Deck 15: Inequality in Earnings
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Inequality in Earnings
1
If technical change in the form of an increase in the use of capital increased the demand for skilled labor, then capital and skilled labor must be
A) gross substitutes.
B) substitutes in production.
C) gross complements.
D) perfect complements.
A) gross substitutes.
B) substitutes in production.
C) gross complements.
D) perfect complements.
C
2
Which of the following could NOT increase the earnings gap between highly-educated and less-educated workers?
A) a faster increase in the demand for highly-educated workers than for less-educated workers
B) a faster increase in the supply of highly-educated workers than of less-educated workers
C) a decrease in the demand for less-educated workers
D) a decrease in the average strength of unions
A) a faster increase in the demand for highly-educated workers than for less-educated workers
B) a faster increase in the supply of highly-educated workers than of less-educated workers
C) a decrease in the demand for less-educated workers
D) a decrease in the average strength of unions
B
3
The increase in wage inequality has been more rapid in the United States than in other industrialized countries for all the following reasons EXCEPT
A) the supply of skilled workers has grown less quickly in the United States.
B) wage determination is more decentralized in the United States.
C) unskilled workers are retrained more quickly in the United States.
D) unemployment rates among unskilled workers have risen more rapidly in other countries.
A) the supply of skilled workers has grown less quickly in the United States.
B) wage determination is more decentralized in the United States.
C) unskilled workers are retrained more quickly in the United States.
D) unemployment rates among unskilled workers have risen more rapidly in other countries.
C
4
Table 14.1 Incomes in Pololand
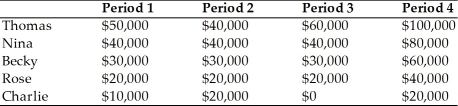
According to Table 14.1, in which period is the Gini coefficient lowest?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

According to Table 14.1, in which period is the Gini coefficient lowest?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a number of new workers enter the labor force and all of them find jobs at the mean level of wages, then this will cause the variance of wages to
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If all incomes were to fall by ten percent (due to deflation, for example) then the variance of income will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the wages of less-educated workers were reduced by supply shifts, then we would expect to see
A) an increase in the employment level of these workers.
B) a decrease in the employment level of these workers.
C) no change in the employment level of these workers.
D) either an increase or a decrease in the employment level of these workers.
A) an increase in the employment level of these workers.
B) a decrease in the employment level of these workers.
C) no change in the employment level of these workers.
D) either an increase or a decrease in the employment level of these workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of these wage trends has reduced the rate of increase in income inequality since 1980?
A) the trend in the wages of men versus the wages of women
B) the trend in the wages of high-school-educated workers versus the wages of college-educated workers
C) the narrowing of earnings within narrowly defined human capital groups
D) high levels of immigration
A) the trend in the wages of men versus the wages of women
B) the trend in the wages of high-school-educated workers versus the wages of college-educated workers
C) the narrowing of earnings within narrowly defined human capital groups
D) high levels of immigration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Much of the recent growth in income inequality was caused by
A) increases in real earnings of high school graduates.
B) decreasing returns to experience.
C) increases in the number of part-time workers.
D) increasing returns to education.
A) increases in real earnings of high school graduates.
B) decreasing returns to experience.
C) increases in the number of part-time workers.
D) increasing returns to education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If supply shifts were the primary cause behind the increasing wage gap between highly-educated and less-educated workers then
A) both supply curves must shift in the same direction.
B) the employment of less-educated workers would increase relative to the employment of college-educated workers.
C) the employment of less-educated workers would decrease relative to the employment of college-educated workers.
D) the relative employment of the two groups would not change.
A) both supply curves must shift in the same direction.
B) the employment of less-educated workers would increase relative to the employment of college-educated workers.
C) the employment of less-educated workers would decrease relative to the employment of college-educated workers.
D) the relative employment of the two groups would not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A decrease in the price of capital will cause the demand for unskilled labor to shift to the left if capital and unskilled labor are
A) gross complements.
B) gross substitutes.
C) gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) complements in production.
A) gross complements.
B) gross substitutes.
C) gross complements or gross substitutes.
D) complements in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Technological change
A) is the equivalent of a decrease in the price of capital.
B) is the equivalent of an increase in international trade.
C) will always decrease the demand for less-educated workers.
D) will always decrease the demand for well-educated workers.
