Deck 16: Food and Industrial Microbiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Food and Industrial Microbiology
1
Alkaline fermentations raise pH through the catabolism of
A) lipids.
B) proteins.
C) sugars.
D) nucleic acids.
E) starches.
A) lipids.
B) proteins.
C) sugars.
D) nucleic acids.
E) starches.
B
2
Few bacteria are edible as isolated organisms because of their high content of
A) proteins.
B) nucleic acids.
C) sugars.
D) carbohydrates.
E) lipids.
A) proteins.
B) nucleic acids.
C) sugars.
D) carbohydrates.
E) lipids.
B
3
Sauerkraut is primarily fermented with the bacterium ________ that uses a ________ type of fermentation.
A) Lactobacillus; heterolactic
B) Lactobacillus; homolactic
C) Leuconostoc; heterolactic
D) Leuconostoc; homolactic
E) Propionibacterium; heterolactic
A) Lactobacillus; heterolactic
B) Lactobacillus; homolactic
C) Leuconostoc; heterolactic
D) Leuconostoc; homolactic
E) Propionibacterium; heterolactic
C
4
What proportion of known species of mushrooms are poisonous?
A) one-half
B) one-quarter
C) 10%
D) 5%
E) 1%
A) one-half
B) one-quarter
C) 10%
D) 5%
E) 1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following food products is NOT produced by alkaline fermentation?
A) natto
B) kimchi
C) dawadawa
D) pidan
E) thousand-year eggs
A) natto
B) kimchi
C) dawadawa
D) pidan
E) thousand-year eggs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is classified as a form of single-celled protein?
A) Porphyra
B) Lentinula
C) Spirulina
D) Rhizopus
E) Macrocystis
A) Porphyra
B) Lentinula
C) Spirulina
D) Rhizopus
E) Macrocystis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Miso is a fermented Japanese condiment made primarily from ________, which is salted and fermented with ________ for two months.
A) cabbage; Leuconostoc
B) rice; Leuconostoc
C) cabbage; Bacillus
D) cabbage; Aspergillus oryzae
E) ground soy and rice; Aspergillus oryzae
A) cabbage; Leuconostoc
B) rice; Leuconostoc
C) cabbage; Bacillus
D) cabbage; Aspergillus oryzae
E) ground soy and rice; Aspergillus oryzae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following microbes is responsible for the flavor of Camembert cheese?
A) lactic acid bacteria
B) Propionibacterium
C) Saccharomyces
D) Penicillium
E) Aspergillus
A) lactic acid bacteria
B) Propionibacterium
C) Saccharomyces
D) Penicillium
E) Aspergillus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The ________ of milk proteins results in the formation of curds.
A) filtration
B) lyophilization
C) pasteurization
D) coagulation
E) radiation
A) filtration
B) lyophilization
C) pasteurization
D) coagulation
E) radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What are the three stages in the fermentation of cocoa beans for chocolate (in order)?
A) 1) Bacillus, 2) lactic acid bacteria, 3) yeasts
B) 1) acetic acid bacteria, 2) yeasts, 3) lactic acid bacteria
C) 1) yeasts, 2) lactic acid bacteria, 3) acetic acid bacteria
D) 1) Leuconostoc, 2) Bacillus, 3) Rhizopus
E) 1) Leuconostoc, 2) Bacillus, 3) yeasts
A) 1) Bacillus, 2) lactic acid bacteria, 3) yeasts
B) 1) acetic acid bacteria, 2) yeasts, 3) lactic acid bacteria
C) 1) yeasts, 2) lactic acid bacteria, 3) acetic acid bacteria
D) 1) Leuconostoc, 2) Bacillus, 3) Rhizopus
E) 1) Leuconostoc, 2) Bacillus, 3) yeasts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Nori used as a sushi wrap is produced by growing Porphyra, a ________, in tanks.
A) green alga
B) red alga
C) brown alga
D) fungus
E) cyanobacterium
A) green alga
B) red alga
C) brown alga
D) fungus
E) cyanobacterium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is the source of alginate, an important food additive?
A) kelp
B) the yeast Saccharomyces
C) shiitake
D) Agaricus bisporus
E) enoki
A) kelp
B) the yeast Saccharomyces
C) shiitake
D) Agaricus bisporus
E) enoki

