Deck 16: Pricing Strategy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/132
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Pricing Strategy
1
Yield management is the practice of
A)determining production functions to minimize production costs.
B)forecasting competitors' responses to price changes.
C)using buyer data to rapidly adjust prices.
D)using information technology to find the best interest rate.
A)determining production functions to minimize production costs.
B)forecasting competitors' responses to price changes.
C)using buyer data to rapidly adjust prices.
D)using information technology to find the best interest rate.
C
2
The law of one price states that identical products should sell for the same price everywhere as long as transactions costs are zero.
True
3
Arbitrage
A)is the act of buying an item at a low price and reselling the item at a higher price.
B)is the act of selling an item on consignment and collecting a huge portion of the proceeds to compensate for the seller's time.
C)is the act of buying an item at a low price, bundling it with another and selling the new package at a much higher price.
D)is any act of buying and selling that results in the seller earning an above normal profit.
A)is the act of buying an item at a low price and reselling the item at a higher price.
B)is the act of selling an item on consignment and collecting a huge portion of the proceeds to compensate for the seller's time.
C)is the act of buying an item at a low price, bundling it with another and selling the new package at a much higher price.
D)is any act of buying and selling that results in the seller earning an above normal profit.
A
4
If firms differentiate their products in different ways and charge different price because of these differentiation factors, then
A)the law of one price is not violated.
B)transaction costs are being ignored.
C)the firm must not be maximizing profit.
D)demand must be perfectly elastic.
A)the law of one price is not violated.
B)transaction costs are being ignored.
C)the firm must not be maximizing profit.
D)demand must be perfectly elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Assuming zero transaction cost, if your local grocer buys oranges at a low price from an orchard and resells them to you at a higher price, then the grocer's revenue minus costs is known as
A)arbitrage profits.
B)transactions profits.
C)pure profits.
D)excess profits.
A)arbitrage profits.
B)transactions profits.
C)pure profits.
D)excess profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Many Canadians living close to the US border regularly cross the border to buy milk, eggs, and other goods at considerably lower prices.
Is this an example of arbitrage?
A)Yes, because shoppers were able to purchase items at lower prices even after deducting their transaction costs.
B)No, "arbitrage" means buying at a low price and reselling at a higher price but no resale takes place here.
C)Yes, arbitrage applies even if no resale takes place; in this case the profits are pocketed by the customers themselves.
D)No, "arbitrage" does not apply to markets that are not in the same geographic area.
Is this an example of arbitrage?
A)Yes, because shoppers were able to purchase items at lower prices even after deducting their transaction costs.
B)No, "arbitrage" means buying at a low price and reselling at a higher price but no resale takes place here.
C)Yes, arbitrage applies even if no resale takes place; in this case the profits are pocketed by the customers themselves.
D)No, "arbitrage" does not apply to markets that are not in the same geographic area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the real world,
A)all sellers charge one price equal to the marginal cost of production.
B)profitable sellers will set one price based on the average elasticity of demand of buyers.
C)many firms charge different prices based on consumers' willingness to pay.
D)all sellers charge one price set by the government.
A)all sellers charge one price equal to the marginal cost of production.
B)profitable sellers will set one price based on the average elasticity of demand of buyers.
C)many firms charge different prices based on consumers' willingness to pay.
D)all sellers charge one price set by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When you buy at a low price in one market then sell at a higher price in another market you are engaging in
A)odd pricing.
B)arbitrage.
C)an antitrust prohibited practice.
D)price discrimination.
A)odd pricing.
B)arbitrage.
C)an antitrust prohibited practice.
D)price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The act of buying a product at a low price in one market and reselling the product at a higher price in another market is called arbitrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 16.1
Table 16.1 shows the price for the novel, Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows at four online bookstores.
-Refer to Table 16.1.Which of the following can one conclude from the data above?
A)The data provides clear evidence of price discrimination in online bookstore market.
B)Amazon.com is able to charge a lower price for the item because it is more cost efficient than the other three companies.
C)The item offered for sale is similar but not identical; the quality of service and delivery time might vary from store to store, which justifies the price differences.
D)BarnesandNoble.com and Amazon.com have deliberately under-priced their product to force the other two companies out of business.
Table 16.1 shows the price for the novel, Harry Potter and The Deathly Hallows at four online bookstores.
-Refer to Table 16.1.Which of the following can one conclude from the data above?
A)The data provides clear evidence of price discrimination in online bookstore market.
B)Amazon.com is able to charge a lower price for the item because it is more cost efficient than the other three companies.
C)The item offered for sale is similar but not identical; the quality of service and delivery time might vary from store to store, which justifies the price differences.
D)BarnesandNoble.com and Amazon.com have deliberately under-priced their product to force the other two companies out of business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For many products, such as fast foods, a variety of prices can be found, but sellers with higher prices can expect to sell their products because
A) consumers are not sensitive to prices.
B)arbitrage will quickly eliminate price differences.
C)firms differentiate products in many ways, for example, higher priced fast food restaurants may offer better service.
D)their demand is perfectly inelastic.
A) consumers are not sensitive to prices.
B)arbitrage will quickly eliminate price differences.
C)firms differentiate products in many ways, for example, higher priced fast food restaurants may offer better service.
D)their demand is perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A firm's efforts to increase profit by price discrimination can be undermined by
A)arbitrage by buyers.
B)consumer ignorance.
C)differences in elasticity of demand.
D)seller market power.
A)arbitrage by buyers.
B)consumer ignorance.
C)differences in elasticity of demand.
D)seller market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The law of one price holds exactly only if
A)antitrust laws are being enforced.
B)buyers have complete information.
C)transactions costs are zero.
D)it is impossible for buyers to resell the good.
A)antitrust laws are being enforced.
B)buyers have complete information.
C)transactions costs are zero.
D)it is impossible for buyers to resell the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Lou buys classic video games at a garage sale for $30 and resells it on eBay to Kyle for $60.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The transaction has made Lou better off and Kyle worse off.
B)The transaction is economically inefficient.
C)The transaction has made Lou and Kyle better off.
D)It is not possible for Kyle to enjoy any consumer surplus from this transaction.
A)The transaction has made Lou better off and Kyle worse off.
B)The transaction is economically inefficient.
C)The transaction has made Lou and Kyle better off.
D)It is not possible for Kyle to enjoy any consumer surplus from this transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Athenian Theatre sells play tickets for the same play at different prices: a lower price to those who opt for the seats at the back of the theatre and a higher price for those who purchase seats in the front, around the stage.Which of the following statements is true?
A)This is an example of product differentiation but not price discrimination.