A) is the equivalent of a decrease in the price of capital.
B) is the equivalent of an increase in international trade.
C) will always decrease the demand for less-educated workers.
D) will always decrease the demand for well-educated workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Since 1980 the earnings of middle-aged college-educated males has ________ relative to those of high-school-educated males; and the earnings of middle-aged college-educated females has ________ relative to those of high-school-educated females.
A) increased; increased
B) increased; decreased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased
A) increased; increased
B) increased; decreased
C) decreased; increased
D) decreased; decreased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Among male college graduates, returns to experience have ________ since 1980, tending to
A) increased; equalize earnings
B) increased; increase earnings inequality
C) decreased; equalize earnings
D) decreased; increase earnings inequality
A) increased; equalize earnings
B) increased; increase earnings inequality
C) decreased; equalize earnings
D) decreased; increase earnings inequality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Data on the ratio of wages of full-time workers at the 90th percentile to those at the 10th percentile show all the following EXCEPT
A) the ratio is generally higher among men than among women.
B) the ratio has climbed in almost all industrialized countries.
C) the ratios are higher in the United States and Canada than elsewhere.
D) the ratios in industrialized countries generally range between 3 and 5.
A) the ratio is generally higher among men than among women.
B) the ratio has climbed in almost all industrialized countries.
C) the ratios are higher in the United States and Canada than elsewhere.
D) the ratios in industrialized countries generally range between 3 and 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Since 1980 the real wages of unskilled workers in most of Western Europe have ________ and this helps explain why their unemployment rates have ________.
A) fallen; fallen
B) not fallen; fallen
C) fallen; risen
D) not fallen; risen
A) fallen; fallen
B) not fallen; fallen
C) fallen; risen
D) not fallen; risen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If all incomes were to double (due to inflation, for example) then the coefficient of variation of income will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) either increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Changes in labor demand can result from changes in either product demand or the capital-labor mix. During the 1980s,
A) changes in product demand were more influential due to changes in import-export ratios.
B) changes in product demand were more influential due to changes in income levels.
C) changes in capital-labor mixes were more important.
D) changes in both areas were of roughly equal importance.
A) changes in product demand were more influential due to changes in import-export ratios.
B) changes in product demand were more influential due to changes in income levels.
C) changes in capital-labor mixes were more important.
D) changes in both areas were of roughly equal importance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The earnings and employment of those with more human capital have both increased dramatically since 1980. This suggests that their ________ curve capital had shifted ________.
A) demand, leftward
B) demand, rightward
C) supply, leftward
D) supply, rightward
A) demand, leftward
B) demand, rightward
C) supply, leftward
D) supply, rightward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The coefficient of variation of incomes of full-time workers is highest among
A) older workers.
B) younger workers.
C) middle-aged workers.
D) high school graduates.
A) older workers.
B) younger workers.
C) middle-aged workers.
D) high school graduates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In nation X, inequality is measured with reported income and does not include welfare benefits. Suppose welfare benefits are increased and those on welfare who continue to work cut slightly back on their hours of work. Measured inequality will ________ and true inequality will likely ________.
A) increase, increase
B) decrease, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) increase, decrease
A) increase, increase
B) decrease, decrease
C) decrease, increase
D) increase, decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assume the demand for high tech good is perfectly inelastic. If workers producing high tech goods become more productive, then these workers employment will ________ and their wages will ________.
A) fall, rise
B) fall, fall
C) rise, rise
D) rise, fall
A) fall, rise
B) fall, fall
C) rise, rise
D) rise, fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The greatest growth of earnings disparities within an occupation in the 1980s occurred
A) within the sales profession.
B) among government workers.
C) within the teaching profession.
D) among assembly line workers.
A) within the sales profession.
B) among government workers.
C) within the teaching profession.
D) among assembly line workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of these decades had the greatest increase in inequality?
A) The 80s
B) The 90s
C) 2000-2008
D) Inequality has had about the same increase in each decade.
A) The 80s
B) The 90s
C) 2000-2008
D) Inequality has had about the same increase in each decade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Jeb and his brother John are in manufacturing jobs that pay the mean earnings in the United States. They then become farmers and their usual earnings, while remaining the same on average as the mean earings in the United States, vary from year to year. In one year, Jeb earns $20,000 more than usual while John earns $20,000 less than usual. If this occurred for many workers, then
A) inequality will increase.
