Deck 11: The Cell Cycle
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/31
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Cell Cycle
1
The mitotic spindle is a microtubular structure that is involved in _____.
A)splitting of the cell (cytokinesis)following mitosis
B)triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
C)dissolving the nuclear membrane
D)separation of sister chromatids
A)splitting of the cell (cytokinesis)following mitosis
B)triggering the compaction and condensation of chromosomes
C)dissolving the nuclear membrane
D)separation of sister chromatids
D
2
Myosin is a motor protein involved in animal cell cytokinesis.It binds to ATP or ADP,causing the myosin to move with respect to actin.What is the effect of the interaction between myosin and actin?
A)Vesicles containing plasma membrane constituents are transported to the metaphase plate,where cytokinesis takes place.
B)Excess cytoplasm is removed.
C)The cleavage furrow deepens.
D)It triggers the re-formation of the daughter nuclei.
A)Vesicles containing plasma membrane constituents are transported to the metaphase plate,where cytokinesis takes place.
B)Excess cytoplasm is removed.
C)The cleavage furrow deepens.
D)It triggers the re-formation of the daughter nuclei.
C
3
In human and many other eukaryotic species' cells,the nuclear membrane has to disappear in order for what to take place?
A)cytokinesis
B)attachment of mitotic spindle to kinetochores
C)splitting of the centrosomes
D)disassembly of the nucleolus
A)cytokinesis
B)attachment of mitotic spindle to kinetochores
C)splitting of the centrosomes
D)disassembly of the nucleolus
B
4
Which of the following statements about cancer is not true?
A)Cancer is very often associated with problems at the G₁ checkpoint.
B)For a tumor to be defined as "cancer," it must first metastasize.
C)Cancer cells often have a defective form of the tumor repressor p53.
D)Many cancer cells have defective forms of the signal transduction protein Ras that do not become deactivated.
A)Cancer is very often associated with problems at the G₁ checkpoint.
B)For a tumor to be defined as "cancer," it must first metastasize.
C)Cancer cells often have a defective form of the tumor repressor p53.
D)Many cancer cells have defective forms of the signal transduction protein Ras that do not become deactivated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which cytoskeletal proteins are important constituents of the contractile structures that form the cleavage furrows involved in animal cell cytokinesis?
A)actin
B)dynein
C)tubulin
D)myosin
A)actin
B)dynein
C)tubulin
D)myosin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How is plant cell cytokinesis different from animal cell cytokinesis?
A)The cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of protein contractile filaments;the contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates.
B)Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell-wall building blocks on the metaphase plate;animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
C)The structural carbohydrates of the plant cells separate the two cells,whereas in animal cells,a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
D)Animal cells have centrosomes that are involved in this process,but plant cells have microtubule-organizing centers that are not detectable during most of the cell cycle.
A)The cleavage furrow in animal cells is composed of protein contractile filaments;the contractile filaments found in plant cells are structures composed of carbohydrates.
B)Plant cells deposit vesicles containing cell-wall building blocks on the metaphase plate;animal cells form a cleavage furrow.
C)The structural carbohydrates of the plant cells separate the two cells,whereas in animal cells,a cell membrane separates the two daughter cells.
D)Animal cells have centrosomes that are involved in this process,but plant cells have microtubule-organizing centers that are not detectable during most of the cell cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In eukaryotic cells,chromosomes are composed of _____.
A)DNA and RNA
B)DNA only
C)DNA and proteins
D)DNA and phospholipids
A)DNA and RNA
B)DNA only
C)DNA and proteins
D)DNA and phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Metaphase occurs prior to the splitting of centromeres.It is characterized by _____.
A)aligning of chromosomes on the equator
B)splitting of the centromeres
C)cytokinesis
D)separation of sister chromatids
A)aligning of chromosomes on the equator
B)splitting of the centromeres
C)cytokinesis
D)separation of sister chromatids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A parent cell divides to form two genetically identical daughter cells in the process of mitosis.For mitosis to take place _____.
A)the parent cell must first dissolve its nuclear membrane
B)the parent cell must first replicate its entire genome
C)the parent cell must first achieve a specified size
D)the parent cell must divide its DNA in half so that each daughter cell gets only the genes it needs
A)the parent cell must first dissolve its nuclear membrane
B)the parent cell must first replicate its entire genome
C)the parent cell must first achieve a specified size
D)the parent cell must divide its DNA in half so that each daughter cell gets only the genes it needs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The first gap in the cell cycle (G₁)corresponds to _____.
A)normal growth and cell function
B)the phase in which DNA is being replicated
C)the beginning of mitosis
D)the phase between DNA replication and the M phase
A)normal growth and cell function
B)the phase in which DNA is being replicated
C)the beginning of mitosis
D)the phase between DNA replication and the M phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Scientists isolate cells in various phases of the cell cycle.They find a group of cells that have 1½ times more DNA than do G₁ phase cells.The cells of this group are _____.
