Deck 3: Cell Structure and Function
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/72
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cell Structure and Function
1
You are studying life-forms in extreme environments, and you have discovered a microorganism with cardiolipin, hopanoids, and ester linkages in the membrane. It also has teichoic acids, galactans, and phenolic glycolipids in the cell wall. In addition, it is a porin similar to OmpA. This microorganism is most likely related to
A) eukaryotic cells.
B) archaea.
C) mycobacteria.
D) Gram-positive bacteria.
E) Gram-negative bacteria.
A) eukaryotic cells.
B) archaea.
C) mycobacteria.
D) Gram-positive bacteria.
E) Gram-negative bacteria.
C
2
In the figure below, which of the four fatty acids adds fluidity to a membrane, and what type of bond allows this to happen? 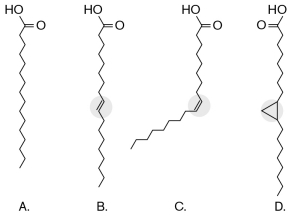
A) A; saturated bond
B) B; trans
C) B; cis
D) C; cis
E) D; double

A) A; saturated bond
B) B; trans
C) B; cis
D) C; cis
E) D; double
D
3
All of the statements about genetic analysis of cells complementing cell fractionation are true EXCEPT that it
A) is used to identify which genes and proteins are involved in a process.
B) can be used by identifying phenotypes under a microscope.
C) can be used to identify the exact change in protein sequences giving a particular phenotype.
D) has never been used to study FtsZ.
E) can be used to study cell division.
A) is used to identify which genes and proteins are involved in a process.
B) can be used by identifying phenotypes under a microscope.
C) can be used to identify the exact change in protein sequences giving a particular phenotype.
D) has never been used to study FtsZ.
E) can be used to study cell division.
D
4
We cannot see the molecules within a cell, but ________ and ________ analysis generate a remarkably detailed view.
A) structural; genetic
B) microscopy; genetic
C) chemical; subcellular
D) microscopy; subcellular
E) chemical; genetic
A) structural; genetic
B) microscopy; genetic
C) chemical; subcellular
D) microscopy; subcellular
E) chemical; genetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Some bacterial cells are inedible for humans because of the
A) high ion content in the cytoplasm.
B) high proportion of nucleic acids that humans degrade to the waste product uric acid.
C) peptide-linked sugars in the cell wall cannot be digested.
D) high uric acid content of the cytoplasm.
E) high polyamine content, which is toxic.
A) high ion content in the cytoplasm.
B) high proportion of nucleic acids that humans degrade to the waste product uric acid.
C) peptide-linked sugars in the cell wall cannot be digested.
D) high uric acid content of the cytoplasm.
E) high polyamine content, which is toxic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of these experiments would NOT be a reason to fractionate bacterial cells?
A) to obtain membrane fractions to study transport proteins
B) to purify ribosome subunits to study translation
C) to obtain periplasmic proteins to study chaperons from that space
D) to obtain cytoplasmic proteins such as FtsZ
E) to study the growth rate of E. coli in the presence of lactose
A) to obtain membrane fractions to study transport proteins
B) to purify ribosome subunits to study translation
C) to obtain periplasmic proteins to study chaperons from that space
D) to obtain cytoplasmic proteins such as FtsZ
E) to study the growth rate of E. coli in the presence of lactose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
You study a bacterium that grows in very low-nutrient aqueous environments. Which type of transport mechanism is required to deliver nutrients from these environments where they are at a lower concentration than inside the cell?
A) aquaporins
B) active transport
C) facilitated diffusion
D) passive diffusion
E) Such bacteria cannot exist.
A) aquaporins
B) active transport
C) facilitated diffusion
D) passive diffusion
E) Such bacteria cannot exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following types of molecules may passively diffuse across a membrane?
A) an amino acid in a low pH environment
B) a weak acid in a high pH environment
C) a large polar molecule such as a sugar
D) a small uncharged molecule such as water
E) No molecules can diffuse across a membrane.
