Deck 24: Evolution by Natural Selection
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Evolution by Natural Selection
1
Which of the following is the best modern definition of evolution?
A)descent without modification
B)change in allele frequencies in a population over time
C)survival of the fittest
D)inheritance of acquired characters
A)descent without modification
B)change in allele frequencies in a population over time
C)survival of the fittest
D)inheritance of acquired characters
B
2
Why was Darwin and Wallace's theory of evolution by natural selection revolutionary?
A)It was the first theory to refute the ideas of special creation.
B)It proved that individuals acclimated to their environment over time.
C)It dismissed the idea that species are constant and emphasized the importance of variation and change in populations.
D)It was the first time a biologist had proposed that species changed through time.
A)It was the first theory to refute the ideas of special creation.
B)It proved that individuals acclimated to their environment over time.
C)It dismissed the idea that species are constant and emphasized the importance of variation and change in populations.
D)It was the first time a biologist had proposed that species changed through time.
C
3
Evolutionary theory predicts that species are related,not independent.Four of the following examples provide support for this prediction.Which one of these examples does not support the claim that species are related?
A)Plants that live in desert regions typically have thickened leaf surfaces to prevent water loss.
B)The endostyle of lancelets (invertebrate chordates)and the thyroid gland of vertebrates develop similarly,and both produce iodinated proteins.
C)All prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA to carry their genetic information.
D)Ground squirrel species found on the north and south sides of the Grand Canyon are similar behaviorally,despite being very different physically.
E)Before synthetic insulin was available,diabetics used injections of purified pig insulin to manage their disease.
A)Plants that live in desert regions typically have thickened leaf surfaces to prevent water loss.
B)The endostyle of lancelets (invertebrate chordates)and the thyroid gland of vertebrates develop similarly,and both produce iodinated proteins.
C)All prokaryotes and eukaryotes use DNA to carry their genetic information.
D)Ground squirrel species found on the north and south sides of the Grand Canyon are similar behaviorally,despite being very different physically.
E)Before synthetic insulin was available,diabetics used injections of purified pig insulin to manage their disease.
A
4
Your text discusses the evolution of antibiotic-resistant M.tuberculosis bacteria in a patient.Researchers discovered that the strain of M.tuberculosis taken from the dead patient has a point mutation in the rpoB gene that codes for part of the RNA polymerase enzyme.This mutant form of RNA polymerase does not normally function as well as the more common form,but a commonly used antibiotic called rifampin does not affect the mutant rpoB.A researcher places M.tuberculosis isolated from the patient a year before death (no rpoB mutation)in cell cultures with M.tuberculosis isolated from the dead patient (with rpoB mutation).Half the cell cultures contain just standard nutrients,and the other cell cultures contain rifampin in addition to the standard nutrients.After many cell generations,the researcher finds that _____.(choose one)
A)very few M.tuberculosis in the standard nutrient cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation,but almost all of the M.tuberculosis in the cell cultures with rifampin carry the rpoB mutation
B)almost all M.tuberculosis in the standard nutrient cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation,but very few of the M.tuberculosis in the cell cultures with rifampin carry the rpoB mutation
C)very few M.tuberculosis in any of the cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation
D)almost all of the M.tuberculosis in both types of cell cultures carry the rpoB mutation
E)a mix of both M.tuberculosis strains thrive in the standard cell cultures,but no living bacteria can be found in the cell cultures that contain rifampin
A)very few M.tuberculosis in the standard nutrient cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation,but almost all of the M.tuberculosis in the cell cultures with rifampin carry the rpoB mutation
B)almost all M.tuberculosis in the standard nutrient cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation,but very few of the M.tuberculosis in the cell cultures with rifampin carry the rpoB mutation
C)very few M.tuberculosis in any of the cell cultures carry the rpoB gene mutation
D)almost all of the M.tuberculosis in both types of cell cultures carry the rpoB mutation
E)a mix of both M.tuberculosis strains thrive in the standard cell cultures,but no living bacteria can be found in the cell cultures that contain rifampin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Gill pouches in chick,human,and house-cat embryos are an example of _____.
