Deck 13: Monopoly and Antitrust Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/146
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Monopoly and Antitrust Policy
1
Peet's Coffee and Teas produces some flavourful varieties of Peet's brand coffee.Is Peet's a monopoly?
A)Yes, there are no substitutes to Peet's coffee.
B)No, although Peet's coffee is a unique product, there are many different brands of coffee that are very close substitutes.
C)Yes, Peet's is the only supplier of Peet's coffee in a market where there are high barriers to entry.
D)No, Peet's is not a monopoly because there are many branches of Peet's.
A)Yes, there are no substitutes to Peet's coffee.
B)No, although Peet's coffee is a unique product, there are many different brands of coffee that are very close substitutes.
C)Yes, Peet's is the only supplier of Peet's coffee in a market where there are high barriers to entry.
D)No, Peet's is not a monopoly because there are many branches of Peet's.
B
2
To enter a local cable television market, a firm needs a license from the CRTC.This is an example of
A)a government-imposed barrier.
B)monopoly due to control of a resource.
C)a natural monopoly.
D)the government maintaining consistent standards in the broadcast industry.
A)a government-imposed barrier.
B)monopoly due to control of a resource.
C)a natural monopoly.
D)the government maintaining consistent standards in the broadcast industry.
A
3
Which of the following is the best example of a monopoly if we use a broader definition of monopoly?
A)Spuds McKenzie, a wealthy potato farmer in Prince Edward Island
B)Cheap Gas, one of two gasoline stations in a large rural community
C)Sushi NOW!, the only Japanese restaurant in the small town of Rouleau
D)Zippie Rentals, a sports car rental service in the downtown Calgary area
A)Spuds McKenzie, a wealthy potato farmer in Prince Edward Island
B)Cheap Gas, one of two gasoline stations in a large rural community
C)Sushi NOW!, the only Japanese restaurant in the small town of Rouleau
D)Zippie Rentals, a sports car rental service in the downtown Calgary area
C
4
If we use a narrow definition of monopoly, then a monopoly is defined as a firm
A)that has been granted special production rights by the government.
B)that can ignore the actions of all other firms because it produces a superior product compared to its rivals' products.
C)that can ignore the actions of all other firms because it produces a product for which there are no close substitutes.
D)that has the largest market share in an industry.
A)that has been granted special production rights by the government.
B)that can ignore the actions of all other firms because it produces a superior product compared to its rivals' products.
C)that can ignore the actions of all other firms because it produces a product for which there are no close substitutes.
D)that has the largest market share in an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Compared to a monopolistic competitor, a monopolist faces
A)a more elastic demand curve.
B)a more inelastic demand curve.
C)a more elastic demand curve at higher prices and a more inelastic demand curve at lower prices.
D)a demand curve that has a price elasticity coefficient of zero.
A)a more elastic demand curve.
B)a more inelastic demand curve.
C)a more elastic demand curve at higher prices and a more inelastic demand curve at lower prices.
D)a demand curve that has a price elasticity coefficient of zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Joe Santos owns the only pizza parlor in a small town that is also home to a McDonald's, a Taco Bell and a Kentucky Fried Chicken.Using a broad definition of a monopoly, Joe has a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A monopoly differs from monopolistic competition in that
A)a monopoly has market power while a firm in monopolistic competition does not have any market power.
B)a monopoly can never make a loss but a firm in monopolistic competition can.
C)in a monopoly there are significant entry barriers but there are low barriers to entry in a monopolistically competitive market structure.
D)a monopoly faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve while a monopolistic competitor faces an elastic demand curve.
A)a monopoly has market power while a firm in monopolistic competition does not have any market power.
B)a monopoly can never make a loss but a firm in monopolistic competition can.
C)in a monopoly there are significant entry barriers but there are low barriers to entry in a monopolistically competitive market structure.
D)a monopoly faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve while a monopolistic competitor faces an elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In 2011, Microsoft filed a complaint with the European Commission accusing Google of taking steps to monopolize the Internet search engine business.Microsoft's primary complaint was that
A)Google is the only Internet search engine available to Windows operating system users.
B)the European Union contracts exclusively with Google for its Internet search engine use.
C)Google has prevented competitors from gaining access to needed content and data to provide search results to consumers.
D)Google owns the Internet advertising companies that pay for ads on search engine sites, and has prohibited ads from being sold to competitors.
