Deck 4: Economic Efficiency, Government Price Setting, and Taxes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/127
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Economic Efficiency, Government Price Setting, and Taxes
1
Marginal benefit is equal to the ________ benefit to a consumer receives from consuming one more unit of a good or service
A)total
B)unintended
C)additional
D)surplus
A)total
B)unintended
C)additional
D)surplus
C
2
The difference between the highest price a consumer is willing to pay for a good and the price the consumer actually pays is called
A)producer surplus.
B)the substitution effect.
C)the income effect.
D)consumer surplus.
A)producer surplus.
B)the substitution effect.
C)the income effect.
D)consumer surplus.
D
3
Table 4.1
-Refer to Table 4.1.The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Tom, Dick and Harriet, are willing to pay for a short-sleeved polo shirt.If the price of one of the shirts is $28 dollars
A)Tom will buy two shirts, Dick will buy one shirt and Harriet will buy no shirts.
B)Tom will receive $12 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt.
C)Tom and Dick receive a total of $70 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt each. Harriet will buy no shirts.
D)Harriet will receive $25 of consumer surplus since she will buy no shirts.
-Refer to Table 4.1.The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Tom, Dick and Harriet, are willing to pay for a short-sleeved polo shirt.If the price of one of the shirts is $28 dollars
A)Tom will buy two shirts, Dick will buy one shirt and Harriet will buy no shirts.
B)Tom will receive $12 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt.
C)Tom and Dick receive a total of $70 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt each. Harriet will buy no shirts.
D)Harriet will receive $25 of consumer surplus since she will buy no shirts.
Tom will receive $12 of consumer surplus from buying one shirt.
4
Marginal cost is
A)the total cost of producing one unit of a good or service.
B)the average cost of producing a good or service.
C)the difference between the lowest price a firm would have been willing to accept and the price it actually receives.
D)the additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit of a good or service.
A)the total cost of producing one unit of a good or service.
B)the average cost of producing a good or service.
C)the difference between the lowest price a firm would have been willing to accept and the price it actually receives.
D)the additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Table 4.1
-Refer to Table 4.1.The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Tom, Dick and Harriet, are willing to pay for a short-sleeved polo shirt.If the price of the shirts falls from $28 to $20
A)consumer surplus increases from $14 to $35.
B)Tom will buy two shirts; Dick and Harriet will each buy one shirt.
C)consumer surplus will increase from $70 to $95.
D)Harriet will receive more consumer surplus than Tom or Dick.
-Refer to Table 4.1.The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Tom, Dick and Harriet, are willing to pay for a short-sleeved polo shirt.If the price of the shirts falls from $28 to $20
A)consumer surplus increases from $14 to $35.
B)Tom will buy two shirts; Dick and Harriet will each buy one shirt.
C)consumer surplus will increase from $70 to $95.
D)Harriet will receive more consumer surplus than Tom or Dick.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The total amount of producer surplus in a market is equal to
A)the difference between quantity supplied and quantity demanded.
B)the area above the market supply curve and below the market price.
C)the area above the market supply curve.
D)the area between the demand curve and the supply curve below the market price.
A)the difference between quantity supplied and quantity demanded.
B)the area above the market supply curve and below the market price.
C)the area above the market supply curve.
D)the area between the demand curve and the supply curve below the market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Table 4.2
-Refer to Table 4.2.The table above lists the marginal cost of cowboy hats by The Lethbridge Kid, a firm that specializes in producing western wear.If the price of cowboy hats increases from $38 to $46
A)consumers will buy no cowboy hats.
B)the marginal cost of producing the third cowboy hat will increase to $46.
C)producer surplus will rise from $22 to $46.
D)producer surplus will rise from $38 to $46.
-Refer to Table 4.2.The table above lists the marginal cost of cowboy hats by The Lethbridge Kid, a firm that specializes in producing western wear.If the price of cowboy hats increases from $38 to $46
A)consumers will buy no cowboy hats.
B)the marginal cost of producing the third cowboy hat will increase to $46.
C)producer surplus will rise from $22 to $46.
D)producer surplus will rise from $38 to $46.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Willingness to pay measures
A)the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay for a product minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it.
B)the amount a seller actually receives for a good minus the minimum amount the seller is willing to accept for the good.
C)the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a good.
D)the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay minus the minimum price a seller is willing to accept.
A)the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay for a product minus the amount the buyer actually pays for it.
B)the amount a seller actually receives for a good minus the minimum amount the seller is willing to accept for the good.
C)the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a good.
D)the maximum price a buyer is willing to pay minus the minimum price a seller is willing to accept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a province with rent-controlled apartments, all of the following are true except
A)apartments usually rent for rates lower than the market rate.
B)apartments are often in shorter supply than they would be without rent control.
C)it usually takes more time to find an apartment than it would without rent control.
D)landlords have an incentive to rent more apartments than they would without rent control.
A)apartments usually rent for rates lower than the market rate.
B)apartments are often in shorter supply than they would be without rent control.
C)it usually takes more time to find an apartment than it would without rent control.
D)landlords have an incentive to rent more apartments than they would without rent control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 4.2
-Refer to Table 4.2.The table above lists the marginal cost of cowboy hats by The Lethbridge Kid, a firm that specializes in producing western wear.If the market price of The Lethbridge Kid's cowboy hats is $40
A)The Lethbridge Kid will produce four hats.
B)producer surplus will be equal to $16.
C)producer surplus will equal $28.
D)there will be a surplus; as a result, the price will fall to $24.
-Refer to Table 4.2.The table above lists the marginal cost of cowboy hats by The Lethbridge Kid, a firm that specializes in producing western wear.If the market price of The Lethbridge Kid's cowboy hats is $40
A)The Lethbridge Kid will produce four hats.
B)producer surplus will be equal to $16.
C)producer surplus will equal $28.
D)there will be a surplus; as a result, the price will fall to $24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Paul goes to SportChek to buy a new tennis racquet.He is willing to pay $200 for a new racquet, but buys one on sale for $125.Paul's consumer surplus from the purchase is
A)$325
B)$200
C)$125
D)$75
A)$325
B)$200
C)$125
D)$75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements best describes the concept of consumer surplus?
A)"Sobey's was having a sale on Chapman's ice cream so I bought 6 litres."
B)"I was all ready to pay $300 for a new leather jacket that I had seen in Hudson's Bay, but I ended up paying only $180 for the same jacket."
C)"I paid $130 for a printer last week. This week the same store is selling the same printer for $110."
D)"I sold my Blu-ray copy of Ben-Hur for $18 at a garage sale even though I was willing to sell it for $10."
A)"Sobey's was having a sale on Chapman's ice cream so I bought 6 litres."
B)"I was all ready to pay $300 for a new leather jacket that I had seen in Hudson's Bay, but I ended up paying only $180 for the same jacket."
C)"I paid $130 for a printer last week. This week the same store is selling the same printer for $110."
D)"I sold my Blu-ray copy of Ben-Hur for $18 at a garage sale even though I was willing to sell it for $10."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Provincial governments in BC, Manitoba, Ontario and Quebec have various forms of rent control.Rent control
A)puts a legal limit on the rent that landlords can charge for an apartment.
B)is a price floor which sets a minimum rent for apartments.
C)only applies to those apartments which are owned and rented out by the local government.
D)is a government policy which limits apartment rental to those people whose incomes are less than $50,000 per year.
A)puts a legal limit on the rent that landlords can charge for an apartment.
B)is a price floor which sets a minimum rent for apartments.
C)only applies to those apartments which are owned and rented out by the local government.
D)is a government policy which limits apartment rental to those people whose incomes are less than $50,000 per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The area ________ the market supply curve and ________ the market price is equal to the total amount of producer surplus in a market.
A)above; above
B)above; below
C)below; above
D)below; below
A)above; above
B)above; below
C)below; above
D)below; below