A)structural homology
B)developmental homology
C)genetic homology
D)the inheritance of acquired characters
A)structural homology
B)developmental homology
C)genetic homology
D)the inheritance of acquired characters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A farmer uses triazine herbicide to control pigweed in his field.For the first few years,the triazine works well and almost all the pigweed dies;but after several years,the farmer sees more and more pigweed.Which of these explanations best describes this observation?
A)The herbicide company lost its triazine formula and started selling poor-quality triazine.
B)Natural selection caused the pigweed to mutate,creating a new triazine-resistant species.
C)Triazine-resistant pigweed has less-efficient photosynthesis metabolism.
D)Only triazine-resistant weeds survived and reproduced,so each year more pigweed was triazine-resistant.
A)The herbicide company lost its triazine formula and started selling poor-quality triazine.
B)Natural selection caused the pigweed to mutate,creating a new triazine-resistant species.
C)Triazine-resistant pigweed has less-efficient photosynthesis metabolism.
D)Only triazine-resistant weeds survived and reproduced,so each year more pigweed was triazine-resistant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Fossils of Thrinaxodon,a species that lived during the Triassic period,have been found in both South Africa and Antarctica.Thrinaxodon had a reptile-like skeleton and laid eggs,but small depressions on the front of its skull suggest it had whiskers and,therefore,fur.Thrinaxodon may have been warm-blooded.Thrinaxodon shows _____.
A)that fossils found in a given area look like the modern species in that same area
B)that species must adapt to their environment
C)that mammals likely evolved from a reptilian ancestor
D)that Antarctica and South Africa separated after Thrinaxodon went extinct
E)that organisms have stable traits over time
A)that fossils found in a given area look like the modern species in that same area
B)that species must adapt to their environment
C)that mammals likely evolved from a reptilian ancestor
D)that Antarctica and South Africa separated after Thrinaxodon went extinct
E)that organisms have stable traits over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following,if discovered,could refute our current understanding of the theory of evolution?
A)no fossils of soft-bodied animals
B)a modern bird having reptile-like scales on its legs
C)radioactive dating of rocks close to the Earth's surface as younger than lower rock strata
D)fossils of animals that arose in the Cambrian in Precambrian rock strata
A)no fossils of soft-bodied animals
B)a modern bird having reptile-like scales on its legs
C)radioactive dating of rocks close to the Earth's surface as younger than lower rock strata
D)fossils of animals that arose in the Cambrian in Precambrian rock strata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Who proposed that organisms could be organized into a great chain of being?
A)Aristotle
B)Lamarck
C)Linnaeus
D)Darwin
E)Wallace
A)Aristotle
B)Lamarck
C)Linnaeus
D)Darwin
E)Wallace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
After the drought of 1977,researchers hypothesized that on Daphne Major,medium ground finches with large,deep beaks survived better than those with smaller beaks did because they could more easily crack and eat the tough Tribulus cistoides fruits.If this hypothesis is true,what would you expect to observe if a population of these medium ground finches colonizes a nearby island where Tribulus cistoides is the primary available food in all years?
Assume that (1)even the survivors of the 1977 drought sometimes had difficulty cracking the tough T.cistoides fruits and would eat other seeds when offered a choice;and (2)food availability is the primary limit on finch fitness on this new island.
A)evolution of yet larger,deeper beaks over time
B)evolution of smaller,pointier beaks over time
C)random fluctuations in beak size and shape
D)no change in beak size and shape
Assume that (1)even the survivors of the 1977 drought sometimes had difficulty cracking the tough T.cistoides fruits and would eat other seeds when offered a choice;and (2)food availability is the primary limit on finch fitness on this new island.
A)evolution of yet larger,deeper beaks over time
B)evolution of smaller,pointier beaks over time
C)random fluctuations in beak size and shape
D)no change in beak size and shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Many crustaceans (e.g. ,lobsters,shrimp,and crayfish)use their tails to swim,but crabs have reduced tails that curl under their shells and are not used in swimming.This is an example of _____.
A)an adaptation
B)a homologous structure
C)natural selection
D)a vestigial trait
A)an adaptation
B)a homologous structure
C)natural selection
D)a vestigial trait

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The same basic internal organs (kidneys,stomach,heart,lungs)are found in frogs,birds,snakes,and rodents.This is primarily an example of _____.