B) inequality will decrease.
C) inequality will remain unchanged.
D) it is uncertain how inequality will change.
A) inequality will increase.
B) inequality will decrease.
C) inequality will remain unchanged.
D) it is uncertain how inequality will change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the fraction of the people in the middle of the income distribution decreases by 20 percent with half of these moving to the lower end and the other half to the upper end, then income inequality will
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) be unaffected.
D) uncertain.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) be unaffected.
D) uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An economist in a foreign land observes that the earnings of college graduates have increased relative to the earnings of high school graduates. Over the same period, the relative number of college graduates has gone down. Which of the following explanations is consistent with these two observations? The increase in earnings inequality between high school and college graduates
A) is due to technical change making college graduates more productive relative to high school graduates.
B) is due an increase in the demand for college graduates relative to high school graduates.
C) is due to the increase in cost of going to college.
D) is due to an increase in the returns to a college education.
A) is due to technical change making college graduates more productive relative to high school graduates.
B) is due an increase in the demand for college graduates relative to high school graduates.
C) is due to the increase in cost of going to college.
D) is due to an increase in the returns to a college education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following will reduce inequality?
A) The rich and poor earn more, but the rich earn proportionately more.
B) The poor and rich earn less, but the earnings of the rich go down proportionately more.
C) The poor and the rich earn proportionately more.
D) The poor and rich earn less, but the earnings of the poor go down proportionately more.
A) The rich and poor earn more, but the rich earn proportionately more.
B) The poor and rich earn less, but the earnings of the rich go down proportionately more.
C) The poor and the rich earn proportionately more.
D) The poor and rich earn less, but the earnings of the poor go down proportionately more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Gini coefficient is 0.20. What is the area under the Lorenz curve?
A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.30
D) 0.40
A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.30
D) 0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not a major cause of the increase in the inequality since 1980?
A) increase returns to investments in higher education
B) increased earnings disparities within human-capital groups
C) the change in female relative to male earnings since 1980
D) increase in the price of high-tech goods
A) increase returns to investments in higher education
B) increased earnings disparities within human-capital groups
C) the change in female relative to male earnings since 1980
D) increase in the price of high-tech goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best describes the statement "Earnings at the 80th percentile were $20,000"?
A) 80% were earning $20,000 or less
B) 80% were earning $20,000 or more
C) The average earnings of those in the top 80% was $20,000
D) The average earnings of those in the bottom 80% was $20,000
A) 80% were earning $20,000 or less
B) 80% were earning $20,000 or more
C) The average earnings of those in the top 80% was $20,000
D) The average earnings of those in the bottom 80% was $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the text, the main reason for the increase in inequality since 1980 is
A) the policies favored by Ronald Reagan.
B) higher compensation of corporation bosses.
C) technical change favoring those with more human capital.
D) decreased international trade.
A) the policies favored by Ronald Reagan.
B) higher compensation of corporation bosses.
C) technical change favoring those with more human capital.
D) decreased international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Gini coefficient in a society where all families have equal incomes would be
A) 0.
B) 0.5.
C) 1.0.
D) 2.0.
A) 0.
B) 0.5.
C) 1.0.
D) 2.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a competitive industry, output is produced with skilled and unskilled labor. Factor-biased technical change that increases the productivity of skilled labor, will, at a given ratio of skilled to unskilled labor, shift any given isoproduct curve ________ the origin and ________ the absolute slope of the isoproduct curve (when the number of skilled labor is along the horizontal axis). Pick the best pair of answers
A) towards, steeper
B) towards, flatter
C) away from, steeper
D) away from, steeper
A) towards, steeper
B) towards, flatter
C) away from, steeper
D) away from, steeper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Lorenz curve will ________ whenever the distribution of family income becomes less equal.
A) move closer to the diagonal line
B) become straighter
C) move farther from the diagonal line
D) cross the previous Lorenz Curve
A) move closer to the diagonal line
B) become straighter
C) move farther from the diagonal line
D) cross the previous Lorenz Curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The area under a Lorenz curve is 0.30. What is its Gini coefficient?
A) 0.15
B) 0.20
C) 0.30
D) 0.40
A) 0.15
B) 0.20
C) 0.30
D) 0.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to the Gini coefficient, income EQUALITY in the United States during the 1980s
A) increased.