A)Google is the only Internet search engine available to Windows operating system users.
B)the European Union contracts exclusively with Google for its Internet search engine use.
C)Google has prevented competitors from gaining access to needed content and data to provide search results to consumers.
D)Google owns the Internet advertising companies that pay for ads on search engine sites, and has prohibited ads from being sold to competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following characteristics:
A)a market structure with barriers to entry
B)demand curves that are easily identified
C)firm cannot make zero profits in the long run
D)firm can reap long run profits
Which of the characteristics in the list above is shared by an oligopolist and a monopolist?
A)a, b and d
B)a, c, and d
C)a and d
D)a, b, c and d
A)a market structure with barriers to entry
B)demand curves that are easily identified
C)firm cannot make zero profits in the long run
D)firm can reap long run profits
Which of the characteristics in the list above is shared by an oligopolist and a monopolist?
A)a, b and d
B)a, c, and d
C)a and d
D)a, b, c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The market demand curve facing a monopolist is more elastic than the market demand curve facing a monopolistic competitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monopoly is characterized by all of the following except
A)there are only a few sellers each selling a unique product.
B)entry barriers are high.
C)there are no close substitutes to the firm's product.
D)the firm has market power.
A)there are only a few sellers each selling a unique product.
B)entry barriers are high.
C)there are no close substitutes to the firm's product.
D)the firm has market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A firm that has the ability to control to some degree the price of the product it sells
A)is also able to dictate the quantity purchased.
B)faces a demand curve that is inelastic throughout the range of market demand.
C)is a price maker.
D)faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
A)is also able to dictate the quantity purchased.
B)faces a demand curve that is inelastic throughout the range of market demand.
C)is a price maker.
D)faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A monopolist faces
A)a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
C)a horizontal demand curve.
D)a downward-sloping demand curve.
A)a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B)a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
C)a horizontal demand curve.
D)a downward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A monopoly is a seller of a product
A)with many substitutes.
B) without a close substitute.
C)with a perfectly inelastic demand.
D)without a well-defined demand curve.
A)with many substitutes.
B) without a close substitute.
C)with a perfectly inelastic demand.
D)without a well-defined demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a characteristic shared by a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly?
A)Each must lower its price to sell more output.
B)Each sets a price for its product that will maximize its revenue.
C)Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which price equals marginal cost.
A)Each must lower its price to sell more output.
B)Each sets a price for its product that will maximize its revenue.
C)Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D)Each maximizes profits by producing a quantity for which price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A monopoly is defined as a firm that has the largest market share in an industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is a monopoly? Can a firm be a monopoly if close substitutes for its product exists?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Tickets to Toronto Maple Leafs games regularly sell out, despite a relatively high price.The Pheonix Coyotes have struggled financially for years.What is an economic reason why the National Hockey League would prevent the Coyotes from moving to the greater Toronto area?
A)The commisioner of the league is from the southern US.
B)The Toronto City Council refuses to grant permission.
C)The National Hockey League understands that a new team in Toronto could reduce the Maple Leaf's profits.
D)A second team in Toronto would be too confusing for fans.
A)The commisioner of the league is from the southern US.
B)The Toronto City Council refuses to grant permission.
C)The National Hockey League understands that a new team in Toronto could reduce the Maple Leaf's profits.
D)A second team in Toronto would be too confusing for fans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To maintain a monopoly, a firm must have
A)a perfectly inelastic demand.
B)an insurmountable barrier to entry.
C)marginal revenue equal to demand.
D)few competitors.
A)a perfectly inelastic demand.
B)an insurmountable barrier to entry.
C)marginal revenue equal to demand.
D)few competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In Hamilton, Ontario there are three very popular supermarkets: Superstore, Fortinos, and Sobeys.While Sobey's remains open twenty-four hours a day, Superstore and Fortinos close at 11 pm.Which of the following statements is true?
A)Sobeys is a monopoly all day because it produces a service that has no close substitutes.
