Deck 7: Comparative Advantage and the Gains From International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Comparative Advantage and the Gains From International Trade
1
Exports are domestically produced goods and services
A)sold to other countries.
B)sold to the government.
C)sold at home.
D)which are used to produce other goods and services.
A)sold to other countries.
B)sold to the government.
C)sold at home.
D)which are used to produce other goods and services.
A
2
Twenty-seven countries in Europe have eliminated all tariffs with each other.This group of countries is known as the
A)European Union.
B)United Federation of Europe.
C)Gruppo Euro.
D)European Free Trade Association.
A)European Union.
B)United Federation of Europe.
C)Gruppo Euro.
D)European Free Trade Association.
A
3
How have Canadian imports and exports, as a fraction of GDP, changed from 1981 to the present?
Since 1981, both exports and imports have been steadily increasing as a fraction of GDP.In 1981, exports were about 17 percent of GDP and imports were about 14 percent of GDP.In 2012, exports were about 30 percent of GDP and imports were about 34 percent of GDP.
4
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on
A)exports.
B)services.
C)imports.
D)luxury items.
A)exports.
B)services.
C)imports.
D)luxury items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In 2012 ________ of Magna International sales were outside Canada.
A)23 percent
B)more than 75 percent
C)less than half
D)95 percent
A)23 percent
B)more than 75 percent
C)less than half
D)95 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The intention of the "Buy American" provision in the 2009 stimulus bill was to
A)increase jobs in the United States.
B)prevent foreign firms from dumping product in the United States.
C)insure that products used to build roads and bridges meet U.S. quality and safety standards.
D)save the government money by restricting the sale of more expensive foreign-made products.
A)increase jobs in the United States.
B)prevent foreign firms from dumping product in the United States.
C)insure that products used to build roads and bridges meet U.S. quality and safety standards.
D)save the government money by restricting the sale of more expensive foreign-made products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Japan is more dependent on foreign trade than Canada.
B)Imports and exports account for over one-half of the GDP of the Netherlands.
C)France is the leading exporting country, accounting for 10 percent of total world exports.
D)Because the cost of labour used on farms is so high, Canada exports very little of its wheat, canola, and barley crops.
A)Japan is more dependent on foreign trade than Canada.
B)Imports and exports account for over one-half of the GDP of the Netherlands.
C)France is the leading exporting country, accounting for 10 percent of total world exports.
D)Because the cost of labour used on farms is so high, Canada exports very little of its wheat, canola, and barley crops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
NAFTA refers to a 1994 agreement that eliminated most tariffs among which countries?
A)Canada, the United Kingdom and Mexico
B)the United States, the United Kingdom and Mexico
C)the United States, Canada and Mexico
D)the United States, Mexico and Cuba
A)Canada, the United Kingdom and Mexico
B)the United States, the United Kingdom and Mexico
C)the United States, Canada and Mexico
D)the United States, Mexico and Cuba