B)The theatre practices first-degree price discrimination by setting prices based on willingness to pay.
C)Since the cost of producing the play does not change with the seating configuration, this is evidence of price discrimination based on market segmentation.
D)Charging two different prices is an effective way to avoid an excess demand for play tickets; the higher price lowers quantity demanded to some extent.
A)This is an example of product differentiation but not price discrimination.
B)The theatre practices first-degree price discrimination by setting prices based on willingness to pay.
C)Since the cost of producing the play does not change with the seating configuration, this is evidence of price discrimination based on market segmentation.
D)Charging two different prices is an effective way to avoid an excess demand for play tickets; the higher price lowers quantity demanded to some extent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The law of one price states
A)federal and state statutes that prohibit price discrimination.
B)that all customers should pay the same price.
C)that identical products should sell for the same price everywhere.
D)government regulation of prices for all firms.
A)federal and state statutes that prohibit price discrimination.
B)that all customers should pay the same price.
C)that identical products should sell for the same price everywhere.
D)government regulation of prices for all firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Lou buys a classic Mario Bros.game from Evan for $30 and resells it on eBay for $60.Which of the following statements is false?
A)Lou has earned some arbitrage profits, assuming that transaction costs are negligible.
B)The transaction has made Evan worse off because he underpriced the poster.
C)Lou has probably incurred some costs in connection with this sale.
D)It is possible that Evan has earned some producer surplus from this transaction.
A)Lou has earned some arbitrage profits, assuming that transaction costs are negligible.
B)The transaction has made Evan worse off because he underpriced the poster.
C)Lou has probably incurred some costs in connection with this sale.
D)It is possible that Evan has earned some producer surplus from this transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Price discrimination
A)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers based on a seller's personal preferences and prejudices.
B)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers based on the different costs of supplying the product to different customers.
C)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers when the price differences cannot be attributed to variations in cost.
D)is the practice of giving preferential treatment to certain groups of customers based on their long-standing relationship to the producer.
A)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers based on a seller's personal preferences and prejudices.
B)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers based on the different costs of supplying the product to different customers.
C)is the practice of charging different prices to different customers when the price differences cannot be attributed to variations in cost.
D)is the practice of giving preferential treatment to certain groups of customers based on their long-standing relationship to the producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The expenses you encounter when you buy in one market and sell in a distant market are known as
A)production costs.
B)fixed costs.
C)transactions costs.
D)sunk costs.
A)production costs.
B)fixed costs.
C)transactions costs.
D)sunk costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Buying at a low price in one market and reselling at a higher price in another market will
A)not generate any profit because of transportation costs.
B)not generate any profit because of transactions costs.
C)eventually eliminate all of the price differences.
D)eventually eliminate most, but not necessarily all, of the price differences.
A)not generate any profit because of transportation costs.
B)not generate any profit because of transactions costs.
C)eventually eliminate all of the price differences.
D)eventually eliminate most, but not necessarily all, of the price differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Differentiating products to suit customers' tastes is a form of price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is a necessary condition for successful price discrimination?
A)The seller must possess market power.
B)The buyer must possess market power.
C)Transaction costs must be zero.
D)Buyers must have identical inelastic demands.
A)The seller must possess market power.
B)The buyer must possess market power.
C)Transaction costs must be zero.
D)Buyers must have identical inelastic demands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following products allows the seller to identify different groups of consumers (segment the market)at virtually no cost?
A)early bird dinner specials
B)books sold online
C)a pair of Bose speakers
D)iPhones
A)early bird dinner specials
B)books sold online
C)a pair of Bose speakers
D)iPhones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following firms is not able to practice price discrimination?
A)movie theaters
B)commercial airlines
C)cell phone companies
D)the largest wheat farmer in Saskatchewan
A)movie theaters
B)commercial airlines
C)cell phone companies
D)the largest wheat farmer in Saskatchewan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a firm charges different consumers different prices for the same product and the difference cannot be attributed to cost variations, then it is engaging in
A)odd pricing.
B)cost-plus pricing.
C)price discrimination.
D)markup pricing.
A)odd pricing.
B)cost-plus pricing.
C)price discrimination.
D)markup pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Are sellers who practice arbitrage taking advantage of buyers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Firms price discriminate
A)to reduce the quantity sold so as to reduce production costs.
B)to increase profits.
C)to take advantage of customers.
D)to increase total economic surplus.
A)to reduce the quantity sold so as to reduce production costs.
B)to increase profits.
C)to take advantage of customers.
D)to increase total economic surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following are necessary condition(s)for successful price discrimination?
A)zero transaction cost
B)a perfectly competitive market structure
C)an imperfectly competitive market structure
D)at least two different markets with different price elasticities of demand
E)at least two different markets with different price elasticities of supply
A)a, b, and d only
B)c and d only
C)a, c, d and, e only
D)a and c only
A)zero transaction cost
B)a perfectly competitive market structure
C)an imperfectly competitive market structure
D)at least two different markets with different price elasticities of demand
E)at least two different markets with different price elasticities of supply
A)a, b, and d only
B)c and d only
C)a, c, d and, e only
D)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Table 16.2
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.How many tubes of toothpaste will Neem sell in West Fall and at what price?
A) Q = 2 units; P = $4.50
B) Q = 3 units; P = $4
C) Q = 4 units; P = $3.50
D)Q = 5 units; P = $3
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.How many tubes of toothpaste will Neem sell in West Fall and at what price?
A) Q = 2 units; P = $4.50
B) Q = 3 units; P = $4
C) Q = 4 units; P = $3.50
D)Q = 5 units; P = $3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Most movie theatres charge different prices to different groups of customers for movie admission but not on movie popcorn.Which of the following is a reason for this?
A)because the markup on movie popcorn is very high and movie theatres do not want to forego this source of revenue
B)because the demand for popcorn is very high relative to the demand for movie admissions
C)because it is easier to limit resale in movie admissions but not in popcorn
D)because the cost of operating a concession stand in a movie theatre is very high compared to the cost of showing a movie
A)because the markup on movie popcorn is very high and movie theatres do not want to forego this source of revenue
B)because the demand for popcorn is very high relative to the demand for movie admissions
C)because it is easier to limit resale in movie admissions but not in popcorn
D)because the cost of operating a concession stand in a movie theatre is very high compared to the cost of showing a movie