A)structural homology
B)developmental homology
C)genetic correlation
D)inheritance of acquired characteristics
A)structural homology
B)developmental homology
C)genetic correlation
D)inheritance of acquired characteristics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Cotton-topped tamarins are small primates with tufts of long white hair on their heads.While studying these creatures,you notice that males with longer hair get more opportunities to mate and father more offspring.You believe that having longer hair is adaptive to these males.You should _____.
A)conclude that natural selection will lead to males with longer hair in your population
B)conclude that there is not enough variation in hair length for natural selection to act
C)look for evidence that longer haired males have higher fitness
D)conclude that longer haired males survive better than their shorter haired counterparts
E)determine if hair length is heritable
A)conclude that natural selection will lead to males with longer hair in your population
B)conclude that there is not enough variation in hair length for natural selection to act
C)look for evidence that longer haired males have higher fitness
D)conclude that longer haired males survive better than their shorter haired counterparts
E)determine if hair length is heritable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Explain how one of the following supports the idea that species change through time:
artificial selection,extinction,transitional forms,vestigial traits,antibiotic resistance.
artificial selection,extinction,transitional forms,vestigial traits,antibiotic resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The Irish "elk" described by Georges Cuvier suggests that _____.
A)organisms could not have originated by special creation
B)organisms could go extinct
C)the great flood or some other catastrophe killed many once living organisms
D)the Earth is old enough for evolution to have occurred
A)organisms could not have originated by special creation
B)organisms could go extinct
C)the great flood or some other catastrophe killed many once living organisms
D)the Earth is old enough for evolution to have occurred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of these conditions are always true of populations evolving due to natural selection?
Condition 1:
The population must vary in traits that are heritable.
Condition 2:
Some heritable traits must increase reproductive success.
Condition 3:
Individuals pass on all traits they acquire during their lifetime.
A)Condition 1 only
B)Condition 2 only
C)Conditions 1 and 2
D)Conditions 2 and 3
E)Conditions 1,2,and 3
Condition 1:
The population must vary in traits that are heritable.
Condition 2:
Some heritable traits must increase reproductive success.
Condition 3:
Individuals pass on all traits they acquire during their lifetime.
A)Condition 1 only
B)Condition 2 only
C)Conditions 1 and 2
D)Conditions 2 and 3
E)Conditions 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following scientists argued that variation among individuals allows evolution to occur?
A)Aristotle
B)Lamarck
C)Linnaeus
D)Wallace
A)Aristotle
B)Lamarck
C)Linnaeus
D)Wallace

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
There is a population of beetles that typically have black wings.A scientist studying these beetles knows that their eggs hatch in early spring,the baby insects grow through the late spring and summer,they lay eggs in the early fall,and die in the early winter.Recently some beetles have been born with white wings.Early in life the black and white winged beetles seem to be very similar in number of mating events,eggs laid,and survival rates,but shortly after laying their eggs the white beetles die and there are only black winged beetles during the late fall.Which of the following is a true statement about the beetles?
A)White and black winged beetles have equal fitness.
B)Black winged beetles have a higher fitness than white winged beetles.
C)The number of baby white winged beetles will decrease in frequency over time.
D)White wings are an adaptation.
A)White and black winged beetles have equal fitness.
B)Black winged beetles have a higher fitness than white winged beetles.
C)The number of baby white winged beetles will decrease in frequency over time.
D)White wings are an adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is an example of typological thinking?
A)The variety of dog shape and size is truly amazing.
B)Women are shorter than men,have longer hair and like to shop.
C)It is best to choose the seeds from the plants with the largest fruits to set aside for next year's plantings.
D)The type of beak that is most advantageous varies depending on how much rain falls in a given year.
A)The variety of dog shape and size is truly amazing.
B)Women are shorter than men,have longer hair and like to shop.
C)It is best to choose the seeds from the plants with the largest fruits to set aside for next year's plantings.
D)The type of beak that is most advantageous varies depending on how much rain falls in a given year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If two organisms show a developmental homology,you would also definitely expect them to _____.