A) an amino acid in a low pH environment
B) a weak acid in a high pH environment
C) a large polar molecule such as a sugar
D) a small uncharged molecule such as water
E) No molecules can diffuse across a membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The z-ring is
A) made up of an actin-like polymer.
B) involved in segregation of two to four nucleoids.
C) controlled by a nutrient-dependent regulator.
D) involved in replication but not cytokinesis.
E) involved in preventing transcription of noncoding regions of DNA.
A) made up of an actin-like polymer.
B) involved in segregation of two to four nucleoids.
C) controlled by a nutrient-dependent regulator.
D) involved in replication but not cytokinesis.
E) involved in preventing transcription of noncoding regions of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following reinforces and stiffens membranes in bacteria?
A) hopanoids
B) polyamines
C) sterols
D) peptidoglycans
E) lipids
A) hopanoids
B) polyamines
C) sterols
D) peptidoglycans
E) lipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Polyamines are ________ charged when the pH is near neutral.
A) not
B) negatively
C) positively
D) super
E) randomly
A) not
B) negatively
C) positively
D) super
E) randomly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Specific membrane components, particularly ________, determine which substances are transported across the membrane.
A) phospholipids
B) proteins
C) ions
D) polysaccharides
E) leaflets
A) phospholipids
B) proteins
C) ions
D) polysaccharides
E) leaflets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A medically important example of active transport is that of drug ________ proteins powered by the hydrogen ion gradient.
A) efflux
B) porin
C) membrane-permeant
D) diffusion
E) lysis
A) efflux
B) porin
C) membrane-permeant
D) diffusion
E) lysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The proteins embedded in a membrane require that region to be
A) crystalline.
B) hydrophobic.
C) flexible.
D) negatively charged.
E) positively charged.
A) crystalline.
B) hydrophobic.
C) flexible.
D) negatively charged.
E) positively charged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
E. coli and Sinorhizobium cell-surface proteins enable colonization of ________ and ________, respectively.
A) the human intestinal epithelium; animal skin
B) legume plants; the human intestinal epithelium
C) the human intestinal epithelium; legume plants
D) legume plants; animal skin
E) cantaloupe; spinach
A) the human intestinal epithelium; animal skin
B) legume plants; the human intestinal epithelium
C) the human intestinal epithelium; legume plants
D) legume plants; animal skin
E) cantaloupe; spinach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Extreme thermophiles have ________ chains in their membrane in order to maintain membrane stability.
A) lipoprotein
B) hopanoid
C) cholesterol
D) terpenoid
E) cardiolipin
A) lipoprotein
B) hopanoid
C) cholesterol
D) terpenoid
E) cardiolipin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Cells must be broken open in order to then fractionate the components. Each of the following can be used in bacterial cell breakage EXCEPT
A) French press.
B) lysozyme .
C) mild detergent.
D) ultracentrifugation.
E) ultrasonic vibration.
A) French press.
B) lysozyme .
C) mild detergent.
D) ultracentrifugation.
E) ultrasonic vibration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The capsule polysaccharides form a slippery mucous layer that inhibits
A) diffusion.
B) phagocytosis.
C) attachment.
D) lysis.
E) osmosis.
A) diffusion.
B) phagocytosis.
C) attachment.
D) lysis.
E) osmosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Mary Jane Osborn discovered that inner and outer membranes are different in density by using
A) genetic analysis.
B) X-ray crystallography.
C) ultracentrifugation.
D) protein synthesis.
E) fluorescent.
A) genetic analysis.
B) X-ray crystallography.
C) ultracentrifugation.
D) protein synthesis.