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following undermines a firm's ability to engage in price discrimination?
A)the seller's market power
B)the inability to prevent resale of the product from one market segment to another
C)buyers having different elasticities of demand for the product
D)the seller's ability to segment the total market
A)the seller's market power
B)the inability to prevent resale of the product from one market segment to another
C)buyers having different elasticities of demand for the product
D)the seller's ability to segment the total market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Consider the following actions undertaken by a firm:
A)charging the same price for products of different quality
B)charging different prices to different consumers for the same product when the variation cannot be explained by cost differences
C)charging different prices for products of different qualities
D)charging a lower price to match a competitor's price
Which of the above will be considered price discrimination?
A)a, b, and d only
B)b and d only
C)a and b only
D)a, b, c, and d
A)charging the same price for products of different quality
B)charging different prices to different consumers for the same product when the variation cannot be explained by cost differences
C)charging different prices for products of different qualities
D)charging a lower price to match a competitor's price
Which of the above will be considered price discrimination?
A)a, b, and d only
B)b and d only
C)a and b only
D)a, b, c, and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Why is price discrimination legal but not discrimination based on race or gender?
A)because price discrimination increases profits and therefore tax revenues for the government, but discrimination based on race or gender reduces tax revenues
B)because price discrimination reduces deadweight loss, but discrimination based on race or gender increases deadweight loss
C)because price discrimination involves charging people different prices based on their willingness to pay rather than on the basis of arbitrary characteristics
D)because price discrimination enables firms to increase output and employment, but race or gender based discrimination reduces employment
A)because price discrimination increases profits and therefore tax revenues for the government, but discrimination based on race or gender reduces tax revenues
B)because price discrimination reduces deadweight loss, but discrimination based on race or gender increases deadweight loss
C)because price discrimination involves charging people different prices based on their willingness to pay rather than on the basis of arbitrary characteristics
D)because price discrimination enables firms to increase output and employment, but race or gender based discrimination reduces employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following table contains the actual prices charged by four websites for a blu-ray copy of the movie Despicable Me 2.
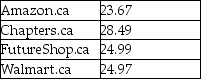
Explain whether the information in this table contradicts the law of one price.