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In Canada, imports and exports combined make up more than half of GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Absolute advantage is
A)the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors when using the same amount of resources.
B)the ability to produce higher quality goods compared to one's competitors.
C)the ability to produce a good or service at a higher opportunity cost than one's competitors.
D)the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors that have more resources.
A)the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors when using the same amount of resources.
B)the ability to produce higher quality goods compared to one's competitors.
C)the ability to produce a good or service at a higher opportunity cost than one's competitors.
D)the ability to produce more of a good or service than competitors that have more resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Exports benefit trading countries because exports create jobs. Imports do not benefit trading countries because they result in a loss of jobs.
B)China plays little role in global trade.
C)Most of the leading exporting countries are high-income countries.
D)All sectors of the Canadian economy are affected equally by international trade.
A)Exports benefit trading countries because exports create jobs. Imports do not benefit trading countries because they result in a loss of jobs.
B)China plays little role in global trade.
C)Most of the leading exporting countries are high-income countries.
D)All sectors of the Canadian economy are affected equally by international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Workers in industries protected by tariffs and quotas are likely to support these trade restrictions because
A)they do not want to offend their employers who want them.
B)politicians lobby to convince workers the restrictions will make them better off.
C)they believe the restrictions will protect their jobs.
D)they don't understand that the restrictions will threaten their jobs.
A)they do not want to offend their employers who want them.
B)politicians lobby to convince workers the restrictions will make them better off.
C)they believe the restrictions will protect their jobs.
D)they don't understand that the restrictions will threaten their jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When Roxanne, a Canadian citizen, purchases a designer dress from Holt Renfrew that was made in Milan (Italy), the purchase is
A)a Canadian import and an Italian export.
B)a Canadian export and an Italian import.
C)both a Canadian and an Italian import.
D)neither an export nor an import for either country.
A)a Canadian import and an Italian export.
B)a Canadian export and an Italian import.
C)both a Canadian and an Italian import.
D)neither an export nor an import for either country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Early international trade in Canada involved
A)exporting consumer goods and importing raw materials.
B)greater costs than in any other country.
C)importing consumer goods and exporting furs and agricultural products.
D)importing raw materials and exporting intermediate goods.
A)exporting consumer goods and importing raw materials.
B)greater costs than in any other country.
C)importing consumer goods and exporting furs and agricultural products.
D)importing raw materials and exporting intermediate goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In 2012, Magna International sold ________ of what it made to countries outside the North American Free Trade Agreement.
A)more than 75 percent
B)a little more than half
C)almost 80 percent
D)less than 20 percent
A)more than 75 percent
B)a little more than half
C)almost 80 percent
D)less than 20 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Magna International's sales are larger outside Canada than inside Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why would Canadian firms that sell products in foreign markets protest a "Buy Canadian" policy?
A)Foreign countries would likely retaliate by limiting Canadian exports.
B)Foreign firms would stop selling all products in Canada.
C)Canadian firms would never be able to meet the increased demand for Canadian-produced goods.
D)Eventually the government would demand price cuts from Canadian manufacturers.
A)Foreign countries would likely retaliate by limiting Canadian exports.
B)Foreign firms would stop selling all products in Canada.
C)Canadian firms would never be able to meet the increased demand for Canadian-produced goods.
D)Eventually the government would demand price cuts from Canadian manufacturers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements about the importance of trade to the Canadian economy is true?
A)Since 1981, both exports and imports have steadily decreased as a fraction of U.S. gross domestic product.
B)Overall, about 80 percent of Canadian jobs depend directly or indirectly on exports.
C)Canadian exports account for approximately one-third of GDP.
D)International trade plays very little part in the Canadian economy.
A)Since 1981, both exports and imports have steadily decreased as a fraction of U.S. gross domestic product.
B)Overall, about 80 percent of Canadian jobs depend directly or indirectly on exports.
C)Canadian exports account for approximately one-third of GDP.