A)between the G₁ and S phases in the cell cycle
B)in the G₂ phase of the cell cycle
C)in the M phase of the cell cycle
D)in the S phase of the cell cycle
A)between the G₁ and S phases in the cell cycle
B)in the G₂ phase of the cell cycle
C)in the M phase of the cell cycle
D)in the S phase of the cell cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Mitosis is the process of chromosome separation.Cytoplasm is divided between the two daughter cells in a process known as _____.
A)cloning
B)cytokinesis
C)binary fission
D)G₁ phase
A)cloning
B)cytokinesis
C)binary fission
D)G₁ phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The microtubule-organizing center found in animal cells is an identifiable structure present during all phases of the cell cycle.Specifically,it is known as which of the following?
A)microtubulin
B)centrosome
C)centromere
D)kinetochore
A)microtubulin
B)centrosome
C)centromere
D)kinetochore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Researchers pulsed rapidly dividing cultured cells for 30 minutes with radioactive thymidine.The cells were then exposed to a solution containing non-radiolabeled thymidine.Cells were analyzed at 2-hour intervals.At the 2-hour time point,no cells appeared to be dividing.Only after 4 hours did some labeled cells appear to be in M phase.This result can be explained in the following way:
A)Radiolabeled compounds are somewhat cytotoxic,and so cell division was initially inhibited.
B)The cells were arrested in a nondividing state because of the treatment and could not enter M phase until several hours after the label was removed.
C)Synthesis (S)phase is lengthy about 12 hours in most cell types and the radioactive thymidine was not present long enough for most cells to be labeled.
D)There seems to be a gap or a lag in the cell cycle,between the synthesis of DNA and cell division.
A)Radiolabeled compounds are somewhat cytotoxic,and so cell division was initially inhibited.
B)The cells were arrested in a nondividing state because of the treatment and could not enter M phase until several hours after the label was removed.
C)Synthesis (S)phase is lengthy about 12 hours in most cell types and the radioactive thymidine was not present long enough for most cells to be labeled.
D)There seems to be a gap or a lag in the cell cycle,between the synthesis of DNA and cell division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
FtsZ is a bacterial cytoskeletal protein that forms a contractile ring involved in bacterial cytokinesis.Its function is analogous to _____.
A)the cleavage furrow of eukaryotic animal cells
B)the cell plate of eukaryotic plant cells
C)the mitotic spindle of eukaryotic cells
D)the microtubule-organizing center of eukaryotic cells
A)the cleavage furrow of eukaryotic animal cells
B)the cell plate of eukaryotic plant cells
C)the mitotic spindle of eukaryotic cells
D)the microtubule-organizing center of eukaryotic cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How might spindle microtubules assist in the process of splitting centromeres?
A)the use of motor proteins to split the centromere at specific arginine residues
B)creating tension by pulling toward opposite poles
C)sliding past each other like actin filaments
D)phosphorylating the centromere,thereby changing its conformation
A)the use of motor proteins to split the centromere at specific arginine residues
B)creating tension by pulling toward opposite poles
C)sliding past each other like actin filaments
D)phosphorylating the centromere,thereby changing its conformation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Following the attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochores,chromosomes are moved around by _____.
A)myosin motor proteins
B)actin filaments
C)elongation and shortening of microtubules
D)motor activity taking place in the centrosomes
A)myosin motor proteins
B)actin filaments
C)elongation and shortening of microtubules
D)motor activity taking place in the centrosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the final result of mitosis?
A)genetically identical 2n somatic cells
B)genetically different 2n somatic cells
C)genetically identical 1n somatic cells
D)genetically identical 2n gamete cells
A)genetically identical 2n somatic cells
B)genetically different 2n somatic cells
C)genetically identical 1n somatic cells
D)genetically identical 2n gamete cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Some cells have several nuclei per cell.How could such multinucleated cells be explained?
A)The cell underwent repeated cytokinesis but no mitosis.
B)The cell underwent repeated mitosis with simultaneous cytokinesis.
C)The cell underwent repeated mitosis,but cytokinesis did not occur.
D)The cell had multiple S phases before it entered mitosis.
A)The cell underwent repeated cytokinesis but no mitosis.
B)The cell underwent repeated mitosis with simultaneous cytokinesis.
C)The cell underwent repeated mitosis,but cytokinesis did not occur.
D)The cell had multiple S phases before it entered mitosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
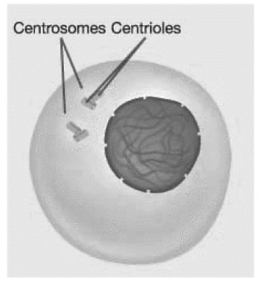
Figure 11.1
Based on structures present in Figure 11.1,this cell is in which substage of interphase?
A)S phase
B)G₁ phase
C)G₀ phase
D)G₂ phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The M-phase checkpoint is designed to make sure all chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle.If this fails to happen,in which stage of mitosis would the cells be most likely to arrest?
A)telophase
B)prophase
C)prometaphase
D)metaphase
A)telophase
B)prophase
C)prometaphase
D)metaphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What happens when MPF (mitosis-promoting factor)is introduced into immature frog oocytes that are arrested in G₂?
A)Nothing happens.
B)The cells undergo meiosis.
C)The cells enter mitosis.
D)Cell differentiation is triggered.
A)Nothing happens.
