Deck 33: How the Baby Came to Be: Human Reproduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 33: How the Baby Came to Be: Human Reproduction
1
Which of the following is a structure in which sperm mature and are stored?
A)vas deferens
B)testis
C)accessory glands
D)epididymis
A)vas deferens
B)testis
C)accessory glands
D)epididymis
D
2
Which of the following is considered a gamete?
A)embryo
B)child
C)oocyte
D)zygote
A)embryo
B)child
C)oocyte
D)zygote
C
3
What changes occur in the endometrium as the time of possible fertilization approaches?
A)Menstruation occurs.
B)The endometrium enters the proliferative phase.
C)The endometrium enters the secretory phase.
D)The endometrium secretes estrogen.
A)Menstruation occurs.
B)The endometrium enters the proliferative phase.
C)The endometrium enters the secretory phase.
D)The endometrium secretes estrogen.
C
4
Implantation occurs in the:
A)ovary.
B)vagina.
C)uterine tube.
D)uterus.
A)ovary.
B)vagina.
C)uterine tube.
D)uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why does a female have millions of ovarian follicles as a fetus but has perhaps just over a thousand in her early fifties?
A)Several hundred follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate.
B)Several thousand follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate.
C)Natural degeneration of follicles speeds up in later years.
D)Production of new follicles from stem cells slows in her fifties.
A)Several hundred follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate.
B)Several thousand follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate.
C)Natural degeneration of follicles speeds up in later years.
D)Production of new follicles from stem cells slows in her fifties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sperm are made in the:
A)testes.
B)epididymis.
C)ovary.
D)vas deferens.
A)testes.
B)epididymis.
C)ovary.
D)vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If a chemical were to destroy all oocytes:
A)sperm would not form.
B)sperm would form but have no chromosomes.
C)eggs would not form.
D)eggs would form but have no chromosomes.
A)sperm would not form.
B)sperm would form but have no chromosomes.
C)eggs would not form.
D)eggs would form but have no chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which statement concerning gamete production is correct?
A)Sperm cells can be produced only at certain points in the reproductive cycle.
B)The number of sperm a man can produce is essentially unlimited, whereas the number of eggs a woman can potentially produce is limited.
C)A man is born with all of the sperm he will need for the rest of his life.
D)Progestins stimulate development of new follicles.
A)Sperm cells can be produced only at certain points in the reproductive cycle.
B)The number of sperm a man can produce is essentially unlimited, whereas the number of eggs a woman can potentially produce is limited.
C)A man is born with all of the sperm he will need for the rest of his life.
D)Progestins stimulate development of new follicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Development of sperm occurs from the:
A)inside of the seminiferous tubule toward the outside.
B)outside of the epididymis toward the inside.
C)outside of the seminiferous tubule toward the inside.
D)middle of the penis toward the prostate gland.
A)inside of the seminiferous tubule toward the outside.
B)outside of the epididymis toward the inside.
C)outside of the seminiferous tubule toward the inside.
D)middle of the penis toward the prostate gland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
From which structure does the corpus luteum develop?
A)oocyte
B)tertiary follicle
C)primary follicle
D)secondary follicle
A)oocyte
B)tertiary follicle
C)primary follicle
D)secondary follicle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which structure would be best described as helping to prepare the female tract for pregnancy and maintain it during the early phases of pregnancy?
A)vagina
B)uterine tube
C)oocyte
D)corpus luteum
A)vagina
B)uterine tube
C)oocyte
D)corpus luteum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sperm development begins in the:
A)prostate gland.
B)seminiferous tubules.
C)epididymis.
D)vas deferens.
A)prostate gland.
B)seminiferous tubules.
C)epididymis.
D)vas deferens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The specialized tissue of the uterus where implantation occurs is the:
A)cervix.
B)vagina.
C)endometrium.
D)uterine tube.
A)cervix.
B)vagina.
C)endometrium.
D)uterine tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Through what structure does an oocyte travel on its way to the uterus?