D)International trade plays very little part in the Canadian economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Goods and services bought domestically but produced in other countries are referred to as
A)exports.
B)imports.
C)transfer payments.
D)foreign consumption.
A)exports.
B)imports.
C)transfer payments.
D)foreign consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Over the last 50 years, most countries have
A)increased tariffs
B)completely eliminated tariffs
C)doubled tariffs
D)dramatically reduced tariffs
A)increased tariffs
B)completely eliminated tariffs
C)doubled tariffs
D)dramatically reduced tariffs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
________ is the ability of an individual, a firm, or a country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than competitors.
A)Absolute advantage
B)Specialization
C)Autarky
D)Comparative advantage
A)Absolute advantage
B)Specialization
C)Autarky
D)Comparative advantage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If Japanese workers are more productive than French workers, then trade between Japan and France
A)can take place only if France has an absolute advantage in producing a good or service Japanese buyers want.
B)cannot take place because Japanese goods and services will be less expensive than French goods and services.
C)cannot take place until French workers become more productive.
D)will take place so long as each country has a comparative advantage in a good or service that buyers in the other country want.
A)can take place only if France has an absolute advantage in producing a good or service Japanese buyers want.
B)cannot take place because Japanese goods and services will be less expensive than French goods and services.
C)cannot take place until French workers become more productive.
D)will take place so long as each country has a comparative advantage in a good or service that buyers in the other country want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Table 7.1
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Sandy has a greater opportunity cost than Linda for dog grooming.
B)Sandy's opportunity cost for dog grooming is less than Linda's.
C)Linda has a greater opportunity cost than Sandy for dog bathing.
D)Sandy's opportunity cost for dog grooming and dog bathing are both greater than Linda's.
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Sandy has a greater opportunity cost than Linda for dog grooming.
B)Sandy's opportunity cost for dog grooming is less than Linda's.
C)Linda has a greater opportunity cost than Sandy for dog bathing.
D)Sandy's opportunity cost for dog grooming and dog bathing are both greater than Linda's.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The ratio at which a country can trade its exports for imports from other countries is called
A)a trade barrier.
B)the terms of trade.
C)autarky.
D)a free trade agreement.
A)a trade barrier.
B)the terms of trade.
C)autarky.
D)a free trade agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Examples of ________ show how trade between two countries can make each better off.
A)absolute advantage
B)comparative advantage
C)autarky
D)trade barriers
A)absolute advantage
B)comparative advantage
C)autarky
D)trade barriers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If Canada has a comparative advantage relative to Mexico in the production of timber, then
A)the explicit cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.
B)the opportunity cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.
C)the implicit costs of production for timber are lower in Canada than in Mexico.
D)the average cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.
A)the explicit cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.
B)the opportunity cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.
C)the implicit costs of production for timber are lower in Canada than in Mexico.
D)the average cost of production for timber is lower in Canada than in Mexico.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 7.1
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Linda has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog grooming.
B)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and Linda has an absolute advantage in dog grooming.
C)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and dog grooming.
D)Linda has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and dog grooming.
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Linda has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog grooming.
B)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and Linda has an absolute advantage in dog grooming.
C)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and dog grooming.
D)Linda has an absolute advantage in dog bathing and dog grooming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A situation in which a country does not trade with other countries is called
A)autarky.
B)self-actualization.
C)autonomy.
D)independence.
A)autarky.
B)self-actualization.
C)autonomy.
D)independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Countries that engage in trade will tend to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have ________ and will ________ these goods and services.
A)a comparative advantage; import
B)an absolute advantage; export
C)a comparative advantage; export
D)an absolute advantage; import
A)a comparative advantage; import
B)an absolute advantage; export
C)a comparative advantage; export
D)an absolute advantage; import

