have equal brightness,but star B is eight times as far from Earth as star A.How much more luminous is star A than star B?
A) 1/64
B) 1/8
C) 8
D) 64
A) 1/64
B) 1/8
C) 8
D) 64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Two stars orbit their common center of mass on circular orbits.Star A is four times more massive than star B.How do their orbital periods compare to each other?
A) Star A has a longer orbital period than star B.
B) Star B has a longer orbital period than star A.
C) They are the same.
D) The orbital periods cannot be determined without knowing their initial velocities.
A) Star A has a longer orbital period than star B.
B) Star B has a longer orbital period than star A.
C) They are the same.
D) The orbital periods cannot be determined without knowing their initial velocities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Hubble Space Telescope has detected galaxies with apparent magnitudes of about 30.Approximately how much fainter are these galaxies than stars with an apparent magnitude of 5?
A) 1025 times
B) 1010 times
C) 2,500 times
D) 25 times
A) 1025 times
B) 1010 times
C) 2,500 times
D) 25 times

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a relational property of stars?
A) radius
B) temperature
C) luminosity
D) distance
A) radius
B) temperature
C) luminosity
D) distance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
On the main sequence,a star's spectral type is ultimately determined by its:
A) distance.
B) luminosity.
C) composition.
D) mass.
A) distance.
B) luminosity.
C) composition.
D) mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following correctly orders the spectral types of stars from coolest to hottest?
A) OMKGFBA
B) MKGFABO
C) ABFGKMO
D) OBAFGKM
A) OMKGFBA
B) MKGFABO
C) ABFGKMO
D) OBAFGKM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The figure below shows the apparent position of star A on the sky at two different positions in Earth's orbit.How far away is the star? 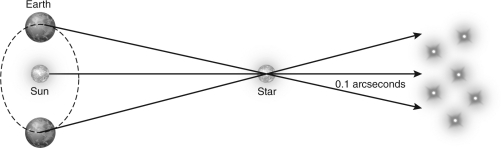
A) 0.1 parsec
B) 1 parsec
C) 10 parsecs
D) 100 parsecs

A) 0.1 parsec
B) 1 parsec
C) 10 parsecs
D) 100 parsecs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the Sun spends 10 billion years on the main sequence,how long will a star 100 times more massive than the Sun spend there?
A) 105 years
B) 3 × 106 years
C) 109 years
D) 1011 years
A) 105 years
B) 3 × 106 years
C) 109 years
D) 1011 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The figure below shows an HR diagram.What is the name for the feature marked "X"? 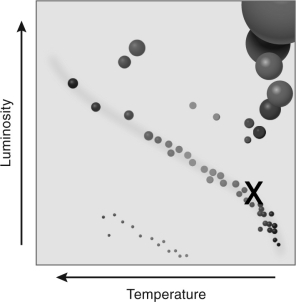
A) asymptotic giant branch
B) T Tauri track
C) main sequence
D) red giant branch

A) asymptotic giant branch
B) T Tauri track
C) main sequence
D) red giant branch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What determines the location of a star on the main sequence?
A) age
B) mass
C) composition
D) the star's principal fusion reaction
A) age
B) mass
C) composition
D) the star's principal fusion reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
On an HR diagram,the star Mira appears directly below the star Betelgeuse.Compared to Betelgeuse,Mira has a:
A) lower surface temperature.
B) higher surface temperature.
C) larger radius.
D) smaller radius.
A) lower surface temperature.
B) higher surface temperature.
C) larger radius.
D) smaller radius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following stellar properties does NOT increase as you trace the main sequence from right to left on an HR diagram?
A) fusion rate
B) peak wavelength
C) surface area
D) temperature
A) fusion rate
B) peak wavelength
C) surface area
D) temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The figure below shows a binary star system.Which of the following correctly characterizes the spectrum of this system at the instant shown in the figure? 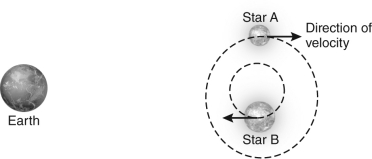
A) Star A's spectral lines have a smaller blueshift, while star B's spectral lines have a larger redshift.
B) Star A's spectral lines have a larger blueshift, while star B's spectral lines have a smaller redshift.
C) Star A's spectral lines have a smaller redshift, while star B's spectral lines have a larger blueshift.
D) Star A's spectral lines have a larger redshift, while star B's spectral lines have a smaller blueshift.