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Consumer surplus measures the total benefit from participating in a market.
B)When a market is in equilibrium consumer surplus equals producer surplus.
C)Consumer surplus measures the net benefit from participating in a market.
D)Producer surplus measures the total benefit received by producers from participating in a market.
A)Consumer surplus measures the total benefit from participating in a market.
B)When a market is in equilibrium consumer surplus equals producer surplus.
C)Consumer surplus measures the net benefit from participating in a market.
D)Producer surplus measures the total benefit received by producers from participating in a market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consumers are willing to purchase a product up to the point where
A)the marginal benefit of consuming the product is equal to the marginal cost of consuming it.
B)the consumer surplus is equal to the producer surplus.
C)the marginal benefit of consuming the product equals the area below the supply curve and above the market price.
D)the marginal benefit of consuming a product is equal to its price.
A)the marginal benefit of consuming the product is equal to the marginal cost of consuming it.
B)the consumer surplus is equal to the producer surplus.
C)the marginal benefit of consuming the product equals the area below the supply curve and above the market price.
D)the marginal benefit of consuming a product is equal to its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Each point on a ________ curve shows the willingness of consumers to purchase a product at different prices.
A)demand
B)supply
C)production possibilities
D)marginal cost
A)demand
B)supply
C)production possibilities
D)marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A ________ curve shows the marginal cost of producing one more unit of a good or service.
A)demand
B)supply
C)production possibilities
D)marginal benefit
A)demand
B)supply
C)production possibilities
D)marginal benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Lucinda buys a new GPS system for $250.She receives consumer surplus of $75 from the purchase.How much does Lucinda value her GPS system?
A)$75
B)$175
C)$250
D)$325
A)$75
B)$175
C)$250
D)$325