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Whenever a buyer and a seller agree to trade,
A)the agreement is made based on absolute advantage.
B)they must have identical opportunity costs in producing their respective products.
C)one party will always be worse off.
D)both must believe they will be made better off.
A)the agreement is made based on absolute advantage.
B)they must have identical opportunity costs in producing their respective products.
C)one party will always be worse off.
D)both must believe they will be made better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the opportunity cost of production for two goods is different between two countries, then
A)trade cannot benefit either country.
B)only one country can be made better off by trade.
C)mutually beneficial trade is possible.
D)trade will only benefit both countries if one can lower its opportunity costs.
A)trade cannot benefit either country.
B)only one country can be made better off by trade.
C)mutually beneficial trade is possible.
D)trade will only benefit both countries if one can lower its opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ability of a firm or country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than other producers is called absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Table 7.2
Output Per Hour of Work

Table 7.2 shows the output per hour of work for handbags and jackets in Cambodia and in Thailand.
Refer to Table 7.2.
a.Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of handbags and jackets?
b.Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of handbags?
c.Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of jackets?
Output Per Hour of Work

Table 7.2 shows the output per hour of work for handbags and jackets in Cambodia and in Thailand.
Refer to Table 7.2.
a.Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of handbags and jackets?
b.Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of handbags?
c.Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of jackets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Assume that China has a comparative advantage in producing corn and exports corn to Japan.We can conclude that
A)China also has an absolute advantage in producing corn relative to Japan.
B)China has a lower opportunity cost of producing corn relative to Japan.
C)Japan has an absolute disadvantage in producing corn relative to China.
D)labour costs are higher for corn producers in Japan than in China.
A)China also has an absolute advantage in producing corn relative to Japan.
B)China has a lower opportunity cost of producing corn relative to Japan.
C)Japan has an absolute disadvantage in producing corn relative to China.
D)labour costs are higher for corn producers in Japan than in China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If Canada imports fishing poles from Mexico and Mexico imports bacon from Canada, which of the following would explain this pattern of trade?
A)Mexico has a lower opportunity cost of producing bacon than Mexico and Mexico has a comparative advantage in producing fishing poles.
B)The opportunity cost of producing fishing poles in Canada is higher than the opportunity cost of producing bacon in Mexico.
C)Mexico must have an absolute advantage in producing fishing poles and Canada must have an absolute advantage in bacon.
D)Mexico has a higher opportunity cost of producing fishing poles than Canada, and Canada has a higher opportunity cost of producing bacon.
A)Mexico has a lower opportunity cost of producing bacon than Mexico and Mexico has a comparative advantage in producing fishing poles.
B)The opportunity cost of producing fishing poles in Canada is higher than the opportunity cost of producing bacon in Mexico.
C)Mexico must have an absolute advantage in producing fishing poles and Canada must have an absolute advantage in bacon.
D)Mexico has a higher opportunity cost of producing fishing poles than Canada, and Canada has a higher opportunity cost of producing bacon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If Estonia has an absolute advantage in the production of two goods compared to Norway, Estonia can not benefit from trade with Norway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An economic principle that explains why countries produce different goods and services is
A)absolute advantage.
B)trade as a percentage of GDP.
C)comparative advantage.
D)NAFTA.
A)absolute advantage.
B)trade as a percentage of GDP.
C)comparative advantage.
D)NAFTA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Table 7.1
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.
B)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing.
C)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.
D)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming and dog bathing.
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.
B)Sandy has an absolute advantage in dog bathing.
C)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.
D)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming and dog bathing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Table 7.1
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog grooming.
B)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming.
C)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming and dog bathing.
D)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.
Linda and Sandy own The Preppy Puppy, a dog grooming business. Table 7.1 lists the number of dogs Linda and Sandy can each bathe and groom in one week.
-Refer to Table 7.1.Select the statement that accurately interprets the data in the table.
A)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog grooming.
B)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming.
C)Linda has a comparative advantage in dog grooming and dog bathing.
D)Sandy has a comparative advantage in dog bathing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Table 7.2
Output Per Hour of Work

Table 7.2 shows the output per hour of work for handbags and jackets in Cambodia and in Thailand.
Refer to Table 7.2.Fill in the following table with the opportunity costs of producing handbags and jackets for Cambodia and Thailand.
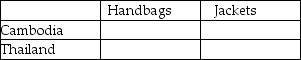
Output Per Hour of Work