A)share structural homologies
B)share genetic homologies
C)share genetic and structural homologies
D)be evolutionarily closely related
E)be evolutionarily distantly related
A)share structural homologies
B)share genetic homologies
C)share genetic and structural homologies
D)be evolutionarily closely related
E)be evolutionarily distantly related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tourist companies start visiting Island X,where a population of medium ground finches (see question 20)feeds on the tough-fruited Tribulus cistoides.The tourist companies set up reliable feeding stations with a variety of bird seeds (different types and sizes),so that tourists can get a better look at the finches.Which of these events is now most likely to occur to finch beaks on Island X?
A)evolution of yet larger,deeper beaks over time,until all birds have relatively large,deep beaks
B)evolution of smaller,pointier beaks over time,until all birds have relatively small,pointy beaks
C)increased variation in beak size and shape over time
D)no change in beak size and shape over time
A)evolution of yet larger,deeper beaks over time,until all birds have relatively large,deep beaks
B)evolution of smaller,pointier beaks over time,until all birds have relatively small,pointy beaks
C)increased variation in beak size and shape over time
D)no change in beak size and shape over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the following information when answering the corresponding question(s).
The following question(s)are based on information from Frank M.Frey,"Opposing Natural Selection from Herbivores and Pathogens May Maintain Floral-Color Variation in Claytonia virginica (Portulacaceae)," Evolution 58(11),2004: 2426-37.
Claytonia virginica is a woodland spring herb with flowers that vary from white to pale pink to bright pink.Slugs prefer to eat pink-flowering over white-flowering plants (due to chemical differences between the two),and plants experiencing severe herbivory were more likely to die.The bees that pollinate this plant also prefer pink to white flowers,so that Claytonia with pink flowers have greater relative fruit set than Claytonia with white flowers.A researcher observes that the percentage of different flower colors remains stable in the study population from year to year.Given no other information,if the researcher removes all slugs from the study population,what do you expect to happen to the distribution of flower colors in the population over time?
A)The percentage of pink flowers should increase over time.
B)The percentage of white flowers should increase over time.
C)The distribution of flower colors should not change.
D)The distribution of flower colors should randomly fluctuate over time.
The following question(s)are based on information from Frank M.Frey,"Opposing Natural Selection from Herbivores and Pathogens May Maintain Floral-Color Variation in Claytonia virginica (Portulacaceae)," Evolution 58(11),2004: 2426-37.
Claytonia virginica is a woodland spring herb with flowers that vary from white to pale pink to bright pink.Slugs prefer to eat pink-flowering over white-flowering plants (due to chemical differences between the two),and plants experiencing severe herbivory were more likely to die.The bees that pollinate this plant also prefer pink to white flowers,so that Claytonia with pink flowers have greater relative fruit set than Claytonia with white flowers.A researcher observes that the percentage of different flower colors remains stable in the study population from year to year.Given no other information,if the researcher removes all slugs from the study population,what do you expect to happen to the distribution of flower colors in the population over time?
A)The percentage of pink flowers should increase over time.
B)The percentage of white flowers should increase over time.
C)The distribution of flower colors should not change.
D)The distribution of flower colors should randomly fluctuate over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 24.3
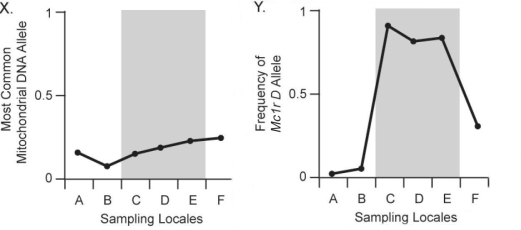
In Figure 24.3,chart X above shows the frequency of the most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele (an allele for a gene that does not affect and is not linked to coat color)across six pocket-mouse populations.Populations C,D,and E live on dark volcanic rock;populations A,B,and F live on light-colored granite.Compare this figure with chart Y above.What should you conclude after comparing these two figures?
A)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele is strongly associated with substrate color.
B)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele is strongly associated with the frequency of the Mc1r D allele.