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Consumer surplus in a market for a product would be equal to ________ if the market price was zero.
A)zero
B)the area between the supply curve and the demand curve
C)the area above the supply curve
D)the area under the demand curve
A)zero
B)the area between the supply curve and the demand curve
C)the area above the supply curve
D)the area under the demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Two economists estimated the benefit people get from visiting Gros Morn Nation Park in Newfoundland and Labrador.The economists found
A)the consumer surplus from provincial parks exceeded the consumer surplus from national parks.
B)the average visitor to the park received a marginal benefit of $24.
C)most visitors to the park would not be willing to pay more than $44 per visit.
D)the annual benefit to park visitors was approximately $192 million.
A)the consumer surplus from provincial parks exceeded the consumer surplus from national parks.
B)the average visitor to the park received a marginal benefit of $24.
C)most visitors to the park would not be willing to pay more than $44 per visit.
D)the annual benefit to park visitors was approximately $192 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What is producer surplus? What does producer surplus measure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The marginal cost for Java Joe's to produce its first cup of coffee is $0.75.Its marginal cost to produce its second cup of coffee is $1.25.Its marginal cost increases by $0.50 for each additional cup of coffee it produces.Suppose the market price for coffee is $2.25.Construct a graph showing the producer surplus for each cup of coffee Java Joe's will sell.How many cups of coffee will Java Joe's sell? What is the value of the producer surplus Java Joe's receives for each cup of coffee it sells?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Assume the market price for lemon grass is $4.00 per pound, but most buyers are willing to pay more than the market price.At the market price of $4.00, the quantity of lemon grass demanded is 1,500 pounds per month, and quantity demanded does not reach zero until the price reaches $30.00 per pound.Construct a graph showing this data, calculate the total consumer surplus in the market for lemon grass, and show the consumer surplus on the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 4.1
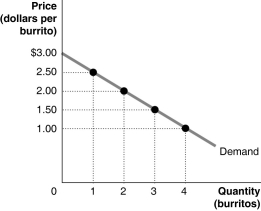
Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.Arnold's marginal benefit from consuming the third burrito is
A)$1.25.
B)$1.50.
C)$2.50.
D)$6.00.

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.Arnold's marginal benefit from consuming the third burrito is
A)$1.25.
B)$1.50.
C)$2.50.
D)$6.00.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 4.1

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is the consumer surplus on the third burrito?
A)$0.50
B)$1.00
C)$1.50
D)$7.50

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is the consumer surplus on the third burrito?
A)$0.50
B)$1.00
C)$1.50
D)$7.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 4.1

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.What is the total amount that Arnold is willing to pay for 4 burritos?
A)$1.00
B)$4.00
C)$7.00
D)$10.00