B)Sobeys has a monopoly at midnight but not during the day.
C)Sobeys can ignore the pricing decisions of the other two supermarkets.
D)Sobeys probably has a higher markup to compensate for its higher cost of production.
A)Sobeys is a monopoly all day because it produces a service that has no close substitutes.
B)Sobeys has a monopoly at midnight but not during the day.
C)Sobeys can ignore the pricing decisions of the other two supermarkets.
D)Sobeys probably has a higher markup to compensate for its higher cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A public franchise
A)is a corporation that is owned by stockholders.
B)results from ownership of a key raw material.
C)is a government designation that a private firm is the only legal producer of a good or service.
D)is an unregulated monopoly necessary for the public good.
A)is a corporation that is owned by stockholders.
B)results from ownership of a key raw material.
C)is a government designation that a private firm is the only legal producer of a good or service.
D)is an unregulated monopoly necessary for the public good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
One reason patent protection is vitally important to pharmaceutical firms is
A)successful new drugs are not profitable. If firms are not granted patents many would go out of business and health care would be severely diminished.
B)the approval process for new drugs through the Food and Drug Administration can take more than 10 years and is very costly. Patents enable firms to recover costs incurred during this process.
C)that taxes on profits from drugs are very high; profits from patent protection enable firms to pay these taxes.
D)the high salaries pharmaceutical firms pay to scientists and doctors make their labour costs higher than for any other business. Profits from patents are needed to pay these labour costs.
A)successful new drugs are not profitable. If firms are not granted patents many would go out of business and health care would be severely diminished.
B)the approval process for new drugs through the Food and Drug Administration can take more than 10 years and is very costly. Patents enable firms to recover costs incurred during this process.
C)that taxes on profits from drugs are very high; profits from patent protection enable firms to pay these taxes.
D)the high salaries pharmaceutical firms pay to scientists and doctors make their labour costs higher than for any other business. Profits from patents are needed to pay these labour costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A virtuous cycle occurs
A)when lobbyists petition Parliament a public franchise; the lobbyist then raise money for the political party that granted the franchise.
B)when monopoly profits are used to create new products for additional monopoly profits.
C)when a firm can attract enough buyers initially to increase a product's usefulness to attract even more buyers.
D)when a firm's sales volume reaches a level where the firm can take advantage of economies of scale; thereby reducing the price of the product to further boost its sales.
A)when lobbyists petition Parliament a public franchise; the lobbyist then raise money for the political party that granted the franchise.
B)when monopoly profits are used to create new products for additional monopoly profits.
C)when a firm can attract enough buyers initially to increase a product's usefulness to attract even more buyers.
D)when a firm's sales volume reaches a level where the firm can take advantage of economies of scale; thereby reducing the price of the product to further boost its sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For which of the following firms is patent protection of vital importance?
A)furniture producers
B)software firms
C)pharmaceutical firms
D)auto makers
A)furniture producers
B)software firms
C)pharmaceutical firms
D)auto makers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A local or provincial electrical company has a monopoly that is protected by an entry barrier that takes the form of
A)control of a key raw material.
B)network externalities.
C)economies of scale.
D)perfectly inelastic demand curve.
A)control of a key raw material.
B)network externalities.
C)economies of scale.
D)perfectly inelastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a natural monopoly, throughout the range of market demand
A)marginal cost is above average total cost and pulls average total cost upward.
B)average total cost is above marginal cost and pulls marginal cost upward.
C)marginal cost is below average total cost and pulls average total cost downward.
D)there are diseconomies of scale.
A)marginal cost is above average total cost and pulls average total cost upward.
B)average total cost is above marginal cost and pulls marginal cost upward.
C)marginal cost is below average total cost and pulls average total cost downward.
D)there are diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The Ecke's family virtual monopoly on commercial poinsettia production by grafting together two varieties of the plant ended around 1996 when university researchers were able to independently make the same discovery.The Ecke family did not patent their grafting process.Would the Ecke's have been better off if they had patented their process of growing poinsettias?
A)Yes, it would have allowed them to earn economic profits indefinitely.