A) Star A's spectral lines have a smaller blueshift, while star B's spectral lines have a larger redshift.
B) Star A's spectral lines have a larger blueshift, while star B's spectral lines have a smaller redshift.
C) Star A's spectral lines have a smaller redshift, while star B's spectral lines have a larger blueshift.
D) Star A's spectral lines have a larger redshift, while star B's spectral lines have a smaller blueshift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is necessary to construct a modern model of a star?
A) equations of hydrostatic equilibrium
B) computers
C) equations of energy transport
D) all of the above
A) equations of hydrostatic equilibrium
B) computers
C) equations of energy transport
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The figure below shows four stars on an HR diagram.Which star has the largest radius? 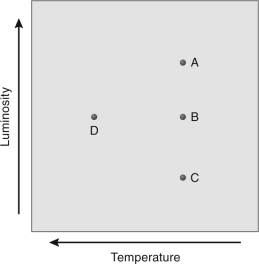
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A stellar model:
A) requires a model for the formation of the star.
B) requires detailed observations of a star's interior.
C) predicts the nature of energy transport within the star.
D) all of the above.
A) requires a model for the formation of the star.
B) requires detailed observations of a star's interior.
C) predicts the nature of energy transport within the star.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following environments would allow astronomers to produce an HR diagram that includes all phases of stellar evolution for stars with a wide range of masses?
A) an open cluster of stars that formed less than 106 years ago
B) a globular cluster of stars that formed 1010 years ago
C) an open cluster of stars that formed 1010 years ago
D) a galactic center field with a mixture of ages
A) an open cluster of stars that formed less than 106 years ago
B) a globular cluster of stars that formed 1010 years ago
C) an open cluster of stars that formed 1010 years ago
D) a galactic center field with a mixture of ages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Star A is twice as luminous as star B but has half the temperature of star B.How large is the radius of star A compared to star B?
A) 23/2 as large
B) 22 as large
C) 25/2 as large
D) 23 as large
A) 23/2 as large
B) 22 as large
C) 25/2 as large
D) 23 as large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Over the course of their hydrogen-fusing lives,stars:
A) move along the main sequence, from left to right.
B) remain in nearly the same location on the main sequence.
C) move along the main sequence, from right to left.
D) move up the red giant branch.
A) move along the main sequence, from left to right.
B) remain in nearly the same location on the main sequence.
C) move along the main sequence, from right to left.
D) move up the red giant branch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose that astronomers discover an error in our understanding of Cepheid variable stars,such that stars of a given oscillation period have a smaller luminosity than previously assumed.How would that change the estimated distances to other galaxies?
A) The distance estimates would not change.
B) The distance estimates would have greater variation.
C) The distance estimates would become larger.
D) The distance estimates would become smaller.
A) The distance estimates would not change.
B) The distance estimates would have greater variation.
C) The distance estimates would become larger.
D) The distance estimates would become smaller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Stellar evolution has been best understood by:
A) analyzing the properties of a large number of stars at a single instant.
B) observing the entire life cycles of individual high-mass stars.
C) measuring stars moving along the main sequence.
D) computer models without the input of observations.
A) analyzing the properties of a large number of stars at a single instant.
B) observing the entire life cycles of individual high-mass stars.
C) measuring stars moving along the main sequence.
D) computer models without the input of observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Massive stars:
A) burn their fuel rapidly, so they have shorter lifetimes than low-mass stars.
B) have large fuel supplies, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.
C) use the efficient CNO cycle, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.
D) burn more elements, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.
A) burn their fuel rapidly, so they have shorter lifetimes than low-mass stars.
B) have large fuel supplies, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.
C) use the efficient CNO cycle, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.
D) burn more elements, so they have longer lifetimes than low-mass stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Star A is four times as luminous as star B.Star B's spectrum peaks at 300 nm,while star A's spectrum peaks at 150 nm.How large is the radius of star A compared to star B?
A) 1/2 as large
B) 1/4 as large
C) twice as large
D) four times as large
A) 1/2 as large
B) 1/4 as large
C) twice as large
D) four times as large

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following stellar spectral types shows the most molecular absorption lines?
A) O
B) A
C) M
D) G
A) O
B) A
C) M
D) G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A stellar evolutionary track is the sequence of:
A) spatial locations occupied by a star over its lifetime.
B) luminosities and surface temperatures of a star over its lifetime.
C) fuel supplies of a star over its lifetime.
D) star formation and supernovae in a galaxy.
A) spatial locations occupied by a star over its lifetime.
B) luminosities and surface temperatures of a star over its lifetime.
C) fuel supplies of a star over its lifetime.
D) star formation and supernovae in a galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A star has a surface temperature of 15,000 K.At what wavelength does the star produce the most energy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An astronomer studies two globular clusters,A and B.Cluster A has a higher metallicity than cluster B,but their properties are otherwise identical.The astronomer should expect that:
A) cluster A's main sequence turnoff occurs at a higher mass than cluster B.
B) cluster A is more distant than cluster B.
C) cluster A is older than cluster B.
D) cluster A is more massive than cluster B.
A) cluster A's main sequence turnoff occurs at a higher mass than cluster B.
B) cluster A is more distant than cluster B.
C) cluster A is older than cluster B.
D) cluster A is more massive than cluster B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is an astrometric binary?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why does the nature of a star's energy source require a star to change over time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Stars A and B are identical,except that star A has a parallax of 0.1 arcseconds while star B has a parallax of 0.4 arcseconds.How does the brightness of stars A and B compare?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Why are globular clusters useful for studies of stellar evolution?
A) Their stars span a wide range of masses.
B) Their stars are the same age.
C) Their stars all have the same composition.
D) All of the above.
A) Their stars span a wide range of masses.
B) Their stars are the same age.
C) Their stars all have the same composition.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Star A moves 1 arcsecond/year across the sky while star B moves 0.5 arcseconds/year.Star A has a parallax angle three times as large as star B.If neither star shows a Doppler effect,how do the space velocities of the two stars compare to each other?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following quantities changes significantly during a star's main sequence lifetime?
A) luminosity
B) mass
C) core composition
D) color
A) luminosity
B) mass
C) core composition
D) color