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.What is the total amount that Arnold is willing to pay for 4 burritos?
A)$1.00
B)$4.00
C)$7.00
D)$10.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In a competitive market equilibrium
A)total consumer surplus equals total producer surplus.
B)marginal benefit and marginal cost are maximized.
C)consumers and producers benefit equally.
D)the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of the last unit sold.
A)total consumer surplus equals total producer surplus.
B)marginal benefit and marginal cost are maximized.
C)consumers and producers benefit equally.
D)the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost of the last unit sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A demand curve shows
A)the willingness of consumers to buy a product at different prices.
B)the willingness of consumers to substitute one product for another product.
C)the relationship between the price of a product and the demand for the product.
D)the relationship between the price of a product and the total benefit consumers receive from the product.
A)the willingness of consumers to buy a product at different prices.
B)the willingness of consumers to substitute one product for another product.
C)the relationship between the price of a product and the demand for the product.
D)the relationship between the price of a product and the total benefit consumers receive from the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 4.2
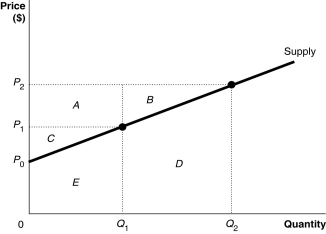
Refer to Figure 4.2.What area represents the increase in producer surplus when the market price rises from P₁ to P₂?
A) B + D
B)A + C + E
C)C + E
D)A + B

Refer to Figure 4.2.What area represents the increase in producer surplus when the market price rises from P₁ to P₂?
A) B + D
B)A + C + E
C)C + E
D)A + B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppliers will be willing to supply a product only if
A)the price received is less than the additional cost of producing the product.
B)the price received is at least equal to the additional cost of producing the product.
C)the price is higher than the average cost of producing the product.
D)the price received is at least double the additional cost of producing the product.
A)the price received is less than the additional cost of producing the product.
B)the price received is at least equal to the additional cost of producing the product.
C)the price is higher than the average cost of producing the product.
D)the price received is at least double the additional cost of producing the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consumer surplus is the difference between the highest price someone is willing to pay for a product and the price he actually pays for the product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The total amount of consumer surplus in a market is equal to the area below the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 4.2

Refer to Figure 4.2.What area represents producer surplus at a price of P₂?
A)A + B
B)B + D
C)A + B + C
D)A + B + C + D + E

Refer to Figure 4.2.What area represents producer surplus at a price of P₂?
A)A + B
B)B + D
C)A + B + C
D)A + B + C + D + E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Economic efficiency in a competitive market is achieved when
A)economic surplus is equal to consumer surplus.
B)consumers and producers are satisfied.
C)the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost from the last unit sold.
D)producer surplus equals the total amount firms receive from consumers minus the cost of production.
A)economic surplus is equal to consumer surplus.
B)consumers and producers are satisfied.
C)the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost from the last unit sold.
D)producer surplus equals the total amount firms receive from consumers minus the cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The difference between the ________ and the ________ from the sale of a product is called producer surplus.
A)lowest price a firm would have been willing to accept; price it actually receives
B)highest price a firm wold have been willing to accept; lowest price it was willing to accept
C)cost to produce a product; price a firm actually receives
D)cost to produce a product; profit received
A)lowest price a firm would have been willing to accept; price it actually receives
B)highest price a firm wold have been willing to accept; lowest price it was willing to accept
C)cost to produce a product; price a firm actually receives
D)cost to produce a product; profit received

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 4.3
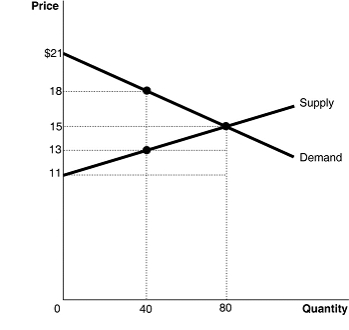
Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of consumer surplus at a price of $18?
A)$60
B)$120
C)$180
D)$240

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of consumer surplus at a price of $18?
A)$60
B)$120
C)$180
D)$240

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 4.1

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is the maximum number of burritos that Arnold will buy?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is the maximum number of burritos that Arnold will buy?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 4.1

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is Arnold's consumer surplus?
A)$1.00
B)$2.00
C)$6.00
D)$7.00