A)uterine tube
B)cervix
C)vagina
D)ovary
A)uterine tube
B)cervix
C)vagina
D)ovary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The vas deferens ducts empty sperm into the:
A)seminal vesicles.
B)epididymis.
C)uterus.
D)urethra.
A)seminal vesicles.
B)epididymis.
C)uterus.
D)urethra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
On average,about how often does ovulation occur?
A)every 6 months
B)every 28 days
C)every 14 days
D)every day
A)every 6 months
B)every 28 days
C)every 14 days
D)every day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Spermatids are produced by:
A)spermatogonia.
B)primary spermatocytes.
C)secondary spermatocytes.
D)sertiary spermatocytes.
A)spermatogonia.
B)primary spermatocytes.
C)secondary spermatocytes.
D)sertiary spermatocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The stages of follicle development are:
A)tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle, corpus luteum.
B)ovarian follicle, mature follicle, oocyte.
C)corpus luteum, tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle.
D)primary follicle, secondary follicle, tertiary follicle, corpus luteum.
A)tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle, corpus luteum.
B)ovarian follicle, mature follicle, oocyte.
C)corpus luteum, tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle.
D)primary follicle, secondary follicle, tertiary follicle, corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Fraternal twins develop when:
A)one egg is fertilized by two sperm.
B)two eggs are fertilized by one sperm.
C)multiple ovulations occur, and two eggs are fertilized.
D)one egg is fertilized by one sperm, but the resulting cells separate from one another and continue development.
A)one egg is fertilized by two sperm.
B)two eggs are fertilized by one sperm.
C)multiple ovulations occur, and two eggs are fertilized.
D)one egg is fertilized by one sperm, but the resulting cells separate from one another and continue development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these is not a supporting gland in males?
A)prostate gland
B)seminal vesicle
C)epididymis
D)bulbourethral gland
A)prostate gland
B)seminal vesicle
C)epididymis
D)bulbourethral gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The portion of a sperm that carries enzymes needed for fertilization is the:
A)tail.
B)nucleus.
C)acrosome.
D)mitochondrion.
A)tail.
B)nucleus.
C)acrosome.
D)mitochondrion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When does the fetus achieve about 15 percent of its birth weight and start kicking?
A)at the end of embryonic phase
B)at the start of organogenesis
C)in the first trimester
D)in the second trimester
E)in the third trimester
A)at the end of embryonic phase
B)at the start of organogenesis
C)in the first trimester
D)in the second trimester
E)in the third trimester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which hormone stimulates the muscular contractions associated with birth of a child?
A)estrogen
B)progesterone
C)luteinizing hormone
D)oxytocin
A)estrogen
B)progesterone
C)luteinizing hormone
D)oxytocin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When a spermatogonium divides,it produces one primary spermatocyte and:
A)two secondary spermatocytes.
B)one spermatogonium.
C)one spermatid.
D)one nurse cell.
A)two secondary spermatocytes.
B)one spermatogonium.
C)one spermatid.
D)one nurse cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why is production of lung surfactant important for a baby?
A)Without lung surfactant, the baby's lungs do not develop properly.
B)Lung surfactant may block the placenta from exchanging oxygen.
C)Lung surfactant keeps the lung sacs from collapsing.
D)Lung surfactant keeps the lungs from sticking to the diaphragm.
A)Without lung surfactant, the baby's lungs do not develop properly.
B)Lung surfactant may block the placenta from exchanging oxygen.
C)Lung surfactant keeps the lung sacs from collapsing.
D)Lung surfactant keeps the lungs from sticking to the diaphragm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Three weeks after conception,which of the following has happened in an embryo?
A)organ formation
B)neural tube formation
C)limb bud formation
D)primitive eye formation
A)organ formation
B)neural tube formation
C)limb bud formation
D)primitive eye formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The sequence of development of sperm is:
A)primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, tertiary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm.
B)primary spermatocyte, spermatogonia, sperm.
C)immature sperm, mature sperm, secondary sperm, spermatocyte.
D)spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm.
A)primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, tertiary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm.
B)primary spermatocyte, spermatogonia, sperm.