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What are two types of mushrooms that are both cultures of Agaricus bisporus that are harvested at different stages?
A) portobello and shiitake
B) morel and truffle
C) button and portobello
D) shiitake and truffle
E) nori and morel
A) portobello and shiitake
B) morel and truffle
C) button and portobello
D) shiitake and truffle
E) nori and morel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In the process of ________, NO standard starter culture is available.
A) sourdough bread making
B) yogurt making
C) chocolate production
D) cheese making
E) beer making
A) sourdough bread making
B) yogurt making
C) chocolate production
D) cheese making
E) beer making

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following contains protein as high as 25% dry weight and are an excellent source of all the essential dietary amino acids?
A) algae
B) bacteria
C) mushrooms
D) yeast cells
E) plants
A) algae
B) bacteria
C) mushrooms
D) yeast cells
E) plants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Within a mound of cocoa beans, ________ generates heat so that the mound temperature increases up to 50°C.
A) indigenous fungi
B) aerobic acetic acid bacteria
C) Candida and Kloeckera yeasts
D) Saccharomyces and other yeasts
E) Lactobacillus species
A) indigenous fungi
B) aerobic acetic acid bacteria
C) Candida and Kloeckera yeasts
D) Saccharomyces and other yeasts
E) Lactobacillus species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Mold ripening refers to the secondary ________ stage of cheese production.
A) respiration
B) curd
C) contamination
D) bacterial
E) fermentation
A) respiration
B) curd
C) contamination
D) bacterial
E) fermentation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Tempeh, a staple food of Indonesia, is produced by an initial fermentation of soybeans with ________, followed by ________.
A) lactic acid bacteria; Aspergillus oryzae
B) lactic acid bacteria; Rhizopus oligosporus
C) Propionibacterium spp.; Aspergillus oryzae
D) Propionibacterium spp.; Leuconostoc mesenteroides
E) Propionibacterium spp.; Rhizopus oligosporus
A) lactic acid bacteria; Aspergillus oryzae
B) lactic acid bacteria; Rhizopus oligosporus
C) Propionibacterium spp.; Aspergillus oryzae
D) Propionibacterium spp.; Leuconostoc mesenteroides
E) Propionibacterium spp.; Rhizopus oligosporus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Production of traditionally fermented foods typically relies on ________ microbiota, whereas commercial fermentation generally relies on ________.
A) soil; edible
B) edible; indigenous
C) airborne; indigenous
D) indigenous; starter cultures
E) indigenous; chemicals
A) soil; edible
B) edible; indigenous
C) airborne; indigenous
D) indigenous; starter cultures
E) indigenous; chemicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The flavors of ________ are generated by side products of fermentation, such as flavorful alcohols, esters, and sulfur compounds.
A) cheese
B) yogurt
C) kimchi
D) natto
E) sauerkraut
A) cheese
B) yogurt
C) kimchi
D) natto
E) sauerkraut