B)That depends on how long they had a monopoly before university researchers made the discovery. If the discovery was made after the period of time when patents expire, then the Ecke family is not any better off.
C)No, even with a patent protection, the Ecke family cannot prevent government-funded academic institutions from researching into plant breeding.
D)No, seeking patent protection necessitates divulging enough information that would enable others to information to discover ways of grafting poinsettias that were similar to the Ecke method but that did not violate the patent.
A)Yes, it would have allowed them to earn economic profits indefinitely.
B)That depends on how long they had a monopoly before university researchers made the discovery. If the discovery was made after the period of time when patents expire, then the Ecke family is not any better off.
C)No, even with a patent protection, the Ecke family cannot prevent government-funded academic institutions from researching into plant breeding.
D)No, seeking patent protection necessitates divulging enough information that would enable others to information to discover ways of grafting poinsettias that were similar to the Ecke method but that did not violate the patent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the difference between a public franchise and a public enterprise?
A)A public franchise grants a firm the right to be the sole legal provider of a good or service. A public enterprise refers to a service that is provided directly to consumers through the government.
B)A public enterprise grants a firm the right to be the sole legal provider of a good or service. A public franchise refers to a service that is provided directly to consumers through the government.
C)A public enterprise is owned by the public through its holdings of shares of stock in the enterprise. A public franchise is a firm owned by the government.
D)Both refer to a service provided directly to consumers through the government, but "public franchise" is a term more commonly used in the United States while "public enterprise" is more commonly used in European countries.
A)A public franchise grants a firm the right to be the sole legal provider of a good or service. A public enterprise refers to a service that is provided directly to consumers through the government.
B)A public enterprise grants a firm the right to be the sole legal provider of a good or service. A public franchise refers to a service that is provided directly to consumers through the government.
C)A public enterprise is owned by the public through its holdings of shares of stock in the enterprise. A public franchise is a firm owned by the government.
D)Both refer to a service provided directly to consumers through the government, but "public franchise" is a term more commonly used in the United States while "public enterprise" is more commonly used in European countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Canada Post
A)faces no competition for its mail services.
B)has a monopoly in the provision of general mail delivery.
C)can safely ignore the prices for mail services charges by its rivals such as FedEx and Purolator.
D)is an example of a monopoly that results from the ownership of a key resource: letter carriers.
A)faces no competition for its mail services.
B)has a monopoly in the provision of general mail delivery.
C)can safely ignore the prices for mail services charges by its rivals such as FedEx and Purolator.
D)is an example of a monopoly that results from the ownership of a key resource: letter carriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For a natural monopoly to exist,
A)a firm must continually buy up its rivals.
B)a firm's long-run average cost curve must exhibit diseconomies of scale beyond the economically efficient output level.
C)a firm's long-run average cost curve must exhibit economies of scale throughout the relevant range of market demand.
D)a firm must have a government-imposed barrier.
A)a firm must continually buy up its rivals.
B)a firm's long-run average cost curve must exhibit diseconomies of scale beyond the economically efficient output level.
C)a firm's long-run average cost curve must exhibit economies of scale throughout the relevant range of market demand.
D)a firm must have a government-imposed barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The De Beers Company, one of the longest-lived monopolies, is facing increasing competition.One source of competition comes from people who might resell their previously owned diamonds.Why is De Beers worried that people might resell their previously owned diamonds?
A)because De Beers will not be able to guarantee the quality of previously owned diamonds and fears that its reputation might be harmed
B)because the availability of previously owned diamonds would increase the market demand for diamonds and dilute De Beers' monopoly
C)because previously owned diamonds would be a close substitute to newly mined diamonds and therefore reduce De Beers' market power
D)because the availability of previously owned diamonds would make the market demand curve for diamonds more inelastic and force De Beers to lower its price
A)because De Beers will not be able to guarantee the quality of previously owned diamonds and fears that its reputation might be harmed