Table 7.2 shows the output per hour of work for handbags and jackets in Cambodia and in Thailand.
Refer to Table 7.2.Fill in the following table with the opportunity costs of producing handbags and jackets for Cambodia and Thailand.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose in Finland a worker can produce either 32 cell phones or 4 kayaks, while in Canada a worker can produce either 40 cell phones or 10 kayaks.
a.Which country has an absolute advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production?
b.What is the opportunity cost of 1 cell phone in Finland? In Canada?
c.What is the opportunity cost of 1 kayak in Finland? In Canada?
d.Which country has a comparative advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production?
e.Suppose each country has 1,000 workers.Currently, each country devotes 40 percent of its labour force to cell phone production and 60 percent to kayak production.What is the output of cell phones and kayaks for each country and what is the total output of cell phones and kayaks between the two countries?
f.Suppose each country specializes in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantage.What is the total output of cell phones and kayaks in the two countries?
g.Provide a numerical example to show how Finland and Canada can both gain from trade.Assume that the terms of trade are established at 6 cell phones for 1 kayak.
a.Which country has an absolute advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production?
b.What is the opportunity cost of 1 cell phone in Finland? In Canada?
c.What is the opportunity cost of 1 kayak in Finland? In Canada?
d.Which country has a comparative advantage in cell phone production? In kayak production?
e.Suppose each country has 1,000 workers.Currently, each country devotes 40 percent of its labour force to cell phone production and 60 percent to kayak production.What is the output of cell phones and kayaks for each country and what is the total output of cell phones and kayaks between the two countries?
f.Suppose each country specializes in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantage.What is the total output of cell phones and kayaks in the two countries?
g.Provide a numerical example to show how Finland and Canada can both gain from trade.Assume that the terms of trade are established at 6 cell phones for 1 kayak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Canada is a leading exporter of wheat.What explains the comparative advantage of Canada in wheat production?
A)positive externalities
B)investment by large firms such as Viterra and Pioneer
C)climate and soil conditions in Canada which are well-suited for wheat production
D)a large supply of unskilled labour
A)positive externalities
B)investment by large firms such as Viterra and Pioneer
C)climate and soil conditions in Canada which are well-suited for wheat production
D)a large supply of unskilled labour

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A consequence of increasing marginal costs of producing digital music players in Japan is
A)Japan will not export digital music players.
B)Japan will stop short of complete specialization in the production of digital music players.
C)Japan will import digital music players from countries that don't experience increasing marginal costs.
D)Japan will likely impose trade restrictions on imported digital music players.
A)Japan will not export digital music players.
B)Japan will stop short of complete specialization in the production of digital music players.
C)Japan will import digital music players from countries that don't experience increasing marginal costs.
D)Japan will likely impose trade restrictions on imported digital music players.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the 1970s and 1980s, North America lost its comparative advantage in consumer electronics goods to Japan.What factor was most responsible for the development of Japan's comparative advantage in consumer electronics goods?
A)Japanese firms benefited from external economies.
B)Japan has abundant supplies of labour.
C)Japanese firms excelled in process technology.
D)Japan has abundant supplies of natural resources needed to produce electronics goods.
A)Japanese firms benefited from external economies.
B)Japan has abundant supplies of labour.
C)Japanese firms excelled in process technology.
D)Japan has abundant supplies of natural resources needed to produce electronics goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is autarky?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Tastes for products such as beer differ.As a result
A)we see countries specializing completely in the production of beer.
B)consumers of beer have difficulty deciding what type of imported beer to buy.
C)the quality of imported beer is less than it could be.
D)different countries may each have a comparative advantage in producing different types of beer.
A)we see countries specializing completely in the production of beer.
B)consumers of beer have difficulty deciding what type of imported beer to buy.
C)the quality of imported beer is less than it could be.
D)different countries may each have a comparative advantage in producing different types of beer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What are the four main sources of comparative advantage? Briefly explain each source and provide examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Once a country has lost its comparative advantage in producing a good, its income will be ________ and its economy will be ________ if it switches from producing the good to importing it.
A)higher; less efficient
B)higher; more efficient
C)lower; less efficient
D)lower; more efficient
A)higher; less efficient
B)higher; more efficient
C)lower; less efficient
D)lower; more efficient