E) fluorescent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The molecule shown below is ________ and may play a role in ________. 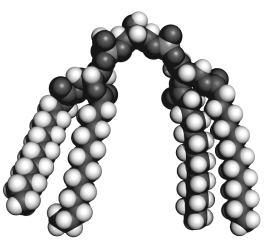
A) phosphatidylethanolamine; heat response
B) cardiolipin; heat response
C) phosphatidylglycerol; heat response
D) cardiolipin; starvation
E) phosphatidylglycerol; heat response

A) phosphatidylethanolamine; heat response
B) cardiolipin; heat response
C) phosphatidylglycerol; heat response
D) cardiolipin; starvation
E) phosphatidylglycerol; heat response

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A ________ is a term used to designate a single messenger RNA molecule being translated by multiple ribosomes.
A) couple
B) periplasm
C) carboxysome
D) thylakoid
E) polysome
A) couple
B) periplasm
C) carboxysome
D) thylakoid
E) polysome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The structure shown below is found in the ________ of some bacteria and the larger molecules are connected by the ________ cross-link shown at the arrow. 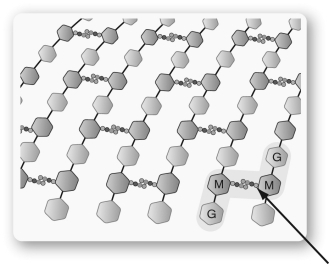
A) cell wall; sugar
B) cell membrane; peptide
C) cell membrane; sugar
D) cell wall; peptide
E) nucleoid membrane; peptide

A) cell wall; sugar
B) cell membrane; peptide
C) cell membrane; sugar
D) cell wall; peptide
E) nucleoid membrane; peptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The bacterial cell wall of mycobacteria is highly hydrophobic due to presence of
A) lipoproteins.
B) phenolic glycolipids.
C) phospholipids.
D) polysaccharides.
E) glycoproteins.
A) lipoproteins.
B) phenolic glycolipids.
C) phospholipids.
D) polysaccharides.
E) glycoproteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The ________ is the region between the cytoplasmic membrane and the outer membrane in Gram-negative cells.
A) periplasm
B) cytoplasm
C) lysozyme
D) lipopolysaccharide
E) S-layer
A) periplasm
B) cytoplasm
C) lysozyme
D) lipopolysaccharide
E) S-layer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Water can move across a membrane via passive diffusion but that movement is aided by
A) aquaporins.
B) ion transporters.
C) active transport.
D) ethanol2.
E) weak acids and bases.
A) aquaporins.
B) ion transporters.
C) active transport.
D) ethanol2.
E) weak acids and bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
All of the following are true of supercoiling in chromosomal DNA EXCEPT that it
A) doubles back and twists upon itself.
B) facilitates RNA transcription.
C) results in compaction.
D) is generated by gyrase.
E) is maintained by DNA-binding proteins.
A) doubles back and twists upon itself.
B) facilitates RNA transcription.
C) results in compaction.
D) is generated by gyrase.
E) is maintained by DNA-binding proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The lipopolysaccharide of the outer membrane is of medical importance because it acts as a(n)
A) endotoxin.
B) exotoxin.
C) toxoid.
D) enterotoxin.
E) antibiotic.
A) endotoxin.
B) exotoxin.
C) toxoid.
D) enterotoxin.
E) antibiotic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Lipopolysaccharides are found in
A) all bacteria.
B) Gram-positive bacteria.
C) Gram-negative bacteria.
D) archaea.
E) eukaryotes.
A) all bacteria.
B) Gram-positive bacteria.
C) Gram-negative bacteria.
D) archaea.
E) eukaryotes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
All of the following are true statements about bacterial S-layers EXCEPT that they
A) are commonly found in Gram-positive cells as well as in archaea.
B) are a crystalline layer consisting of protein or glycoprotein.
C) present a formidable physical barrier to predators or parasites.
D) are found in bacteria freshly isolated from natural sources.
E) are found in bacteria isolated from laboratory cultures.
A) are commonly found in Gram-positive cells as well as in archaea.
B) are a crystalline layer consisting of protein or glycoprotein.
C) present a formidable physical barrier to predators or parasites.
D) are found in bacteria freshly isolated from natural sources.
E) are found in bacteria isolated from laboratory cultures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How can weak acids and weak bases cause pH stress to cells?