B)because the availability of previously owned diamonds would increase the market demand for diamonds and dilute De Beers' monopoly
C)because previously owned diamonds would be a close substitute to newly mined diamonds and therefore reduce De Beers' market power
D)because the availability of previously owned diamonds would make the market demand curve for diamonds more inelastic and force De Beers to lower its price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Research has shown that most economic profits from selling a prescription drug are eliminated 20 years after the drug is first offered for sale.The main reason for the elimination of profits is
A)after 20 years most people who have taken the drug have passed away or are cured of the illness the drug was intended to treat.
B)firms sell their patent rights to other firms so that they can concentrate on finding drugs to treat new illnesses.
C)the quantity demanded of the drug has increased enough that the demand becomes inelastic and revenue falls.
D)after 20 years patent protection is ended and other firms can produce less expensive generic versions of the drug.
A)after 20 years most people who have taken the drug have passed away or are cured of the illness the drug was intended to treat.
B)firms sell their patent rights to other firms so that they can concentrate on finding drugs to treat new illnesses.
C)the quantity demanded of the drug has increased enough that the demand becomes inelastic and revenue falls.
D)after 20 years patent protection is ended and other firms can produce less expensive generic versions of the drug.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The International Nickel Company of Canada had a monopoly until the end of World War II because
A)it was a public enterprise.
B)it had a patent on the manufacture of aluminum.
C)the company had a secret technique for making aluminum from bauxite.
D)it had control of almost all the available supply of nickel ore.
A)it was a public enterprise.
B)it had a patent on the manufacture of aluminum.
C)the company had a secret technique for making aluminum from bauxite.
D)it had control of almost all the available supply of nickel ore.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which one of the following about a monopoly is false?
A)A monopoly could make profits in the long run.
B)A monopoly could break even in the long run.
C)A monopoly must have some kind of government privilege or government imposed barrier to maintain its monopoly.
D)A monopoly status could be temporary.
A)A monopoly could make profits in the long run.
B)A monopoly could break even in the long run.
C)A monopoly must have some kind of government privilege or government imposed barrier to maintain its monopoly.
D)A monopoly status could be temporary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Governments grant patents to encourage
A)research and development on new products.
B)competition.
C)low prices.
D)firms to form public enterprises.
A)research and development on new products.
B)competition.
C)low prices.
D)firms to form public enterprises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is a network externality?
A)It refers to having a network of suppliers and buyers for a good or service.
B)It refers to lobbying to form a public enterprise.
C)It refers to a situation in which a product's usefulness increases with the number of people using it.
D)It refers to a product that requires connection to a network for it to be useful.
A)It refers to having a network of suppliers and buyers for a good or service.
B)It refers to lobbying to form a public enterprise.
C)It refers to a situation in which a product's usefulness increases with the number of people using it.
D)It refers to a product that requires connection to a network for it to be useful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An example of a monopoly based on control of a key resource is
A)the National Hockey League.
B)the Paul Ecke Ranch monopoly on poinsettias.
C)Microsoft's Windows operating system.
D)Health Canada.
A)the National Hockey League.
B)the Paul Ecke Ranch monopoly on poinsettias.
C)Microsoft's Windows operating system.
D)Health Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A patent or copyright is a barrier to entry based on
A)ownership of a key necessary raw material.
B)large economies of scale as output increases.
C)government action to protect a producer.
D)widespread network externalities.
A)ownership of a key necessary raw material.
B)large economies of scale as output increases.
C)government action to protect a producer.
D)widespread network externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Governments grant patents to
A)compensate firms for research and development costs.
B)encourage competition.
C)encourage low prices.
D)encourage firms to reveal secret production techniques.
A)compensate firms for research and development costs.
B)encourage competition.
C)encourage low prices.
D)encourage firms to reveal secret production techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A Canadian government patent lasts
A)forever.
B)50 years.
C)20 years.
D)7 years.
A)forever.
B)50 years.
C)20 years.
D)7 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 13.1
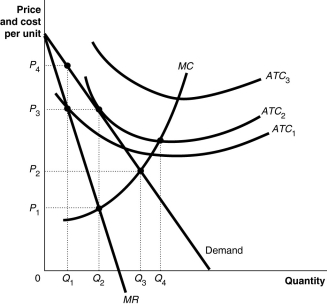
Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.To maximize profit, the firm will produce
A)Q₁.
B)Q₂.
C)Q₃.
D)Q₄.