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The virulence genes of Salmonella are found in a genomic region referred to as pathogenicity
A) islands.
B) plasmids.
C) groups.
D) operons.
E) hotspots.
A) islands.
B) plasmids.
C) groups.
D) operons.
E) hotspots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Wines are produced from fermentation of crushed grapes. What causes the either white or red color of wine?
A) In white wine production, additional aging removes pigments by oxidation.
B) To produce white wine, red pigments are chemically removed prior to bottling.
C) Additional fermentation degrades the red pigments of red wine, rendering it white.
D) To make white wine, grape skins are removed (pressing) before inoculation with yeast.
E) Ultracentrifugation of red wine removes pigments, leading to rosé or white wines.
A) In white wine production, additional aging removes pigments by oxidation.
B) To produce white wine, red pigments are chemically removed prior to bottling.
C) Additional fermentation degrades the red pigments of red wine, rendering it white.
D) To make white wine, grape skins are removed (pressing) before inoculation with yeast.
E) Ultracentrifugation of red wine removes pigments, leading to rosé or white wines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following organisms or processes is NOT involved in the chocolate-making process?
A) yeasts
B) lactic acid bacteria
C) acetic acid bacteria
D) thermophilic bacteria
E) both anaerobic and aerobic processes
A) yeasts
B) lactic acid bacteria
C) acetic acid bacteria
D) thermophilic bacteria
E) both anaerobic and aerobic processes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Until the recent invention of ________, all foods contained live microbes.
A) steam-pressure sterilization
B) irradiation
C) lyophilization
D) freezing
E) refrigeration
A) steam-pressure sterilization
B) irradiation
C) lyophilization
D) freezing
E) refrigeration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Ethanolic fermentation of ________ was important to early civilizations because it provided a drink free of waterborne pathogens.
A) roots
B) flowers and leaves
C) leaves
D) grain and fruit
E) stems and leaves
A) roots
B) flowers and leaves
C) leaves
D) grain and fruit
E) stems and leaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In beer making, enzymatic activities during germination of barley produce the ________ used for fermentation.
A) ethanol
B) maltose
C) malic acid
D) lactic acid
E) 2-oxo acids
A) ethanol
B) maltose
C) malic acid
D) lactic acid
E) 2-oxo acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The purpose of malolactic fermentation in the second stage of production of some wines is to
A) impart wines with a fruity flavor.
B) eliminate phenolics.
C) eliminate acidity caused by malic acid.
D) destroy acetaldehyde (off-flavor).
E) produce esters (desirable flavors).
A) impart wines with a fruity flavor.
B) eliminate phenolics.
C) eliminate acidity caused by malic acid.
D) destroy acetaldehyde (off-flavor).
E) produce esters (desirable flavors).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Alcohol dehydrogenase in the ________ detoxifies alcohol produced in the intestines.
A) lungs
B) liver
C) mouth
D) pancreas
E) spleen
A) lungs
B) liver
C) mouth
D) pancreas
E) spleen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following aids microbial growth?
A) drying
B) radiation
C) addition of spices
D) refrigeration
E) warming the food to body temperature
A) drying
B) radiation
C) addition of spices
D) refrigeration
E) warming the food to body temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A modest level of ethanol enters the human circulation naturally from ________, equivalent to a fraction of a drink per day.
A) intestinal microbiota byproducts
B) food
C) drink
D) cell metabolism
E) the environment
A) intestinal microbiota byproducts
B) food
C) drink
D) cell metabolism
E) the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The filtered mash in beer making is referred to as
A) hops.
B) barley.
C) yeast extract.
D) malt.
E) wort.
A) hops.
B) barley.
C) yeast extract.
D) malt.
E) wort.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Another term for freeze-drying is
A) radiation.
B) dehydration.
C) filtration.
D) pasteurization.
E) lyophilization.
A) radiation.
B) dehydration.
C) filtration.
D) pasteurization.
E) lyophilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Food spoilage can be brought about by all the following, EXCEPT
A) chemical reactions with the environment, such as oxidation of lipids.
B) meat tenderization.
C) putrefaction of food by decomposition of protein and amino acids.
D) action of bacterial fermentations to make food sours.
E) conversion of sugar into starch in freshly picked corn.
A) chemical reactions with the environment, such as oxidation of lipids.
B) meat tenderization.
C) putrefaction of food by decomposition of protein and amino acids.
D) action of bacterial fermentations to make food sours.
E) conversion of sugar into starch in freshly picked corn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following products of beer making and winemaking result in off-flavors?
A) esters
B) ethanol
C) acetaldehyde
D) long-chain alcohols
E) amino acids
A) esters
B) ethanol
C) acetaldehyde
D) long-chain alcohols
E) amino acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Brewer's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, conducts ________ fermentation of maltose, a ________, which is produced by the action of amylases on starch.
A) ethanolic; pectin
B) lactic acid; lactone
C) ethanolic; disaccharide
D) mixed; fructose
E) ethanolic; monosaccharide
A) ethanolic; pectin
B) lactic acid; lactone
C) ethanolic; disaccharide
D) mixed; fructose
E) ethanolic; monosaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Listeria is a(n) ________ organism, which means that it readily grows at refrigeration temperatures.
A) neutrophilic
B) acidophilic
C) mesophilic
D) autotrophic
E) psychrotrophic
A) neutrophilic
B) acidophilic
C) mesophilic
D) autotrophic
E) psychrotrophic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cinnamon and cloves contain a ________ derivative that is a potent microbial inhibitor.
A) lipid
B) nucleotide
C) benzene
D) bacterial
E) fungal
A) lipid
B) nucleotide
C) benzene
D) bacterial
E) fungal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Escherichia coli O157:H7 was first observed in fast-food hamburger meat. More recently, it has been associated with contamination of spinach and other vegetables. How did the spread of this strain from meat to vegetables happen?
A) It picked up genes for plant virulence.
B) Strain O157:H7 can grow as a plant endophyte.
C) It has become a psychrotroph and can grow in refrigerated foods.
D) It produces toxins that can survive on plant material.
E) This bacterial strain has lost genes needed to grow in meat.
A) It picked up genes for plant virulence.
B) Strain O157:H7 can grow as a plant endophyte.
C) It has become a psychrotroph and can grow in refrigerated foods.
D) It produces toxins that can survive on plant material.
E) This bacterial strain has lost genes needed to grow in meat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Leavening of commercial bread dough is brought about by CO₂ from ________ fermentation by ________.
A) mixed; Propionibacterium species
B) ethanolic; Oenococcus
C) alkaline; Bacillus species
D) ethanolic; Saccharomyces cerevisiae
E) acid; lactic acid bacteria
A) mixed; Propionibacterium species
B) ethanolic; Oenococcus
C) alkaline; Bacillus species
D) ethanolic; Saccharomyces cerevisiae
E) acid; lactic acid bacteria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The most common food-borne cause of death in the United States is
A) norovirus.
B) Salmonella enterica.
C) Campylobacter sp.
D) Clostridium botulinum.
E) Escherichia coli O157:H7.
A) norovirus.
B) Salmonella enterica.
C) Campylobacter sp.
D) Clostridium botulinum.
E) Escherichia coli O157:H7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Recombinant Escherichia coli is used in the production of the following EXCEPT
A) interferon.
B) CC10 lung development protein.
C) human growth hormone.
D) insulin.
E) antibodies.
A) interferon.
B) CC10 lung development protein.
C) human growth hormone.
D) insulin.
E) antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How is injera produced and why is it nutritionally better than quick-rising wheat breads?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The ________ gene products stimulate plasmid transfer from Agrobacterium to the host plant.
A) Ti
B) promoter
C) recombinant
D) auxin synthesis
E) vir
A) Ti
B) promoter
C) recombinant
D) auxin synthesis
E) vir