C)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele varies more among populations than does the Mc1r D allele.
D)Little to no correlation exists between neutral mitochondrial DNA alleles and habitat color.

In Figure 24.3,chart X above shows the frequency of the most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele (an allele for a gene that does not affect and is not linked to coat color)across six pocket-mouse populations.Populations C,D,and E live on dark volcanic rock;populations A,B,and F live on light-colored granite.Compare this figure with chart Y above.What should you conclude after comparing these two figures?
A)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele is strongly associated with substrate color.
B)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele is strongly associated with the frequency of the Mc1r D allele.
C)The most common neutral mitochondrial DNA allele varies more among populations than does the Mc1r D allele.
D)Little to no correlation exists between neutral mitochondrial DNA alleles and habitat color.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Figure 24.1
The following question(s)are based on information in Hopi E.Hoekstra,Kristen E.Drumm,and Michael W.Nachman,"Ecological Genetics of Adaptive Color Polymorphism in Pocket Mice: Geographic Variation in Selected and Neutral Genes," Evolution 58(6),2004: 1329-41.
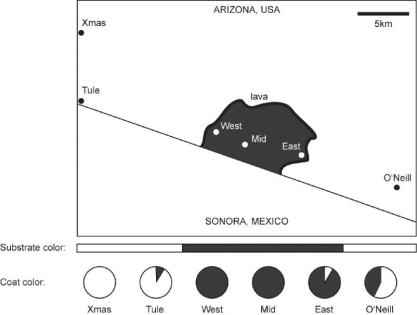
Refer to Figure 24.1.In their investigation of natural selection on Mc1r alleles (the gene that determines coat color)in Arizona pocket mice,Hoekstra et al.determined the frequency of the D and d alleles in each population.They also determined the frequency of alleles for two neutral mitochondrial DNA genes (genes that do not affect and are not linked to coat color).Why did the researchers include the mitochondrial DNA genes as part of their experimental design?
A)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as an experimental group and gives information on any general background genetic difference among these populations.
B)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as a control and determines coat-color differences among these populations.
C)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as an experimental group and gives information on coat-color differences among these populations.
D)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as a control and gives information on any general background genetic difference among these populations.
E)None of the above answers apply.
The following question(s)are based on information in Hopi E.Hoekstra,Kristen E.Drumm,and Michael W.Nachman,"Ecological Genetics of Adaptive Color Polymorphism in Pocket Mice: Geographic Variation in Selected and Neutral Genes," Evolution 58(6),2004: 1329-41.

Refer to Figure 24.1.In their investigation of natural selection on Mc1r alleles (the gene that determines coat color)in Arizona pocket mice,Hoekstra et al.determined the frequency of the D and d alleles in each population.They also determined the frequency of alleles for two neutral mitochondrial DNA genes (genes that do not affect and are not linked to coat color).Why did the researchers include the mitochondrial DNA genes as part of their experimental design?
A)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as an experimental group and gives information on any general background genetic difference among these populations.
B)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as a control and determines coat-color differences among these populations.
C)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as an experimental group and gives information on coat-color differences among these populations.
D)Allele change for the neutral mitochondrial genes serves as a control and gives information on any general background genetic difference among these populations.
E)None of the above answers apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Figure 24.1
The following question(s)are based on information in Hopi E.Hoekstra,Kristen E.Drumm,and Michael W.Nachman,"Ecological Genetics of Adaptive Color Polymorphism in Pocket Mice: Geographic Variation in Selected and Neutral Genes," Evolution 58(6),2004: 1329-41.

The figure above shows the distribution of pocket-mouse coat colors in several Arizona populations found either on light-colored granite substrate or on dark volcanic rock (dark substrate).The Melanocortin-1 receptor (Mc1r)alleles,D and d,differ by four amino acids.Mice with DD and Dd genotypes have dark coats,whereas mice with the dd genotype are light colored.What sort of genotype frequencies might you expect to find in the Xmas,Mid,and O'Neill populations?