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.To maximize profit, the firm will produce
A)Q₁.
B)Q₂.
C)Q₃.
D)Q₄.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 13.1

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.The firm's profit-maximizing price is
A)P₁.
B)P₂.
C)P₃.
D)P₄.

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.The firm's profit-maximizing price is
A)P₁.
B)P₂.
C)P₃.
D)P₄.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a monopolist's marginal revenue is $25 a unit and its marginal cost is $25, then
A)to maximize profit the firm should increase output.
B)to maximize profit the firm should decrease output.
C)to maximize profit the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)Not enough information is given to say what the firm should do to maximize profit.
A)to maximize profit the firm should increase output.
B)to maximize profit the firm should decrease output.
C)to maximize profit the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)Not enough information is given to say what the firm should do to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 13.1

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₂, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₂, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Most pharmaceutical firms selling prescription drugs continue to earn economic profits long after the patents on the prescription drugs expire because they have established a strong foothold in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Figure 13.1

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₁, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₁, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Provide two examples of a government barrier to entry?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The National Hockey League has long-term leases with the arenas in major cities.Control of these arenas is an entry barrier to a potential new hockey league.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How does a network externality serve as a barrier to entry? Is this barrier surmountable? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The demand curve for the monopoly's product is
A)the market demand for the product.
B)more elastic than the market demand for the product.
C)more inelastic than the market demand for the product.
D)undefined.
A)the market demand for the product.
B)more elastic than the market demand for the product.
C)more inelastic than the market demand for the product.
D)undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
For a natural monopoly, the marginal cost of producing an additional unit of its product is relatively small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a theatre company expects $250,000 in ticket revenue from five performances and $288,000 in ticket revenue if it adds a sixth performance, the
A)marginal revenue of the sixth performance is $48,000.
B)marginal revenue of the sixth performance is $38,000.
C)cost of staging the sixth performance is probably higher than the cost of staging the previous five.
D)company will be making a loss on the sixth performance because its ticket sales will be less than the average received from the previous five.
A)marginal revenue of the sixth performance is $48,000.
B)marginal revenue of the sixth performance is $38,000.
C)cost of staging the sixth performance is probably higher than the cost of staging the previous five.
D)company will be making a loss on the sixth performance because its ticket sales will be less than the average received from the previous five.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What gives rise to a natural monopoly? How do consumers benefit from a natural monopoly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Because a monopoly's demand curve is the same as the market demand curve for its product,
A)the monopoly's marginal revenue equals its price.
B)the monopoly is a price taker.
C)the monopoly must lower its price to sell more of its product.
D)the monopoly's average total cost always falls as it increases its output.
A)the monopoly's marginal revenue equals its price.
B)the monopoly is a price taker.
C)the monopoly must lower its price to sell more of its product.
D)the monopoly's average total cost always falls as it increases its output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Microsoft hires marketing and sales specialists to decide what prices it should set for its products, whereas a wealthy wheat farmer in Saskatchewan, who sells his output in the world commodity market, does not.Why is this so?
A)because Microsoft is large enough to hire the best people in the field
B)because Microsoft could potentially lose sales if it sets prices indiscriminately
C)because the wealthy wheat farmer is a price taker who chooses his optimal output independently of market price but Microsoft's optimal output depends on the price it selects
D)because unlike Microsoft, the wealthy wheat farmer is probably a monopolist
A)because Microsoft is large enough to hire the best people in the field
B)because Microsoft could potentially lose sales if it sets prices indiscriminately
C)because the wealthy wheat farmer is a price taker who chooses his optimal output independently of market price but Microsoft's optimal output depends on the price it selects
D)because unlike Microsoft, the wealthy wheat farmer is probably a monopolist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure 13.1