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the figure below and find the INCORRECT statement regarding the development process for the antituberculosis compound SQ109. 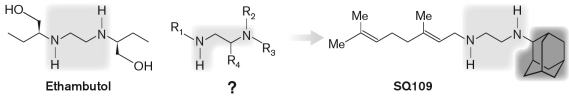
A) The question mark (?) indicates to the general formula for 62,238 compounds made in a combinatorial library of ethambutol derivatives.
B) The yellow highlighted portion of the molecules correspond to the ethambutol diamine core.
C) All 63,238 diamine molecules in the combinatorial library were tested in tissue culture, activity in infected macrophages and in live animals.
D) Out of 69 compounds showing the best activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, SQ109 had the greatest efficacy and fewer side effects.
E) Out of 63,238 diamine molecules in the combinatorial library, 2,796 showed activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro.

A) The question mark (?) indicates to the general formula for 62,238 compounds made in a combinatorial library of ethambutol derivatives.
B) The yellow highlighted portion of the molecules correspond to the ethambutol diamine core.
C) All 63,238 diamine molecules in the combinatorial library were tested in tissue culture, activity in infected macrophages and in live animals.
D) Out of 69 compounds showing the best activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, SQ109 had the greatest efficacy and fewer side effects.
E) Out of 63,238 diamine molecules in the combinatorial library, 2,796 showed activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vitro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Briefly describe the cheese-making process. Use the figure below to explain why different cheeses have different flavors.
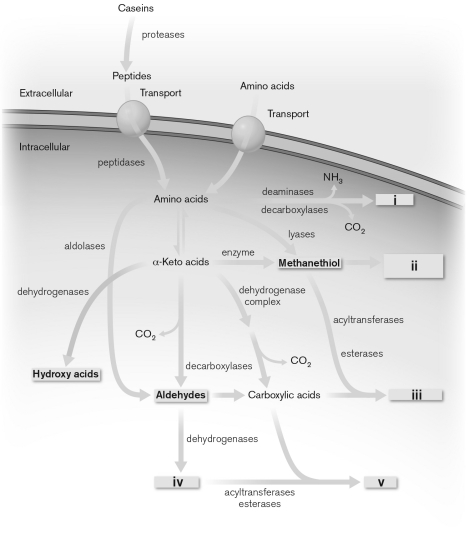