Explain whether the information in this table contradicts the law of one price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In a perfectly competitive market, in the long run, arbitrage profits will be bid away.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Price discrimination is possible in which of the following market structures?
A)perfect competition
B)monopoly
C)oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition
A)c and d only
B)b and c only
C)b, c, and d only
D)a, b, c, and d
A)perfect competition
B)monopoly
C)oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition
A)c and d only
B)b and c only
C)b, c, and d only
D)a, b, c, and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Under what circumstances will the law of one price hold, and when might it not hold?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not a way by which price discriminating firms can segment a market?
A)on the basis of time of purchase, for example matinee theatre tickets
B)by requiring an advance purchase, for example air travel tickets
C)on basis of the buyer's location, for example requiring international students to pay higher tuition
D)on the basis of the supplier's marginal cost of production, for example requiring customers to pay a premium for customizing options
A)on the basis of time of purchase, for example matinee theatre tickets
B)by requiring an advance purchase, for example air travel tickets
C)on basis of the buyer's location, for example requiring international students to pay higher tuition
D)on the basis of the supplier's marginal cost of production, for example requiring customers to pay a premium for customizing options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Successful price discrimination cannot take place if
A)the market is perfectly competitive.
B)the market can be segmented into different buyer groups.
C)customers are not able to resell the product.
D)the demand curve facing the firm is downward-sloping.
A)the market is perfectly competitive.
B)the market can be segmented into different buyer groups.
C)customers are not able to resell the product.
D)the demand curve facing the firm is downward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Table 16.2
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.How many tubes of toothpaste will Neem sell in Middle Fall and at what price?
A) Q = 2 units; P = $7
B) Q = 3 units; P = $6
C) Q = 4 units; P = $5
D)Q = 5 units; P = $4
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.How many tubes of toothpaste will Neem sell in Middle Fall and at what price?
A) Q = 2 units; P = $7
B) Q = 3 units; P = $6
C) Q = 4 units; P = $5
D)Q = 5 units; P = $4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Joss is a marketing consultant.Iris and Daphne are potential customers interested in commissioning Joss to undertake a market survey and compile the findings in a report.Iris is willing to pay $500 for the service while Daphne is willing to pay $800.Suppose that the opportunity cost of Joss's time is $1,200.Assume that Iris and Daphne do not know each other.If Joss charges the same price per copy to both Iris and Daphne,
A)the report will not get written.
B)only Daphne will commission the job and the report will be written.
C)both Iris and Daphne will commission the job and the report will be written.
D)no conclusion can be drawn without information on the price.
A)the report will not get written.
B)only Daphne will commission the job and the report will be written.
C)both Iris and Daphne will commission the job and the report will be written.
D)no conclusion can be drawn without information on the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Table 16.2
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.What are the total profits from both markets combined?
A)$50
B)$48
C)$18
D)$15
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.What are the total profits from both markets combined?
A)$50
B)$48
C)$18
D)$15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Yield management and price discrimination have enabled firms to increase profits and, at the same time,
A)reduce the cost of production.
B)capture some consumer surplus.
C)reduce transactions costs.
D)transfer some producer surplus to consumers.
A)reduce the cost of production.
B)capture some consumer surplus.
C)reduce transactions costs.
D)transfer some producer surplus to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Booking a flight at the last minute is often much more expensive than booking months in advance.Why is this the case?
A)Airlines hope to discourage customers from flying last minute to keep their labour costs down.
B)The cost of adding a passenger at the last minute is significantly highly than adding one to a flight months ahead of time.
C)People wanting to book flights at the last minute generally have few alternatives and are therefore willing to pay a lot more than those booking months ahead.
D)Increasingly, business travel is being replaced with tele-presence (Skye, Facetime, etc.), thereby reducing demand for business travel. To make up for this fall in demand, airlines charge higher rates.
A)Airlines hope to discourage customers from flying last minute to keep their labour costs down.
B)The cost of adding a passenger at the last minute is significantly highly than adding one to a flight months ahead of time.
C)People wanting to book flights at the last minute generally have few alternatives and are therefore willing to pay a lot more than those booking months ahead.
D)Increasingly, business travel is being replaced with tele-presence (Skye, Facetime, etc.), thereby reducing demand for business travel. To make up for this fall in demand, airlines charge higher rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Table 16.2
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.What is the total revenue received from both markets combined?
A)$30
B)$34
C)$68
D)$70
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.What is the total revenue received from both markets combined?
A)$30
B)$34
C)$68
D)$70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is a reason why airline yield management is an effective method to increase revenue?
A)because airlines have invested heavily in developing computer models that identify optimal pricing strategies in the various market segments
B)because airlines have successfully induced customers to reveal their resources and preferences by offering them different versions of the product such as business class and coach plane tickets
C)because a ticket is a contract to transport a specific person, and is not transferable
D)because airlines have a monopoly in long-distance carriage
A)because airlines have invested heavily in developing computer models that identify optimal pricing strategies in the various market segments
B)because airlines have successfully induced customers to reveal their resources and preferences by offering them different versions of the product such as business class and coach plane tickets
C)because a ticket is a contract to transport a specific person, and is not transferable
D)because airlines have a monopoly in long-distance carriage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following does not arise from price discrimination?
A)an increase in producer surplus
B)an increase in consumer surplus
C)an increase in quantity sold
D)an increase in profits
A)an increase in producer surplus
B)an increase in consumer surplus
C)an increase in quantity sold
D)an increase in profits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For a firm that can effectively price discriminate, who will be charged a lower price?
A)customers who have an elastic demand for the product
B)customers who have an inelastic demand for the product
C)buyers that are members of the largest market segment
D)buyers that are members of the smallest market segment
A)customers who have an elastic demand for the product
B)customers who have an inelastic demand for the product
C)buyers that are members of the largest market segment
D)buyers that are members of the smallest market segment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Joss is a marketing consultant.Iris and Daphne are potential customers interested in commissioning Joss to undertake a market survey and compile the findings in a report.Iris is willing to pay $500 for the service while Daphne is willing to pay $800.Suppose that the opportunity cost of Joss's time is $1,200.Assume that Iris and Daphne do not know each other.If the price is $500 per copy,
A)only Iris will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
B)only Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
C)both Iris and Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job.
D)both Iris and Daphne will want to purchase Joss's services but Joss will not be willing to undertake the job.
A)only Iris will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
B)only Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
C)both Iris and Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job.
D)both Iris and Daphne will want to purchase Joss's services but Joss will not be willing to undertake the job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The Toronto Transit Commission (TTC)subway system offers senior citizens discounted fares for TTC rides.This suggests that the TTC believe that senior citizens have a ________ demand for subway, bus, and streetcar rides.
A)more income elastic
B)less income elastic
C)more price elastic
D)less price elastic
A)more income elastic
B)less income elastic
C)more price elastic
D)less price elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Table 16.2
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.Which of the following statements is true about the two markets?
A)The demand in Middle Fall is more price elastic than the demand in West Fall.
B)The demand in Middle Fall is less price elastic than the demand in West Fall.
C)The demand in Middle Fall is more income elastic than the demand in West Fall.
D)The demand in Middle Fall is less income elastic than the demand in West Fall.
Neem Products sells its Ayurvedic Neem toothpaste in two completely isolated markets with demand schedules as shown in Table 16.2. The average cost of production is constant at $2 per tube.
-Refer to Table 16.2.Which of the following statements is true about the two markets?