A)Xmas high DD frequency;Mid high Dd frequency,O'Neill high dd frequency
B)Xmas high Dd frequency;Mid high DD frequency,O'Neill high dd frequency
C)Xmas high Dd frequency;Mid high dd frequency,O'Neill high DD frequency
D)Xmas high dd frequency;Mid high Dd frequency,O'Neill high DD frequency
E)Xmas high dd frequency;Mid high DD frequency,O'Neill high Dd frequency
The following question(s)are based on information in Hopi E.Hoekstra,Kristen E.Drumm,and Michael W.Nachman,"Ecological Genetics of Adaptive Color Polymorphism in Pocket Mice: Geographic Variation in Selected and Neutral Genes," Evolution 58(6),2004: 1329-41.

The figure above shows the distribution of pocket-mouse coat colors in several Arizona populations found either on light-colored granite substrate or on dark volcanic rock (dark substrate).The Melanocortin-1 receptor (Mc1r)alleles,D and d,differ by four amino acids.Mice with DD and Dd genotypes have dark coats,whereas mice with the dd genotype are light colored.What sort of genotype frequencies might you expect to find in the Xmas,Mid,and O'Neill populations?
A)Xmas high DD frequency;Mid high Dd frequency,O'Neill high dd frequency
B)Xmas high Dd frequency;Mid high DD frequency,O'Neill high dd frequency
C)Xmas high Dd frequency;Mid high dd frequency,O'Neill high DD frequency
D)Xmas high dd frequency;Mid high Dd frequency,O'Neill high DD frequency
E)Xmas high dd frequency;Mid high DD frequency,O'Neill high Dd frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 24.2
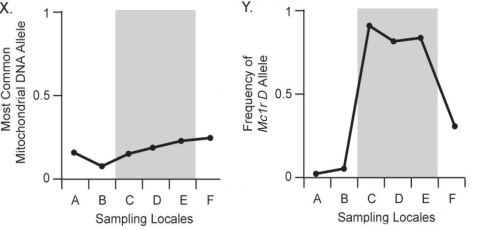
The distribution of pocket-mouse coat colors in several Arizona populations is associated with substrate color.Some populations live on light-colored granite substrate,and others live on dark volcanic rock.In Figure 24.2,chart A shows the frequency of the melanic (dark)coat phenotype across six populations.Populations C,D,and E live on dark volcanic rock;populations A,B,and F live on light-colored granite.Chart B shows the frequency of the Melanocortin-1 receptor (Mc1r)allele across these populations.The Mc1r alleles,D and d,differ by four amino acids;mice with DD and Dd genotypes have dark coats,whereas mice with dd genotype are light colored.Which of the following statements best interprets the results shown in charts A and B?
A)Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with the melanic phenotype,but is unrelated to the presence of dark substrate color.
B)Frequency of the D allele is not associated with the melanic phenotype,but is associated with the presence of dark substrate color.
C)Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with both the melanic phenotype and the presence of dark substrate color.
D)Frequency of the D allele is associated neither with the melanic phenotype nor with the presence of dark substrate color.
E)Frequency of the D allele does not vary.

The distribution of pocket-mouse coat colors in several Arizona populations is associated with substrate color.Some populations live on light-colored granite substrate,and others live on dark volcanic rock.In Figure 24.2,chart A shows the frequency of the melanic (dark)coat phenotype across six populations.Populations C,D,and E live on dark volcanic rock;populations A,B,and F live on light-colored granite.Chart B shows the frequency of the Melanocortin-1 receptor (Mc1r)allele across these populations.The Mc1r alleles,D and d,differ by four amino acids;mice with DD and Dd genotypes have dark coats,whereas mice with dd genotype are light colored.Which of the following statements best interprets the results shown in charts A and B?
A)Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with the melanic phenotype,but is unrelated to the presence of dark substrate color.
B)Frequency of the D allele is not associated with the melanic phenotype,but is associated with the presence of dark substrate color.
C)Frequency of the D allele is closely associated with both the melanic phenotype and the presence of dark substrate color.
D)Frequency of the D allele is associated neither with the melanic phenotype nor with the presence of dark substrate color.
E)Frequency of the D allele does not vary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following situations could not lead to evolution via natural selection?
A)Some hemoglobins have a higher affinity for oxygen than do others.
