Deck 7: The Demand for Health Insurance
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/20
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: The Demand for Health Insurance
1
Which of the following types of reimbursement would hospitals support?
A)Indemnity benefit
B)Service-benefit
C)Both a and b
D)Neither a nor b
A)Indemnity benefit
B)Service-benefit
C)Both a and b
D)Neither a nor b
B
Hospitals would prefer service-benefits because insurance companies would reimburse hospitals directly for the cost of treatment.Indemnity benefits reimburse only the patients and up to a fixed amount,causing patients to actively seek to minimize cost.
Hospitals would prefer service-benefits because insurance companies would reimburse hospitals directly for the cost of treatment.Indemnity benefits reimburse only the patients and up to a fixed amount,causing patients to actively seek to minimize cost.
2
Suppose there are two types of people in an insurance market: high and low risks.The high-risk person is sick 10% of the time and the low-risk person is sick 5% of the time.The probability that any individual is high risk is 40%.Upon getting sick,an individual loses $10,000 in medical expenses.What are the actuarially fair premiums for the types?
The actuarially fair premiums are equivalent to each individual's expected loss.For a high premium,(high)= $10,000(Pr[ sick | high ])= $10,000(.10)= $1,000.For a low premium (low)= $10,000*(Pr[ sick | low ])= $10,000(.05)= $500.
3
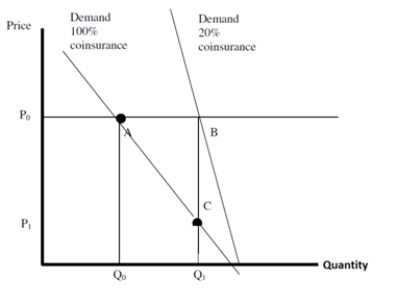
In the figure above, the change in insurance coverage causes a consumer's private benefits to increase (area under the demand curve) by:
A)120
B)90
C)60
D)30
C
4
A public option in the health insurance market has been proposed as a remedy to the increasing cost of health care.Critics state that a public option requiring all citizens to purchase health insurance would decrease health insurance premiums on average by mitigating
A)The adverse selection problem
B)The moral hazard problem
C)A failure of the market for externalities
D)The existence of spillover benefits
A)The adverse selection problem
B)The moral hazard problem
C)A failure of the market for externalities
D)The existence of spillover benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
As it applies to health insurance,the adverse selection problem is the tendency for:
A)Those most likely to collect on insurance,i.e.,sick people,to buy it.
B)Those who buy insurance to take less precaution in avoiding illness.
C)Sellers to price-discriminate.
D)Sellers to restrict output and charge high prices.
A)Those most likely to collect on insurance,i.e.,sick people,to buy it.
B)Those who buy insurance to take less precaution in avoiding illness.
C)Sellers to price-discriminate.
D)Sellers to restrict output and charge high prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Purchasing additional medical services because you are covered by health insurance is an illustration of
A)The adverse selection problem
B)The moral hazard problem
C)A failure of the market for externalities
D)The existence of spillover benefits
A)The adverse selection problem
B)The moral hazard problem
C)A failure of the market for externalities
D)The existence of spillover benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For a risk-averse consumer
A)The expected utility of wealth is greater than the utility of expected wealth
B)The expected utility of wealth is equal to the utility of expected wealth
C)The expected utility of wealth is less than the utility of expected wealth
D)There is no relationship between the expected utility of wealth and the utility of expected wealth
A)The expected utility of wealth is greater than the utility of expected wealth
B)The expected utility of wealth is equal to the utility of expected wealth
C)The expected utility of wealth is less than the utility of expected wealth
D)There is no relationship between the expected utility of wealth and the utility of expected wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following figure for questions 8 through 10
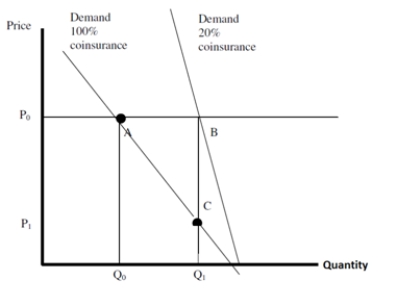
Suppose that Q₀ = 10 office visits,Q₁ = 20 office visits,P₀ = 10,and P₁ = 2.The increased expenditures due to insurance are:
A)$50
B)$100
C)$200
D)$300

Suppose that Q₀ = 10 office visits,Q₁ = 20 office visits,P₀ = 10,and P₁ = 2.The increased expenditures due to insurance are:
A)$50
B)$100
C)$200
D)$300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
It is flu season,and you are trying to decide if you should get a flu shot.When you are healthy,you earn $144 a day,but if you become ill,you will only earn $100 a day.There is a 25% chance you will get the flu without a flu shot.If you do receive the flu shot,then you definitely will not get the flu.What is the actuarially fair price for the flu shot given this information?