A)The demand in Middle Fall is more price elastic than the demand in West Fall.
B)The demand in Middle Fall is less price elastic than the demand in West Fall.
C)The demand in Middle Fall is more income elastic than the demand in West Fall.
D)The demand in Middle Fall is less income elastic than the demand in West Fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A firm that can effectively price discriminate will charge a higher price to
A)customers who have the more elastic demand for the product.
B)customers who have the more inelastic demand for the product.
C)buyers who belong to the largest market segment.
D)buyers who are members of the smallest market segment.
A)customers who have the more elastic demand for the product.
B)customers who have the more inelastic demand for the product.
C)buyers who belong to the largest market segment.
D)buyers who are members of the smallest market segment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a firm could practice perfect price discrimination, it would
A)allow resale of its product.
B)charge every buyer a different price.
C)charge a price based on the quantity of a product bought.
D)use odd pricing.
A)allow resale of its product.
B)charge every buyer a different price.
C)charge a price based on the quantity of a product bought.
D)use odd pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In January of 2014, Rogers cable was offering new customers cable TV, internet access, and a PVR, for $19.95 a month.Renting just a PVR from Roger's would cost existing customers $25.07 a month.Is Rogers engaging in price discrimination, and if so, why?
A)No, it is not; it is merely differentiating its product by offering different levels of service.
B)No, it is not. Its decision to give priority to new customers is a business strategy independent of pricing.
C)Yes it is; Rogers is charging different prices for the same service. It does this to increase its profit.
D)Yes it is; Rogers wants to discourage those existing customers from watching too much TV because they lower the firm's profits.
A)No, it is not; it is merely differentiating its product by offering different levels of service.
B)No, it is not. Its decision to give priority to new customers is a business strategy independent of pricing.
C)Yes it is; Rogers is charging different prices for the same service. It does this to increase its profit.
D)Yes it is; Rogers wants to discourage those existing customers from watching too much TV because they lower the firm's profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Hotels routinely increase the prices they charge for rooms on weekends when large numbers of tourists are in town.It is not uncommon for a hotel room that normally costs $149 to cost as much as $649 during the Grey Cup, or the Stanley Cup.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The hotels are practicing first-degree price discrimination by charging what the market will bear.
B)This is evidence of third-degree price discrimination because hotel accommodation on a particular day is not a product that can be resold later.
C)There is no evidence of price discrimination; the hotels are responding to increased demand for hotel rooms in the face of constant supply.
D)The hotels have adopted this pricing strategy to capitalize on arbitrage profits.
A)The hotels are practicing first-degree price discrimination by charging what the market will bear.
B)This is evidence of third-degree price discrimination because hotel accommodation on a particular day is not a product that can be resold later.
C)There is no evidence of price discrimination; the hotels are responding to increased demand for hotel rooms in the face of constant supply.
D)The hotels have adopted this pricing strategy to capitalize on arbitrage profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
With perfect price discrimination there is
A)no deadweight loss.
B)no producer surplus.
C)one single price.
D)an increase in consumer surplus.
A)no deadweight loss.
B)no producer surplus.
C)one single price.
D)an increase in consumer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
From an economic perspective, price discrimination is desirable because
A)the increase in profits is more than offset by the loss in consumer surplus, resulting in a net increase in economic surplus.
B)it enables firms to increase profits with no loss in economic surplus, and in turn, this could provide firms with incentives to engage in beneficial product innovation.
C)the increase in profits results in higher corporate tax revenues received by the government which could be used to subsidize consumption for low-income individuals.
D)it redistributes wealth from wealthy consumers to highly innovative firms.
A)the increase in profits is more than offset by the loss in consumer surplus, resulting in a net increase in economic surplus.
B)it enables firms to increase profits with no loss in economic surplus, and in turn, this could provide firms with incentives to engage in beneficial product innovation.
C)the increase in profits results in higher corporate tax revenues received by the government which could be used to subsidize consumption for low-income individuals.
D)it redistributes wealth from wealthy consumers to highly innovative firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Joss is a marketing consultant.Iris and Daphne are potential customers interested in commissioning Joss to undertake a market survey and compile the findings in a report.Iris is willing to pay $500 for the service while Daphne is willing to pay $800.Suppose that the opportunity cost of Joss's time is $1,200.Assume that Iris and Daphne do not know each other.If the price is $800 per copy,
A)both Iris and Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job.
B)only Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
C)only Daphne will want to purchase Joss's services but Joss will not be willing to do the work.
D)neither Iris nor Daphne will commission the work.
A)both Iris and Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job.
B)only Daphne will purchase Joss's services and Joss will undertake the job for her.
C)only Daphne will want to purchase Joss's services but Joss will not be willing to do the work.
D)neither Iris nor Daphne will commission the work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In January of 2014, Rogers cable was offering new customers cable TV, internet access, and a PVR, for $19.95 a month.Renting just a PVR from Roger's would cost existing customers $25.07 a month.What can you conclude about the price elasticity of demand for Rogers cable TV, internet access, and PVR rental?
A)Existing subscribers likely have more elastic demand than potential new subscribers.
B)Existing subscribers are likely to have less elastic demand than potential new subscribers.
C)Existing subscribers are likely to view cable TV and internet as substitutions and thus not be interested in this bundle.
D)New subscribers are the only ones likely to view TV and internet as complements.
A)Existing subscribers likely have more elastic demand than potential new subscribers.
B)Existing subscribers are likely to have less elastic demand than potential new subscribers.
C)Existing subscribers are likely to view cable TV and internet as substitutions and thus not be interested in this bundle.
D)New subscribers are the only ones likely to view TV and internet as complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Joss is a marketing consultant.Iris and Daphne are potential customers interested in commissioning Joss to undertake a market survey and compile the findings in a report.Iris is willing to pay $500 for the service while Daphne is willing to pay $800.Suppose that the opportunity cost of Joss's time is $1,200.Assume that Iris and Daphne do not know each other.Which of the following statements is true?
A)Joss should charge each customer $600; that way he will earn his opportunity cost and it will be fair to both Iris and Daphne.
B)Joss should charge Iris $500 and Daphne no more than $700; that way he earns his opportunity cost and there is no loss in economic surplus.
C)Joss should charge Iris $500 and Daphne $800; that way economic surplus is maximized.
D)Joss should charge Iris $500 but charging Daphne $800 is unfair because it allows Joss to earn more than his opportunity cost.
A)Joss should charge each customer $600; that way he will earn his opportunity cost and it will be fair to both Iris and Daphne.
B)Joss should charge Iris $500 and Daphne no more than $700; that way he earns his opportunity cost and there is no loss in economic surplus.
C)Joss should charge Iris $500 and Daphne $800; that way economic surplus is maximized.
D)Joss should charge Iris $500 but charging Daphne $800 is unfair because it allows Joss to earn more than his opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider the following pricing strategies:
A)perfect price discrimination
B)charging different prices to different groups of customers
C)optimal two-part tariff
D)single-price monopoly pricing
Which of the pricing strategies leads to the economically efficient output level?
A)a only
B)a and b only
C)a and c only
D)a, b, and c only
A)perfect price discrimination
B)charging different prices to different groups of customers
C)optimal two-part tariff
D)single-price monopoly pricing
Which of the pricing strategies leads to the economically efficient output level?
A)a only
B)a and b only
C)a and c only
D)a, b, and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Universities offer merit awards to students who ordinarily would not qualify for other financial help.Some have criticized this on grounds that merit awards disproportionately benefit students from wealthier communities with better school systems, siphoning resources away from lower-income students with greater financial need.A university's decision to grant merit awards is motivated by economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
To successfully price discriminate, a firm must ensure that there are no opportunities for arbitrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 16.1
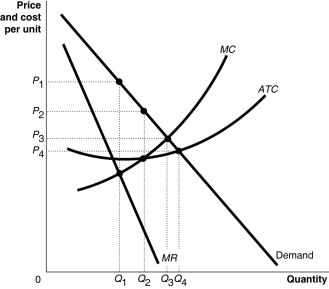
Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the price charged under perfect price discrimination?
A)P₃
B)P₄
C)a range of prices corresponding to the demand curve from P₃ and above
D)a range of prices corresponding to the demand curve from P₄ and above

Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the price charged under perfect price discrimination?
A)P₃
B)P₄
C)a range of prices corresponding to the demand curve from P₃ and above
D)a range of prices corresponding to the demand curve from P₄ and above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Some consumer electronic products such as plasma TVs, DVD players and digital cameras, are introduced at very high prices but over time, their prices start falling (beyond what could be attributed to falling costs as companies take advantage of economies of scale and cheaper technologies).Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
A)More firms are likely to enter the consumer electronic market over time, forcing market prices down.
B)Early adopters of these new products typically have a higher demand and higher income compared to those who are willing to wait.
C)Early adopters are more quality conscious and are willing to pay higher prices for the initial production of these goods.
D)After satisfying the demand for early adopters, firms lower price to attract the more price sensitive consumers.
A)More firms are likely to enter the consumer electronic market over time, forcing market prices down.
B)Early adopters of these new products typically have a higher demand and higher income compared to those who are willing to wait.
C)Early adopters are more quality conscious and are willing to pay higher prices for the initial production of these goods.
D)After satisfying the demand for early adopters, firms lower price to attract the more price sensitive consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 16.2
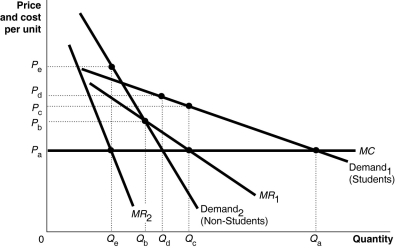
Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.Suppose Plato Playhouse charges a single price of Pd for each performance.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The company is selling more than the profit-maximizing quantity in the non-student market and less than the profit-maximizing quantity in the student market.
B)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in the non-student market and more than the profit-maximizing quantity in the student market.
C)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in both markets but it is maximizing its revenue.
D)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in both markets.