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Japan has developed a comparative advantage in designing and producing automobiles.The source of its comparative advantage in these products is
A)abundant supplies of natural resources.
B)a favorable climate.
C)a strong central government.
D)technology.
A)abundant supplies of natural resources.
B)a favorable climate.
C)a strong central government.
D)technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
One of the main sources of comparative advantage is internal economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is not a source of comparative advantage?
A)relative abundance of labour and capital
B)technology
C)climate and natural resources
D)a strong foreign currency exchange rate
A)relative abundance of labour and capital
B)technology
C)climate and natural resources
D)a strong foreign currency exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The first example used to explain comparative advantage used two countries (England and Portugal)and two goods (wine and cloth)to show that
A)each country would be better off from trade if it had an absolute advantage in producing one of the goods.
B)each country would have a comparative advantage in the production of the good for which it had an absolute advantage.
C)mutually beneficial trade was possible between two countries even if one had an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
D)mutually beneficial trade was possible between two countries even if one had a comparative advantage in the production of both goods.
A)each country would be better off from trade if it had an absolute advantage in producing one of the goods.
B)each country would have a comparative advantage in the production of the good for which it had an absolute advantage.
C)mutually beneficial trade was possible between two countries even if one had an absolute advantage in the production of both goods.
D)mutually beneficial trade was possible between two countries even if one had a comparative advantage in the production of both goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the real world we don't observe countries completely specializing in the production of goods for which they have a comparative advantage.One reasons for this is
A)comparative advantage works better in theory than in practice.
B)some countries have more resources than other countries.
C)tastes for many traded goods are similar in many countries because of globalization.
D)production of most goods involves increasing opportunity costs.
A)comparative advantage works better in theory than in practice.
B)some countries have more resources than other countries.
C)tastes for many traded goods are similar in many countries because of globalization.
D)production of most goods involves increasing opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements is true?
A)All individuals in both countries are made better off as a result of international trade.
B)Within each country, some individuals are made better off as a result of international trade, but one of the countries will be worse off overall.
C)Although some individuals are made better off as a result of international trade, both countries may be made worse off overall.
D)Each country as a whole is made better off as a result of international trade, but individuals within each country may be made worse off.
A)All individuals in both countries are made better off as a result of international trade.
B)Within each country, some individuals are made better off as a result of international trade, but one of the countries will be worse off overall.
C)Although some individuals are made better off as a result of international trade, both countries may be made worse off overall.
D)Each country as a whole is made better off as a result of international trade, but individuals within each country may be made worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Bay Street, in Toronto, is the heart of the Canadian financial system, where banks, brokerage houses, other financial firms, and the Toronto Stock Exchange are all located.What is the reason for Toronto's comparative advantage in the financial market?
A)the development of superior information technology
B)an abundant supply of skilled labour
C)Toronto has a central location in the country
D)external economies
A)the development of superior information technology
B)an abundant supply of skilled labour
C)Toronto has a central location in the country
D)external economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Many proponents of globalization claim "Trade is a win-win situation for all countries that participate." This statement is
A)false since it ignores the workers who lose their jobs as result of international trade.
B)false since not all countries participate in international trade.
C)true because it refers to countries; individuals may be losers as a result of international trade.
D)true because all consumers and workers benefit from international trade.
A)false since it ignores the workers who lose their jobs as result of international trade.
B)false since not all countries participate in international trade.
C)true because it refers to countries; individuals may be losers as a result of international trade.
D)true because all consumers and workers benefit from international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The simple trade model demonstrates that countries can expand consumption by specializing in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage.In reality we do not see complete specialization in production.State three reasons why this is case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
One reason a country does not specialize completely in production is that not all goods and services are traded internationally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
________ refers to reductions in a firm's costs that result from an increase in the size of an industry.
A)Internal economies
B)External economies
C)Autarkial dominance
D)Streamlining
A)Internal economies
B)External economies
C)Autarkial dominance
D)Streamlining