A) Only weak acids can cause stress by diffusing across a membrane at low pH.
B) Weak acids and weak bases do not cause stress.
C) If a cell has transporters that are not well regulated, weak acids or weak bases can accumulate inside the cells and cause stress.
D) At certain pHs, both weak acids or weak bases will be uncharged and thus are small uncharged molecules that can diffuse across a membrane and cause pH stress inside the cell.
E) Weak bases will only cause pH stress at low pH.
A) Only weak acids can cause stress by diffusing across a membrane at low pH.
B) Weak acids and weak bases do not cause stress.
C) If a cell has transporters that are not well regulated, weak acids or weak bases can accumulate inside the cells and cause stress.
D) At certain pHs, both weak acids or weak bases will be uncharged and thus are small uncharged molecules that can diffuse across a membrane and cause pH stress inside the cell.
E) Weak bases will only cause pH stress at low pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is true of Fts proteins?
A) They form a ring in the area where cell division will occur.
B) They aid in DNA replication.
C) They are involved in peptidoglycan synthesis.
D) They are involved in making proteins.
E) They are important in transcription.
A) They form a ring in the area where cell division will occur.
B) They aid in DNA replication.
C) They are involved in peptidoglycan synthesis.
D) They are involved in making proteins.
E) They are important in transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
All of the following are true for DNA-binding proteins EXCEPT that they
A) can form protective crystalline structures around organized DNA.
B) condense prokaryotic DNA.
C) can act as regulators of gene expression.
D) determine the shape of the cell.
E) help to keep cells viable for a longer duration of time.
A) can form protective crystalline structures around organized DNA.
B) condense prokaryotic DNA.
C) can act as regulators of gene expression.
D) determine the shape of the cell.
E) help to keep cells viable for a longer duration of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One similarity between a Gram-negative cell envelope and that of mycobacteria is that mycobacteria have
A) lipid A.
B) teichoic acids.
C) a porin.
D) S-layers.
E) ampicillin.
A) lipid A.
B) teichoic acids.
C) a porin.
D) S-layers.
E) ampicillin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
All of the following are true about prokaryotic outer membranes EXCEPT that they
A) are lipid bilayers composed of identical phospholipids.
B) are found only in Gram-negative bacteria.
C) contain endotoxin.
D) contain proteins involved in transport.
E) contain lipopolysaccharide.
A) are lipid bilayers composed of identical phospholipids.
B) are found only in Gram-negative bacteria.
C) contain endotoxin.
D) contain proteins involved in transport.
E) contain lipopolysaccharide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Bacterial shape is determined by
A) tubulin and actin.
B) cell membrane.
C) cytoskeleton.
D) S-layers.
E) a protein called crescentin.
A) tubulin and actin.
B) cell membrane.
C) cytoskeleton.
D) S-layers.
E) a protein called crescentin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Efflux pumps send antibiotics, such as the protein synthesis-inhibitor tetracycline, out of the bacterial cells, enabling them to grow in the presence of antibiotics. Which of the following therapeutic approaches will be LEAST effective?
A) Switch to an antibiotic that is not a substrate of the efflux pump.
B) Augment the treatment with an efflux inhibitor.
C) Increase the concentration of tetracycline.
D) Augment the treatment with an ATP synthase inhibitor.
E) Add a second antibiotic to the therapy.
A) Switch to an antibiotic that is not a substrate of the efflux pump.
B) Augment the treatment with an efflux inhibitor.
C) Increase the concentration of tetracycline.
D) Augment the treatment with an ATP synthase inhibitor.
E) Add a second antibiotic to the therapy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
All of the following are components of peptidoglycan EXCEPT
A) N-acetylglucosamine.
B) N-acetylmuramic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharide.
D) amino acids.
E) peptide cross-links.
A) N-acetylglucosamine.
B) N-acetylmuramic acid.
C) lipopolysaccharide.
D) amino acids.
E) peptide cross-links.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which is NOT a component of a Gram-negative bacterium's wall?