C)immature sperm, mature sperm, secondary sperm, spermatocyte.
D)spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Immature versions of all the major organ systems have formed by about what point in pregnancy?
A)16 days
B)3 weeks
C)12 weeks
D)not until at least 30 weeks
A)16 days
B)3 weeks
C)12 weeks
D)not until at least 30 weeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A man has been experiencing reduced urine flow problems.After examination by his doctor,the diagnosis is an enlarged prostate gland.What is the connection between prostate enlargement and reduced urine flow?
A)The prostate is located where the ureters enter the bladder.
B)The prostate surrounds the urethra, the tube that transmits sperm and urine.
C)An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the kidneys.
D)An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the bladder.
A)The prostate is located where the ureters enter the bladder.
B)The prostate surrounds the urethra, the tube that transmits sperm and urine.
C)An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the kidneys.
D)An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the bladder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following best describes the period during which the developing offspring is considered a fetus?
A)from fertilization to three weeks
B)from fertilization to eight weeks
C)the first trimester only
D)the third trimester only
E)from nine weeks until birth
A)from fertilization to three weeks
B)from fertilization to eight weeks
C)the first trimester only
D)the third trimester only
E)from nine weeks until birth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many sperm participate in the formation of fraternal twins?
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four
A)one
B)two
C)three
D)four

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What prevents multiple sperm from fertilizing one egg?
A)release of granules that harden the membrane outside of the oocyte
B)atresia
C)phagocytosis by accessory cells once one sperm contacts the membrane
D)egg immediately divides and becomes impervious to sperm
A)release of granules that harden the membrane outside of the oocyte
B)atresia
C)phagocytosis by accessory cells once one sperm contacts the membrane
D)egg immediately divides and becomes impervious to sperm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the "afterbirth" associated with the birth process?
A)the amniotic fluid
B)the blood lost from the uterus in the weeks after birth
C)the placenta
D)the process of cutting the umbilical cord
A)the amniotic fluid
B)the blood lost from the uterus in the weeks after birth
C)the placenta
D)the process of cutting the umbilical cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these becomes the baby?
A)outer cell mass
B)trophoblast
C)inner cell mass
D)placenta
A)outer cell mass
B)trophoblast
C)inner cell mass
D)placenta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements concerning sperm and fertilization is correct?
A)The first sperm that approaches the egg is the one to fertilize the egg.
B)Many sperm release their enzymes before one can get through.
C)The first capacitated sperm fertilizes the egg.
D)Several sperm must contribute their DNA to the egg for fertilization to occur.
A)The first sperm that approaches the egg is the one to fertilize the egg.
B)Many sperm release their enzymes before one can get through.
C)The first capacitated sperm fertilizes the egg.
D)Several sperm must contribute their DNA to the egg for fertilization to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An ectopic pregnancy is:
A)implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
B)another name for fraternal twins.
C)another name for identical twins.
D)attachment of an embryo outside the uterus.
A)implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
B)another name for fraternal twins.
C)another name for identical twins.
D)attachment of an embryo outside the uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the human birth process,what does labor refer to?
A)the period between birth and expulsion of the placenta
B)the period between the first contraction and dilation of the cervix
C)the last part of the process when the fetus is expelled from the vagina
D)regular contractions of uterine muscles
A)the period between birth and expulsion of the placenta
B)the period between the first contraction and dilation of the cervix
C)the last part of the process when the fetus is expelled from the vagina
D)regular contractions of uterine muscles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why is it useful for accessory glands to produce alkaline substances to accompany sperm?
A)Alkaline substances neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina.
B)Alkaline substances produce a pH optimum for nutrient absorption.
C)Alkaline substances are mainly fats used for energy.
D)Alkaline substances function as enzymes needed for swimming.
A)Alkaline substances neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina.
B)Alkaline substances produce a pH optimum for nutrient absorption.
C)Alkaline substances are mainly fats used for energy.