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
China has developed a comparative advantage in the production of clothing.The source of this comparative advantage is
A)a large supply of natural resources.
B)a large supply of unskilled workers and relatively little capital.
C)investment in capital used to produce clothing.
D)superior process technology.
A)a large supply of natural resources.
B)a large supply of unskilled workers and relatively little capital.
C)investment in capital used to produce clothing.
D)superior process technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figure 7.2
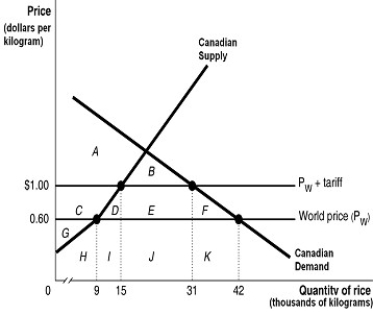
Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The tariff revenue collected by the government equals the area
A)D + E + F.
B)E)
C)B + D + E + F.
D)C + D + E + F.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The tariff revenue collected by the government equals the area
A)D + E + F.
B)E)
C)B + D + E + F.
D)C + D + E + F.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.Without the tariff in place, Canadians consume
A)9 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)42 thousand kilograms of rice.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.Without the tariff in place, Canadians consume
A)9 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)42 thousand kilograms of rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.Without the tariff in place, Canadians produce
A)9 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)42 thousand kilograms of rice.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.Without the tariff in place, Canadians produce
A)9 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)42 thousand kilograms of rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A numerical limit imposed by a government on the quantity of a good that can be imported into the country is called a
A)tariff.
B)quota.
C)quantity floor.
D)barricade.
A)tariff.
B)quota.
C)quantity floor.
D)barricade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A tariff is
A)a limit placed on the quantity of goods that can be imported into a country.
B)a tax imposed by a government on goods imported into a country.
C)a subsidy granted to importers of a vital input.
D)a health and safety restriction imposed on an imported product.
A)a limit placed on the quantity of goods that can be imported into a country.
B)a tax imposed by a government on goods imported into a country.
C)a subsidy granted to importers of a vital input.
D)a health and safety restriction imposed on an imported product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.If the tariff was replaced by a quota which limited rice imports to 16 thousand kilograms, the amount of revenue received by rice importers would equal
A)$6.4 thousand.
B)$9.6 thousand.
C)$16 thousand.
D)$19.8 thousand.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.If the tariff was replaced by a quota which limited rice imports to 16 thousand kilograms, the amount of revenue received by rice importers would equal
A)$6.4 thousand.
B)$9.6 thousand.
C)$16 thousand.
D)$19.8 thousand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not an example of a trade restriction?
A)tariffs
B)quotas and voluntary export restraints
C)legislation requiring that cars sold in a country have a 50 percent domestic content
D)consumer preferences for goods produced domestically
A)tariffs
B)quotas and voluntary export restraints
C)legislation requiring that cars sold in a country have a 50 percent domestic content
D)consumer preferences for goods produced domestically

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Trade between countries that is without restrictions is called
A)unobstructed commerce.
B)unabated trade.
C)free trade.
D)unencumbered trade.
A)unobstructed commerce.
B)unabated trade.
C)free trade.
D)unencumbered trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The tariff causes domestic consumption of rice
A)to fall by 27 thousand kilograms.
B)to fall by 11 thousand kilograms.
C)to rise by 6 thousand kilograms.
D)to rise by 16 thousand kilograms.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The tariff causes domestic consumption of rice
A)to fall by 27 thousand kilograms.
B)to fall by 11 thousand kilograms.
C)to rise by 6 thousand kilograms.
D)to rise by 16 thousand kilograms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.As a result of the tariff, domestic producers increase their quantity supplied by
A)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)22 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)6 thousand kilograms of rice.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.As a result of the tariff, domestic producers increase their quantity supplied by
A)31 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)22 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)15 thousand kilograms of rice.
D)6 thousand kilograms of rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The increase in domestic producer surplus as a result of the tariff is equal to the area
A)C)
B)C + G.
C)A + C + G.
D)C + D + G + H + I.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The increase in domestic producer surplus as a result of the tariff is equal to the area
A)C)
B)C + G.
C)A + C + G.
D)C + D + G + H + I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A tariff on imports
A)makes domestic consumers worse off.
B)makes both domestic producers and consumers worse off.
C)makes everyone better off.
D)makes domestic producers worse off.
A)makes domestic consumers worse off.
B)makes both domestic producers and consumers worse off.
C)makes everyone better off.
D)makes domestic producers worse off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 7.1
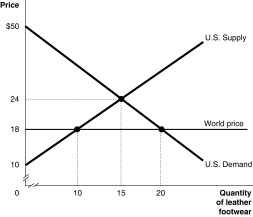
Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Suppose the government allows imports of leather footwear into the United States.What happens to the market price and what is the quantity of imports?
A)The price equals $24 and imports equal 20 units.
B)The price falls to $24 and imports equal 5 units.
C)The price falls to $18 and imports equal 15 units.
D)The price equals $18 and imports equal 10 units.