Figure 4.1 shows Arnold's demand curve for burritos.
Refer to Figure 4.1.If the market price is $1.00, what is Arnold's consumer surplus?
A)$1.00
B)$2.00
C)$6.00
D)$7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Marginal cost is the additional cost to a firm of producing one more unit of a good or service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
________ is maximized in a competitive market when marginal benefit equals marginal cost.
A)Deadweight loss
B)Marginal profit
C)Economic surplus
D)Selling price
A)Deadweight loss
B)Marginal profit
C)Economic surplus
D)Selling price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
________ refers to the reduction in economic surplus resulting from not being in competitive equilibrium.
A)Marginal cost
B)Producer atrophy
C)Deadweight loss
D)Economic shortage
A)Marginal cost
B)Producer atrophy
C)Deadweight loss
D)Economic shortage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure 4.4
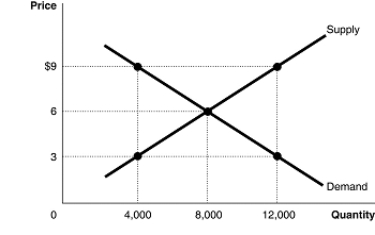
Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If the price of pecans is $3, what changes in the market would result in an economically efficient output?
A)The price would increase, the quantity supplied would decrease, and the quantity demanded would increase.
B)The quantity supplied would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease and the equilibrium price would increase.
C)The price would increase, the demand would decrease and the supply would increase.
D)The price would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease and the quantity supplied would increase.

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If the price of pecans is $3, what changes in the market would result in an economically efficient output?
A)The price would increase, the quantity supplied would decrease, and the quantity demanded would increase.
B)The quantity supplied would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease and the equilibrium price would increase.
C)The price would increase, the demand would decrease and the supply would increase.
D)The price would increase, the quantity demanded would decrease and the quantity supplied would increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 4.4

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If 8,000 pounds of pecans are sold
A)the deadweight loss is equal to economic surplus.
B)producer surplus equals consumer surplus.
C)the marginal benefit of each of the 8,000 pounds of pecans equals $9.
D)marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If 8,000 pounds of pecans are sold
A)the deadweight loss is equal to economic surplus.
B)producer surplus equals consumer surplus.
C)the marginal benefit of each of the 8,000 pounds of pecans equals $9.
D)marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a competitive market the demand curve shows the ________ received by consumers and the supply curve shows the ________.
A)utility; average cost
B)marginal benefit; marginal cost
C)economic surplus; opportunity cost
D)net benefit; net cost
A)utility; average cost
B)marginal benefit; marginal cost
C)economic surplus; opportunity cost
D)net benefit; net cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If equilibrium is achieved in a competitive market
A)there is no deadweight loss.
B)the deadweight loss will be maximized.
C)the deadweight loss will equal the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
D)the deadweight loss will be the same as the opportunity cost of the last unit of output sold.
A)there is no deadweight loss.
B)the deadweight loss will be maximized.
C)the deadweight loss will equal the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
D)the deadweight loss will be the same as the opportunity cost of the last unit of output sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Economic surplus
A)does not exist when a competitive market is in equilibrium.
B)is equal to the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
C)is the difference between quantity demanded and quantity supplied when the market price for a product is greater than the equilibrium price.
D)is equal to the difference between consumer surplus and producer surplus.
A)does not exist when a competitive market is in equilibrium.
B)is equal to the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
C)is the difference between quantity demanded and quantity supplied when the market price for a product is greater than the equilibrium price.
D)is equal to the difference between consumer surplus and producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If, in a competitive market, marginal benefit is less than marginal cost,
A)the net benefit to consumers from participating in the market is less than the net benefit to producers.
B)the government must force producers to raise prices in order to achieve economic efficiency.
C)the quantity sold is greater than the equilibrium quantity.
D)the quantity sold is less than the equilibrium quantity.
A)the net benefit to consumers from participating in the market is less than the net benefit to producers.
B)the government must force producers to raise prices in order to achieve economic efficiency.
C)the quantity sold is greater than the equilibrium quantity.
D)the quantity sold is less than the equilibrium quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 4.3

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of producer surplus at a price of $18?
A)$240
B)$300
C)$340
D)$720

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of producer surplus at a price of $18?
A)$240
B)$300
C)$340
D)$720