B)The cells undergo meiosis.
C)The cells enter mitosis.
D)Cell differentiation is triggered.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is not an effect of mitosis-promoting factor (MPF)involved in moving a cell into M phase?
A)phosphorylation of lamins,initiating breakdown of the nuclear membrane
B)phosphorylation of microtubule associated proteins,triggering the formation of the mitotic spindle
C)phosphorylation of an enzyme that breaks down the cyclin molecule
D)degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase
A)phosphorylation of lamins,initiating breakdown of the nuclear membrane
B)phosphorylation of microtubule associated proteins,triggering the formation of the mitotic spindle
C)phosphorylation of an enzyme that breaks down the cyclin molecule
D)degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
For cells to divide more rapidly,increased production would likely be required of each of the following proteins except _____.
A)p53
B)cyclins
C)activated MPF
D)PDGF
A)p53
B)cyclins
C)activated MPF
D)PDGF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a cell has accumulated DNA damage,it is unlikely to _____.
A)pass the G₂ checkpoint
B)activate DNA repair mechanisms
C)enter G₁ from mitosis
D)synthesize cyclin-dependent kinases
A)pass the G₂ checkpoint
B)activate DNA repair mechanisms
C)enter G₁ from mitosis
D)synthesize cyclin-dependent kinases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Regulatory proteins that serve to prevent a cell from entering the S phase under conditions of DNA damage are also known as _____.
A)cyclins
B)cyclin-dependent kinases
C)antibodies
D)tumor suppressors
A)cyclins
B)cyclin-dependent kinases
C)antibodies
D)tumor suppressors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the process of chromosome separation,how do microtubules maintain contact with the kinetochores and shorten at the same time?
A)Motor proteins move chromosomes down the microtubular structures of the mitotic spindle.
B)Actin microfilaments cause the microtubular proteins to slide past each other.
C)The centrosomes move apart,so the microtubular proteins do not need to shorten.
D)The centrosomes create the shortening/depolymerization of the microtubular proteins.
A)Motor proteins move chromosomes down the microtubular structures of the mitotic spindle.
B)Actin microfilaments cause the microtubular proteins to slide past each other.
C)The centrosomes move apart,so the microtubular proteins do not need to shorten.
D)The centrosomes create the shortening/depolymerization of the microtubular proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Nerve cells lose their ability to undergo mitosis.Instead,they are permanently stuck in _____.
A)G₀
B)G₂
C)S of interphase
D)metaphase
A)G₀
B)G₂
C)S of interphase
D)metaphase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Once researchers understood that chromosomes are moved by the spindle microtubules,the next question they wanted to answer is how the microtubules function to bring about this process.They used fluorescent labels to make the chromosomes and the microtubular structures fluoresce.When anaphase began (centromeres split),they photobleached a section of microtubules.As chromosomes moved toward the poles of the daughter cells,the photobleached sections of the microtubules remained stationary.This result suggests that _____.
A)the microtubules elongate and shorten at the centrosome end
B)the microtubules overlap,and slide with respect to one another,effectively shortening the microtubules without depolymerizing the actual fiber
C)the microtubules elongate and shorten at their kinetochore end
D)the microtubules are of constant length;centrosomes move farther apart to separate chromosomes
A)the microtubules elongate and shorten at the centrosome end
B)the microtubules overlap,and slide with respect to one another,effectively shortening the microtubules without depolymerizing the actual fiber
C)the microtubules elongate and shorten at their kinetochore end
D)the microtubules are of constant length;centrosomes move farther apart to separate chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Once a cell completes mitosis,molecular division triggers must be turned off.What happens to MPF during mitosis?
A)It is completely degraded.
B)It is exported from the cell.
C)Cyclin is degraded;the concentration of cyclin-dependent kinase remains unchanged,but without cyclin,MPF is not formed.
D)Cyclin-dependent kinase is degraded;cyclin concentration remains constant,but without cyclin-dependent kinase,MPF is not formed.
A)It is completely degraded.
B)It is exported from the cell.
C)Cyclin is degraded;the concentration of cyclin-dependent kinase remains unchanged,but without cyclin,MPF is not formed.
D)Cyclin-dependent kinase is degraded;cyclin concentration remains constant,but without cyclin-dependent kinase,MPF is not formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exposure of zebrafish nuclei to meiotic cytosol resulted in phosphorylation of NEP55 and L68 proteins by cyclin-dependent kinase 2.NEP55 is a protein of the inner nuclear membrane,and L68 is a protein of the nuclear lamina.What is the most likely role of phosphorylation of these proteins in the process of mitosis?
A)They enable the attachment of the spindle microtubules to kinetochore regions of the centromere.
B)They are involved in the disassembly and dispersal of the nucleolus.
C)They are involved in the disassembly of the nuclear envelope.
D)They assist in the movement of the centrosomes to opposite sides of the nucleus.
A)They enable the attachment of the spindle microtubules to kinetochore regions of the centromere.
B)They are involved in the disassembly and dispersal of the nucleolus.
C)They are involved in the disassembly of the nuclear envelope.
D)They assist in the movement of the centrosomes to opposite sides of the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 31 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