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₃, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Figure 13.1 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.1.If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC₃, the firm will
A)suffer a loss.
B)break even.
C)make a profit.
D)face competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A natural monopoly is characterized by large fixed costs relative to variable costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a firm's average total cost is less than price where MR=MC,
A)the firm should shut down.
B)the firm should raise its price.
C)the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)the firm should cut back on its output to lower its cost.
A)the firm should shut down.
B)the firm should raise its price.
C)the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)the firm should cut back on its output to lower its cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a monopolist's price is $50 per unit and its marginal cost is $25, then
A)to maximize profit the firm should increase output.
B)to maximize profit the firm should decrease output.
C)to maximize profit the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)Not enough information is given to say what the firm should do to maximize profit.
A)to maximize profit the firm should increase output.
B)to maximize profit the firm should decrease output.
C)to maximize profit the firm should continue to produce the output it is producing.
D)Not enough information is given to say what the firm should do to maximize profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A monopolist's profit maximizing price and output correspond to the point on a graph
A)where average total cost is minimized.
B)where total costs are the smallest relative to price.
C)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charging the price on the market demand curve for that output.
D)where price is as high as possible.
A)where average total cost is minimized.
B)where total costs are the smallest relative to price.
C)where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charging the price on the market demand curve for that output.
D)where price is as high as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 13.1
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the marginal revenue from the sale of the 12th unit?
A)$75
B)$50
C)$20
D)-$5
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the marginal revenue from the sale of the 12th unit?
A)$75
B)$50
C)$20
D)-$5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Table 13.1
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the firm's profit-maximizing output and what is the price charged to sell this output?
A)P = $85; Q = 10
B)P = $80; Q = 11
C)P = $70; Q = 13
D)P = $65; Q = 14
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the firm's profit-maximizing output and what is the price charged to sell this output?
A)P = $85; Q = 10
B)P = $80; Q = 11
C)P = $70; Q = 13
D)P = $65; Q = 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 13.3
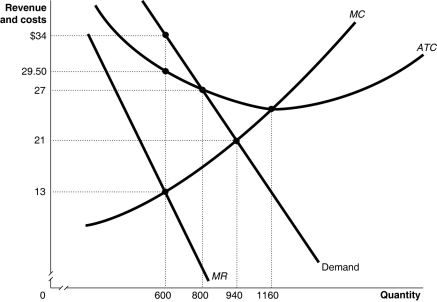
Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is likely to happen to this monopoly in the long run?
A)New firms will enter the market to eliminate its profits.
B)It will expand its output to take advantage of economies of scale so as to further increase its profit.
C)As long as there are entry barriers, this firm will continue to enjoy economic profits.
D)It will be regulated by the government because of its excess profits.