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
All of the following are examples of the use of alginates derived from Macrocystis pyrifera, EXCEPT
A) fermentation substrate for cheese production.
B) textile printing agent.
C) modeling material for dental applications.
D) skin-safe life casting.
E) ice cream thickener.
A) fermentation substrate for cheese production.
B) textile printing agent.
C) modeling material for dental applications.
D) skin-safe life casting.
E) ice cream thickener.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Actinovate is a preparation of Streptomyces lydicus, an example of a microbe as product. Which of the following is NOT correct regarding Actinovate?
A) It is used to suppress fungi causing seedling damping-off.
B) Streptomyces lydicus produces a protein that is toxic to the larvae of several insect pests.
C) It fends off fungal pathogens on leaves.
D) Streptomyces lydicus feeds off plant exudates while secreting antimicrobial substances.
E) It is used to eliminate root rot.
A) It is used to suppress fungi causing seedling damping-off.
B) Streptomyces lydicus produces a protein that is toxic to the larvae of several insect pests.
C) It fends off fungal pathogens on leaves.
D) Streptomyces lydicus feeds off plant exudates while secreting antimicrobial substances.
E) It is used to eliminate root rot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Describe how the transportation of milk products by herders led to the formation of cheeses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What are some of the purposes of food fermentation? Why have humans been making fermented foods for so long?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The following are desirable characteristics of an industrial strain, EXCEPT
A) efficient gene transfer system.
B) susceptibility to large DNA rearrangements.
C) inexpensive growth and maintenance.
D) safe, non-pathogenic.
E) easy harvesting of product.
A) efficient gene transfer system.
B) susceptibility to large DNA rearrangements.
C) inexpensive growth and maintenance.
D) safe, non-pathogenic.
E) easy harvesting of product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The search for organisms with potential commercial application is called
A) biopanning.
B) bioprospecting.
C) recombinant DNA technology.
D) deep sequencing.
E) metagenomics.
A) biopanning.
B) bioprospecting.
C) recombinant DNA technology.
D) deep sequencing.
E) metagenomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why is it better nutritionally to ferment soybeans than to consume them without fermenting?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An acid or base serves as an effective preservative because
A) pH change is likely to be reversed.
B) pH change is unlikely to be reversed.
C) animals and plants grow at high pH.
D) animals and plants grow at low pH.
E) animals and plants grow at extreme pH.
A) pH change is likely to be reversed.
B) pH change is unlikely to be reversed.
C) animals and plants grow at high pH.
D) animals and plants grow at low pH.
E) animals and plants grow at extreme pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Another term for food contamination is
A) rancid.
B) putrefacation
C) food poisoning.
D) food spoilage.
E) putrefied.
A) rancid.
B) putrefacation
C) food poisoning.
D) food spoilage.
E) putrefied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Bacteria generally can't be eaten as isolated organisms. Why is Spirulina an exception? What is Spirulina and what are its health benefits?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is NOT an example of a microbial enzyme used in industrial or commercial applications?
A) cellulase-improvement of fabric's appearance
B) asparaginase-avoidance of acrylamide production
C) rennin-cheese production
D) lipase B-active in a wide range of temperatures
E) protease-removal of food stains on clothes
A) cellulase-improvement of fabric's appearance
B) asparaginase-avoidance of acrylamide production
C) rennin-cheese production
D) lipase B-active in a wide range of temperatures
E) protease-removal of food stains on clothes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An attribute of an industrial microbial strain is
A) genetic stability and manipulation.
B) expensive growth requirements.
C) a low level of product expression.
D) pathogenic strains.
E) the cell is not easily breakable to liberate product.
A) genetic stability and manipulation.
B) expensive growth requirements.
C) a low level of product expression.
D) pathogenic strains.
E) the cell is not easily breakable to liberate product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What type of processing refers to steps in product recovery and purification?
A) pasteurization
B) finishing
C) upstream
D) downstream
E) lyophilization
A) pasteurization
B) finishing
C) upstream
D) downstream
E) lyophilization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the figure below to describe four types of fermentation used in food preparation. Make sure to indicate what the Roman numerals indicate. Give an example of a product that is made from each type of fermentation.
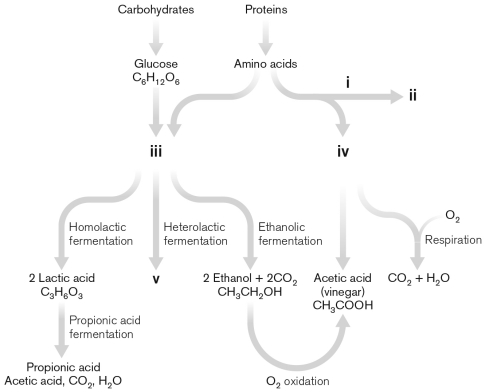