B) remained unchanged.
C) decreased.
D) increased, because the Gini coefficient increased.
A) increased.
B) remained unchanged.
C) decreased.
D) increased, because the Gini coefficient increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Assume that less skilled workers are in the lower half of earnings. Which of the following events would cause the 80:20 ratio of incomes to go from 2.0 to 3.0?
A) a 50% increase in everyone's earnings
B) a relative decrease in the supply of unskilled workers
C) a relative decrease in the demand for unskilled workers
D) an increase in welfare payments causes unskilled workers to leave the work force
A) a 50% increase in everyone's earnings
B) a relative decrease in the supply of unskilled workers
C) a relative decrease in the demand for unskilled workers
D) an increase in welfare payments causes unskilled workers to leave the work force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
During the 1980s, inequality increased. While the wages of high school graduates remained unchanged, the wages of college graduates increased dramatically. Which of the following (if true) could explain why this occurred? (Note that the "quality" of education includes the value of what is being taught)
A) The quality of education at the high school level (and below) fell.
B) The quality of education at the college level (and above) rose.
C) The relative number of college graduates increased.
D) The quality of education at the high school level (and below) rose.
A) The quality of education at the high school level (and below) fell.
B) The quality of education at the college level (and above) rose.
C) The relative number of college graduates increased.
D) The quality of education at the high school level (and below) rose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An increase in inequality will always be accompanied by
A) a reduction of earnings of those in the lowest percentiles.
B) an increase of earnings of those in the highest percentiles.
C) an increase in the dispersion of incomes.
D) all of the above.
A) a reduction of earnings of those in the lowest percentiles.
B) an increase of earnings of those in the highest percentiles.
C) an increase in the dispersion of incomes.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose that earnings instability (such that income can go up or down) increases for the lower 20 percent of the workforce. The increase in inequality as measured by the 90:10 ratio will ________ the increase as measured by the 80:20 ratio
A) be smaller than
B) be about the same as
C) be greater than
D) none of the above: inequality will decrease
A) be smaller than
B) be about the same as
C) be greater than
D) none of the above: inequality will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The widget industry is competitive. Widgets (W) are produced with skilled labor (S) such that each skilled labor produces c widgets such that W = aC. If technological progress makes skilled labor more productive, then more skilled workers will be employed
A) only when the demand for widgets is price inelastic.
B) only when the demand for widgets in price elastic.
C) no matter what the price elasticity of demand is.
D) fewer skilled workers will be employed no matter what else happens.
A) only when the demand for widgets is price inelastic.
B) only when the demand for widgets in price elastic.
C) no matter what the price elasticity of demand is.
D) fewer skilled workers will be employed no matter what else happens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Suppose all persons have the same innate ability and the same access to capital markets. Which of the following will decrease inequality?
A) People vary more in their time horizon.
B) People vary more in the value they place on leisure.
C) People become more willing to leave the labor force when their wages fall.
D) People become more risk-adverse
A) People vary more in their time horizon.
B) People vary more in the value they place on leisure.
C) People become more willing to leave the labor force when their wages fall.
D) People become more risk-adverse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The widget industry is perfectly competitive and produces 1000 widgets. Currently, it takes one unit of skilled labor and two units of unskilled labor to produce one widget. Technological change then increases the productivity of skilled labor only. Afterward, the total employment of skilled workers goes up. Which of the following is consistent with this result?: ________ units of skilled workers and two units of unskilled labor are needed to produce one widget and total output is ________ widgets.
A) 0.75, 1100
B) 1.25, 1600
C) 1.25, 1100
D) 0.75, 1600
A) 0.75, 1100
B) 1.25, 1600
C) 1.25, 1100
D) 0.75, 1600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In an economy, employers cover the cost of health insurance by the difference between what the worker produces and what the worker gets in wages. If the cost of health insurance goes up by $5000 for all workers, what will happen to earnings inequality (as measured by the 80:20 ratio)?
A) Earnings inequality will go up.
B) Earnings inequality will go down.
C) Earnings inequality will remain unchanged.
D) Uncertain: it depends upon who gets sick more.
A) Earnings inequality will go up.
B) Earnings inequality will go down.
C) Earnings inequality will remain unchanged.
D) Uncertain: it depends upon who gets sick more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