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.Suppose Plato Playhouse charges a single price of Pd for each performance.Which of the following statements is true?
A)The company is selling more than the profit-maximizing quantity in the non-student market and less than the profit-maximizing quantity in the student market.
B)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in the non-student market and more than the profit-maximizing quantity in the student market.
C)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in both markets but it is maximizing its revenue.
D)The company is selling less than the profit-maximizing quantity in both markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Because each customer pays according to her willingness to pay, a consumer maximizes her consumer surplus under first-degree price discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Price discrimination became legal in Canada in
A)2004.
B)1993.
C)2009.
D)1930.
A)2004.
B)1993.
C)2009.
D)1930.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
One reason why McDonald's charges a single price for its products is that it is difficult and costly for the company to determine each individual consumer's willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a monopolist engages in perfect price discrimination, it will produce the same output level as a perfectly competitive industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 16.1

Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the consumer surplus received under perfect price discrimination?
A)the area under the demand curve above P₁
B)the area under the demand curve above P₃
C)the area under the demand curve above P₄
D)zero

Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the consumer surplus received under perfect price discrimination?
A)the area under the demand curve above P₁
B)the area under the demand curve above P₃
C)the area under the demand curve above P₄
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If universities were to use yield management techniques, they would increase scholarship offers to students likely to be more price sensitive and they would reduce scholarship offers to students likely to be less price sensitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 16.1

Refer to Figure 16.1.With perfect price discrimination, the firm will produce and sell
A)Q₁ units.
B)Q₂ units.
C)Q₃ units.
D)Q₄ units.