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How do astronomers determine the composition of stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An astronomer observes a cluster of stars and constructs an HR diagram like Figure 11.6.What can he or she learn from the region marked "X"? 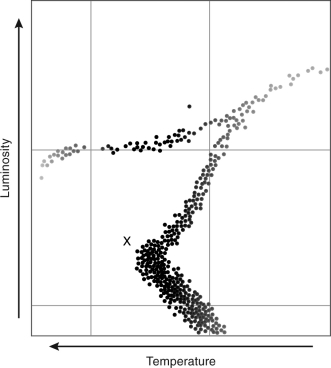
A) the distance to the cluster
B) the radius of the cluster
C) the mass of the cluster
D) the age of the cluster

A) the distance to the cluster
B) the radius of the cluster
C) the mass of the cluster
D) the age of the cluster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Star A has an apparent magnitude of 5,while star B has an apparent magnitude of 10.If star A is twice as far from Earth as star B,how do the luminosities of the two stars compare?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What information do you need to calculate the apparent magnitude of a star? What about the absolute magnitude?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If a star is so large that it cannot be resolved by a telescope on (or near)Earth,what quantities must you measure to determine its radius?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A star 10 times more massive than the Sun fuses hydrogen to helium 3,000 times faster than the Sun.If the Sun spends 10 billion years on the main sequence,how long will the more massive star remain there?
A) 1011 years
B) 109 years
C) 3 × 107 years
D) 3 × 106 years
A) 1011 years
B) 109 years
C) 3 × 107 years
D) 3 × 106 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following quantities is NOT necessary to observe in order to construct an HR diagram of a system of stars?
A) distance to each star
B) mass of each star
C) color of each star
D) brightness of each star
A) distance to each star
B) mass of each star
C) color of each star
D) brightness of each star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What property of Cepheid variable stars makes them useful for distance measures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What will happen when the Sun runs out of hydrogen fuel for fusion?
A) It will explode in a supernova.
B) Its internal structure will change.
C) It will begin fusing helium.
D) It will become a white dwarf.
A) It will explode in a supernova.
B) Its internal structure will change.
C) It will begin fusing helium.
D) It will become a white dwarf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following inputs are necessary for astronomers to compute the stellar evolutionary track of a star?
A) mass and surface temperature
B) mass and luminosity
C) mass and composition
D) luminosity and surface temperature
A) mass and surface temperature
B) mass and luminosity
C) mass and composition
D) luminosity and surface temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What causes a star to leave the main sequence?
A) the decreasing temperature of the star
B) the decreasing temperature of the star's core
C) the consumption of all the star's hydrogen
D) the consumption of the stellar core's hydrogen
A) the decreasing temperature of the star
B) the decreasing temperature of the star's core
C) the consumption of all the star's hydrogen
D) the consumption of the stellar core's hydrogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How does the inclination of a spectroscopic binary star system's orbit affect astronomers' mass estimates of the stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Why does luminosity increase with stellar mass on the main sequence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The Sun is expected to spend about 5 billion more years on the main sequence.If its luminosity increased suddenly to four times its usual value,how much time would it remain on the main sequence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Draw an HR diagram and sketch the location of the main sequence,red giant branch,and white dwarfs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is the name for the force balance illustrated in the figure below?
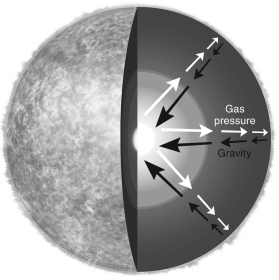


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In a typical observation of a globular cluster,90% of the observed stars will lie on the main sequence.What does this tell you about the life cycle of stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How do astronomers construct stellar evolutionary tracks on the HR diagram?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
All observed stars have roughly the same amount of hydrogen in their atmospheres.Why then are hydrogen lines less prominent in O stars than they are in A stars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
How are globular clusters used to test stellar models?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What aspects of a star change significantly during its time on the main sequence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 70 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