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Deadweight loss refers to the reduction in economic surplus resulting from a market not being in competitive equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is called economic surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Economic efficiency is defined as a market outcome in which the marginal benefit to consumers of the last unit produced is equal to the marginal cost of production, and in which
A)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is at a maximum.
B)economic surplus is minimized.
C)the sum of the benefits to firms is equal to the sum of the benefits to consumers.
D) the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is minimized.
A)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is at a maximum.
B)economic surplus is minimized.
C)the sum of the benefits to firms is equal to the sum of the benefits to consumers.
D) the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If there is a market outcome in which the marginal benefit to consumers of the last unit produced is equal to its marginal cost of production and consumer surplus plus producer surplus is maximized, then
A)maximum deadweight loss occurs.
B)economic efficiency is achieved.
C)profits are maximized.
D)costs are minimized.
A)maximum deadweight loss occurs.
B)economic efficiency is achieved.
C)profits are maximized.
D)costs are minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 4.3

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of the deadweight loss at a price of $18?
A)$100
B)$180
C)$660
D)$1,040

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.What is the value of the deadweight loss at a price of $18?
A)$100
B)$180
C)$660
D)$1,040

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 4.4

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.Which of the following is true?
A)If the price of pecans is $3 the output will be economically efficient but there will be a deadweight loss.
B)If the price of pecans is $9 consumers will purchase more than the economically efficient output.
C)Both 40,000 kilograms and 12,000 kilograms are economically inefficient rates of output.
D)If the price of pecans is $3 producers will sell 12,000 kilograms of pecans but this output will be economically inefficient.

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.Which of the following is true?
A)If the price of pecans is $3 the output will be economically efficient but there will be a deadweight loss.
B)If the price of pecans is $9 consumers will purchase more than the economically efficient output.
C)Both 40,000 kilograms and 12,000 kilograms are economically inefficient rates of output.
D)If the price of pecans is $3 producers will sell 12,000 kilograms of pecans but this output will be economically inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Economic efficiency is a market outcome in which the marginal benefit of consumers is equal to the marginal cost of production and the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Will equilibrium in a market always result in an outcome that is economically efficient? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 4.3

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.At a price of $18 consumers are willing to buy 40 kilograms of tiger shrimp.Is this an economically efficient quantity?
A)No, the marginal benefit of the 40th unit exceeds the marginal cost of that 80th unit.
B)Yes, otherwise consumers would not buy 40 units.
C)Yes, because $18 shows what consumers are willing to pay for the product.
D)No, the marginal cost of the 40th unit exceeds the marginal benefit of the 40th unit.

Figure 4.3 shows the market for tiger shrimp. The market is initially in equilibrium at a price of $15 and a quantity of 80. Now suppose producers decide to cut output to 40 in order to raise the price to $18.
Refer to Figure 4.3.At a price of $18 consumers are willing to buy 40 kilograms of tiger shrimp.Is this an economically efficient quantity?
A)No, the marginal benefit of the 40th unit exceeds the marginal cost of that 80th unit.
B)Yes, otherwise consumers would not buy 40 units.
C)Yes, because $18 shows what consumers are willing to pay for the product.
D)No, the marginal cost of the 40th unit exceeds the marginal benefit of the 40th unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 4.4

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If the price of pecans is $3
A)economic surplus is maximized.
B)not enough consumers want to buy pecans.
C)the quantity supplied is less than the economically efficient quantity.
D)the quantity supplied is economically efficient but the quantity demanded is economically inefficient.

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.If the price of pecans is $3
A)economic surplus is maximized.
B)not enough consumers want to buy pecans.
C)the quantity supplied is less than the economically efficient quantity.
D)the quantity supplied is economically efficient but the quantity demanded is economically inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 4.4

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.At a price of $9
A)the marginal cost of pecans is greater than the marginal benefit; therefore, output is inefficiently low.
B)producers should lower the price to $3 in order to sell the quantity demanded of 4,000.
C)the marginal benefit of pecans is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently high.
D)the marginal benefit of pecans is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently low.