Refer to Figure 16.1.With perfect price discrimination, the firm will produce and sell
A)Q₁ units.
B)Q₂ units.
C)Q₃ units.
D)Q₄ units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 16.1

Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q₁ units
B)Q₂ units
C)Q₃ units
D)Q₄ units

Refer to Figure 16.1.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q₁ units
B)Q₂ units
C)Q₃ units
D)Q₄ units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When a monopolist engages in perfect price discrimination, the quantity produced and sold
A)is lower than the quantity produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
B)is larger than the quantity produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
C)is the same level as that produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
D)could be lower, higher or the same as that produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
A)is lower than the quantity produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
B)is larger than the quantity produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
C)is the same level as that produced and sold if it adopted a single price.
D)could be lower, higher or the same as that produced and sold if it adopted a single price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 16.2

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.What is the quantity sold to each group of customer and what is the total quantity sold?
A)quantity sold to students = Qb; quantity sold to non-students = Qb; total sales = Qₐ
B)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qb; total sales = Qb ₊ Qc
C)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qₑ; total sales = Qₑ ₊ Qc
D)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qd; total sales = Qd ₊ Qc

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.What is the quantity sold to each group of customer and what is the total quantity sold?
A)quantity sold to students = Qb; quantity sold to non-students = Qb; total sales = Qₐ
B)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qb; total sales = Qb ₊ Qc
C)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qₑ; total sales = Qₑ ₊ Qc
D)quantity sold to students = Qc; quantity sold to non-students = Qd; total sales = Qd ₊ Qc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
With perfect price discrimination, the marginal revenue curve
A) is below the demand curve.
B)is above the demand curve.
C)is equal to the demand curve.
D)is horizontal.
A) is below the demand curve.
B)is above the demand curve.
C)is equal to the demand curve.
D)is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 16.2

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.What is the price charged in the two markets?
A)price in the student market = price in the non-student market = Pₐ
B)price in the student market = price in the non-student market = Pb
C)price in the student market = Pd; price in the non-student market = Pₑ
D)price in the student market = Pc; price in the non-student market = Pₑ

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.What is the price charged in the two markets?
A)price in the student market = price in the non-student market = Pₐ
B)price in the student market = price in the non-student market = Pb
C)price in the student market = Pd; price in the non-student market = Pₑ
D)price in the student market = Pc; price in the non-student market = Pₑ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 16.2

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.Suppose Plato Playhouse price discriminates.Which of the following statements is true?
A)By charging two different prices, the theatre company has redistributed some profits from those who can pay higher prices to those who cannot, thereby increasing economic efficiency.
B)By charging two different prices, the theatre company essentially allows those willing to pay higher prices to subsidize those who are not.
C)By charging two different prices, the theatre company has redistributed some profits from those who can pay higher prices to those who cannot, thereby improving equity.
D)Plato Playhouse will earn higher profits if it charges a single price - an average of the two prices - instead of charging two different prices to the two different groups of customers.

Plato Playhouse, a theatre company in the university town of Wegg, caters to two groups of customers: students and the non-student population. Figure 16.2 shows the demand curves for the two groups of customers.
Refer to Figure 16.2.Suppose Plato Playhouse price discriminates.Which of the following statements is true?
A)By charging two different prices, the theatre company has redistributed some profits from those who can pay higher prices to those who cannot, thereby increasing economic efficiency.
B)By charging two different prices, the theatre company essentially allows those willing to pay higher prices to subsidize those who are not.
C)By charging two different prices, the theatre company has redistributed some profits from those who can pay higher prices to those who cannot, thereby improving equity.
D)Plato Playhouse will earn higher profits if it charges a single price - an average of the two prices - instead of charging two different prices to the two different groups of customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the following pricing strategies:
A)perfect price discrimination
B)charging different prices to different groups of customers
C)optimal two-part tariff
D)single-price monopoly pricing
Which of the pricing strategies allows a producer to capture the entire consumer surplus that would have gone to consumers under perfect competitive pricing?
A)a, b, c, and d
B)a, b, and c only
C)a and b only
D)a and c only
A)perfect price discrimination
B)charging different prices to different groups of customers
C)optimal two-part tariff
D)single-price monopoly pricing
Which of the pricing strategies allows a producer to capture the entire consumer surplus that would have gone to consumers under perfect competitive pricing?
A)a, b, c, and d
B)a, b, and c only
C)a and b only
D)a and c only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 132 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