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is likely to happen to this monopoly in the long run?
A)New firms will enter the market to eliminate its profits.
B)It will expand its output to take advantage of economies of scale so as to further increase its profit.
C)As long as there are entry barriers, this firm will continue to enjoy economic profits.
D)It will be regulated by the government because of its excess profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If a monopolist's price is $50 at the output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and average total cost is $43, then the average profit is $7.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 13.2
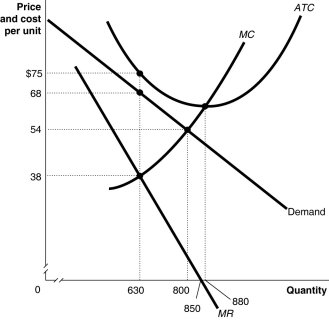
Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the profit/loss per unit?
A)loss of $7 per unit
B)profit of $30 per unit
C)loss of $21 per unit
D)profit of $14 per unit

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the profit/loss per unit?
A)loss of $7 per unit
B)profit of $30 per unit
C)loss of $21 per unit
D)profit of $14 per unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 13.2

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.What happens to the monopolist represented in the diagram in the long run?
A)It will raise its price at least until it breaks even.
B)If the cost and demand curves remain the same, it will exit the market.
C)The government will subsidize the monopoly to enable it to break even.
D)It will be forced out of business by more efficient producers.

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.What happens to the monopolist represented in the diagram in the long run?
A)It will raise its price at least until it breaks even.
B)If the cost and demand curves remain the same, it will exit the market.
C)The government will subsidize the monopoly to enable it to break even.
D)It will be forced out of business by more efficient producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If a monopolist's marginal revenue is $15 per unit and its marginal cost is $25, then to maximize profit the firm should decrease output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Figure 13.3

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's profit?
A)$2,700
B)$4,200
C)$10,400
D)$12,600

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's profit?
A)$2,700
B)$4,200
C)$10,400
D)$12,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To maximize profit, a monopolist will produce and sell a quantity such that for the last unit sold, marginal revenue equals marginal cost, and charges a price given by the demand curve at that output level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 13.3

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's total cost of production?
A)$21,600
B)$17,700
C)$9,340
D)$7,800

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's total cost of production?
A)$21,600
B)$17,700
C)$9,340
D)$7,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
What is the relationship between marginal revenue and average revenue for a monopolist and is it the same for a perfect competitor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Figure 13.2

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)630 units
B)800 units
C)850 units
D)880 units

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)630 units
B)800 units
C)850 units
D)880 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 13.3

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)600 units
B)800 units
C)940 units
D)1,160 units

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)600 units
B)800 units
C)940 units
D)1,160 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Table 13.1
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the amount of the firm's profit?
A)$335
B)$350
C)$880
D)$910
A monopoly producer of foreign language translation software faces a demand and cost structure as given in Table 13.1.
-Refer to Table 13.1.What is the amount of the firm's profit?
A)$335
B)$350
C)$880
D)$910

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 13.3

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the price charged for the profit-maximizing output level?
A)$13
B)$21
C)$27
D)$34

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the price charged for the profit-maximizing output level?
A)$13
B)$21
C)$27
D)$34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 13.2

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the price charged at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)$38
B)$54
C)$68
D)$75

Figure 13.2 above shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the monopolist represented in the diagram above produces positive output.What is the price charged at the profit-maximizing/loss-minimizing output level?
A)$38
B)$54
C)$68
D)$75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements applies to a monopolist but not to a perfectly competitive firm at their profit maximizing outputs?
A)Marginal revenue is less than price.
B)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C)Price equals marginal cost.
D)Average revenue equals average cost.
A)Marginal revenue is less than price.
B)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C)Price equals marginal cost.
D)Average revenue equals average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the short-run, even if a monopoly's total revenue does not cover its variable costs, it should continue to produce because ultimately in the long run, the monopoly will start earning profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 13.3

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's total revenue?
A)$21,600
B)$20,400
C)$19,740
D)$7,800

Figure 13.3 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Refer to Figure 13.3.What is the amount of the monopoly's total revenue?
A)$21,600
B)$20,400
C)$19,740
D)$7,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Long-run economic profits would most likely exist in which market structure?
A)monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly
B)monopoly and oligopoly
C)monopoly and monopolistic competition
D)monopoly only
A)monopoly, monopolistic competition and oligopoly
B)monopoly and oligopoly
C)monopoly and monopolistic competition
D)monopoly only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