Refer to Figure 4.4.The figure above represents the market for pecans.Assume that this is a competitive market.At a price of $9
A)the marginal cost of pecans is greater than the marginal benefit; therefore, output is inefficiently low.
B)producers should lower the price to $3 in order to sell the quantity demanded of 4,000.
C)the marginal benefit of pecans is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently high.
D)the marginal benefit of pecans is greater than the marginal cost; therefore, output is inefficiently low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 4.3
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.Suppose that the quantity of labour demanded decreases by 80,000 at each wage level.What are the new free market equilibrium hourly wage and the new equilibrium quantity of labour?
A)W = $8.50; Q = 550,000
B)W = $12.50; Q = 630,000
C)W = $9.50; Q = 570,000
D)W = $9.50; Q = 590,000
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.Suppose that the quantity of labour demanded decreases by 80,000 at each wage level.What are the new free market equilibrium hourly wage and the new equilibrium quantity of labour?
A)W = $8.50; Q = 550,000
B)W = $12.50; Q = 630,000
C)W = $9.50; Q = 570,000
D)W = $9.50; Q = 590,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The graph below represents the market for walnuts.Identify the values of the marginal benefit and the marginal cost at the output levels of 2,000 kilograms, 4,000 kilograms and 6,000 kilograms.At each of these output levels, state whether output is inefficiently high, inefficiently low, or economically efficient.
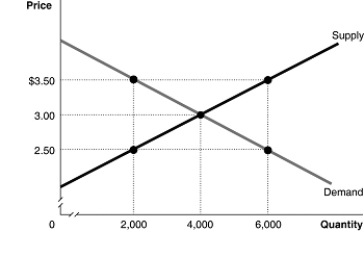


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Table 4.3
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 an hour is mandated, what is the quantity of labour demanded?
A)40,000
B)570,000
C)610,000
D)1,180,000
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 an hour is mandated, what is the quantity of labour demanded?
A)40,000
B)570,000
C)610,000
D)1,180,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In order to prevent a massive surplus of milk, the government
A)forces everyone to purchase at least 2 litres of milk a week
B)requires all producers to acquire one of a limited number of licences.
C) buys any extra milk that producers would like to sell at the regulated price.
D)converts any surplus milk into ice cream.
A)forces everyone to purchase at least 2 litres of milk a week
B)requires all producers to acquire one of a limited number of licences.
C) buys any extra milk that producers would like to sell at the regulated price.
D)converts any surplus milk into ice cream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Table 4.3
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 is mandated there will be a
A)shortage of 20,000 units of labour.
B)surplus of 20,000 units of labour.
C)shortage of 40,000 units of labour.
D)surplus of 40,000 units of labour.
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 is mandated there will be a
A)shortage of 20,000 units of labour.
B)surplus of 20,000 units of labour.
C)shortage of 40,000 units of labour.
D)surplus of 40,000 units of labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 4.3
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.What is the equilibrium hourly wage (W*)and the equilibrium quantity of labour (Q*)?
A)W* = $10.50; Q* = 590,000
B)W* = $11.50; Q* = 570,000
C)W* = $9.50; Q* = 570,000
D)W* = $10.50; Q* = 1,200,000
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.What is the equilibrium hourly wage (W*)and the equilibrium quantity of labour (Q*)?
A)W* = $10.50; Q* = 590,000
B)W* = $11.50; Q* = 570,000
C)W* = $9.50; Q* = 570,000
D)W* = $10.50; Q* = 1,200,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 4.5
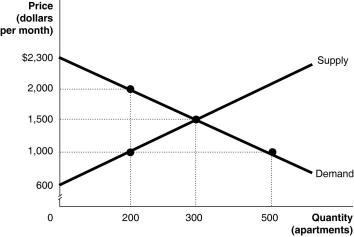
Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of consumer surplus after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$120,000
B)$230,000
C)$270,000
D)$430,000

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of consumer surplus after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$120,000
B)$230,000
C)$270,000
D)$430,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 4.5

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of the deadweight loss after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$50,000
B)$125,000
C)$175,000
D)$260,000

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of the deadweight loss after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$50,000
B)$125,000
C)$175,000
D)$260,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a competitive equilibrium is achieved in a market
A)all individuals are better off than they would be if a price ceiling or price floor was imposed by government.
B)the total net benefit to society is maximized.
C)the total benefits to consumers are equal to the total benefits to producers.
D)economic surplus equals the deadweight loss.
A)all individuals are better off than they would be if a price ceiling or price floor was imposed by government.
B)the total net benefit to society is maximized.
C)the total benefits to consumers are equal to the total benefits to producers.
D)economic surplus equals the deadweight loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The graph below represents the market for lychee nuts.The equilibrium price is $7.00 per bushel, but the market price is $5.00 per bushel.Identify the areas representing consumer surplus, producer surplus, and deadweight loss at the equilibrium price of $7.00 and at the market price of $5.00.
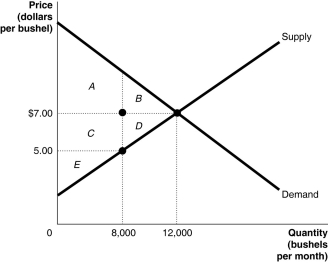