A) peptidoglycan
B) teichoic acid
C) N-acetylmuramic acid
D) diaminopimelic acid
E) MurNac
A) peptidoglycan
B) teichoic acid
C) N-acetylmuramic acid
D) diaminopimelic acid
E) MurNac

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Cell wall growth patterns of a variety of bacteria have been studied using fluorescently labeled D-amino acids. This approach has worked because
A) fluorescent amino acids block further cell wall synthesis and thus provide a snapshot of the cell wall at a particular time.
B) ribosomes cannot incorporate any fluorescence and thus cannot use fluorescent amino acids; it all goes to cell wall.
C) vancomycin can block the incorporation of D-alanine into protein and thus force it into the cell wall.
D) the labeled amino acids are D-amino acids, not L-amino acids.; thus, they only were incorporated into cell wall.
E) This approach has not worked.
A) fluorescent amino acids block further cell wall synthesis and thus provide a snapshot of the cell wall at a particular time.
B) ribosomes cannot incorporate any fluorescence and thus cannot use fluorescent amino acids; it all goes to cell wall.
C) vancomycin can block the incorporation of D-alanine into protein and thus force it into the cell wall.
D) the labeled amino acids are D-amino acids, not L-amino acids.; thus, they only were incorporated into cell wall.
E) This approach has not worked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The partition that results from the inward growth of the cell envelope from opposite directions is known as the
A) divisome.
B) septum.
C) wall.
D) colony.
E) Z-ring.
A) divisome.
B) septum.
C) wall.
D) colony.
E) Z-ring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements about the prokaryotic flagella is INCORRECT?
A) It is driven by the cell's transmembrane proton current.
B) It is embedded in the layers of the cell envelope.
C) It is observed by electron microscopy.
D) It moves with a whiplike motion.
E) It is used for chemotaxis.
A) It is driven by the cell's transmembrane proton current.
B) It is embedded in the layers of the cell envelope.
C) It is observed by electron microscopy.
D) It moves with a whiplike motion.
E) It is used for chemotaxis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The permeability of weak acids and bases across a membrane has implications for pharmaceutical treatment of disease. Assuming equal effectiveness in the lab, what type of molecule would be best to treat a bacterium growing in stomach acid, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following materials is found in aquatic bacteria and used for positioning in the water column?
A) gas vesicle
B) sulfur
C) polyphosphate
D) glycogen
E) magnetosome
A) gas vesicle
B) sulfur
C) polyphosphate
D) glycogen
E) magnetosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The periplasm in Gram-negative bacteria is filled with proteins. Describe the importance of these proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Polar aging of symmetrical bacteria such as E. coli plays a role in stress responses in which of the following ways?
A) Antibiotics only affect older poles of stressed cells.
B) Alternators and accelerators are better at responding to stress.
C) Proteins damaged by stresses accumulate at old poles, thereby allowing new poles to continue growing.
D) Newer poles are more resistant to acidity and heat.
E) Newer poles produce flagella and can swim away from stress.
A) Antibiotics only affect older poles of stressed cells.
B) Alternators and accelerators are better at responding to stress.
C) Proteins damaged by stresses accumulate at old poles, thereby allowing new poles to continue growing.
D) Newer poles are more resistant to acidity and heat.
E) Newer poles produce flagella and can swim away from stress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is described as an attachment organelle that is a membrane-bound extension of the cytoplasm?
A) pili
B) fimbriae
C) sex pili
D) stalks
E) flagella
A) pili
B) fimbriae
C) sex pili
D) stalks
E) flagella

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The bacterial flagellum is a helical protein filament whose ________ motor moves the cell in search of a more favorable environment.
A) shaking
B) vibrating
C) wavelike
D) whiplike
E) propeller-like
A) shaking
B) vibrating
C) wavelike
D) whiplike
E) propeller-like

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain how a genetic approach can be used to understand cell division. Give an example.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Directed movements toward or away from a chemical or physical signal are known as
A) gliding.
B) flagellation.
C) chemotaxis.
D) locomotion.