A)$44
B)$33
C)$22
D)$11
A)$44
B)$33
C)$22
D)$11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following policies limits the extent of moral hazard in the health insurance market?
A)Stop loss
B)Large deductibles
C)Varying co-insurance rates
D)All of the above
E)None of the above
A)Stop loss
B)Large deductibles
C)Varying co-insurance rates
D)All of the above
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
It is flu season.When you are healthy,you will earn $144 a day,but if you become ill,you will only earn $100 a day.There is a 25% chance you will get the flu.If your utility function is equal to 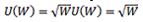 where W is equal to wealth,then what is your expected utility of catching the flu?
where W is equal to wealth,then what is your expected utility of catching the flu?
A)$133
B)$111
C)$11.5
D)$10.5
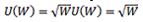 where W is equal to wealth,then what is your expected utility of catching the flu?
where W is equal to wealth,then what is your expected utility of catching the flu?A)$133
B)$111
C)$11.5
D)$10.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Insurance coverage is sold at
A)The actuarially fair price
B)The pure premium
C)The loading fee
D)The actuarially fair price + the loading fee
A)The actuarially fair price
B)The pure premium
C)The loading fee
D)The actuarially fair price + the loading fee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the figure below: By how much do expenditures increase with insurance? What is the deadweight loss to society for insurance?
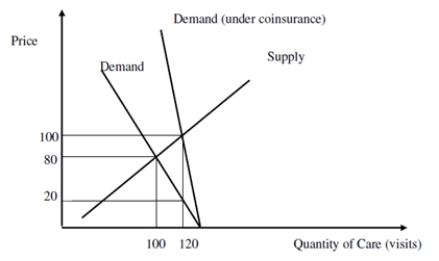


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Lucy Ramirez has $22,500 in income.After a recent trip to Cuba,she discovers that there is a 25% chance of acquiring Cubanitis.The disease is 100% curable but requires the Fidelonomy procedure (at a cost of $12,500).The Kuba-Kuba Insurance Company offers a policy that will cover the Fidelonomy.The premium they charge is $4,000.Of this premium,the pure premium is __________ and the loading fee is _______.
A)$4,000;$0
B)$3,125;$875
C)$875;$3125
D)Not enough information to answer.
A)$4,000;$0
B)$3,125;$875
C)$875;$3125
D)Not enough information to answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When an insurer promises to pay 30% of treatment costs,this amount is known as a
A)Deductible
B)Co-insurance
C)Stop-loss
D)Lifetime maximum
A)Deductible
B)Co-insurance
C)Stop-loss
D)Lifetime maximum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Calculate the expected return (or expected winnings)in a game where a person wins $1 with the probability of 1/3 ,$5 with the probability of1/6 ,and $0 with the probability of 1/2 .
A)0
B)$1 1 / 6
C)$2 1 / 6
D)$3
A)0
B)$1 1 / 6
C)$2 1 / 6
D)$3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose there are two types of people in an insurance market: high and low risks.The high-risk person is sick 10% of the time and the low-risk person is sick 5% of the time.The probability of any individual being high risk is 40%.Upon getting sick,an individual loses $10,000 in medical expenses.If the insurer cannot distinguish between the two types,but the two individuals know their types,what will be the equilibrium premium?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
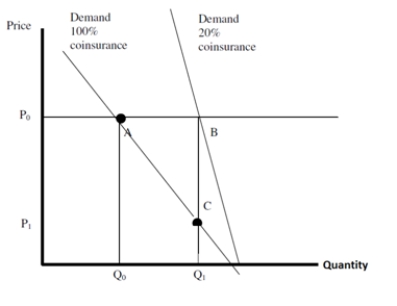
In the figure, the change in insurance coverage causes a social welfare loss equal to:
A)100
B)60
C)40
D)20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose there are two types of people in an insurance market: high and low risks.The high-risk person is sick 10% of the time and the low-risk person is sick 5% of the time.The probability of any individual being high risk is 40%.Upon getting sick,an individual loses $10,000 in medical expenses.What if the individuals do not know their type?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose the inverse demand for physician office visits is P = 1000 - 20Q.Now suppose an insurance policy provides a co-insurance rate of 50%.Graph the new demand function with health insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 20 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