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
To affect the market outcome, a price ceiling
A)must be set below the black market price.
B)must be set below the legal price.
C)must be set below the price floor.
D)must be set below the equilibrium price.
A)must be set below the black market price.
B)must be set below the legal price.
C)must be set below the price floor.
D)must be set below the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Table 4.3
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 an hour is mandated, what is the quantity of labour supplied?
A)40,000
B)570,000
C)610,000
D)1,180,000
Table 4.3 shows the demand and supply schedules for the labour market in the city of Oshawa.
-Refer to Table 4.3.If a minimum wage of $9.50 an hour is mandated, what is the quantity of labour supplied?
A)40,000
B)570,000
C)610,000
D)1,180,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Rent control is an example of
A)a subsidy for low-skilled workers.
B)a price floor.
C)a price ceiling.
D)a black market.
A)a subsidy for low-skilled workers.
B)a price floor.
C)a price ceiling.
D)a black market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 4.5

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of the portion of producer surplus transferred to consumers as a result of the rent ceiling?
A)$40,000
B)$100,000
C)$125,000
D)$140,000

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of the portion of producer surplus transferred to consumers as a result of the rent ceiling?
A)$40,000
B)$100,000
C)$125,000
D)$140,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which term refers to a legally established minimum price that firms may charge?
A)a price ceiling
B)a subsidy
C)a price floor
D)a tariff
A)a price ceiling
B)a subsidy
C)a price floor
D)a tariff

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In order to be binding, a price ceiling
A)must lie above the free market equilibrium price.
B)must lie below the free market equilibrium price.
C)must coincide with the free market equilibrium price.
D)must be high enough for firms to earn a profit.
A)must lie above the free market equilibrium price.
B)must lie below the free market equilibrium price.
C)must coincide with the free market equilibrium price.
D)must be high enough for firms to earn a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Economists refer a to a market where buying and selling take place at prices that violate government price regulations as
A)a black market.
B)an outlaw market.
C)a noncompetitive market.
D)a restricted market.
A)a black market.
B)an outlaw market.
C)a noncompetitive market.
D)a restricted market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is not a consequence of minimum wage laws?
A)Low skilled workers are hurt because minimum wage reduces the number of jobs providing low skilled workers with training.
B)Employers will be reluctant to offer low-skill workers jobs with training.
C)Producers have an incentive to offer workers non-wage benefits such as extra health and dental care benefits and convenient working hours rather than a higher wage.
D)Some workers benefit when the minimum wage is increased.
A)Low skilled workers are hurt because minimum wage reduces the number of jobs providing low skilled workers with training.
B)Employers will be reluctant to offer low-skill workers jobs with training.
C)Producers have an incentive to offer workers non-wage benefits such as extra health and dental care benefits and convenient working hours rather than a higher wage.
D)Some workers benefit when the minimum wage is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 4.5

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.With rent control, the quantity supplied is 200 apartments.Suppose apartment owners ignore the law and rent this quantity for the highest rent they can get.What is the highest rent they can get per month?
A)$1,000
B)$1,500
C)$2,000
D)$2,300

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.With rent control, the quantity supplied is 200 apartments.Suppose apartment owners ignore the law and rent this quantity for the highest rent they can get.What is the highest rent they can get per month?
A)$1,000
B)$1,500
C)$2,000
D)$2,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 4.5

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of producer surplus after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$40,000
B)$100,000
C)$300,000
D)$430,000

Figure 4.5 shows the market for apartments in Springfield. Recently, the government imposed a rent ceiling of $1,000 per month.
Refer to Figure 4.5.What is the value of producer surplus after the imposition of the ceiling?
A)$40,000
B)$100,000
C)$300,000
D)$430,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 127 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