E) slime layer.
A) gliding.
B) flagellation.
C) chemotaxis.
D) locomotion.
E) slime layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe any two roles for membrane proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
As proteins are found in various subcellular fractions, how could they be further analyzed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Explain what happens when a cell comes into contact with water or ethanol. Why is 70% ethanol commonly used to treat wounds and surfaces?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
All of the following are used by prokaryotic cells for attaching to solid surfaces EXCEPT
A) endospore.
B) capsule.
C) stalks.
D) fimbriae.
E) pili.
A) endospore.
B) capsule.
C) stalks.
D) fimbriae.
E) pili.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the polarity and aging of Caulobacter crescentus?
A) The protein TipN is involved.
B) The two poles of the cell are different.
C) It contributes to a life cycle.
D) It results in two cell types (i.e., stalked cell and swarmer).
E) It results in two cell types, each with a monotrichous flagellum.
A) The protein TipN is involved.
B) The two poles of the cell are different.
C) It contributes to a life cycle.
D) It results in two cell types (i.e., stalked cell and swarmer).
E) It results in two cell types, each with a monotrichous flagellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In order for septation to occur, which process must finish first?
A) transcription and translation
B) membrane synthesis
C) DNA replication
D) cell wall synthesis
E) synthesis of mreB
A) transcription and translation
B) membrane synthesis
C) DNA replication
D) cell wall synthesis
E) synthesis of mreB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
List and briefly describe four components of a typical bacterial cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Describe four ways cells can be broken open in order to isolate the cellular components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Light is harvested by protein complexes called
A) thylakoids.
B) carboxysomes.
C) gas vesicles.
D) storage granules.
E) magnetosomes.
A) thylakoids.
B) carboxysomes.
C) gas vesicles.
D) storage granules.
E) magnetosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
With respect to the proteins involved in the polarity of Caulobacter, which of the following statements is FALSE?
A) DivJ is a marker for stalk and is produced at an old pole where PodJ had previously been located.
B) The stalk develops at a pole where PodJ is found.
C) After cell division, TipN localizes at the new cell pole opposite the stalk.
D) PodJ is a marker for flagella and interacts with TipN at the new pole.
E) After elongation and prior to division, TipN localizes to the septum.
A) DivJ is a marker for stalk and is produced at an old pole where PodJ had previously been located.
B) The stalk develops at a pole where PodJ is found.
C) After cell division, TipN localizes at the new cell pole opposite the stalk.
D) PodJ is a marker for flagella and interacts with TipN at the new pole.
E) After elongation and prior to division, TipN localizes to the septum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which name refers to having flagella attached at one or both ends of the cell?
A) peritrichous
B) lophotrichous
C) monotrichous
D) bitrichous
E) flagellated
A) peritrichous
B) lophotrichous
C) monotrichous
D) bitrichous
E) flagellated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Penicillin-binding proteins (pbps) are proteins located in the periplasmic space in Gram-negative bacteria and are involved in synthesizing the cell wall. Thus, they are a target for antibiotics and are of interest to drug developers. Describe how one could obtain these pbps for further study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe two mechanisms that archaea may use to enhance the heat stability of the membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how bacteria can produce proteins more quickly than eukaryotes do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Compare and contrast FtsZ and tubulin. Why do the similarities support evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes from a common ancestor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain how any two specialized structures are involved in bacterial photosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which age class of M. tuberculosis (age 1 or age 3) do you think would be more resistant to quinolones, which block gyrase that supercoils DNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe how vancomycin affects the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. How have some cells developed resistance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain the movement of a bacterium possessing flagella away from a toxic chemical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What unusual lipids are found in mycobacteria, and of what benefit are they to these bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Describe the types of molecules that can move through a membrane via passive diffusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe the Gram-negative cell envelope. Why are porins necessary in the outer membrane of Gram-negative cells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
From your knowledge of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell envelopes, why would penicillin be more effective in killing Gram-positive organisms than Gram-negative organisms?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 72 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