B)Plants growing in soils contaminated with heavy metals upregulate production of enzymes to stop uptake of metals.
C)Bacteria in areas with high sunlight intensity begin to photosynthesize faster,making more sugar in a given time period.
D)Some plant species can absorb nitrogen better than others can.
E)Larger fungi produce more spores than smaller fungi.
A)Some hemoglobins have a higher affinity for oxygen than do others.
B)Plants growing in soils contaminated with heavy metals upregulate production of enzymes to stop uptake of metals.
C)Bacteria in areas with high sunlight intensity begin to photosynthesize faster,making more sugar in a given time period.
D)Some plant species can absorb nitrogen better than others can.
E)Larger fungi produce more spores than smaller fungi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following information when answering the corresponding question(s).
The following question(s)are based on information from Frank M.Frey,"Opposing Natural Selection from Herbivores and Pathogens May Maintain Floral-Color Variation in Claytonia virginica (Portulacaceae)," Evolution 58(11),2004: 2426-37.
Claytonia virginica is a woodland spring herb with flowers that vary from white to pale pink to bright pink.This plant is primarily pollinated by a bee that prefers pink flowers to white flowers.Claytonia with pink flowers have greater relative fruit set than Claytonia with white flowers.Nevertheless,the percentage of different flower colors remains stable in the study population from year to year.Which of these statements might explain this observation?
A)Reproductive success does not affect evolution in this species.
B)Flower color is not heritable but is instead environmentally determined.
C)The white flowers have evolved pollinator resistance.
D)Fitness is primarily determined by fruit set in this species.
E)There are repeated mutations for white flowers in this species.
The following question(s)are based on information from Frank M.Frey,"Opposing Natural Selection from Herbivores and Pathogens May Maintain Floral-Color Variation in Claytonia virginica (Portulacaceae)," Evolution 58(11),2004: 2426-37.
Claytonia virginica is a woodland spring herb with flowers that vary from white to pale pink to bright pink.This plant is primarily pollinated by a bee that prefers pink flowers to white flowers.Claytonia with pink flowers have greater relative fruit set than Claytonia with white flowers.Nevertheless,the percentage of different flower colors remains stable in the study population from year to year.Which of these statements might explain this observation?
A)Reproductive success does not affect evolution in this species.
B)Flower color is not heritable but is instead environmentally determined.
C)The white flowers have evolved pollinator resistance.
D)Fitness is primarily determined by fruit set in this species.
E)There are repeated mutations for white flowers in this species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An individual with a novel adaptation has evolved that adaptation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is a fitness trade-off?
A)In some hornbill species,the male helps seal the female in a tree with her nest until the young are ready to fledge.
B)Moths are the best pollinators for datura flowers,but bees are the best pollinators for orchids.
C)Some lemmings run into the sea when overgrazing threatens the species.
D)Algal genotypes that can grow rapidly in nitrogen-limited environments are easier for predators to digest.
A)In some hornbill species,the male helps seal the female in a tree with her nest until the young are ready to fledge.
B)Moths are the best pollinators for datura flowers,but bees are the best pollinators for orchids.
C)Some lemmings run into the sea when overgrazing threatens the species.
D)Algal genotypes that can grow rapidly in nitrogen-limited environments are easier for predators to digest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Parasitic species tend to have simple morphologies.Which of the following statements best explains this observation?
A)Parasites are lower organisms,and this is why they have simple morphologies.
B)Parasites do not live long enough to inherit acquired characteristics.
C)Simple morphologies have been naturally selected for in most parasites.
D)Parasites have not yet had time to progress,because they are young evolutionarily.
A)Parasites are lower organisms,and this is why they have simple morphologies.
B)Parasites do not live long enough to inherit acquired characteristics.
C)Simple morphologies have been naturally selected for in most parasites.
D)Parasites have not yet had time to progress,because they are young evolutionarily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Vestigial traits and neutral changes in DNA sequences are good examples of _____.
A)adaptation
B)acclimation
C)convergent traits
D)nonadaptive traits
E)developmental homology
A)adaptation
B)acclimation
C)convergent traits
D)nonadaptive traits
E)developmental homology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