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Microorganisms are used in the production of many small molecules, such as amino acids, vitamins, and medicines. Which of the following is NOT produced by a bacterium?
A) steroids
B) L-lysine
C) vitamin B12
D) penicillin
E) tetracycline
A) steroids
B) L-lysine
C) vitamin B12
D) penicillin
E) tetracycline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the figure below to discuss how molecular tools are used in the investigation of pathogen-contaminated food. What does the figure represent? What is the overall conclusion of the analysis?
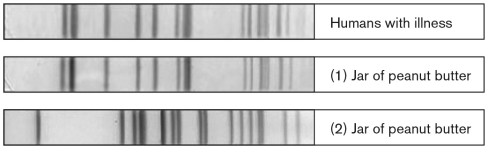


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe some of the characteristics that industrial strains of microbes must possess.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
With respect to an industrial process, what are upstream and downstream processing methods, and how do they differ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Describe the primary and secondary fermentations involved in winemaking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What categories of foods may be spoiled by psychrotrophs? Why are these organisms a problem with fish?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The graph below shows an experiment in which growth of aerobic bacteria in ground beef (CFUs/g) was measured at different refrigeration temperatures. Interpret the graph and explain what the dotted line represents.
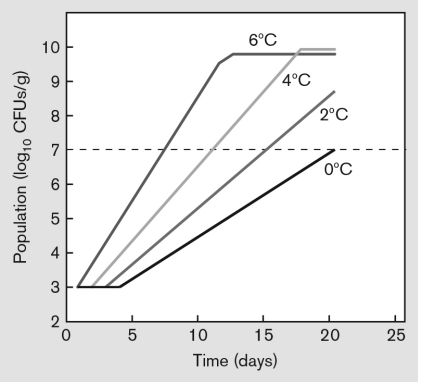


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What makes a company dealing with industrial microbiology a success?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the figure below, identify the carbohydrate substrate for fermentation in the production of beer and wine. Compare and contrast the desirable flavors and off-flavors that may come about during ethanolic fermentation in both cases.
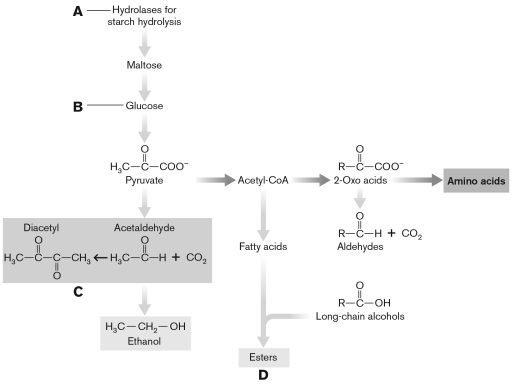


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain the difference between food spoilage and food poisoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The figure below represents microbial growth (CFUs/mL) during the very early stages of chocolate production. Use the numbers to describe the microbial succession involved in the complex fermentation of cocoa pulp.
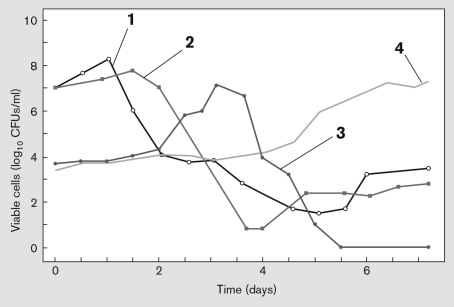


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe several physical means of food preservation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Why is Agrobacterium used in genetic engineering of plants? Briefly explain the Agrobacterium expression system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The strain Escherichia coli O157:H7 is pathogenic for humans. It was first identified in ground beef. What does an infection with it cause and do to humans? Why do you suppose infections are more prevalent in ground meat than on a steak?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