D)Alkaline substances function as enzymes needed for swimming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A fertility doctor is trying to determine why a couple is infertile.It has been determined that the woman is fertile,so the problem may be with the man.In analyzing his semen,the doctor notices adequate sperm production,but the sperm are largely inactive.He concludes that the semen may be lacking in proper nutrients for the sperm.Which structure would be the most likely candidate for the source of the problem?
A)urethra
B)seminiferous tubules
C)vas deferens
D)seminal vesicles
A)urethra
B)seminiferous tubules
C)vas deferens
D)seminal vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Sperm development takes about:
A)1 month.
B)28 days.
C)6 months.
D)2)5 months.
A)1 month.
B)28 days.
C)6 months.
D)2)5 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ovulation refers to growth of the primary follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In humans,females contribute more resources to reproduction and development than males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
There is an epididymis adjacent to each testis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How much does the cervix ultimately dilate during labor?
A)10 centimeters
B)5 centimeters
C)3 centimeters
D)1 centimeter
A)10 centimeters
B)5 centimeters
C)3 centimeters
D)1 centimeter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sperm develop in the seminal vesicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Menstruation refers to the later life cessation of the monthly ovarian cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Sperm are fully mature when they reach the epididymis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An egg implants in the uterus and awaits sperm for fertilization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Ejaculation initially deposits the sperm in the uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As sperm are made,they travel through the vas deferens and are stored in the seminal vesicles until ejaculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The male stem cells in sperm production are the spermatogonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An egg is not a gamete.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Semen is the mixture of sperm and secretions from male reproductive glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Sperm development requires temperatures somewhat cooler than found in the rest of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Corpus luteum translates as "yellow body."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Women produce oocytes from stem cells from puberty all throughout life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A woman begins puberty with about 400,000 follicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An ovarian follicle is a developing oocyte and the follicular cells surrounding it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Normally,anywhere from one to four sperm fertilize the egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Fallopian tube is another name for the uterine tube.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Enzymes are carried in the ________ of a sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Implantation occurs in the ________ of the uterus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Evaluate this statement: By the end of the first trimester,most growth in a fetus is in size,not complexity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Human embryos do not go through a morula stage of development as do most other animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows.
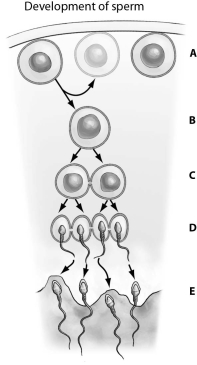
Which item,A,B,C,D,or E,is a secondary spermatocyte?

Which item,A,B,C,D,or E,is a secondary spermatocyte?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
It generally takes the enzymes from dozens of sperm for one sperm to gain access to the oocyte membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The release of an oocyte from an ovary is called ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Sperm cells do not need a nucleus and expel it during development as a weight-saving tactic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Primary and secondary ________ develop into spermatids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the long tube through which mature sperm are transported to the urethra during ejaculation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The normal position of the fetus at the start of labor is "upside down."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows.
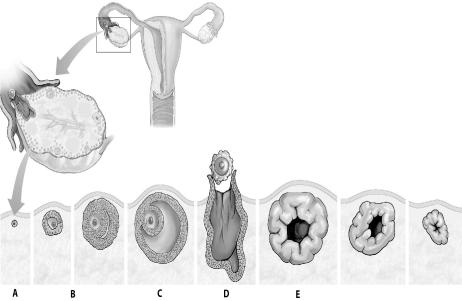
Which item,A,B,C,D,or E,represents the structure that maintains the female reproductive tract during the early part of pregnancy?

Which item,A,B,C,D,or E,represents the structure that maintains the female reproductive tract during the early part of pregnancy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The developing organism is referred to as a fetus during its first eight weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Given the loss of childbearing ability and negative health effects associated with menopause,there is cause to question why it exists given that evolution usually selects against most negative health effects and reduced fertility.Appraise and compare the two possible explanations covered in this section.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which is the only trimester to include both the embryo and fetal stages?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Propose reasons to explain why the female reproductive system evolved a menstrual cycle,but the male system does not adhere to any kind of true cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Human pregnancy lasts an average of about 38 weeks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