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Suppose the government allows imports of leather footwear into the United States.What happens to the market price and what is the quantity of imports?
A)The price equals $24 and imports equal 20 units.
B)The price falls to $24 and imports equal 5 units.
C)The price falls to $18 and imports equal 15 units.
D)The price equals $18 and imports equal 10 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 7.1

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Under autarky, the consumer surplus is ________ and the producer surplus is ________.
A)$195; $105
B)$300; $285
C)$260; $40
D)$555; $105

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Under autarky, the consumer surplus is ________ and the producer surplus is ________.
A)$195; $105
B)$300; $285
C)$260; $40
D)$555; $105

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Under autarky, consumer surplus is represented by the area
A)above the supply curve and below the equilibrium price.
B)above the supply curve and below the demand curve.
C)below the demand curve and above the equilibrium price.
D)above the demand curve and below the supply curve.
A)above the supply curve and below the equilibrium price.
B)above the supply curve and below the demand curve.
C)below the demand curve and above the equilibrium price.
D)above the demand curve and below the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 7.1

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Suppose the government allows imports of leather footwear into Canada.The market price falls to $18.What are the values of consumer surplus and domestic producer surplus?
A)Consumer surplus = $270; producer surplus = $40.
B)Consumer surplus = $320; producer surplus = $40.
C)Consumer surplus = $320; producer surplus = $360.
D)Consumer surplus = $305; producer surplus = $320.

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Suppose the government allows imports of leather footwear into Canada.The market price falls to $18.What are the values of consumer surplus and domestic producer surplus?
A)Consumer surplus = $270; producer surplus = $40.
B)Consumer surplus = $320; producer surplus = $40.
C)Consumer surplus = $320; producer surplus = $360.
D)Consumer surplus = $305; producer surplus = $320.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The loss in domestic consumer surplus as a result of the tariff is equal to the area
A)B + D + E + F.
B)D + E + F.
C)C + D + E + F.
D)B)

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.The loss in domestic consumer surplus as a result of the tariff is equal to the area
A)B + D + E + F.
B)D + E + F.
C)C + D + E + F.
D)B)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is the best example of a tariff?
A)a subsidy from the Canadian government to domestic manufacturers of residential air conditioners to enable them to compete more effectively with foreign producers
B)a limit on the quantity of residential air conditioners that can be imported from a foreign country
C)a $150 fee imposed on all imported residential air conditioners
D)a tax placed on all residential air conditioners sold in the domestic market to help offset the impact of emissions on the environment
A)a subsidy from the Canadian government to domestic manufacturers of residential air conditioners to enable them to compete more effectively with foreign producers
B)a limit on the quantity of residential air conditioners that can be imported from a foreign country
C)a $150 fee imposed on all imported residential air conditioners
D)a tax placed on all residential air conditioners sold in the domestic market to help offset the impact of emissions on the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 7.1

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Under autarky, the deadweight loss is
A)$0.
B)$15.
C)$30.
D)$40.

Figure 7.1 shows Canadian demand and supply for leather footwear.
Refer to Figure 7.1.Under autarky, the deadweight loss is
A)$0.
B)$15.
C)$30.
D)$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 7.2

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.With the tariff in place, Canada
A)imports 16 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)imports 9 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)imports 15 thousand kilgrams of rice.
D)exports 31 thousand kilograms of rice.

Suppose the Canadian government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 7.2 shows the impact of this tariff.
Refer to Figure 7.2.With the tariff in place, Canada
A)imports 16 thousand kilograms of rice.
B)imports 9 thousand kilograms of rice.
C)imports 15 thousand kilgrams of rice.
D)exports 31 thousand kilograms of rice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



